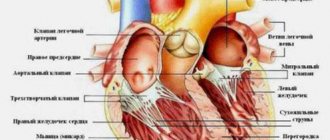
Extrasystole is called untimely depolarization and contraction of the heart or its individual chambers. This is the most frequently recorded type of arrhythmia. Extrasystoles can be found in 60-70% of people. But what is the situation with the draft and are they recruited into the army with extrasystole? A note from a cardiologist about the presence of extrasystole does not yet indicate the presence of significant disruptions in the functionality of the body. Rhythm disturbances can occur even in completely healthy people; for this reason, suitability for service is determined according to certain conditions.
Are they recruited into the army with ventricular extrasystole?
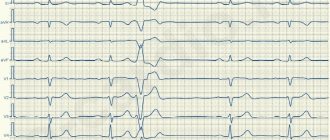
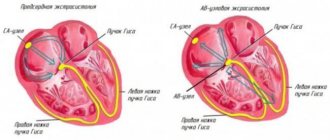
With ventricular extrasystole (one of the types of cardiac arrhythmia), untimely contractions of the ventricles of the heart occur - in other words, such contractions are called extrasystoles. This phenomenon does not always indicate certain diseases; extrasystole in some cases can also occur in absolutely healthy people.
Experts from the draft commission do not consider ventricular extrasystole as a disease. For this reason, all young men with a similar diagnostic conclusion are drafted into the army. Doctors claim that vegetative-vascular dystonia and neurosis are an unqualified diagnosis of other diseases with such symptoms, for example: diseases of the nervous system and psyche, possible heart disease, hypertension, improper functioning of the vascular system.
For this reason, doctors from the military commissariat sign up and take the young man to serve, believing that a healthy diet in the army, regular stay in the fresh air, daily routine and physical activity will cure those suffering from ventricular extrasystole.
Do they take into the army with cardiac extrasystole?
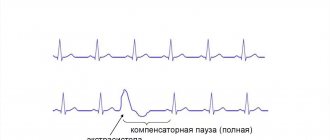
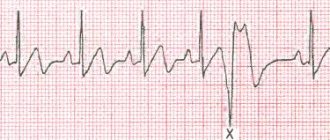
It is believed that this is the most common type of arrhythmia. Extrasystole has the characteristic of increasing the automaticity of individual zones of the myocardium (premature contractions of the heart). It is provoked by an excitation impulse that appears in the focus of heterotropic automatism. There are certain types of extrasystoles depending on the response of the atria. Before answering the question about the suitability of a conscript with extrasystole, you should understand the method of examination for such a disease. The classification is presented below.
According to the Schedule of Diseases, the classification according to Laun and Wolf is used:
- Degree 1 – monomorphic extraordinary contractions are recorded (no more than 30 per hour of observation);
- Degree 2 – contractions occur more frequently, from one focus (more than 30 per hour);
- Degree 3 – polytopic extrasystole;
- Degree 4 – divided from the ECG rhythm pattern;
- Degree 5 – the most dangerous type “R on T” in a prognostic sense is registered, which means that the extrasystole “climbed” onto the previous normal contraction and can lead to rhythm disturbances.
In addition, a “zero” degree is allocated for people who do not have extrasystole.
The intensity of symptom expression will be personal. Typical signs of extrasystole:
- Feeling of heart sinking;
- Interruptions in rhythm;
- Strong tremors in the chest.
In addition, hot flashes, shortness of breath, weakness, feelings of anxiety and discomfort may occur. If the disease occurs in an intense form, then the internal organs will feel a lack of oxygen, especially the coronary, cerebral and renal circulation is reduced. Extrasystole can cause dizziness, angina attacks and fainting.
According to the Schedule of Diseases, Article 42, those young men who have a classification of the degree of ventricular extrasystole according to the Laun-Wolff gradation of 3-4 are exempt from service with the assignment of category “D”. This diagnostic conclusion can only be made by a cardiologist after a thorough examination of the heart’s activity. Persons with severe symptoms of extrasystole will not be hired for service due to sudden complications or cardiac arrest.
Supraventricular extrasystole
Supraventricular extrasystole is one of the types of arrhythmia. In this case, an extraordinary excitation of any part of the heart occurs, caused by the occurrence of a premature impulse in the upper parts of the heart or in the antiventricular node.
The causes of supraventricular extrasystole are varied. Extrasystoles are functional and organic. Functional ones can occur in people with a healthy heart, in particular in children and tall young men. This is a rare single supraventricular extrasystole with the number of contractions less than 30 per hour.
Functional extrasystoles are usually classified as having the following origin: neurogenic; diselectrolyte; dishormonal; toxic; medicinal.
Neurogenic, in turn, are divided into hypoadrenergic, hyperadrenergic and vagal.
Hyperadergic extrasystoles are associated with increased physical and mental work, emotional arousal, drinking alcohol, smoking, and eating spicy foods.
Hypoadergic ones are difficult to recognize. Their existence is confirmed by experimental data and clinical observations.
With vagal extrasystole, interruptions in heart contraction occur after eating and during sleep, that is, in a horizontal position.
Organic supraventricular extrasystoles are caused by heart diseases, including:
- cardiac ischemia;
- heart defects;
- cardiomyopathy;
- myocarditis;
- tricuspid valve prolapse;
- mitral valve prolapse with blood returning to the left atrium;
- minor atrial septal defect;
- expansion of the pulmonary artery trunk;
- atrial dilatation in obesity, diabetes mellitus, chronic alcohol intoxication.
Sinus extrasystole is most often caused by chronic ischemic heart disease. We can talk about the organic nature of supraventricular extrasystole if it develops:
with sinus tachycardia; comes from several foci (polytopic); associated with angina pectoris; extrasystoles more than 30 per hour during ECG monitor recording and more than 5 per minute during examination by a doctor.
Supraventricular extrasystole is one of the types of arrhythmia. In this case, an extraordinary excitation of any part of the heart occurs, caused by the occurrence of a premature impulse in the upper parts of the heart or in the antiventricular node. Etiology and types of supraventricular extrasystoles
The causes of supraventricular extrasystole are varied. Extrasystoles are functional and organic. Functional ones can occur in people with a healthy heart, in particular in children and tall young men. This is a rare single supraventricular extrasystole with the number of contractions less than 30 per hour.
Extrasystoles of the following origin are usually classified as functional:
- neurogenic;
- diselectrolyte;
- dishormonal;
- toxic;
- medicinal.
Enlargement of the thyroid gland and its increased function can often be the cause of supraventricular extrasystole
Neurogenic, in turn, are divided into hypoadrenergic, hyperadrenergic and vagal.
Hyperadergic extrasystoles are associated with increased physical and mental work, emotional arousal, drinking alcohol, smoking, and eating spicy foods.
Hypoadergic ones are difficult to recognize. Their existence is confirmed by experimental data and clinical observations.
With vagal extrasystole, interruptions in heart contraction occur after eating and during sleep, that is, in a horizontal position.
Organic supraventricular extrasystoles are caused by heart diseases, including:
- cardiac ischemia;
- heart defects;
- cardiomyopathy;
- myocarditis;
- tricuspid valve prolapse;
- mitral valve prolapse with blood returning to the left atrium;
- minor atrial septal defect;
- expansion of the pulmonary artery trunk;
- atrial dilatation in obesity, diabetes mellitus, chronic alcohol intoxication.
Sinus extrasystole is most often caused by chronic ischemic heart disease. We can talk about the organic nature of supraventricular extrasystole if it develops:
- with sinus tachycardia;
- comes from several foci (polytopic);
- associated with angina pectoris;
- extrasystoles more than 30 per hour during ECG monitor recording and more than 5 per minute during examination by a doctor.
In addition, supraventricular extrasystole is classified as follows:
- According to the number of ectopic foci: monotopic (one foci), polytopic (several foci).
- By localization: atrial with the source of excitability in the atria and antiventricular - in the septum between the upper and lower parts of the heart.
- By frequency: paired (two extrasystoles in a row), single (less than 5 per minute), multiple (more than 5 per minute), group (several premature contractions in a row).
Often people with supraventricular premature beats have no symptoms. The most characteristic signs:
- Dizziness, feeling of weakness.
- Shortness of breath, lack of air.
- Fear, anxiety, panic, fear of death.
- Interruptions in the work of the heart, a feeling of its revolutions.
- Feeling of heart stopping or freezing.
- After freezing, a push to the chest.
Fitness category with extrasystole
The fitness category is determined by the Schedule of Diseases. A conscript whose complaints are determined by the state of ventricular extrasystole by the commission may not be allowed to serve. However, for this purpose, it is required at the time of passing the medical commission to have in hand the appropriate documentation that will prove this diagnosis.
With problems of this type, according to the Schedule of Diseases and Article 42 of the army, a conscript will be released with fitness category “D”.
How is the medical examination carried out?
When making a decision, the commission members adhere to article number 42 of the Disease Schedule directory. Conscripts who have been diagnosed with class 4 ventricular extrasystole are considered unsuitable for service.
If a young man has an extrasystole of a functional nature, then he is called upon to fulfill his military duty. To obtain a military ID, you must promptly contact a therapist and cardiologist. These doctors issue medical certificates confirming abnormalities in the functioning of the cardiovascular system.
These documents must be provided to members of the medical commission of the military registration and enlistment office. Based on their results, an appropriate decision is made. In most cases, such conscripts are not suitable for service in the field. They are assigned fitness category “G”.
Young people diagnosed with functional extrasystole are sent to the reserve ranks. To alleviate the symptoms of the disease, medications are used that prevent the occurrence of tachycardia and coronary artery disease. The period of such deferment ranges on average from 1 to 6 months from the date of conscription.
When making a decision, the military registration and enlistment commission determines the relationship between extrasystole and military service. Particular importance is given to extrasystoles and their treatment. If they do not cause significant harm to health and can be treated with simple medication, then the conscript can be sent to the reserve reserve and assigned fitness category “B”.
How does the military medical commission make a decision on the fitness of a conscript?
Cardiologists distinguish 2 types of extrasystole: functional and organic. Often young people have type 1 disorder. In this case, arrhythmia is caused by stress, emotional and physical stress, and drinking alcohol, coffee or energy drinks. The pathology of heart contractions, as a rule, does not pose a danger to young men and in most situations does not require therapy: as soon as the condition that provoked the syndrome is eliminated, the heart rhythm will return to normal. Organic type disorders appear with significant cardiovascular diseases: myocardial infarction, ischemic disease, cardiac muscle dystrophy. As a rule, this type of disease is typical for the population over 40-60 years of age.
The second criterion that determines the relationship between extrasystoles and service is whether the extrasystoles are amenable to therapy. They will accept service if the disorder can be easily eliminated with the help of medications or goes away on its own. In order to be released from the army, one must also prove that the violation is of a persistent nature.
Another factor on which the future of a conscript citizen depends is the classification of the violation. The decision on suitability is made after comparing the specialist with the Lown-Wolf characteristics, which were given above in the article.
What affects the fitness category in the presence of extrasystole
Many conscripts diagnosed with extrasystole are sent to the armed ranks of the army to perform military duties. The type and form of the disease influences the decision of the medical commission.
In cardiology, there are two types of extrasystoles. These include:
Author:
Kirill Savchenko
Didn't understand the article?
Ask in the comments right now and get an answer a little later.
auto RU
- Functional;
- Limited.
Many conscripts are owners of the 1st type. A number of reasons can provoke an irregular heart rhythm:
- Prolonged stressful situations;
- Emotional and physical stress;
- Excessive consumption of alcoholic beverages;
- Prolonged physical activity.
In this case, such deviations are not serious for a person. Most often, the changes do not require medical diagnosis or therapeutic treatment. When the factor for which the deviation was identified is eliminated, cardiac function is normalized.
A limited type of extrasystole occurs due to serious changes in the cardiovascular system. An advanced form of the disease can provoke myocardial infarction, coronary artery disease or dystrophy of the heart muscle. Such anomalies most often occur in patients whose age ranges from 40 to 65 years.
If you have a limited type, it is recommended to provide an outpatient card. As a rule, it will display the dynamics of the heart rate throughout the entire period of the disease. If the disease is persistent, then the patient is assigned fitness category “D” and is released from any military obligations.
How to increase extrasystoles?
For those who are trying to avoid the army with such a disease and are wondering how to increase extrasystoles, it is worth keeping in mind that it is not always possible to increase them. But the following methods can help:
- Physical activity (before the examination it is good to run, jump, stress your body).
- Stressful situations.
- Emotional and physical stress.
- Drinking alcohol (not the best option, since you won’t be able to come to the medical examination drunk).
- Coffee or energy drinks.
Reviews
Dear readers, you can leave your feedback on whether they will serve in the army with extrasystole in the comments, your opinion will be useful to other users of the site!
Yaroslav:
They take it with such a disease. Medical commission specialists do not even consider this disorder to be a disease. Well, naturally, if there are already serious pathologies, but they are mainly found in old people.
Andrey:
I was diagnosed with such a disorder, but they accepted me into the army anyway, since my stage was mild. The doctors explained it to me, but I didn’t really understand it. I wasn't going to quit the army.