Causes of extrasystole during pregnancy
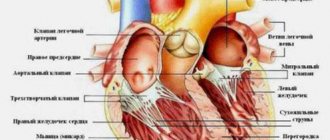
Heart rhythm disturbances are understood as conditions in which the basic properties of the heart change - excitability, conductivity and automaticity.
In this case, the work of the myocardium is disrupted. The frequency and rhythm of heart contractions changes, and the conduction of impulses through tissues slows down. The blood flow through the internal organs deteriorates, and various disturbances occur in their functioning. The reasons for the development of extrasystole in pregnant women are not fully understood. During gestation, there are no changes in the structure of the heart muscle and its conduction system that could lead to rhythm disturbances. But extrasystole occurs - and is often detected only during gestation. After childbirth, in a large number of women, all heart rhythm disturbances disappear without a trace and do not affect the further course of life.
There are several factors that provoke the development of extrasystole during gestation:
- Hemodynamic reasons: increase in BCC - circulating blood volume by 20% of the original; increased cardiac output; increased heart rate.
- Autonomic factors: active release of catecholamines (adrenaline, norepinephrine) and increased tissue sensitivity to them. This is considered a natural reaction to stress - that is, pregnancy.
- Hormonal changes: increased concentrations of estrogen, progesterone, renin, angiotensin in the blood of the expectant mother. These hormones contribute to the normal course of pregnancy and childbirth.
The likelihood of developing pathology increases after 20 weeks. During this period, the load on the myocardium increases, and rhythm disturbances appear. We observed a large number of patients and found that the risk of extrasystole increases in the following situations:
- multiple pregnancy;
- polyhydramnios;
- heart diseases that occurred before pregnancy (including congenital and acquired defects);
- endocrine disorders in the mother (diabetes mellitus, obesity, hyperthyroidism);
- insufficient nutrition and strict diets (lead to a lack of magnesium and potassium, necessary for the full functioning of the heart muscle);
- alcohol abuse, addiction to coffee and strong tea;
- heavy physical work during pregnancy;
- stressful situations.
All these women are at high risk and require special attention from a doctor.
What causes extrasystole?
Among the causes of extrasystoles in healthy people:
- Overwork;
- Lack of sleep;
- Stress;
- Excessive physical and mental stress;
- Potassium or magnesium deficiency;
- Consumption of alcohol, nicotine or coffee.
Extrasystoles can, however, also be a symptom of heart disease, such as:
- Cardiac ischemia;
- Inflammation of the heart muscle;
- Heart valve defect;
- Heart failure;
- Hyperthyroidism.
Symptoms and signs
In approximately half of pregnant women, extrasystole is asymptomatic. The expectant mother feels well, does not notice any interruptions in her heart function, and leads her usual lifestyle. The pathology is detected accidentally during a routine examination - electrocardiography (ECG).
Some women experience the following symptoms due to extrasystole:
- interruptions in the functioning of the heart (feeling of fading);
- discomfort in the chest area;
- shortness of breath with slight exertion;
- causeless anxiety and restlessness;
- weakness and increased fatigue.
In the second half of pregnancy, many women notice changes in the behavior of the fetus. The baby becomes more active or, on the contrary, calms down. Such symptoms indicate possible fetal hypoxia. A mandatory consultation with a gynecologist is required.
Consequences for the fetus
Extrasystole can affect the development of the fetus. Impaired blood flow in the heart muscle interferes with the full supply of oxygen to the tissues. With minor and short-term changes in rhythm, this is not dangerous. The fetus adapts quite well to hypoxia, mobilizing the reserves of the mother's body. With a long course of the disease, oxygen starvation of fetal tissues develops, the woman’s body’s adaptation to pregnancy is disrupted, and complications arise:
- chronic fetal hypoxia due to placental insufficiency;
- intrauterine growth retardation;
- gestosis;
- termination of pregnancy: spontaneous miscarriage up to 22 weeks, premature birth - from 22 to 37 weeks.
Statistics show that the likelihood of developing such complications is higher against the background of existing heart disease.
How to recognize extrasystole?
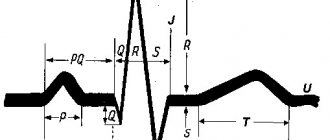
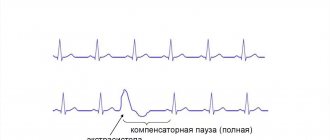
Pathology can be diagnosed by performing an ECG. There are two possible types of rhythm disturbances:
- supraventricular extrasystole (SVES);
- ventricular extrasystole (VES).
The supraventricular variant during the physiological course of pregnancy is more common than other rhythm disturbances and accounts for up to 65%. The ventricular form is less common.
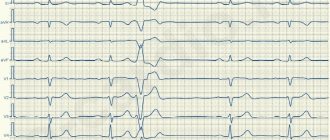
The photo below shows supraventricular extrasystole.
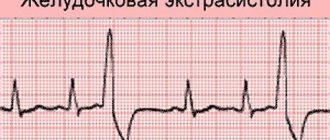
The next photo shows ventricular extrasystole.
If abnormalities are detected on the ECG, the woman is referred for consultation to a therapist and cardiologist. During the examination, the doctor pays attention to the color of the skin and the general condition of the patient. Blood pressure, pulse, and respiratory rate are measured. Auscultation is performed - listening to heart sounds.
Additional information about a woman’s condition is provided by the following research methods:
- daily ECG monitoring;
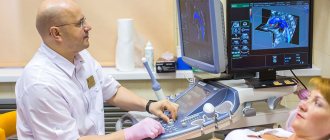
- echocardiography - ultrasound of the heart;
- hemostasiogram - a blood test for clotting.
The condition of the fetus is assessed using auscultation and ultrasound; in the later stages, CTG is connected.
When do you need to see a doctor?
A benign course of extrasystole is noted in the absence of symptoms or good tolerance of attacks. But if a woman’s condition worsens, management tactics need to be reconsidered.
Expert advice
Pregnant women adapt quite well to the rhythm disturbances that arise, and often no special treatment is required. If the expectant mother does not notice attacks of extrasystole or feels well during them (there are minor interruptions in the heart, there may be anxiety, but there is no need to change the usual way of life), it is enough to wait out this period. But if the pregnant woman’s health worsens, chest discomfort, a feeling of fear, and insomnia appear, she needs to consult a doctor. The reason for the examination may also be the appearance of other changes in the cardiogram that are not associated with extrasystole.
conclusions
Extrasystole is an extraordinary generation of an impulse followed by a contraction of cardiomyocytes. Extrasystoles are sometimes harmless, but in other cases they can provoke atrial fibrillation, the consequence of which will be sudden death.
The army will perceive a cardiological conclusion about the presence of polymorphic, paired or group extrasystoles negatively and will deny the man the opportunity to serve.
Prevention of extrasystole - a healthy lifestyle (physical exercises during sedentary work are required).
Principles of treatment
Extrasystole and pregnancy are compatible, and often special therapy is not even required. Drug treatment is prescribed in the following situations:
- severe discomfort – deterioration of the woman’s well-being;
- progression of pathology during pregnancy;
- deterioration of the fetus' condition.
Most proposed antiarrhythmic drugs are prohibited during pregnancy. Some products can only be used after 14 weeks - at a time when the internal organs of the fetus are already formed. We are faced with a non-trivial task - to select medications that can improve the condition of the expectant mother, but will not harm the child. When choosing a drug, it is important to consider: during pregnancy, a larger dosage is often required. This is due to an increase in blood volume, increased metabolism of the drug in the liver and active excretion through the kidneys.
The selection of antiarrhythmic drugs takes into account the recommendations of the FDA (Food and Drug Administration). All drugs according to the FDA are divided into several groups, taking into account the possibility of their use in pregnant women. During gestation, it is allowed to use medications of groups A and B - safe and conditionally safe for the fetus. This means that the studies conducted did not reveal a negative effect of these drugs on the development of the child or found an insignificant risk. In rare cases, it is suggested to take drugs from group C, when the potential benefit outweighs the likely harm.
Patient management tactics are determined by hemodynamic parameters. If, against the background of extrasystole, the functioning of the mother’s cardiovascular system is disrupted or disturbances in the uteroplacental and fetal blood flow occur, mandatory drug therapy is carried out. Priority is given to drugs based on Solatol, Acebutol (FDA category - B). The use of sedatives is indicated - valerian and motherwort extract.
If the condition of the woman and fetus is stable, first of all you need to try to find the cause of the extrasystole (heart and lung diseases, endocrine disorders, neurosis, etc.). By removing the underlying pathology, we can do without other drug correction.
Causes
Extrasystoles occur in the heart as a result of structural or functional changes in the myocardium. They may be due to:
- heart disease (angina pectoris, heart defects, cardiomyopathies, myocarditis, cardiomyofibrosis, heart failure);
- disturbances of electrolyte (hypokalemia, hyperkalemia, hypomagnesemia, hypocalcemia) or acid-base balance;
- hypoxia (due to chronic lung diseases);
- chronically high or low blood pressure;
- injuries (chest, brain and spinal cord);
- manipulations on the heart (surgical and diagnostic interventions);
- dysfunctions of the autonomic nervous system (structural changes, VSD (vegetative-vascular dystonia), lack of sleep, stress and neuroses);
- hormonal imbalance during menopause (estrogens deficiency);
- immaturity of the cardiac conduction system in newborns;
- psycho-emotional stress and constant training in athletes (extraordinary contractions occur against the background of bradycardia);
- redistribution of blood flow and changes in hormonal levels during pregnancy;
- activation of pathological reflexes due to: diseases of the digestive system (pancreatitis, ulcers, cholelithiasis, enterocolitis, severe flatulence);
- pathologies of the cervical and thoracic spine (spondyloarthrosis, osteochondrosis);
- diseases of the bronchopulmonary system (with a strong prolonged cough);
- prostate adenomas;
- endoscopic examinations (bronchoscopy, laparoscopy, gastroscopy, cystoscopy, colposcopy, sigmoidoscopy);
- toxic effects of drugs:
The described factors contribute to the disruption of the functional and structural integrity of the impulse pathways in the myocardium. Instead of a clear directional movement (from the atrium to the ventricle), the wave of depolarization in a circle returns to the starting point, as a result of which the contraction mechanism is restarted and an extraordinary heart beat occurs.
Another mechanism for the occurrence of extraordinary contractions is the presence of ectopic (abnormal) sources of impulse generation. Activating asynchronously with the sinus node (the main pacemaker), they trigger an extraordinary contraction of the myocardium.
Case from practice
A 25-year-old woman, during a follow-up visit to a gynecologist, complained of a feeling of a sinking heart, rapid heartbeat, and anxiety.
After the interview, it became known that such symptoms appeared at 22 weeks, but previously the patient did not pay attention to them, mistaking them for normal manifestations of pregnancy. The duration of this pregnancy is 28 weeks, the symptoms gradually increase. The patient complains that she often wakes up at night, feels tired during the day and cannot work fully. From the anamnesis it is known that the pregnancy is the first, planned. Before conceiving the child, the woman was not registered with a therapist or cardiologist, and does not report any diseases of the cardiovascular system. Currently taking multivitamins for pregnant women (Vitrum prenatal forte). Upon examination, the woman's condition is satisfactory. The condition of the fetus is not impaired (according to auscultation).
The patient was sent for an ECG, which revealed supraventricular tachycardia. After consulting a therapist, the woman underwent further examination; no pathology was found in the internal organs. A diagnosis of “Vegetative-vascular dystonia” was made. The patient was prescribed motherwort extract for 4 weeks. A full night's sleep of at least 8 hours, regular walking, and avoidance of strong tea and coffee are recommended. After 6 weeks, the woman’s condition improved. There were no pregnancy complications identified at the time of the follow-up examination.
In the treatment of extrasystole in pregnant women, special attention is paid to non-drug therapy. Recommended:
- A full night's sleep of at least 8 hours. Daytime sleep – 1-2 hours if possible and necessary.
- Adequate physical activity: regular walking, swimming, yoga for pregnant women.
- Refusal to drink tea, coffee, cocoa, seasonings and spices.
- Correction of the psycho-emotional background: avoidance of stressful situations, psychotherapy.
Prevention
There is no point in treating extrasystole if the main causes of its occurrence are not removed. This is precisely what prevention is aimed at. To this end, it is recommended to follow the following tips:
- avoid stressful situations, get enough rest;
- Get a good night's sleep - this is an important factor in the body's recovery;
- Despite the fact that heavy physical activity can cause attacks, complete adynamia also negatively affects the heart. Moderate exercise is a good preventive measure;
- limit the consumption of alcoholic beverages, coffee, strong tea;
- stop smoking;
- practice massage and breathing exercises;
- Eat foods high in potassium (banana, avocado, baked potatoes, dried apricots, spinach) and magnesium (wheat bran, cocoa, buckwheat, cashews and almonds).
Following these simple rules will help not only get rid of extrasystoles, but also improve your overall health.
Lead tactics
Functional extrasystole does not interfere with the normal course of pregnancy and gestation. We usually do not identify any contraindications to natural delivery. A woman can give birth to a healthy baby at term and avoid complications.
Extrasystole associated with organic damage to the heart or other organs, endocrine disorders and other conditions requires mandatory observation by a specialist. The management tactics for a woman will depend on the severity of the underlying disease.
All pregnant patients, regardless of the severity and form of extrasystole, are under the supervision of a therapist and cardiologist until delivery. If the condition of the woman and fetus is stable, a control examination (ECG) is carried out before birth. If the patient's condition worsens or complications of gestation develop, additional examination is indicated.
Indications for caesarean section for extrasystole are rare. They are usually associated with concomitant pathology or complications of pregnancy. In a planned procedure, the operation is performed at 37-39 weeks, in an emergency - at any time.
Have you encountered such a phenomenon as extrasystole during pregnancy? What did the doctor recommend to you in this situation?