- Home /
- Services and prices /
- Fetal Doppler
What is Doppler ultrasound? In what cases is fetal Doppler testing prescribed? Why is it important to perform Doppler testing during pregnancy? At what stage of pregnancy is it best to perform Doppler? How is the examination carried out? What types of Doppler ultrasound do ultrasound doctors perform?
What is Doppler?
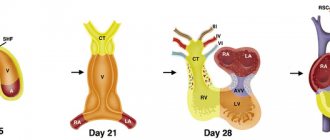
Today, ultrasound diagnostics of the fetus is rightfully considered the most informative examination during pregnancy. Thanks to ultrasound, it has become possible to monitor the growth and development of the baby in the womb, identify defects and anomalies in the early stages, prevent the risks of miscarriages, as well as dangerous complications that threaten the health of the fetus and the expectant mother. In addition to the standard three ultrasound scans during pregnancy, obstetricians-gynecologists prescribe additional ultrasound examinations of the fetus. One of them is Doppler ultrasound.
Fetal Doppler is an ultrasound examination that allows diagnosing blood flow in the circulatory system connecting the unborn baby, the placenta, the umbilical cord and the body of the pregnant woman. Based on the results of Doppler testing, the doctor assesses the state of the fetal blood flow through the vessels and arteries and can identify deviations in their development, a lack of oxygen supply, and so on. The examination is also of particular importance for the diagnosis of fetoplacental insufficiency in cases of delayed fetal development, gestosis, dysfunction of the placenta and other pathologies of pregnancy.
Doppler testing during pregnancy
Doppler ultrasound can be performed from the second trimester, in particular from the 20th week of gestation. Typically, at such relatively early stages, Doppler is prescribed if fetal development is suspected, if there have been previous miscarriages or missed pregnancies, or if there are other pathologies of pregnancy.
At 30-34 weeks, Doppler testing is a mandatory study, and its results are included in the protocol of the third ultrasound.
A simple Doppler allows you to evaluate only one functionality of a blood vessel - its patency, that is, how much blood flow passes through the vessel in a certain period of time.
Triplex study
A triplex study is a study that evaluates not only the patency of the vessel, but also identifies the causes of its violation. The main reasons include stenosis, the formation of a blood clot in a vessel, and the presence of plaques. Triplex allows you to see a color image of blood vessels on the screen and study their anatomy in detail.
When should you undergo a Doppler test?
As a rule, Doppler measurements are performed only after the placenta is fully formed, that is, after the 18th week of pregnancy. According to Appendix No. 5 to the order of the Ministry of Health of Russia dated December 28, 2000 No. 457, Dopplerography of utero-fetoplacental blood flow is carried out at 20-24 weeks of pregnancy. A later order regulates ultrasound examination at gestational ages of 18-22 weeks, 27-32 weeks and 35-37 weeks. During these periods, blood flow readings taken by Doppler become reliable.
Decoding the results
After a Doppler ultrasound during pregnancy, the results are interpreted immediately. Initially, the nature of blood flow in two functioning arteries of the uterus – left and right – is assessed. For this purpose, the resistance index – IR – is used. At the 20th week of pregnancy, RI values can fluctuate in the range of 0.37-07. The longer the pregnancy, the smaller the IR should become. For example, at week 40 it should be 0.32-0.56.
In addition to IR, the pulsatility index (PI) in the uterine artery is also assessed. At the 20th week of pregnancy, PI values can reach 1.04-2.03. As the gestational age increases, the PI value should gradually decrease. For example, at week 40 the PI should be 0.42-1.41.
The third important indicator that is assessed when deciphering Doppler is the systole-diastolic ratio (SDO) in the arteries of the uterus. At 20-24 weeks it should reach 2.5. By the end of the last trimester, the value should drop to 2.3.
If all three blood flow indicators, after decoding, turn out to be above normal according to Doppler ultrasound readings during pregnancy, the attending physician must prescribe the woman certain therapy. Sometimes there is a need to carry out treatment on an outpatient basis using medications and physiotherapeutic procedures. In some cases, when the blood flow is slightly impaired, the doctor may recommend that the pregnant woman move more, sign up for special gymnastics, swimming, and so on.
What does Doppler ultrasound show during pregnancy?
- Doppler ultrasound during pregnancy reveals:
- Hemodynamic disorders. In other words, Doppler can detect disturbances in blood flow between the uterus and placenta or between the placenta and the fetus. Such violations can have varying degrees of complexity. In some cases, having detected such a deviation in a timely manner, it is possible to quickly take action, send the pregnant woman to a hospital, and prescribe her certain therapy (for example, droppers with a drug that enriches the blood with oxygen).
- Intrauterine growth retardation (ratio of fetal size to gestational age).
- Fetal hypoxia (oxygen starvation of varying severity).
- Feto-placental insufficiency is a disruption of the normal supply of nutrients to the fetus through the placenta.
- Preeclampsia is a disruption of the normal course of pregnancy. This condition may be accompanied by edema (not only external, but also swelling of internal organs), increased blood pressure, dizziness, nausea and vomiting, and so on. Of course, such an uncomfortable state of a woman can negatively affect the development of her child. An important advantage of Doppler is that it helps to recognize the very first signs of gestosis. In this case, in the protocol, ultrasound specialists write “threat of gestosis.”
Doppler allows you to visualize a specific blood vessel and estimate the speed of blood movement in it.
Indications for Doppler testing
An obstetrician-gynecologist prescribes Doppler ultrasound in cases of any deviations from a normal pregnancy. For example, when the health status of a pregnant woman requires it or if, based on the results of previous studies, any deviations from standard indicators of fetal development were identified:
- Woman over 35 years old;
- Multiple pregnancy;
- Pregnancy is complicated by chronic diseases of the expectant mother;
- Previous pregnancies were missed and ended in miscarriage;
- Suspicion of fetal malformation;
- Rh conflict between mother and fetus;
- The fetus is developmentally delayed;
- The entanglement of the umbilical cord around the fetal neck, detected on ultrasound;
- Unsatisfactory CTG results;
- Oligohydramnios or polyhydramnios and others.
In addition, the order of the Russian Ministry of Health states that ultrasound examination can be performed if necessary, without explaining the “exact characteristics of the need.”
DOPPLEROMETRY OF UROPLACENTAL, FETAL-PLACENTAL AND FETAL BLOOD FLOW
Doppler ultrasound is an ultrasound examination that can be used to detect disturbances in blood flow in the vessels.
Studies of utero-placental blood flow in the uterine arteries and fetal-placental blood flow in the umbilical cord artery have the greatest practical value during pregnancy; as well as fetal hemodynamics in the aorta and cerebral vessels of the fetus. Currently, an important diagnostic method is the study of venous blood flow in the fetus in the ductus venosus.
INDICATIONS FOR DOPPLER METRY DURING PREGNANCY
The main indications for Doppler study of blood flow in the “mother-placenta-fetus” system are extragenital diseases and complications of pregnancy: hypertension, hypotension, kidney disease, collagenosis, vascular diseases, diabetes mellitus, preeclampsia, fetal growth restriction or post-term pregnancy, oligohydramnios, polyhydramnios. , multiple pregnancy, resusensitization, etc.
| Blood flow in the uterine artery | Blood flow in the umbilical cord artery | Blood flow in the fetal MCA |
Information for specialists
Dynamics of Doppler studies in various obstetric situations
When assessing blood flow in the uterine arteries, the pulsatility index (PI>1.2) and the presence or absence of a dicrotic notch at the beginning of diastole are used. When assessing resistance in the uterine arteries, scoring criteria (UAS) are used. Select 4(UAS). UAS 0 – normal blood flow in both uterine arteries UAS 1 – presence of one pathological blood flow parameter (PI>1, 2 or the presence of a notch) UAS 2 – presence of two pathological blood flow parameters UAS 3 – presence of 3 pathological blood flow parameters UAS 4 – presence of pathological blood flow in both uterine arteries (PI>1, 2 and presence of notch)
When assessing blood flow in the umbilical cord arteries, the values of the pulsatility index and the presence or absence of diastolic blood flow are used. There are four types of blood flow (BFC) BFC 0 - normal blood flow in the umbilical cord arteries BFC 1 - PI greater than 2-3 standard deviations, diastolic blood flow is preserved. BFC 2 - PI greater than 3 standard deviations, diastolic blood flow is preserved BFC 3A - zero diastolic blood flow in the umbilical cord artery BFC 3B - reverse diastolic blood flow in the umbilical cord artery
Suspicion of intrauterine growth retardation
In the absence of abnormalities in the umbilical cord artery and BMD disorders: If the weight deviates from 22-27%: - type 0-2 - Doppler measurements once every 2 weeks; — type 3 – Doppler once a week; — type 4 – Doppler 2 times a week; Fetometry once every 2 weeks
In the absence of abnormalities in the umbilical cord artery and uterine arteries - deviation in weight from 28-34% - Doppler measurements 2 times a week; - weight deviation of 34% or more - Doppler measurements 2-3 times a week; Fetometry once every 2 weeks
In the presence of disturbances in the umbilical cord artery and the absence of disturbances in the uterine arteries - type 1 - Doppler and CTG 2 times a week; -type 2 - Doppler and CTG 3 times a week; -type 3A - resolve the issue of hospitalization and delivery. For a period of less than 34 weeks - Doppler measurements daily, CTG 2 times a day. - type 3B - emergency delivery, with a period of less than 26-27 weeks - decision of the council. Fetometry once every 2 weeks.
Clinical management of patients with a normal pregnancy and normal blood flow in the umbilical arteries, but with signs of increased resistance in the uterine arteries. UAS 0-1 - routine outpatient observation UAS 2 - outpatient observation, Doppler monitoring once a month UAS 3 - if dynamic ultrasound shows no changes in the dynamics of fetal growth - Doppler monitoring once a month; if the dynamics in weight changes from 9 to 10% - Doppler measurements and fetometry once every 2-3 weeks UAS -4 - Doppler measurements weekly, fetometry once every two weeks.
What is special about Doppler during pregnancy?
Doppler is a modern leading research method in obstetrics, which allows you to assess the state of the fetoplacental system of the unborn child.
Distinctive features of Doppler (Doppler) during pregnancy:
- the operating principle of Doppler ultrasound is based on changes in the frequency of the ultrasound wave depending on the speed of blood in various vessels of the umbilical cord, the aorta and cerebral arteries of the fetus, and the arteries of the uterus;
- Dopplerography (Doppler) during pregnancy is similar to the usual ultrasound procedure. The study is carried out using a special Doppler sensor, which is equipped with all modern ultrasound diagnostic devices;
- If a regular ultrasound gives an idea only of the structure of blood vessels, then Dopplerography also shows the movement of blood in the form of a two-dimensional color image.
Unlike conventional ultrasound, Doppler is capable of:
- determine the health status of the baby’s heart;
- listen to the heartbeat, determine the patency and lumen of the fetal umbilical cord vessels;
- determine how well the fetal vessels are supplied with blood;
- detect insufficient functioning of the placenta and fetal hypoxia in the early stages.
What is color Doppler during pregnancy?
During Doppler ultrasound during pregnancy, a high-resolution color device is used. This allows the blood flow of mother and child to be painted in different colors, which is especially important for the early diagnosis of childhood heart defects and developmental abnormalities. Different colors are also used to represent different directions of blood flow.
Special indications for fetal Doppler sonography
This diagnostic method is recommended for use if the patient has the following problems:
- When the size of the fetus does not correspond to the gestational age.
- Abnormal amount of amniotic fluid.
- When pathological conditions of the placenta are observed: premature ripening, etc.
- If fetal abnormalities or chromosomal abnormalities are suspected.
- When a woman has diseases such as diabetes, anemia, kidney disease, etc.
- The presence of pathologies during previous pregnancies.
- When the fetal heart rate is abnormal. If you suspect a heart defect or other heart disease.
- In case of premature contractions, they are visible on CTG (cardiotocography).
- With gestosis in a pregnant woman.
- In case of Rh conflict.
- With high maternal blood pressure.
- During multiple pregnancy.
- If there is a threat of miscarriage or premature birth.
What is Doppler?
Doppler, Doppler (Doppler), vascular duplex ultrasound is an ultrasound method that measures the speed of blood flow in the vessels.
Using the Doppler blood flow assessment method, you can identify blood clots or atherosclerotic plaques that contribute to the disruption of blood flow.
When conducting a duplex examination, these two methods (conventional ultrasound and Doppler) are used simultaneously. Conventional ultrasound produces images of blood vessel structures, while Doppler ultrasound allows us to image and evaluate the characteristics of blood flow moving through the vessels. With a duplex study, the doctor receives a color image of the vessel, with a specific color coding for the speed and direction of blood flow.
What is being studied
Brachiocephalic arteries and vessels of the cervical spine
Vessels of the brain and vertebral arteries
Veins and arteries of the lower extremities
Veins of the upper extremities
Aorta, iliac vessels.
Indications and contraindications
The main indications for examination include the following:
- osteochondrosis;
- suffered a stroke;
- vegetative-vascular dystonia;
- diabetes;
- hypertension;
- ischemic disease;
- phlebeurysm;
- risk of blood clots;
- excess body weight.
As for contraindications for this procedure, there are virtually none, since ultrasound examination is considered safe for health. However, the temporary limitation for the technique is acute inflammatory diseases.
Preparation and execution
The advantage of the technique is that it does not require special preparation from the patient.
The only limitation is taking vascular medications, which it is advisable to stop 2-3 days before diagnosis. You should also avoid smoking and alcohol. During an ultrasound scan, the patient lies down on the couch and removes the desired area of the body from clothing. Next, a special conductive gel is applied and the sensor is applied to the skin. By moving this sensor, the doctor conducts a study, recording the necessary data in the process and taking pictures of the resulting images.