The importance of the carotid arteries, located in the neck and chest, in the human body is difficult to overestimate. The carotid arteries participate in the general blood flow and play a critical role in supplying the brain with oxygen. Any problems related to the carotid arteries can have a negative impact on your overall health. Therefore, today there are quite a lot of examination methods, including ultrasound of the carotid arteries.
In what cases is ultrasound of the neck vessels prescribed?
Experts agreed that preventive testing of the functioning of blood vessels is necessary in the following cases:
- After 45 years, both men and women;
- If you have a history of diabetes;
- With regular use of oral contraceptives;
- Persons who have had a stroke or heart attack;
- With elevated blood cholesterol levels;
- Heavy smokers and anyone who regularly drinks alcohol;
- For acute and chronic diseases of the heart and blood vessels;
- For epilepsy;
- With high or low blood pressure, as well as its fluctuations;
- With strong weather sensitivity;
- If there is a suspicion of migraine;
- For osteochondrosis of the cervical spine.
An ultrasound examination may also be prescribed to a patient before surgery on blood vessels or the heart. In addition to specific diagnoses, research can be carried out due to the following complaints:
- There is a creaking or constant whistling in the ears;
- Frequent headaches bother you;
- There is regular dizziness;
- There are problems with memory and concentration;
- “Floaters” often flash before your eyes.
If we are talking about a newborn, diagnostics of the neck vessels can be carried out if the baby’s head is irregularly shaped or if there are suspicions of the presence of serious pathological processes. This often happens if the child was not born naturally, but through surgery, or if the birth was complicated.
This examination has absolutely no contraindications, since ultrasound has no harmful effects. If the doctor has sent you for an examination, do not refuse under any circumstances and be sure to go for an ultrasound. With the help of ultrasound, you can prevent dangerous complications by detecting ailments in the initial stages of development.
Decoding the results
The interpretation of the diagnosis of ultrasound of the carotid arteries is carried out by the attending physician based on the results obtained. However, a sonologist can also clarify the situation by recording the examination results at the end of the procedure. Typically, a sonologist comments on the visible echostructure of the vessel during scanning and blood flow.
The norm for ultrasound of the carotid arteries is that the blood flow in the internal and external arteries is equal in power, as well as the location of the carotid artery to the left of the aorta. The thickness of the vessel walls should not exceed 1.2 mm, and the pulsation in a healthy artery should be continuous.
What diseases can be detected by ultrasound of the carotid arteries?
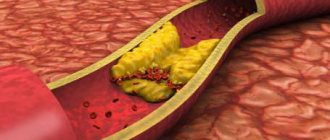
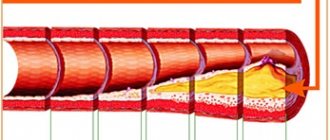
Ultrasound of the carotid arteries allows you to examine not only the brachiocephalic arteries, but also simultaneously assess the condition of the vertebral vessels of the neck. The norm for ultrasound of the carotid arteries implies an internal and external diameter of the walls sufficient for good blood flow. Ultrasound of the carotid arteries most often reveals atherosclerotic plaques and kinks, which cause strokes. Ultrasound of the carotid arteries allows you to see even the structure of plaques, for example, those that have calcium impurities and are especially difficult to treat.
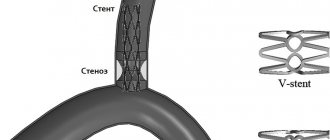
No less dangerous are blood clots and aneurysms, which are clearly visible using ultrasound. Stenosis visible on ultrasound of the carotid arteries may explain ischemic attacks, since blood flow worsened due to narrowing of the artery does not allow the brain to receive enough oxygen. An alarming symptom is a change in the level of the bifurcation of the carotid artery, visible on ultrasound. However, one must understand that ultrasound of the carotid artery can only identify these problems; subsequently, it is recommended to conduct a more in-depth study.
Do I need to prepare for an ultrasound of the neck vessels?
No special preparation is required, but in 1-2 days it is advisable to minimize the impact of factors that may affect the state of the cardiovascular system. Try not to drink a lot of tonic drinks - strong tea, coffee, energy drinks, give up alcohol. It is better not to smoke before the test. If you take any medications regularly, talk to your doctor about taking them on the day of the test - some medications can affect blood flow, and your doctor may advise stopping them for the day or delaying taking them.
After research
After the examination, the doctor gives you a napkin to wipe off the gel. During this time, a diagnostic protocol is drawn up. If necessary, the protocol can be supplemented by printing an ultrasound image on a printer, although most often a conclusion from an experienced specialist is sufficient. Duplex ultrasound scanning of the neck arteries is a safe and non-invasive method for diagnosing the pathology of the carotid and vertebral arteries and allows us to identify many dangerous diseases. Duplex MAG scanning should be performed in all patients at risk of ischemic stroke or before complex vascular interventions.
How to study the vessels of the neck
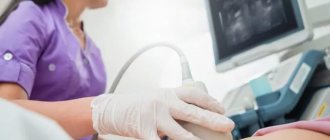
When visiting an ultrasound diagnostician’s office, the doctor usually asks you to remove jewelry from your neck and ears and put your long hair in a ponytail so that nothing interferes with the examination process. Next, the patient lies on a flat couch, with his head towards the doctor. The gel is applied to the skin of the neck and the sensor is moved over it. The head is thrown back or tilted. First, the carotid artery is examined, then all other vessels located in the neck.
The procedure lasts no more than 45 minutes. The doctor may also conduct the examination in a sitting or standing position and ask you to tilt your head. At the end of the procedure, the doctor gives the results of the study to the patient.
How is the carotid artery ultrasound procedure performed?
The ultrasound procedure of the carotid arteries does not cause discomfort or pain and is performed with the patient in a supine position. A special pillow is placed under the patient's shoulders so that nothing interferes with the view of the arteries. Throughout the procedure, the sonologist moves the scanner over the skin of the neck, lubricated with gel, and from time to time changes the sensitivity of the device.
There are several methods for ultrasound of the carotid arteries. However, it does not depend on this how ultrasound of the carotid arteries is done - in any case, the sonologist moves the scanner in the neck area, if necessary, telling the patient to turn his head or stretch his neck, examining the subclavian region.
Dopplerography
Using Doppler ultrasound, disturbances in blood flow in the vessels are detected, and ultrasound of the carotid arteries is one of the most effective diagnostic methods. If the blood flow is not visible, the sonologist can apply digital pressure on the artery to obtain more accurate information. In some cases, signals obtained using Doppler ultrasound can be converted into sound, this helps when examining seriously ill patients.
Duplex scanning
Duplex scanning is a combination of Doppler ultrasound, which determines blood flow disturbances, with traditional scanning, which shows the echostructure of the arteries. Duplex scanning of the carotid and vertebral arteries is the most common procedure, since it solves two problems simultaneously.
Triplex scanning
Triplex scanning of the carotid arteries involves research in three modes. The greyscale scanning mode provides information about the structure and shape of the artery, as well as any changes in it. Dopplerography
reveals the quality of blood flow inside the artery. And color Doppler mapping provides a color image that provides comprehensive information about any changes in the structure and blood flow of the artery.
Advantages and disadvantages of the procedure
Today, almost every medical institution has the necessary equipment to conduct ultrasound of the neck vessels. Let's consider the advantages of this technique:
- This method is absolutely safe;
- The procedure can be performed at any age;
- She has no direct contraindications;
- The process is absolutely painless and does not cause discomfort.
- The only disadvantage we can note is the lack of information content - this is not the main method of diagnosing diseases, but only an auxiliary one.
Ultrasound of the carotid arteries
Ultrasound of the carotid arteries reliably shows the condition of the blood vessels and is one of the safest and most painless technologies. Ultrasound waves do not harm the body, and the non-invasiveness of the method negates the risk of vessel damage. Therefore, this type of diagnosis of diseases and pathologies of the carotid arteries is the most common. There are practically no obstacles in the path of ultrasonic waves when examining the carotid arteries using ultrasound, which makes it possible to obtain reliable readings about the condition of the vessel. A pleasant advantage of this research method is its low cost.
Advantages of performing ultrasound scanning of the carotid and vertebral arteries in CELT
The multidisciplinary clinic CELT invites you to undergo a diagnostic test in accordance with international standards. Our name is well known in the capital, since we have been working in the domestic market of paid services since 1993. During this time, our specialists correctly diagnosed and restored health to thousands of patients, earning positive reviews and a good reputation.
Our diagnostic department is staffed by doctors of the highest category and candidates of medical sciences with at least fifteen years of experience. They know how to scan in such a way as to detect pathological changes even in the initial stages. This is important because timely treatment increases the chances of success, and especially when it comes to vascular diseases and cerebrovascular disorders.
Our specialists have two ultrasound devices in their arsenal: “Electric Medical System” (USA) and “Philips” (Holland), which allow duplex and triplex diagnostics in real time and provide high-quality images.
You can find out prices for services in this section of the website by going to the “Services and Prices” tab. To avoid misunderstandings, we ask you to contact our operators to clarify the cost: +7 (495) 788-33-88.
Center location: 3 minutes walk from the metro station 1905 Goda Street
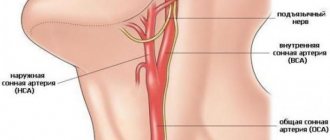
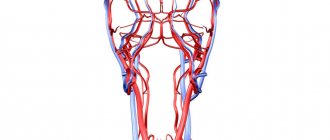
What vessels of the neck are examined during an ultrasound? First of all, the common and external carotid arteries, which carry blood to the brain. Abnormalities in them often do not cause symptoms, but increase the risk of stroke. The doctor may also examine:
- Vertebral arteries, which pass to the right and left through openings in the lateral parts of the cervical vertebrae. They take part in the blood supply to the muscles of the neck, brain and spinal cord.
- The jugular veins collect blood from the head and neck and carry it to the superior vena cava.
- The subclavian artery and vein are large vessels whose branches provide blood supply to the head and neck.
MRI and CT of the vessels of the brain and neck - the main differences
CT and MRI of cerebral vessels are expert forms of diagnosis. Even small arteries and veins will be clearly displayed on tomographs. This is a more detailed and accurate form of diagnosis compared to ultrasound. In terms of information content, MRI and CT angiography of the head and neck are comparable. However, the principle of image acquisition differs between these two forms of tomography. Magnetic resonance imaging uses the effect of nuclear magnetic resonance. When the human body is placed in a magnetic field, hydrogen ions present in the blood and tissues begin to oscillate. Depending on the impulses of the MRI machine, they line up in a given direction. All changes in the movement of hydrogen atoms are recorded by tomograph sensors, and based on them, three-dimensional images of the vascular bed are constructed.
Computed tomography uses the principle of X-ray radiation, that is, the ability of X-rays to pass through tissues of different densities at different speeds. Computed angiography always uses iodine-enhanced contrast. Without contrast, the vascular bed on CT images is poorly visualized, and the examination loses its informative character. In MR angiography of the brain, gadolinium-based contrast is rarely used, since blood itself is a good paramagnetic, and in most cases no additional enhancement is required.