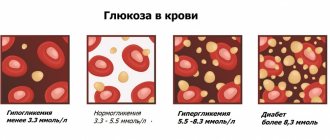
According to various authors, the cause of infant mortality in 56–75% of cases is intrauterine hypoxia (oxygen deficiency). Diagnosing this condition as early as possible is the goal of midwifery services as it is preventable.
The abbreviation “CTG” has a double meaning in medicine. It is used as an abbreviation for “computed tomography,” but the term is better known to obstetricians and gynecologists as “cardiotocography.” This is a way to simultaneously record the fetal heart rate and tonic changes in the uterus.
The device (cardiotocograph) “draws” 2 graphic images on the tape: on the first - the changing fetal heart rate (HR), on the second - a hysterogram (uterine muscle tone).
The technique is quite informative, easier to perform than electrocardiography and phonocardiography, and allows one to suspect circulatory disorders in the fetus in the early stages of pregnancy. This is important for providing assistance to an unborn child and predicting the birth of the mother.
Background
Since the end of the eighteenth century, leading doctors in European countries have tried to diagnose the pathological condition of a child in the prenatal period at the stage of pregnancy. Laennec is considered the inventor of the stethoscope. The French doctor Kargaradek used this method in listening to the fetal heart and formulated the main provisions about the capabilities of the method in diagnosis.
However, a long period was spent challenging the diagnostic significance.
At that time, most obstetricians had no doubt that even by placing their ear to the belly of a pregnant woman, it was possible to determine whether the fetus was alive, but they refused to consider auscultation as a way to detect pathology
There was no question of any use in wider diagnostics. In 1906–1908, primitive methods of performing intrauterine ECG and phonocardiography appeared. Russian scientists L. Persianinov, V. Demidov, A. Aristov successfully conducted clinical studies to introduce these methods into practice. But the lack of convenient equipment limited the results.
The CTG method was introduced in the 60s of the twentieth century by E. Chon, who proposed simultaneous recording of the activity of uterine tone and fetal heart contractions. Improved equipment now makes it possible to successfully use the technique in antenatal clinics, maternity hospitals and perinatal centers not only during pregnancy, but also during childbirth.
Modern devices automatically decipher the obtained indicators, objectively evaluate, record and store their dynamics in the memory of computer equipment.
conclusions
{banner_banstat10}
Cardiotocography is rightfully one of the most widely used studies in obstetrics. However, like any other technique, it is effective only if it is applied correctly (in accordance with all standards), as well as with proper interpretation of the results obtained.
Unfortunately, there are still disputes and different interpretations of some complex and dubious cases. For this reason, we should not forget that there are also additional research methods that can either confirm or refute possible concerns.
In addition, CTG results remain relevant and informative for no more than 1 week, which means that the key to a favorable pregnancy is regular monitoring of the condition of the fetus.
Technical basis of the method
The device is based on:
- a mechanism for recording heartbeats using one of the types of ultrasound (Doppler effect) through an ultrasound sensor;
- The tone of the uterus is determined by tensometric method.
The graphical representation of the calibration curve is evaluated continuously for 60 seconds.
In addition to obtaining a tachogram and hysterogram, some devices are capable of detecting fetal movements and recording them on tape
How does a cardiotocograph work and what does it show?
This device has the following sensors:
- Ultrasound, which detects the movements of the fetal heart valves (cardiogram);
- Tensometric, determining the tone of the uterus (tocogram);
- In addition, modern cardiac monitors are equipped with a remote control with a button that must be pressed at the moment the fetus moves. This allows you to assess the nature of the baby’s movements (actogram).
Information from these sensors enters the cardiac monitor, where it is processed and displayed on an electronic display in digital equivalent, and is also recorded by a recording device on thermal paper. The speed of the tape drive differs among different types of fetal heart monitors. However, on average, it ranges from 10 to 30 mm per minute. It is important to remember that there is special thermal paper for each cardiotocograph.
example of a CTG tape: above - fetal heartbeat, below - uterine tone values
Types of examination
CTG is carried out in two types.
Indirect cardiotocography (external) - used to examine pregnant women, as well as when labor has already begun, but the amniotic sac is still intact. When installing sensors, the most convenient locations are selected for better signal receipt:
- The ultrasound sensor is fixed in the place of optimal audibility of the heartbeat on the expectant mother’s stomach, depending on the position of the fetus;
- tensometry is carried out from the uterine fundus area.
Direct or internal - performed when the integrity of the membrane of the amniotic sac is compromised. To measure heart rate, a needle electrode is inserted into the nearest part of the fetal body. Tonic contractions of the uterus are recorded with a special catheter located inside the uterine cavity. It allows you to register intrauterine pressure.
CTG is distinguished according to its effect on the fetus:
- non-stressful - the curve is recorded without extraneous influences;
- stress - tests are used to determine the reaction.
The most common tests are the administration of solutions of Atropine and Oxytocin.
The atropine test indicates good permeability of the placenta and the normal condition of the fetus, since the sympathetic nervous system is disinhibited and tachycardia necessarily appears. In case of poor permeability, the proper reaction will not follow. Some scientists provide data on the low accuracy of assessing the health of the unborn child using this test (69.2%).
Oxytocin triggers the onset of contractions, which reduces blood flow to the placenta. A healthy fetus should not react to these changes, but with reduced compensatory capabilities it exhibits a stress reaction.
In relation to the onset of labor there are:
- antenatal cardiotocography (ACTG);
- intrapartum (during childbirth).
What to do if CTG indicators are borderline between normal and pathological?
When registering a CTG and receiving a questionable result, you must:
- Conduct additional research methods (ultrasound, study of blood flow velocity in the uteroplacental system, determination of the biophysical profile).
- After 12 hours, repeat the CTG study.
- Avoid taking medications that may affect the baby's heart rate.
- Carry out CTG with functional tests:
- Non-stress test - consists of studying the heart rate in response to fetal movements. Normally, after the baby moves, the rhythm should speed up. The lack of acceleration after movements is an unfavorable factor.
- Stress test - characterized by a change in heart rate after administration of 0.01 units of oxytocin. Normally, after this drug enters the body of a pregnant woman, the fetal rhythm accelerates, there is no deceleration, while the basal rhythm is within acceptable limits. This indicates the high compensatory capabilities of the fetus. However, if after the administration of oxytocin the fetus does not experience accelerations, but, on the contrary, heart contractions slow down, then this indicates intrauterine hypoxia of the baby.
- A mammary test is an analogue of a stress test, but instead of administering oxytocin, the pregnant woman is asked to massage her nipples for 2 minutes. As a result, the body releases its own oxytocin. The results are evaluated in the same way as in a stress test.
- Physical stress test - a pregnant woman is asked to climb the stairs of the 2nd floor, immediately after this a CTG recording is performed. Normally, the fetal heart rate should increase.
- Breath-hold test - while recording a cardiotocogram, the pregnant woman is asked to hold her breath while inhaling, while the baby’s heart rate should decrease. Then you need to hold your breath as you exhale, after which the fetal rhythm should speed up.
Who is CTG indicated for?
The cardiotocography technique is carried out as prescribed by a doctor, starting from the 28th week of pregnancy. It is not possible to make a recording before this period and it cannot be decrypted. If the norm is recorded and the doctor has no doubts when examining and listening to heartbeats later, then one result is enough.
The study must be repeated if:
- the received recording shows probable signs of pathology;
- the woman’s previous pregnancies had complications (fetal anomalies, intrauterine death, unfavorable genetic history in the family);
- motor activity is impaired (long periods without active tremors appear or, conversely, fetal mobility increases);
- the expectant mother has suffered an acute viral or other infection and is not feeling well;
- the mother has untreated foci of chronic infection;
- any treatment with medication was carried out;
- there is a suspicion of gestosis (the passage of the mother’s blood through the placenta is disrupted, the likelihood of delayed fetal development);
- a woman behaves incorrectly despite pregnancy (smoking, drinking alcohol), including a group of drug-addicted patients;
- pregnancy occurs against the background of various diseases (hypertension, diabetes, kidney and liver diseases, heart defects, obesity);
- the timing shows the possibility of “post-maturity” (41 weeks or more);
- there is a suspicion of delayed fetal development;
- a woman has a multiple pregnancy;
- symptoms suggest preeclampsia;
- bloody discharge from the uterus appears;
- symptoms indicate possible oligohydramnios or polyhydramnios.
Sometimes CTG is performed earlier (before 28 weeks) if it is necessary to confirm the presence of fetal heartbeats if the doctor cannot detect them. The prognostic value of the examination increases at 35–36 weeks.
How does CTG influence medical tactics?
{banner_banstat9}
The results of the study must be taken seriously. The doctor who evaluates the CTG bears great responsibility. It is for this reason that each film recording cardiac activity must be evaluated by the responsible physician, certified by his signature indicating the time of the study and pasted into the birth history.
A normal cardiotocogram is a sign of correct and careful management of labor.
When receiving a questionable CTG, the doctor has no more than 40 minutes to correct labor activity. At this stage, it is necessary to eliminate all risk factors leading to hypoxia:
- Stop administering “oxytocin” and prostaglandin-based drugs;
- Explain to the woman how to breathe correctly during contractions;
- Determine the position of the fetus and exclude compression of the umbilical cord;
- Perform an ultrasound to exclude incipient placental abruption;
- Administer drugs that improve the rheological properties of blood.
Poor CTG is a good reason to change delivery tactics in favor of emergency cesarean section,
or eliminate the causes of acute hypoxia. Ignoring pathological CTG is absolutely unacceptable, because this can cause fetal death.
In other words, CTG is a serious tool in the hands of an obstetrician.
How is the procedure performed?
Recording a cardiotocogram does not require lengthy special preparation. It can be carried out after instructions by nurses and physician assistants.
A woman should not be excited or tired. She should rest after the journey; she is allowed to have a snack, but not overeat.
The sensors are lubricated with a special gel for better contact with the body. Standard recording lasts 10 minutes, longer according to indications. The indicators are more informative if the fetus moved while the device was turned on.
With constant monitoring during labor, the reaction of the fetal heart to uterine contractions is recorded. There was no evidence that the procedure was harmful to the fetus. Sometimes expectant mothers note an increase in the child’s excitement after the study. This is a temporary phenomenon, it proves that the baby hears the operation of the sensors.
The patient is placed in a comfortable position, you can lie on your side, sit
Briefly about the physiology of the fetal heart
The heart is one of the very first organs that is formed in the embryo’s body.
Already at 5 weeks of pregnancy, the first heartbeats can be recorded.
This happens for one simple reason: there are cells in the heart tissue that can independently generate an impulse and cause muscle contractions. They are called pacemakers, or pacemakers. This means that the work of the fetal heart in the early stages of pregnancy is completely independent of the nervous system.
Only by the 18th week of gestation do signals from the vagus nerve arrive to the heart; its fibers are part of the parasympathetic nervous system. Thanks to the influence of the vagus nerve, the heart rate slows down.
stages of fetal heart development
And by the 27th week, the sympathetic innervation of the heart is finally formed, which leads to an acceleration of heart contractions. The influence of the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous system on the heart is the coordinated work of two antagonists, whose signals are opposite.
Thus, after the 28th week of pregnancy, the heart rhythm is a complex system that obeys certain rules and influences.
For example, as a result of the baby’s physical activity, signals from the sympathetic nervous system predominate, which means that the heart rate accelerates. Conversely, when a baby sleeps, signals from the vagus nerve dominate, which leads to a slower heart rate. Thanks to these processes, the principle of “unity of opposites” is formed, which underlies the myocardial reflex. The essence of this phenomenon is that the work of the fetal heart in the third trimester of pregnancy depends on the motor activity of the baby, as well as the sleep-wake rhythm. Therefore, to adequately assess heart rhythm, it is necessary to take these factors into account.
It is thanks to the peculiarities of the innervation of the heart that it becomes clear why cardiotocography becomes most informative in the third trimester of pregnancy, when the work of the heart obeys certain rules and patterns.
How is the curve estimated?
Long-term debates over visual assessment of the resulting curve showed a difference in results reaching up to 78%. Such an interpretation cannot be attributed to normality or pathology due to low reliability.
In 1976, V. Fischer proposed a scoring system for attributes (assessment). The modified scoring scale made it possible to increase the diagnostic accuracy.
The essence of the Fisher assessment. 5 values of the cardiotocographic recording are analyzed, each of which can have from 0 to 2 points. Calculating the amount is an assessment of the condition of the fetus.
To distinguish the norm from deviations, there are the following evaluation indicators:
- basal rhythm - the average frequency of contractions of the fetal heart (values from 120 to 160 beats per minute are taken as the norm);
- changes in rhythm (variability) - possible in the form of instantaneous deviations or recorded over a time period (minute);
- clear periodicity in rhythm changes;
- The myocardial reflex is the name given to simultaneously recorded tachycardia and an increase in the activity of the child’s movements.
Decoding and evaluation of the performed cardiotocography is carried out only taking into account all indicators
Fischer's interpretation:
- norm - from 8 to 10 points;
- from 5 to 7 points - indicates oxygen starvation, the doctor prescribes treatment to improve uterine blood flow;
- 4 or less points - requires urgent clarification of the cause, since the fetus suffers from severe oxygen deficiency, the patient is admitted to the inpatient department and the decision on further examination is made by a council of doctors.
When is the examination done and how often?
The study is carried out no earlier than 32 weeks. It is by this time that the nervous and cardiovascular systems reach a certain maturity. By 8 months, the myocardial reflex is formed - the relationship between cardiac activity and motor activity of the fetus. At the same time, the activity-rest cycle is established. Rhythmic changes in fetal sleep and wakefulness follow each other throughout the remaining period of pregnancy.
Cardiotocography must be performed 2 times during the 3rd semester. However, the frequency of the study is determined by the doctor based on the mother’s medical history, pregnancy history, results of other examinations and risk factors.
What is the rhythm of heart contractions?
The changed rhythm of contractions is recorded as:
- accelerations (accelerations) - heart rate exceeds the average level by 15 beats or more for a time longer than 15 seconds;
- oscillations - fluctuations in the basal rhythm and frequency are observed from 5 to 15 beats per minute with a certain repeatability of the wave;
- decelerations (slowdowns) - if for a period of 15 seconds the heart rate decreases by more than 15 beats.
Early decelerations are considered to be decreases associated with uterine contractions and pressure on the fetal head.
Late - inconsistent drops in frequency at the “peak” of contraction (considered the most dangerous sign for the fetus).
Variable - changes in frequency over time, depending on the strength of uterine contraction and other reasons.
There are many types of rhythm in the fetus. The most common options are:
- monotonous - may be the norm if the fetus is sleeping, but a lack of oxygen supply cannot be ruled out, which should be regarded as a pathology;
- sinus - the recorded curve has the form of a sinusoid, where the numerical values of accelerations alternate with decelerations, is regarded as the norm during motor activity, as a pathology - during fetal rest.
The waveform on the recording does not resemble an electrocardiogram. There is no need to confuse them and try to make a diagnosis yourself.
Services and prices
CTG: (Multiple pregnancy)
1500 ₽
Sign up
CTG: (Fetal cardiotocography)
1300 ₽
Sign up
Cardiotocography (CTG) is a functional diagnostic method based on recording the fetal heart rate and uterine contractility during pregnancy and childbirth. Cardiotocography is based on the Doppler effect and the principle of ultrasound. An ultrasonic wave emanates from the sensor, which is reflected from the pulsating heart of the fetus, changes the frequency and is sent back. The monitor's electronic system registers and converts the signal. This recording is called a cardiotocogram.
Two sensors are attached to the pregnant woman's belly. For better contact with the skin of the anterior abdominal wall, a special hypoallergenic gel is applied. At the point of best audibility of the heartbeat (usually in the navel area), a cardiac sensor is applied, which records the fetal heartbeat. If the patient is pregnant with twins, then use two sensors at once or take measurements one by one. The strain gauge records the contractile activity of the uterus and the motor activity of the fetus.
Sometimes the baby's movements are recorded using an additional sensor. During the examination, the device makes loud sounds, which should not be alarmed. This is the baby's heartbeat. The fetus may change its position during the examination, which will lead to incorrect recording. However, thanks to the sound component of the procedure, the doctor can control the correct location of the sensors and rearrange them in time to follow the child.
Cardiotocography, together with the results of other studies, makes it possible to recognize serious disorders, including fetoplacental insufficiency, intrauterine fetal hypoxia, various anomalies in the development of the fetal cardiovascular system, indirect signs of intrauterine infections, and the threat of premature birth.
Types of devices
Existing CTG machines have a simpler design and have a complex automatic application.
For simple ones, cardiotocography is done in any obstetrician-gynecologist's office. You will have to manually calculate the indicators and scores yourself.
Modern analysis is carried out by computer, resulting in very sensitive data on accuracy (from 87 to 90%) about intrauterine pathology
According to automatic analysis:
- up to 1.0 points – confirm the complete health of the fetus;
- with a score from 1.1 to 2.0, the results are regarded as initial violations;
- from 2.1 to 3.0 points - you can make a statement about pronounced violations;
- with 3.1–4.0 points, the conclusion indicates pronounced changes in the condition of the fetus.
Modern devices have their own rating scales. The automated cardiac monitor "Unicos" shows a score of up to 4.0 and provides conclusions as:
- norm,
- initial changes
- pronounced violations,
- urgent critical condition.
Using a cardiotocograph of the “Intrapartum Automated Monitor” type, the calculation is based on 10 points, and labor activity (intensity, regularity, duration of contractions) is simultaneously analyzed. The monitor shows the optimal time for delivery and preservation of fetal viability, the reactivity index (the degree of severity of the reaction to external stimuli).
The device settings for examinations during labor and pregnancy are different.
Indications for the study
The purpose of cardiotocography is timely diagnosis and detection of fetal disorders. Based on data from a number of functional diagnostic studies, such as ultrasound, CTG, Doppler measurements, anamnesis, the obstetrician-gynecologist chooses pregnancy management tactics, treatment, the optimal date and method of delivery.
Indications for additional cardiotocography may include:
- Rhesus conflict
- Preeclampsia in the second half of pregnancy
- Maternal diseases
- Post-term pregnancy
- History of premature birth
- Fetal growth restriction
- Pregnancy pathologies and fetal development abnormalities identified by ultrasound
- Oligohydramnios or polyhydramnios
- Multiple pregnancy
- Complicated obstetric and gynecological history (previous abortions, miscarriages, premature births)
- Changes in the nature of fetal movements (complaints about a decrease or increase in the number of fetal movements per day)
What pathology do the study results warn about?
It is impossible to make a diagnosis based on CTG alone. The examination always includes blood and urine tests, ultrasound diagnostics, Doppler sonography and others. A cardiotocogram allows you to quickly conduct an initial examination and exclude the possibility of fetal pathology.
It is believed that abnormal CTG data indicate:
- the possibility of entwining or pressing the umbilical cord;
- formation of congenital heart defects, arrhythmias;
- hypoxic condition.
If the mother has any disease that requires prenatal hospitalization, then CTG is performed daily.
Fetal hypoxia may be associated with impaired blood circulation in the placenta
Preparation for the procedure
The study does not require special preparation. However, it is worth considering the duration of the procedure. It will be important for mom to relax and be calm. On the eve of the procedure, the pregnant woman is recommended to get a good night's sleep and rest. On the day of the study, you should take care of a light meal 1-2 hours before. And immediately before the procedure, go to the toilet. During CTG, the expectant mother should not be distracted or disturbed by anything. You can take a book or magazine with you, but electronic devices, including your phone, will have to be turned off, as the equipment creates interference with the recording.
Possible misinterpretation
According to the CTG conclusion, pathology is sometimes visually determined, but it is subsequently not found. This happens if:
- the woman ate too much and came for examination;
- the timing is poorly chosen, the child is “sleeping”, his activity is low;
- the mother shows signs of obesity (signals are received with insufficient clarity through a thick layer of fat);
- the baby is overly active;
- not enough gel applied to the sensor;
- multiple pregnancy.
Usually the doctor recognizes these errors with the help of repeated examination.
The use of the cardiotocography method in clinical practice shows a significant impact on the prevention of intrauterine mortality in children. The experience of various institutions has proven a reduction in this indicator by 20–46%. These are very significant figures in improving public health.
How long does CTG last?
The procedure lasts from 30 to 60 minutes depending on the baby’s activity. After 32 weeks, the fetus is characterized by periods of sleep and wakefulness. The active state lasts 50-60 minutes, while the calm state lasts 20-30 minutes. When assessing cardiotocography, the leading period is the period of fetal wakefulness. Therefore, the duration of the study may vary.
Evaluation of fetal cardiotocography
CTG results may not always be accurate - for this, certain conditions must be met, and the first of them is to conduct the study only during those hours when the child is most active (usually from 9 to 14 hours and from 19 to 24 hours).
“Bad” CTG: reasons why distorted research results may be obtained
- Carrying out CTG on an empty stomach or after a heavy lunch (it is better to carry out the procedure a couple of hours after breakfast or a light dinner);
- Before the procedure, you should not use certain drugs that distort CTG readings: glucose, magnesium, sedatives;
- interpretation of cardiotocography will be unreliable if the study is carried out under stress or after physical activity (for example, immediately after cleaning or walking up the stairs);
- You should also not conduct research after drinking alcohol or smoking;
- in a pregnant woman with excess body weight, CTG interpretation can also give distorted results (due to the fat layer, which prevents the sensor from “hearing” the baby’s heartbeat);
- sometimes with fetal CTG, the decoding gives the result of a heartbeat of 65-80 beats per minute; There is no need to panic: these are indicators of the woman’s heart rate, not the fetus, due to incorrect application of the sensor (just apply the sensor correctly and conduct the study again).
How to get the results of a “good” CTG:
- get some sleep and have a snack;
- After eating, move around, but before the test, rest so that your heart rate is restored;
- Go to the toilet in advance to feel calm during the 30 minutes of the study;
- do not smoke at least 2 hours before the procedure.
Consequences of pathology
Initial hypoxia is a condition that can lead to the development of various somatic diseases in a child. The most dangerous consequences:
- disturbance of cerebral blood flow;
- hydrocephalus (accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid under the membranes of the brain and/or in its cavities);
- the body's predisposition to sudden onset of seizures;
- pathologies in the development of internal organs;
- intracranial hemorrhage;
- Cerebral palsy.
Prolonged oxygen starvation during pregnancy can lead to childhood disability, mental retardation and poor social adaptation.
Fetal reactivity index and non-stress test
The first indicator reflects the state of the fetal nervous system in response to external influences. Such stressful situations primarily affect the state of the cardiovascular system. Points are used for calculation, where:
- 0 – complete absence of response to external stimulus.
- 1 – pronounced decrease in reactivity.
- 2 – noticeable decrease in reactivity.
- 3 – moderately expressed response to external influence.
- 4 – initial degree of pathological reactivity.
- 5 – adequate response to external influences.
Applying a warm or cold object to the pregnant woman's abdomen is used to assess fetal reactivity
A non-stress test is carried out to assess the state of the baby’s cardiovascular system during his voluntary movements. Normally, such a test should be negative, which implies the presence of 2 or 3 increases in heart rate by 15 beats, lasting no more than 20 seconds.
Despite the large number of indicators, cardiotocography is only an additional diagnostic method. For a comprehensive assessment of the condition of the mother and fetus, other instrumental examinations, laboratory test data and consultation with an experienced specialist are necessary.
Indications for the procedure at 32 weeks
Cardiotocography makes it possible to identify disorders such as polyhydramnios and oligohydramnios, fetal hypoxia, intrauterine infection, abnormalities in the structure of the heart and blood vessels, and fetoplacental insufficiency.
The procedure is prescribed in the following cases:
- The presence of endocrine or systemic diseases in the mother (diabetes mellitus, anemia of various origins, etc.).
- Conditions that threaten the course of pregnancy (malpresentation of the baby, multiple and post-term pregnancy, severe toxicosis, persistent increase in body temperature, etc.).
- Previously identified abnormalities during ultrasound diagnostics (deviation of the fetal size from the norm, decrease in its motor activity, developmental delay, pathology in the amniotic fluid and placental circulatory system).
- Previously recorded cases of premature birth and spontaneous termination of pregnancy in the early stages.
- Rhesus conflict between mother and fetus.
This type of diagnosis does not require special preparatory measures. In order for the results to be most accurate, the expectant mother should lie as still as possible, so before the study it is better to go to the toilet in advance. It is prohibited to take analgesics or sedatives 11–12 hours before the start of CTG.
It is allowed to carry out the procedure in a position on your side or half-sitting, resting your back on a previously prepared pillow. A special device consisting of two parts is attached to the expectant mother’s belly. The first sensor is lubricated with gel and installed in the projection of the best audibility of the fetal heartbeat.
The second - to the area of the fundus of the uterus to record its excitation and further contractions. Next, the pregnant woman is offered a special button that she will press during periods when the baby moves. The appointment is made by a doctor within 30–60 minutes. A special device records all data in the form of graphs on paper tape.
Correct placement of sensors during CTG reduces errors in the study
Possible reasons for poor results
If at any period after 28 weeks - 35 weeks, 36 weeks or some other period, the result of the CTG reading showed 7 points - this does not mean that everything is bad. A bad result can be obtained erroneously for a number of reasons:
- The results of cardiotocography can be affected by stressful situations and nervous breakdowns. It is possible that to avoid distorting the result, the doctor will recommend taking some sedatives before recording a CTG.
- Excessive exercise before the examination may also give incorrect results. It is more correct to achieve a decrease in muscle tension before starting CTG recording and only then begin diagnostics.
- A poor cardiotocography result can be obtained if the baby is not very active. This problem can be eliminated if the pregnant woman eats something sweet before the examination and is moderately active.
Women do not choose when to have cardiotocography during pregnancy. In this matter, you must strictly adhere to the recommendations of your doctor. In some cases, this procedure has to be repeated several times, and in case of poor performance (7 points and below), it happens every day.
What does CTG show during pregnancy?
Using the KTG method, specialists are able to identify possible pathological abnormalities or refute their presence.
The study can determine the development of such dangerous conditions during pregnancy as:
- lack of oxygen in the fetus (hypoxia);
- development of infectious processes of an intrauterine nature;
- lack or excess of amniotic fluid;
- abnormal processes in the baby’s cardiac activity;
- functional disorders in the placenta (placental insufficiency);
- accelerated maturation of the placenta, which threatens premature birth.
Early detection of abnormalities using cardiotocography allows a specialist to adjust pregnancy management or prescribe special treatment to prevent serious complications.
Can there be errors when determining accelerations?
Of course yes! The indicators of the CTG curve are considered taking into account data from the anamnesis, clinical picture and other studies. A change in the functional activity of the fetal heart muscle is a response of the autonomic system, which only indirectly reflects the processes occurring in the body of a developing baby.
If, with insufficient oxygen supply, the fetal tissues have managed to adapt to this condition, hypoxia will not affect the study graph in any way. That is why practicing specialists consider CTG, although a very important technique for diagnosing pathologies of fetal development, but only an additional one. Its indicators reflect only part of the “mother-placenta-fetus” system and the results of cardiotocography alone do not make a diagnosis.
What is the essence of the diagnostic technique?
During pregnancy, CTG is one of the mandatory examinations; it is prescribed from the 28th obstetric week. The basis of the method is to record uterine contractions and electrical activity of the fetal heart muscle. CTG recording is performed in the functional diagnostics room. The procedure can be performed in any position convenient for the expectant mother - sitting, lying on her side or back.
The uterine and fetal sensors are attached to the woman’s bare belly with elastic bands. The device is equipped with a special button - the doctor asks the woman to press it in cases where the fetus begins to move. The data obtained during the diagnostic procedure is a graphical representation of curves depicting the contractions of the uterus and the baby's cardiac activity, as well as points that indicate its movement.
Modern cardiotocographs have a function for automatically decoding the study - the protocol for such analysis contains a list of letters and numbers. That is why we want to dwell in detail on the criteria for assessing CTG.