Reception is conducted by:
Krivonosov Denis Sergeevich -
cardiologist, candidate of medical sciences
Make an appointment
Svitova Elena Olegovna —
Obstetrician-gynecologist. Functional diagnostics doctor. Ultrasound diagnostics doctor. Doctor of prenatal ultrasound diagnostics.
Make an appointment
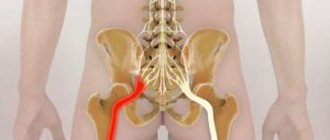
Pelvic varicose veins (PVVD) is a chronic vascular pathology characterized by dilation of the pelvic veins. With the disease, the return flow of blood worsens, causing stagnation and poor circulation. Symptoms of pelvic varicose veins in women are nonspecific and are inherent in many gynecological pathologies, so literally a few decades ago the disease could not be diagnosed in time and only the symptoms were stopped, and their root causes were not eliminated.
According to a study conducted in 1999, in approximately 15-20% of cases in patients with vein disease, the reason for visiting a gynecologist was pain in the lower abdomen. However, the diagnosis was correctly made only in 2% of cases. It’s scary to imagine that about 15% of women had their uterus removed as a result of an incorrect diagnosis.
The Profimedica clinic employs professionals with extensive experience. Modern equipment from the world's best manufacturers allows specialists to diagnose and eliminate pathology at the earliest stages.
Causes of development of varicose veins of the pelvis
Today, the main cause of varicose veins is considered to be a history of pregnancy. The situation arises due to the fact that the growing fetus puts pressure on nearby organs and vessels, disrupting blood circulation. A healthy female body after childbirth is able to restore blood circulation on its own and no problems arise. However, under the influence of certain provoking factors, the tone in the vessels is not restored, leading to vascular pathology.
Factors contributing to the occurrence of the disease:
- excessive physical activity;
- sedentary lifestyle;
- diseases of the reproductive system (tumors, polycystic disease, endometriosis, etc.).
It is worth noting that varicose veins of the venous vessels of the pelvis can occur not only during pregnancy. Recently, scientists have been actively discussing the effect of hormonal contraceptives and hormone-containing drugs on the development of venous pathology. This assumption is based on the fact that the disease occurs much more often in women of childbearing age, which means hormones play a major role in this process.
Causes of varicose veins in pregnant women
During pregnancy, a woman's hormonal background changes, the volume of blood in the body increases, the uterus increases in volume and compresses the lumen of the inferior vena cava. What happens to the body:
- blood flow is redistributed - an additional, embryonic circle of blood circulation appears;
- the venous load on the circulatory bed of the pelvis and lower extremities increases, complicating the outflow of blood from the legs to the heart;
- body weight increases;
- the volume of circulating blood doubles;
- the load on the heart muscle increases;
- blood clotting increases;
- venous blood flow slows down;
- venous vascular walls weaken under the influence of progesterone;
- intravascular venous pressure increases (especially in the legs).
How does varicose veins develop?
Increased levels of progesterone , characteristic of the hormonal background of pregnancy, weaken the muscle tone of the venous wall throughout the vascular bed of the body. The increased volume of blood in blood vessels with weakened walls overwhelms and deforms them. Many pregnant women develop varicose veins.
Varicose veins are also possible due to the growth of the fetus and uterus . When expanded, they put pressure on the large vessels of the pelvic cavity (especially the inferior vena cava and right ovarian vein), which disrupts the outflow of venous blood to the heart. Venous stagnation of the underlying sections fills the vascular bed with blood, dilating the veins of the pelvis, genitals, groin, and lower extremities. As a result, varicose veins of the superficial system occur. In this case, the deep vein system of the lower extremities does not suffer, since they are located in a muscular sheath.
Signs of varicose veins
Most often, it all starts with visual manifestations. Spider veins and reticular veins appear. Then there are clinical symptoms: swelling of the lower extremities at the end of the working day, heaviness, fatigue, a feeling as if the legs are on fire. Some patients experience a condition called restless legs syndrome. In more advanced stages, skin changes (redness, thickening, soreness) may be observed along the course of varicose veins. This condition is characterized as thrombophlebitis. Trophic changes in the skin and the formation of trophic ulcers on the affected lower limb may also occur.
Symptoms of varicose veins of the pelvis
All women of childbearing age need to be aware of the symptoms of varicose veins. Since the disease has a non-specific clinical picture, contacting a specialist is required when the following signs appear:
- Constant pain in the lower abdomen.
- When pain is relieved with analgesics and antispasmodics, the effect does not last long.
- The pain intensifies during and after sexual intercourse.
- There is a pronounced premenstrual syndrome.
- Painful sensations occur during hypothermia and overheating of the body, as well as during physical exertion and prolonged stay in one position.
In half of the cases with pelvic varicose veins, veins can be visualized in the area of the inner thigh, buttocks, and external genitalia. However, in the initial stages of the disease, this manifestation is absent, and it is quite difficult to independently suspect the pathology.
Medicine distinguishes 3 stages of the disease, depending on its severity. At the first stage, the diameter of the vein expansion is up to 0.5 cm. At the second stage, the expansion reaches 0.6-1 cm. At the third stage – over 1 cm.
Varicose veins of the vulva and vagina
A characteristic venous pattern appears in the genital area. Gradually, varicose veins enlarge and swell. This makes the woman uncomfortable. If she does not consult a doctor for help, inflammation, thrombosis, and ulceration join the varicose veins. Varicose veins in the vagina are more difficult to notice due to their similarity to ordinary inflammation of the genitourinary system.
Symptoms:
- heaviness, discomfort, aching pain in the lower abdomen;
- burning sensation when urinating; itching at the entrance to the vagina after emptying the bladder;
- pain during defecation;
- discomfort and pain during sexual intercourse.
Women turn to a gynecologist complaining of discomfort, pain, and spotting during sex . During examination (vaginal examination), the doctor makes a diagnosis. He gives recommendations that must be followed.
A timely diagnosis prevents the possibility of complications. Using modern treatment methods for emergency indications, a pregnant woman is relieved of vaginal varicose veins long before giving birth.
Therefore it is important :
- register for pregnancy early ;
- do tests on time ;
- discuss changes in health, especially painful ones, with your doctor;
- do not engage in sexual intercourse , which is dangerous with varicose changes in the vagina and vulva.
During childbirth, varicose veins of the vaginal veins are complicated by injury to the changed vessels and venous bleeding . This becomes a serious complication in the postpartum period.
If the doctor has serious reasons to avoid such a risk, shortly before the expected date of birth, the woman is admitted to the hospital and undergoes a planned caesarean section .
Diagnostics
Timely detection of the process of vascular dilatation increases the likelihood of its cure and prevention of relapses.
To diagnose pelvic varicose veins, doctors at our clinic use instrumental research methods. One of the most effective ways to detect the disease is ultrasonography. This method is carried out in conjunction with transvaginal and abdominal ultrasound, which allows specialists to obtain the necessary data for diagnosis. During ultrasonography, vascular dilation can be identified by multi-colored spots of irregular shape.
Another research method is laparoscopy. In this case, the presence of pathology is signaled by bluish-colored formations that have a thin, tense wall in the area of the uterine ligament or ovaries.
Recently, a modern diagnostic method – selective oophorography – has been gaining popularity. During the study, a contrast is performed on the patient's blood vessels, thanks to which the doctor is able to see any deviations in their structure.
A CT scan may also be performed. The method helps to see the vessels in the woman’s internal genital organs.
Pronounced discomfort during sexual intercourse and other unpleasant manifestations of the disease contribute to the deterioration of the psychosomatics of patients, which often causes diagnostic errors. The presence of a clear pathognomonic symptom, combined with the absence of signs of pathology of the pelvic organs during a traditional examination and manifestations of clear psychosomatic disorders, often leads specialists to think about the psychoneurological nature of the disease. As a result, instead of treating varicose veins, patients are prescribed consultations with sex therapists and psychotherapists.
Prevention of varicose veins and its complications during pregnancy
Basic recommendations:
- Early contact with a gynecologist, registration for pregnancy. Following the recommendations of a specialist. Regular visits to the antenatal clinic.
- Healthy, active lifestyle : walks in the fresh air, Pilates for pregnant women, yoga, swimming, aqua aerobics. Avoidance of saunas, steam baths, hot tubs, and exposure to the open sun.
- Proper nutrition with enough vitamins, microelements, fiber. Exclusion of sweet, fatty, fried, smoked, flour, starchy foods. Body weight monitoring .
- Drinking enough water.
- Rejection of bad habits.
- Loose clothing made from natural fabrics. Refusal of high-heeled shoes and tight ballet shoes. Wearing comfortable, soft shoes made of natural materials with a comfortable last and instep supports.
- Breaks during work to warm up and walk.
- Sleeping on the left side , which reduces the pressure of the uterus on the inferior vena cava and right ovarian vein.
This will prevent further development of varicose veins and its complications.
Diagnostics
If the superficial veins of the lower extremities, vulva, or vaginal opening are affected, or external hemorrhoids appear, there are no problems with making a diagnosis. The doctor assigns it during examination, taking into account the patient’s complaints and general information from the medical history.
It is more difficult to detect varicose veins of the internal organs of the pelvis : deep hemorrhoids, vagina, uterus and bladder. Signs:
- dilation of the veins of the uterus, visualized on ultrasound.
- internal hemorrhoids can be palpated during rectal digital examination.
- Vaginal varicose veins are determined during a vaginal examination.
- damage to the bladder when blood appears in the urine - if there are no other reasons and there are changes in the veins in neighboring organs.
The results of routine examinations of the pregnant woman, which are carried out in accordance with the standard protocol for pregnancy management, are important. For example, a urine test containing blood.
A decrease in hemoglobin levels is often associated with internal chronic bleeding from damaged vessels. Increased sugar increases the vulnerability of vascular walls to infection.
During pregnancy, it is safe to perform Doppler ultrasound ( USDG ) of the venous vessels .
The method defines:
- degree of development of varicose veins;
- localization and degree of deformation of venous valves;
- the severity of the disturbance in the direction of blood movement through the veins (in the opposite direction from the heart down and towards emergency collaterals);
- the presence of changes in surrounding tissues.
In severe cases (if spontaneous rupture of internal dilated venous vessels and bleeding is suspected), magnetic resonance imaging is performed .
Treatment methods for pelvic varicose veins
At the Profimedica clinic, treatment of pelvic varicose veins is carried out in two ways: conservative and surgical.
In order to identify pathology, differential diagnosis is carried out using laparoscopy. The presence of varicose veins is indicated by bluish formations with a thin, tense wall in the area of the ovaries and the broad uterine ligament detected by this method.
Conservative treatment
The first method is used if the patient consults a doctor in the early stages of the disease. Conservative treatment methods include:
- Elimination of factors that provoke the development of pathology (change of sedentary or standing work, increased activity, etc.).
- Avoiding excessive physical activity.
- A balanced diet, including more fresh vegetables and fruits and excluding alcohol, cigarettes, fatty and spicy foods.
- Using a contrast shower to improve blood circulation in the body.
- Carrying out a daily set of exercises (“scissors”, “birch tree”, “bicycle”, etc.).
- The use of special breathing exercises, which are based on breathing using the muscles of the anterior abdominal wall.
- Constantly wearing compression tights.
- Taking medications that accelerate blood flow (phleboprotectors).
Surgery
If the disease was detected already in severe stages, or it was not possible to cure pelvic varicose veins in women using conservative methods, doctors may recommend surgical intervention.
During the operation, the surgeon eliminates the abnormal reflux of blood by passing through the dilated gonadal arteries. When eliminating the disease, as a rule, the method of embolization of ovarian vessels is used. For maximum precision of surgical intervention, all manipulations are carried out under the control of parallel angiography.
In rare cases, open resection or vein clipping techniques during laparotomy may also be used. In this case, the progress of the operation is monitored using an endoscope.
How to understand that varicose veins are developing on the legs
Many people believe that the first signs of varicose veins are spider veins, swollen areas of veins and other external manifestations. But the pathology is very insidious and for a long time disguises itself as ordinary fatigue of the lower extremities, without revealing itself from the outside.
Get an online consultation
right now.
Get
Signs of the development of varicose veins that you need to pay attention to:
- Frequent muscle cramps. Since the blood does not circulate in the required mode through the veins, it stagnates and, as a result, oxygen starvation of the tissues. These factors lead to seizures.
- Unhealthy skin color on legs. Lymph and blood do not circulate well in the affected areas of the lower extremities. The skin color here becomes lighter with dark spots. As the disease progresses, these spots begin to become red, swollen, and itchy. If treatment is not started, the likelihood of trophic ulcers increases significantly.
- The legs and ankles begin to itch for no reason . In the vessels that are adjacent to the skin, transformations occur due to stagnation of blood and lymph. Metabolic products are not removed from these areas properly, which leads to itching, burning, peeling of the skin of the legs and its excessive dryness.
- Tingling, numbness of the limbs. At the initial stage of varicose veins, the feet may become numb for no reason. The patient will feel a tingling sensation. These symptoms arise due to poor functioning of the joints and tissue hypoxia. Normal motor activity is disrupted because the tissues lack interarticular fluid. If numbness becomes regular, then you should not postpone a visit to the doctor.
- Swelling . When the valve does not work at full strength, fluid accumulates in the intercellular space and swelling occurs. People prone to varicose veins are recommended to measure the volume of their legs in the morning and in the evening. A reason to sound the alarm and visit a phlebologist will be a change in indicators of 1 cm upward in the evening.
- Pain in the legs after a static position. If a person sat or just stood for a long time, and after that the lower limbs began to hurt and “hum,” then it is worth paying special attention to this factor.
At the final stages, dilated veins clearly appear on the skin of the lower extremities against a background of swelling and pain. During the period of decompensation in the last stages of varicose veins, signs of thrombophlebitis and trophic ulcers may appear.
Indications and contraindications for CT of the pelvic vessels
MSCT is performed using ionizing radiation, so scanning is done only if indicated. CT angiography is recommended for patients if they have the following symptoms:
- pain in the legs of unknown etiology, numbness, swelling, cramps in the area of large muscles;
- signs of pelvic organ dysfunction;
- abdominal pain in the absence of objective reasons;
- signs of internal bleeding in the pelvic area;
- violation of reproductive function against the background of changes in the nature of the blood supply to the organs of the genitourinary system;
- post-traumatic conditions when injuries are localized in the pelvic area.
A referral for tomographic angiography of the pelvic vessels is given by the attending physician: surgeon, phlebologist, gynecologist, urologist and other specialized specialists.
The use of modern equipment when performing MSCT angiography allows us to reduce the radiation dose to the patient. But the combination of side effects of X-ray scanning and the administration of a contrast solution determines a number of contraindications to this examination method:
- pregnancy in the first trimester;
- conditions and diseases that exclude the possibility of scanning organs and systems using ionizing radiation;
- early childhood (due to difficulties with catheter installation and the need to remain still during the study);
- allergy to iodine preparations;
- severe renal failure;
- diabetes mellitus during therapy with Metformin and analogues;
- hyperfunction of the thyroid gland.
A relative contraindication for CT angiography of the pelvic vessels is a patient weight of more than 150 kg or a chest/abdominal circumference of more than 150 cm, which is associated with the size of the annular part of the tomograph and the load capacity of the scanner table. If there are one or more restrictions, the doctor will select another method of hardware examination of the bloodstream.
MSCT angiography of the pelvic vessels: acute arterial thrombosis with 3D reconstruction (A) and on frontal images (B)
Preparation for CT angiography of the pelvis in women
Angiography of the pelvic vessels using a computed tomograph in women is often performed to assess the blood supply to the reproductive system. The study reflects the condition of the uterine arteries, vessels of the rectum and bladder. Using layer-by-layer photos, the radiologist notes the peculiarities of the blood supply to the ovaries, fallopian tubes, and cervix.
To improve the quality of the examination, women are advised to follow the following recommendations:
- fast for 6 hours before the procedure, water an hour before the examination;
- donate blood for creatinine to assess kidney function;
- the study is carried out with an empty bowel: if you are prone to constipation, consult a doctor;
- warn about the presence of allergic reactions to iodine;
- tell the specialist about existing diseases and medications taken, possible or confirmed pregnancy.
Before scanning, you must change into comfortable clothes, remove belts, piercings, accessories, jewelry that may distort the image on the tomogram. Women during lactation are advised to express milk before the contrast agent is administered, and after the procedure is completed, two feedings should be skipped.
Patients are advised to bring the results of previous studies and existing doctor’s reports (if available). The creatinine test is valid for 10 days, then a repeat blood draw is required. The Clinic “Medicine of the Northern Capital” offers to do a rapid test before performing a tomography, which will allow a qualitative assessment of the filtration function of the kidneys.
CT angiography of Leriche syndrome
CT angiography of the pelvic vessels is a modern informative method for diagnosing diseases of the circulatory system in this area. Compliance with the doctor’s recommendations reduces the risk of complications and helps improve the quality of the images obtained.
The likelihood of developing male infertility
The time has passed when women were considered the main “culprits” of infertile marriages. According to modern data, more than 40% of cases of infertility in men are associated with dilation of the veins of the spermatic cord and testicles, and the prognosis worsens over time. Therefore, operations to eliminate varicocele should be performed at a young age. After successful treatment, the risk of testicular atrophy and infertility is significantly reduced. It is now possible to treat varicocele of any degree using endovascular surgery without incisions and pain, so you should not delay this treatment for a long time.