© Author: A. Olesya Valerievna, candidate of medical sciences, practicing physician, teacher at a medical university, especially for SosudInfo.ru (about the authors)
During operation, the heart produces many sound effects that characterize the process of myocardial contraction, valve movement, and the impact of moving blood on the walls of blood vessels. To register and evaluate these sounds, FCG - phonocardiography is used.
The most accessible way to determine sounds is auscultation, when the doctor listens to the heart using a phonendoscope. However, not all sound waves can be caught by the ear, even “armed” with this simple device, and much remains unheard. To detect various noises, the phonocardiography method was proposed , when sounds are amplified using a microphone, and the nature of the sound waves is analyzed by their graphic recording.
In cardiology, FCG is used in conjunction with electrocardiography, then the doctor is able to more accurately determine the time of occurrence of a specific noise and its connection with the contraction of certain parts of the heart. The method is applicable for both adults and children, including newborns.
The essence of the technique
Physiology involves the formation of different sounds that have individual differences. Sometimes it is difficult even for a professional to distinguish them. However, it’s not difficult to figure out the strength of sounds and frequency. Strength is a unique value proportional to the amplitude of the wave that is produced. It is measured in decibels. The louder the final sound comes out, the greater the force with amplitude is reflected in the graph. Frequency is measured in hertz. The value is the number of vibrations of sounds per specific time unit.
Note! The ear can only detect a small range at 20-20000Hz. Everything that goes beyond this data can be covered by converting it into a graph only with special medical equipment.
People usually go to see a doctor to detect diseases that respond with low frequencies, which cannot be detected without special equipment. Problems will be added by the fact that of the basic tones, the doctor himself hears only the first two at best. Against the background of other sound options, it is problematic to recognize the 3rd and 4th myocardial sounds. They are the basis for confirming suspicions of various pathologies.
The scheme of all heart sounds is divided into 2 equal camps. The first point is:
- loud;
- clear;
- clear sound.
In case of illness, in addition to tone, you can hear various noises. They are not interrelated, but have different:
- strength;
- frequency
The main part of the noise along with the tones can be determined even simply by using auscultation. Their volume will change at different points. If a patient hears from medical personnel during a procedure something like: “Prepare a PCG,” this means that the doctor suspects rare or complex abnormal pathologies. They are:
- congenital;
- acquired.
Phonocardiography of the heart helps to hear even minor effects, which are then formed into electrical signals to be presented on paper in the form of graphic information. The operating principle is similar to a standard ECG.
The advantage of a phonocardiograph is the presence of filtering devices aimed at eliminating secondary noise, which do not provide any practical benefit for diagnosis. This is how we get basic data. Since the procedure is non-invasive, it does not cause discomfort or pain. This is why it is loved by cardiologists who work with babies and even newborns. There is no need to prepare for FCG; no dietary restrictions are required.
Basics of FKG
Auscultation provides information about the main sounds that occur in an organ during its contraction, but the procedure is subjective, because everyone hears differently. It is difficult to assess using the ear:
- amplitudes;
- duration;
- interval between individual sounds.
The analysis requires a device that will record everything that happens in the myocardium and the vascular system of the heart.
On a note! Phonocardiography of an organ, despite providing information, cannot be a separate diagnostic technique like ECG or auscultation. The method is only additional.
It is impossible to decipher without detailed knowledge of the auscultatory signs of the organ’s functioning, and for the correct application of electrical sensors it is necessary to listen to the heart muscle with a phonendoscope.
Advantages and disadvantages of phonocardiography
Like any diagnostic method, FCG has pros and cons. Advantages of the technique:
- Objectivity of information about the nature of sounds and their indications on the graph.
- You can determine the physics of sound - strength, frequency, time between tonality or noise.
- It is possible to objectively compare sounds that are formed at a certain interval, which is difficult to do using a regular phonendoscope.
- Determination of the relationship with the electrical activity of the organ when used together with an ECG.
In addition to its advantages, the FCG technique also has disadvantages. It is clear that the equipment can “hear” low frequencies of vibrations that are inaccessible to a specialist, but still the ear is the most sensitive, therefore a certain weak sound in the audibility range can be detected by a physician, but not reflected in the FCG.
In addition to the low-frequency 3rd, 4th and 5th tones, all other sounds should be captured in the phonendoscope and reflected on the FCG. If the technique indicates the presence of sounds that cannot be heard during auscultation, then the physician still draws conclusions based on information from listening with the ear (in addition to low-frequency recording). Thus, without auscultation, FCG analysis is meaningless. In addition, the equipment cannot hear the sound timbre, this is determined by a specialist.
Timbre is a subjective characteristic, but it greatly helps in diagnosing certain valvular heart defects. To place the microphone at the points where sounds are most audible, the process of auscultation is used. Many myocardial pathologies occur through changes:
- configurations;
- sizes;
- enlargement and deformation of boundaries.
Accordingly, the places for better recognition of sounds change, and incorrect placement of the microphone leads to a decrease in the audibility of the organ sound. It is impossible to correctly integrate and decipher FCG information without preliminary auscultation, and sounds are assessed based on:
- subjective data determined by a specialist;
- objective physical information recorded by the equipment.
Today, phonocardiograms have also begun to be used in the prenatal diagnosis of child hypoxia and congenital heart problems.
Advantages and disadvantages of FKG
The phonocardiography method, like any other, has its significant pros and cons. Advantages:
- objectivity of the obtained data on sounds, their graphic representation;
- the ability to determine the characteristics of sound - frequency, strength, intervals between sounds, tones and noises;
- safety – no patient exposure to radiation.
In addition to important advantages, the technique has a number of disadvantages. It happens that some quiet sounds can be heard using a phonendoscope, but a phonocardiogram will not show this. The device can detect low frequencies, but the human ear is more sensitive.
Despite the independence of phonocardiography, analysis of the method without listening with the ear will not make sense. If the third, fourth and fifth tones of low frequencies are analyzed during PCG, then all other sounds will be heard in the phonendoscope. In the case when the doctor, during auscultation, did not hear the sounds that were shown by the results of the PCG, then conclusions are drawn mainly by listening to the doctor’s ear.
Another disadvantage is the inability to determine the timbre of the sound produced, which often helps in the analysis and determination of a number of heart valve defects. The timbre is determined by the person himself.
Note! Preliminary listening with a phonendoscope is necessary in order to place the device’s microphone at the right points where the sound volume will be maximum.
With many heart diseases, the organ changes its position, size, its boundaries can expand or mix, which explains different places where waves can be heard well. Incorrect placement of the FCG will provoke a decrease in volume, as well as sound intensity, so auscultation before the procedure should be carried out to correctly register heart murmurs and draw conclusions.
Indications for phonocardiography
If the doctor hears sounds that are uncharacteristic of the normal functioning of the heart during auscultation, he will refer the patient to an FCG, because usually pathological sounds are inherent in myocardial defects and deviations in its work or structure. The main factors that lead to referral to FCG are:
- Feeling of heartbeat. When a healthy organ is working, a person does not feel a heartbeat. Very active contractions that interfere with human life are a pathology.
- Heavy breathing, both during exercise and at rest.
- Heart valve defects. Valve pathologies that develop due to their narrowing or insufficiency, mitral stenosis.
- Rheumatism, in which the heart muscle becomes inflamed.
- Heart defects from birth. These include narrowing of the aorta or pulmonary trunk, open ductus arteriosus, and deformation of the atrial septum.
- Dizziness with fainting.
- Pain in the heart area of varying severity (especially in youth).
The appointment of an examination occurs after examination by a doctor, in a situation where one of the above factors is suspected. If negative symptoms are observed, it is important to make an appointment with a highly qualified doctor. He will prescribe an FCG, ECG, causes, diagnostics, manifestations, when the heart hurts, and will determine exactly.
Indications for use
If electrocardiography is a preventive diagnostic method, then a referral to PCG is given only when special indications are received. The main reasons for prescribing phonocardiography:
- heart rhythm disturbance;
- cardiomyopathy;
- heart defects.
The ability to graphically display sound waves and effects is valued among cardiologists, therapists, and less often rheumatologists. It is generally accepted that every government hospital or medical center has such a device. But due to the fact that in official medicine it is already recognized as outdated, not all private clinics are in a hurry to buy the device. And in ordinary hospitals, equipment is written off without being replaced with new ones.
If a person has been assigned to conduct a study, it is better to arrange the procedure in the morning after a good, sound sleep. It is not recommended to drink tea, coffee, alcohol, or energy drinks, as they provoke tachycardia and various heart rhythm disorders, and there is no need to skip breakfast.
In addition to conventional phonocardiography, fetal examination can be performed. The microphone is placed in a place where the device can best pick up the tones of the fetal organ. Sometimes in the fetus you can see an increase in heart rate, a change in the duration and amplitude of sound waves of tones, their splitting and the appearance of noise, which indicates perinatal asphyxia.
You can get a referral for FKG if you experience symptoms:
- sudden asphyxia even at rest;
- pronounced shortness of breath when walking or running;
- audibility and physical sensation of the heartbeat;
- severe dizziness up to loss of consciousness (for example, weakening of the blood flow to the brain with aortic insufficiency);
At the beginning of the FCG process, the patient lies down on the couch. Next, he is asked to hold his breath, inhale and hold it again, repeating this several times. During this, the device's microphone moves to different areas of the chest. Sometimes, to dilate blood vessels or change the activity of the heart, pharmacological agents are additionally used. If this is not required, the procedure will last no more than ten minutes.
If you believe the words of therapists and cardiologists, cardiac phonocardiography has almost no contraindications. This procedure is completely safe and painless, therefore it is prescribed even to patients in critical condition. But there are certain cases in which it is physically impossible to attach the FCG device tightly to the chest. These are factors such as: severe obesity, serious injuries, burns, wounds, violation of the integrity of the skin.
Procedure options
A medical room with a high level of sound insulation is allocated for FCG. The temperature in the room is also of particular importance, since its decrease to less than 22 ° C can cause muscle tremors, which interferes with the accuracy of diagnosis. The patient is lying down during the examination. The device for PCG records the functioning of the organ in the exhalation phase. Carry out the procedure correctly:
- in a position on the left side;
- after taking medications and physical activity.
These measures increase the information content of the survey.
Note! Special microphones are attached to the sternum in 5 areas. Before recording, the doctor checks the sound quality. To do this, use an oscilloscope and headphones.
There is no discomfort throughout the examination. It usually lasts several minutes, and if it is carried out with tests (use of medications, physical exercise), then the duration will be different, but no more than half an hour.
In patients with and without test
Initially, a person inhales air and holds his breath. They slowly write a test recording, then set the optimal rhythm of tape movement - 100 mm/sec and get the sound again. In this way, vibrations from each point are recorded sequentially. To clarify the diagnosis, FCG options may be needed:
- At the height of maximum inspiration.
- From a position on the left side.
- After walking on a treadmill or squats.
- Before and a quarter of an hour after taking Nitroglycerin.
Phonocardiogram analysis is carried out only by a professional. The result depends on experience.
In pregnant women to listen to the fetus
The method does not harm the pregnant woman and the child (compared to frequent ultrasounds). The study helps in diagnosis:
- abnormalities in blood circulation between the baby and the placenta;
- functioning of fetal heart valves.
To record, place a microphone on the patient’s abdomen in the area of best audibility of myocardial sounds. After 32 weeks, you can listen to sounds 1 and 2, and additional sounds are observed less often. During delivery, as the baby progresses, you can track his heartbeat by moving the device. Normally, when rhythms are visible on the phonocardiogram, during pushing the 2nd tone increases, and at the end of the contraction it becomes even.
If the child does not have enough oxygen, then the tones change frequency, strength and duration, become loose, and alarming noises. To get a complete picture of the functioning of the heart, PCG and ECG are used. There are no specific contraindications for performing FCG studies. The study is difficult in case of obesity, burns of the area where the electric sensors are applied, the presence of injuries and any deviations in which it is not possible to fully fix the microphone to the skin.
Normal FCG
A healthy myocardium makes it possible to clearly hear the 1st and 2nd sounds without equipment. However, not many people are aware of what makes it possible to evaluate each parameter. The first sound is formed when the valves located between the ventricles and the atria close. Closing the doors gives a rather loud sound, which is different:
- Medium frequency.
- Amplitude – 25 mm.
- Time – 0.15 sec.
Note! It is impossible to cover the effect of each valve individually due to the speed of implementation of the physiological reaction. Therefore, it is much more effective to try to catch at once all the noises characteristic of the slamming of valves, overlapping each other, creating one whole - the 1st tone.
The 2nd tone covers the parameters of closing the aortic valves together with the pulmonary artery. It will be better heard if you move the microphone to the 2nd intercostal space. He speaks of the right and left sides, respectively, because these points more closely touch the base of the myocardium. Unlike the tone of its predecessor, in this situation there is at once a duet of components emanating from each valve. You can distinguish the sound either with your ear or with a device. Easy to listen to:
- Children.
- Teenagers.
- Thin.
The first point marks the closure of the aortic valve. It is much louder than its analogue, and its amplitude is approximately 2 times greater than the sound of the valve from the pulmonary artery. According to the anatomy, the pressure in the aorta is much higher. Problems arise at the stage of the need to cover the 3rd and 4th tone using PCG. However, if suddenly they are heard, this does not mean that the person is sick.
The 3rd tone is sometimes heard in thin people and small children. Collected due to vibration of the walls of the ventricles. It is closely related to overload, appearing after activity. It’s just difficult to hear it, so they record it in the low frequency range. The 4th tone is heard even less frequently than the 3rd. However, if it has already appeared, then this indicates an abnormal development.
What do the changes in the FCG mean?
Pathology is indicated by a decrease or increase in the amplitude of sound waves, a change in their duration, and the appearance of additional noise.
Figure: noises and changes in tones on PCG and auscultation
A decrease in the intensity of the first tone (auscultation - weakening of sound) is detected when:
- Mitral valve insufficiency, when its leaflets are destroyed by an inflammatory process, atherosclerosis, their closure is incomplete and does not provide the proper strength of the sound wave;
- Stenosis with the deposition of calcium salts, shortening of the mitral valve leaflets, with chordal pathology that prevents complete closure of the orifice;
- Decreased contractile function of the left ventricle in myocardial dystrophies, cardiomyopathy, chronic ischemic disease, rheumatic myocarditis.
In addition to cardiac pathology, weakening of the first tone can be caused by other reasons that should be taken into account. These include excess weight, emphysema, effusion pleurisy in the left half of the chest, and pericarditis.
In some diseases, the first tone may even intensify. This phenomenon is characteristic of anemia, thyrotoxicosis, and mitral stenosis. The splitting of the first tone into two sounds coming from both atrioventricular valves is characteristic of bundle branch block and stenosis of both valves.
The second heart sound, like the first, can also increase or decrease. An increase in the amplitude of its components manifests itself in arterial or pulmonary hypertension, thickening of the aortic valve leaflets in syphilis, and normally in young, thin individuals. A weakening of the second tone may indicate aortic valve insufficiency and decreased blood flow through the pulmonary artery.
The third and fourth tones can appear when:
- Myocardial infarction;
- Hypertension;
- Atherosclerotic cardiosclerosis with severe heart failure and overload of the right atrium.
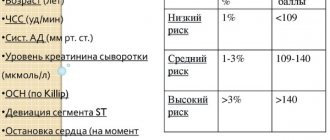
In case of myocardial ischemia, it is not the isolated auscultation of the third sound that matters, but the presence of characteristic changes in the patient on the ECG. The third tone usually appears before the P wave, and in the case of ischemia, the doctor will note characteristic signs in the form of depression of the ST segment, elevation of the T wave, conduction disturbances inside the ventricles, etc.
The third and fourth sounds create the so-called gallop rhythm, which indicates severe pathology - heart attack, valve disease, myocarditis, severe hypertension.
Figure: typical changes on FCG in valvular pathology
Thus, PCG seems to be the most valuable method, allowing a detailed assessment of the entire range of sounds reproduced by the heart. Their comparison with clinical data and auscultation provides an exceptional amount of information for diagnosing cardiac pathology in both adults and children.