Accelerated metabolism and increased oxygen demands cause children's hearts to beat faster. Heart rate norms are individual for each age. If for some reason this indicator exceeds the norm for no apparent reason (emotional experiences or physical exertion, overheating), tachycardia is diagnosed. At the medical center (Moscow, Otradnoye metro station, North-East Administrative District), cardiologists diagnose and treat tachycardia in children. Therapy begins with eliminating the root cause, and along the way, doctors select medications that alleviate the condition.
Causes and types
Restlessness is considered one of the causes of cardiac tachycardia in childhood. Children are constantly moving, which naturally causes an increase in heart rate and heart rate. Other factors are also possible:
- dehydration;
- heart murmurs;
- anemia;
- cardiopathy;
- thyrotoxicosis;
- Congenital heart defect.
In addition, there are two forms of the disease: sinus and paroxysmal, which also develop for certain reasons. Sinus tachycardia in children is a consequence of:
- accelerated growth;
- stress;
- disorders of the endocrine or cardiovascular systems;
- overwork.
Diagnosing the cause of the paroxysmal form is more difficult, since in this case the heart rate increases and slows down suddenly. Seizures occur at any age, including in newborns.
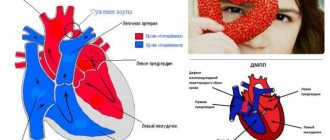
Classification of congenital heart defects in children:
- With unchanged or slightly changed pulmonary blood flow (anomalies of the location of the heart, pathologies of the aortic arch, aortic stenosis, atresia of the aortic valve, insufficiency of the pulmonary valve, stenosis, atresia and insufficiency of the mitral valve, heart with three atria, pathologies of the arteries and conduction system).
- With hypervolemia of the pulmonary circulation: Without early cyanosis (open duct in the arteries, defective septa between the ventricles or atria, aortopulmonary fistula, Lutambashe syndrome).
- With cyanosis (atresia with a septal defect between the ventricles, open ductus in the arteries with pulmonary hypertension and blood flow into the aorta from the pulmonary trunk).
- Without cyanosis (isolated pulmonary stenosis).
There is also a classification of congenital heart defects in newborns, which is more understandable for the common man:
- So-called “blue” defects (accompanied by early cyanosis (blue skin); among them are tetralogy of Fallot, pulmonary atresia, transposition of the great vessels).
- So-called “white” or “pale” defects (may be accompanied by pallor of the skin or occur without pronounced symptoms and are detected randomly during a preventive examination of the child; among them are defects of the septa between the ventricles and atria).
Symptoms
In addition to palpitations, cardiac tachycardia in children manifests itself:
- chest pain;
- shortness of breath;
- dizziness and fainting;
- lethargy and pallor;
- nausea;
- sweating
At such moments, infants become restless and capricious, refusing to eat and sleep. It is important to consult a doctor as soon as you notice the first signs of illness. If tachycardia in children is not treated, the severe pathologies that caused it will lead to serious complications:
- arrhythmogenic shock;
- pulmonary edema;
- heart failure;
- cardiac arrest.
Symptoms of tachycardia
Tachycardia is established by measuring the pulse rate. Patients with tachycardia may also complain of:
Cardiopalmus
Patients with tachycardia usually complain of a feeling of palpitations. However, such a feeling is subjective. It can be observed without an objective increase in rhythm.
More about the symptom
Dyspnea
With tachycardia, shortness of breath and a feeling of lack of air are possible.
More about the symptom
Weakness
Tachycardia may be accompanied by symptoms such as general weakness, dizziness, and increased fatigue. worsening mood, loss of appetite.
More about the symptom
Sleep disorders
A rapid heartbeat can make it difficult to fall asleep and often causes insomnia.
More about the symptom
Diagnostics
The task of a cardiologist who examines a child with suspected tachycardia is to make sure that the signs he has do not indicate other diseases, for example, bronchial asthma. Also during the examination, he looks for the cause of the disease. To do this, the specialist uses:
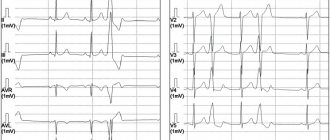
- ECG and daily monitoring to analyze how the heart rhythm changes during the normal activity of a small patient;
- EchoCG and MRI to make sure there are no heart pathologies;
- an electrophysiological study to check how the electrical impulse travels through the heart muscle;
- laboratory methods: urine, blood analysis;
- EEG of the brain to make sure that the activity of the central nervous system is not impaired.
Types of tachycardia
Tachycardia may be due to a normal reaction of the body. In this case, doctors talk about physiological tachycardia
. Physiological tachycardia (that is, increased heart rate in a healthy person) can be caused by:
- strong emotional arousal or stress;
- physical activity;
- sudden change in body position (sudden rise from a lying position, etc.);
- lack of oxygen;
- high air temperature;
- taking coffee, strong tea, alcohol, and some medications.
If tachycardia is not associated with these reasons, then the increased heart rate is apparently caused by the disease. In this case we are talking about pathological tachycardia
.
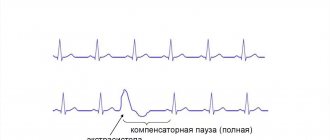
There are also sinus and ectopic (paroxysmal) tachycardia.
Sinus tachycardia
occurs when the activity of the sinus node increases. The sinus node is a bundle of specific cardiovascular tissue in which electrical impulses are generated. These impulses travel throughout the heart, causing the heart muscle to contract. That is, our heart beats at the rhythm set by the sinus node. If it begins to produce impulses at a higher frequency, then sinus tachycardia occurs.
However, in some cases, electrical impulses are generated outside the sinus node. They are called ectopic (“ectopic” means, specifically, “abnormally located”). The frequency of contractions of the heart muscle in this case can reach up to 200 or more beats per minute. Typically, such an increase in rhythm is observed in the form of attacks (paroxysms). This tachycardia is called ectopic
or
paroxysmal
.
Treatment and prognosis
In case of sudden attacks of tachycardia, the child should be taken out into the fresh air, tight clothes should be removed, a damp handkerchief should be placed on the forehead, and then a doctor should be called. If there is no pathology, and hormonal changes and stress lead to an acceleration of the heart rate, to treat tachycardia in children, the cardiologist will prescribe drug therapy (beta-blockers, cardiac glycosides, calcium antagonists, sedatives). Auxiliary measures: physical therapy, valgus techniques. To alleviate the condition, a diet is recommended in which it is undesirable to consume chocolate, tea, spicy, and salty foods.
Children who follow the doctor's recommendations usually return to their previous lives and activities. In rare cases, when the disease develops due to other serious pathologies that cannot be treated conservatively, surgery is prescribed.
Causes of tachycardia
Physiological tachycardia should not be a cause for concern.
But if the heart rate is increased for no apparent external reason, this is worth paying attention to. Tachycardia is often caused by pathologies and heart diseases, in particular:
- acute or chronic heart failure;
- myocardial infarction;
- angina pectoris;
- heart defects;
- myocarditis (inflammation of the heart muscle;
- endocarditis (inflammation of the endocardium - the inner lining of the heart);
- pericarditis (inflammation of the pericardium - the outer lining of the heart).
In addition, tachycardia occurs in the case of:
- increased temperature (typical of various infectious diseases, such as pneumonia, sore throat, sepsis, etc.);
- lowering blood pressure (for example, due to blood loss);
- anemia;
- increased thyroid function;
- states of shock.
Prevention
The following preventive measures will help reduce the risk of tachycardia and the likelihood of complications after it:
- proper nutrition, following a healthy diet (more fruits, grains, vegetables);
- limited consumption of caffeine, which is found in tea and chocolate;
- prevent your child from gaining excess weight;
- avoiding stress and emotional turmoil;
- playing sports without excessive stress;
- proper daily routine, including proper sleep and rest;
- taking sedatives and vitamins for the heart (if necessary);
- control over blood cholesterol levels;
- regular visits to the doctor.
Treatment
Depending on the cause of tachycardia, the specialist determines the tactics of its treatment. If physiological preconditions became the provocateur, after eliminating which the heartbeat returned to normal, there is no need for treatment.
If treatment is required, a set of measures is prescribed, including drug therapy and alternative medicine.
Drug treatment
Antiarrhythmic drugs are used to restore normal heart rhythm and control the contraction rate. They can be taken either orally or by injection.
The choice of drug depends on a number of factors:
- type of tachycardia;
- accompanying illnesses;
- side effects of the chosen drug;
- the child's response to therapy.
If sinus tachycardia is of neurogenic origin, sedatives are selected for school-age children - seduxen, luminal or others at the discretion of the doctor. Up to 7 years of age, only homeopathic remedies are recommended.
If tachycardia is caused by heart problems, the cardiologist will prescribe cardiac glycosides that normalize heart rhythm. Additionally, traditional methods of treatment can be used.
Heart rate norms in children
| Child's age | The heart rate is normal beats per minute. |
| Newborn | 110–170 |
| 1 year | no higher than 162 |
| 1-2 years | up to 154 |
| 2-4 years | up to 140 |
| 4–6 years | up to 126 |
| 6–8 years | up to 118 |
| 9–10 years | up to 108 |
Attention: exceeding the norm by 20-30 beats per minute. - a reason to contact a cardiologist!
Treatment with folk remedies
Alternative medicine can significantly help in the fight against tachycardia, but folk remedies cannot replace drug treatment. Before using any method, you must consult your doctor.
Treatment of tachycardia using traditional medicine involves the following effects:
- general calming effect;
- sleep stabilization;
- normalization of the nervous system;
- decreased myocardial excitability;
- activation of general regulatory processes in the body to protect it.
There are a huge number of recipes with medicinal plants: hawthorn, valerian, chicory, lemon balm, motherwort, honey, etc. The following recipes are most effective:
Calming collection No. 1. Pour a pinch of calendula flowers and motherwort herb into 1 glass of boiling water, leave for 2 hours, strain and drink warm after lunch.
Calming collection No. 2. Pour a tablespoon of dried white willow flowers into a glass of boiling water and leave for 1 hour. Then strain and divide into 6 portions.
Calming collection No. 3. Add a tablespoon of lemon balm to a glass of hot water and steep like regular tea. Drink the drink up to three times a day.
At the pharmacy you can buy ready-made tinctures of hawthorn, motherwort, and valerian. They should be taken 10-15 drops 3 times a day or if your heart rate increases.
Recovery prognosis
As a rule, experts give a favorable prognosis for recovery for children with any type of tachycardia. Effective treatment in almost every case will return the child to a normal lifestyle without restrictions.
In adolescents, tachycardia will most likely persist for the rest of their lives, and therefore they will not stop taking medications. In addition, adherence to the recommended diet and exercise will always have to accompany it, otherwise even slight excess weight will put a strain on the heart and provoke the development of various diseases.
Author : Alexander Kulakov
Certified physician. Graduated from the Moscow Medical School. Clara Zetkin, Moscow Medical and Dental Institute named after. Evdokimov. Author med. content of the site tvou-voleyball.ru