Such different noise: main types
By nature, heart murmurs in a child can be:
- diastolic (occurring when the heart relaxes and fills with blood; often pathological);
- systolic (arising against the background of blood vessels pushing out; in most cases they are safe).
Noises can also be functional or organic. The first arise temporarily during the period of increase in the size of the heart and blood vessels along with human growth. The latter are directly related to damage to valves, blood vessels and pericarditis.
Functional noise
Functional heart murmurs in a child are not dangerous. They are not associated with anomalies in the development of the organs of a small person and do not bring him pain or discomfort. Most often, such heart murmurs occur at 1-2 years of age. As they grow older, they disappear spontaneously.
Such children are monitored by a cardiologist. In this case, no changes or abnormalities are detected on the X-ray image or on the ECG printout.
The causes of noise in this situation may be:
- thinness of the baby's chest;
- strong sound of venous blood flow;
- the presence of an additional chord;
- disturbance of metabolic processes in the heart muscle;
- anemia.
All these violations are not dangerous, they can be easily corrected.
Organic noises
Organic heart murmurs in a 2 or 3 year old child occur due to congenital or acquired heart diseases. They appear due to the formation of abnormal blood flows in large vessels. It is their swirls that are listened to by the doctor.
Such noises are quite loud and continuous. The reasons for their appearance may be:
- rheumatism;
- myocarditis;
- heart defects.
Heart diseases
All nosologies in pediatric cardiology are divided into several large groups:
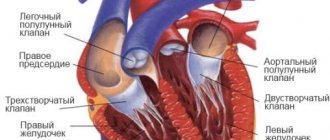
- Congenital heart defects. These are anomalies in the development of the heart, its valves and great (main) vessels that occur in the 2-8th week of intrauterine development. These include defects of the interventricular, interatrial and/or aortopulmonary septa, open atrioventricular canal, ductus arteriosus, stenosis (narrowing) or insufficiency (incomplete closure of the leaflets) of valves, incorrect location of vessels or pathological collaterals between them (connections), absence of an atrium or ventricle, etc. .
- Valvular heart defects. These are acquired pathologies of the valve apparatus - stenosis (narrowing) or insufficiency.
- Diseases of the endocardium - the inner lining of the heart.
- Diseases of the myocardium - the middle (muscular) layer of the heart.
- Pathologies of the pericardium - the cardiac connective tissue sac.
- Pathologies of coronary circulation. This group includes myocardial infarction, Kawasaki disease (vasculitis of medium and small arteries) and anomalies of the origin and number of coronary arteries.
- Pulmonary hypertension. This is an overload of blood in the pulmonary arteries due to increased pressure in the pulmonary arteries.
- Heart damage due to hereditary diseases. They are the result of errors in the genetic code of the parents' germ cells; these mutations are passed on to the offspring. They can appear from birth or already in adulthood.
- Heart tumors.
- Vascular damage. Most often we are talking about arterial hypertension (increased blood pressure) or hypotension (lowered blood pressure).
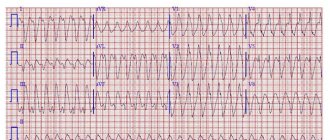
- Heart rhythm disturbances are disturbances in the regularity and sequence of heart contractions. If the heart muscle is damaged, its course is distorted, which leads to an abnormal rhythm of heart contraction.
- Heart failure is a syndrome caused by decompensated dysfunction of the myocardium. That is, the heart is so affected that it is no longer able to provide the necessary blood output and supply blood to all organs.
It is important to clarify that heart disease rarely occurs in isolation. One pathology progresses and leads to another. Thus, aortic stenosis will lead to pulmonary hypertension, and infective endocarditis destroys the valves, resulting in defects. After myocardial infarction or inflammation (myocarditis), the conduction of impulses through the affected area is disrupted, and as a result, the normal rhythm of contractions is disrupted.
Causes of pathology at different ages
Infants
Why does my child have a heart murmur? When analyzing the reasons, pay attention to the age of the young patient. Each age has its own primary sources.
For example, heart murmurs in a newborn baby appear against the background of:
- congenital pathologies;
- unclosed oval window;
- active ductus arteriosus.
Normally, the oval window closes already in the 1st or 2nd year of the baby’s life. But even if it is observed in older children, it is considered not a developmental defect, but an individual feature of the body’s functioning.
Children over one year old
Heart murmurs in a child aged 4, 5, 6 or 7 years can be caused by both health problems and non-dangerous conditions: thinness, mild temporary overload or an unstable psycho-emotional state (whims against the background of the next transition period from the category of small children to the category preschoolers).
The danger comes from those noises that occur in parallel with acute respiratory or viral diseases (sore throat, scarlet fever). The fact is that during illness, pathogenic microflora has a harmful effect on the heart. For this reason, children often develop a disease such as rheumatism.
Pupils
Heart murmurs in an 8-year-old child or even when starting school are associated with:
- with an unbalanced diet;
- with increased physical and mental stress;
- with stress.
Because of this, the myocardium receives much less oxygen and nutrients than it needs. At the same age, there is a discrepancy in the size of the heart sac, which also provokes audible murmurs.
Teenagers
Adolescents are considered a separate category of patients. A heart murmur in a child 10 years of age or older usually occurs due to an imbalance in the influence of the autonomic or sympathetic nervous system. As we grow older, this imbalance disappears along with extraneous noise from our main organ.
At the same time, you still need to control the situation, since various myocardial diseases and other pathologies can be detected in adolescents.
Features of auscultation in children
The therapist gets “scared” when listening to the child. The auscultatory picture is the same as in an adult, but audibility is several times stronger. Especially in infants.
- The baby's chest wall is much thinner, all sounds are transmitted very clearly.
- A newborn needs to be able to listen to a scream. They try to carry out examinations of an infant after feeding, so that he is in a good mood and has the opportunity to listen to the heart in silence.
- Older children have to be distracted by their mothers.
- There are always toys in the offices of local pediatricians; it should be warm.
- The doctor tries to warm the head of the phonendoscope in his hands so as not to frighten the patient by touching a cold object.
This is how you have to explain yourself to a little person
In assessing tones, it is important that in children and adolescents, unlike adults, the third additional tone is heard more often. It does not indicate ventricular pathology, is better audible after exercise and gives a “gallop rhythm”.
Diagnostics
If murmurs are detected during listening by a pediatrician, neurologist or cardiologist, then the patient must undergo a comprehensive diagnosis. It includes:
- conducting an electrocardiogram (shows disturbances in the functioning of the heart, for example, disturbances in rhythmic activity or chamber hypertrophy);
- performing radiography (demonstrates the boundaries of the hematopoietic organ and the condition of both lungs);
- carrying out echocardioscopy (ultrasound examination will show the condition of the valves, vessels and cavity of the heart, growths, narrowings and pathologies).
The main task of the doctor is to accurately differentiate the type of eshum. We need to thoroughly understand what is the true reason for their appearance. This will help you not waste time and prevent a serious illness from developing.
You need to remember that even if you listen to noises, but the child does not have any complaints, there is nothing to worry about. Those noises that are accompanied by pallor of the skin, blueness of the nasolabial triangle, shortness of breath and elevated temperature should be alarming. The baby may complain of chest pain, be capricious and refuse to eat. In such a situation, urgent examination and consultation with a specialist is necessary.
How to make a diagnosis
The diagnosis takes into account:
- clinical symptoms - cyanosis of the child’s lips and face, shortness of breath when moving, changes in rhythm, trembling of the chest when palpating the heart area, the presence of a visible venous network under the skin, pulsating vessels;
- phonocardiography and ECG - clarify the localization of damage to the heart chambers;
- Ultrasound and Dopplerography - allow you to establish blood flow in different phases of myocardial contraction, direction, volume of return, degree of adaptability of the ventricles and atria.
What is the treatment of heart murmurs in children?
If murmurs are detected in children, their treatment is selected based on the cause of the symptom. If there are no organic heart lesions, the child is cheerful, cheerful and visually healthy, then no treatment is prescribed. The absence of complaints indicates that the body is doing its job well.
In the vast majority of cases, the cardiologist prescribes medications. Special medications will help:
- improve myocardial nutrition;
- normalize metabolic processes in the heart muscle;
- strengthen the child’s body’s defense system.
Vitamins and amino acids are also prescribed in combination with medications. In some situations, if prescribed by a doctor, hormonal agents and diuretics are also added to this regimen.
Particular attention is paid to patients in whom congenital or acquired pathologies were identified during diagnostic studies. As a rule, such children undergo surgery. In such cases, it is impossible to solve the problem without surgical intervention.
The operation can be aimed at:
- removal of excess tissue;
- stent insertion;
- valve replacement.
Our clinic provides surgical treatment for children, after which the rehabilitation period does not take much time. Children quickly return to their usual active life. At the same time, they must take blood thinning medications for some time, as well as take medications to speed up recovery and prevent complications.
Treatment
Organic noises require therapy. It can be conservative or surgical. Depends on the original cause of the violation.
The medicinal technique is based on the use of several groups of drugs:
- Antihypertensive. Reduce blood pressure (ACE inhibitors, beta blockers, calcium antagonists, mild potassium-sparing diuretics, for example, Veroshpiron).
There are a huge number of names of funds. However, it is impossible to choose a secure scheme on your own. Therefore, there is no point in clarifying the names.
If used incorrectly, heart failure and renal dysfunction may occur.
- Glycosides. Normalize myocardial contractility. Used in short courses, they restore blood flow. But this is a temporary measure in most cases.
Classic remedies - Digoxin, tincture of lily of the valley. If taken incorrectly (for a long time) or if dosages are not observed, fatal side effects and complications are likely.
It is also possible to use antiarrhythmics (Amiodarone), vitamin-mineral complexes and products based on microelements, magnesium and potassium (Asparkam and analogues).
As part of emergency relief of high blood pressure, Capoten is used in the amount of 1/6 - ¼ of the tablet. It is important that there is no sharp drop in the tonometer reading.
Surgical therapy is indicated in several cases: congenital defects of the heart itself (chambers, valves), blood vessels (type of fusion, blockage, anomalies of shape, anatomical development).
There are two ways to access the changed area (surgical field):
- Endovascular. Low-traumatic, by making pinpoint incisions and introducing surgical instruments. Requires a highly qualified treating specialist, special expensive equipment, and is not possible in all cases, only with small sizes of the altered lesion or insignificant volumes of intervention.
- Open access. In other situations.
The essence of the treatment is to eliminate the narrowing of the artery (ballooning or stenting, mechanical expansion), restore anatomical integrity in case of tissue abnormalities (plastic) or prosthetics (especially often with lesions of the valves, when other methods do not make sense).
With a competent approach, it is possible to achieve a complete cure. In the future, it is recommended to take medications for some time to normalize the rheological properties of the blood, and, if necessary, also to lower blood pressure.
What to do if you find a heart murmur?
It is important to remember that if your baby is diagnosed with a heart murmur, then you need to gather yourself as much as possible, do not panic and do not make any independent predictions in advance. Children's organisms, although small, are endlessly striving for life. Even in the case of pathologies, if the child is given timely help, everything can turn out well.
To understand the situation, determine the original source of these noises and eliminate it, you need to undergo diagnostics, and then a course of treatment from a qualified doctor.
Forecast
In the case of functional noise, the prognosis is always favorable. This is not a disease or a manifestation of a pathological process. There are no disturbances in the activity of cardiac structures or hemodynamic problems.
Outside of organic disorders, anatomical defects are also positive. It is possible to achieve complete recovery in 90-95% of cases.
Compensated defects (not all) can be cured in 80% of situations by surgical methods.
In the most severe cases, the survival rate is 30-40%, which is still quite high. The main thing that parents need to remember is that they should closely monitor the child’s well-being and, if necessary, urgently contact a cardiologist for a full diagnosis.
How to make an appointment with a doctor
There can be many causes of heart murmurs in a child. To exclude dangerous pathologies or receive comprehensive treatment for the disease in a timely manner, you need to seek help from a specialist. The clinic is attended by experienced cardiologists who thoroughly study the situation, compare the results of diagnostic studies, make an accurate diagnosis and take a whole range of measures to effectively combat it.
Our doctors find an approach to each child, taking into account all the developmental features, previous diseases, and return. All this is necessary in order to establish a diagnosis and prescribe a truly appropriate treatment.
To get a consultation with a cardiologist at JSC “Medicine” (academician Roitberg’s clinic), you can call 24/7 or fill out an online appointment form on the website.
The clinic is located at the address: Mayakovskaya metro station, 2nd Tverskoy-Yamskaya lane, 10.
What do parents need to remember?
In order for a child to have a healthy heart, it is necessary to carefully monitor his daily routine, nutrition, general health and correctly distribute loads. Psycho-emotional as well. The heart does not need increased stress, but the child must train his heart, that is, lead an active lifestyle: spend enough time outside, regularly be in nature, and play sports. In your diet, you need to pay attention to complete proteins (meat, fish, cottage cheese, eggs), because the heart is a muscle like all the others, and it needs to be nourished. Fresh fruits and vegetables, as well as dried fruits rich in potassium and magnesium, and decoctions from them are useful. Be careful and do not trigger foci of chronic infection in a child: even the notorious caries that is not cured in time can reduce immunity and trigger a mechanism that indirectly “backfires” on the functioning of the heart. Therefore, regularly take your child for routine examinations not only with a cardiologist and neurologist, but also with other specialized specialists, to whom your local pediatrician will give you a referral.
Olga Chubukova-Reutskaya