Heart murmurs
- an acoustic phenomenon associated with changes in blood flow in the heart and blood vessels. There is a point of view according to which heart murmurs are a problem exclusively for children. Indeed, about 90% of functional noise is found in children and adolescents. However, scientific experts have revealed a fairly wide prevalence of heart murmurs (about 77%) in young people aged 20 to 28 years.
Most cardiologists agree that in adults, the presence of a heart murmur clearly indicates some kind of cardiac pathology and is a reason for a complete cardiac examination.
Types and types of heart murmurs
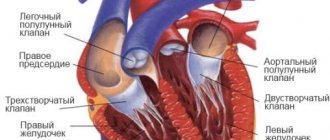
In medicine, it is customary to distinguish between organic heart murmurs
(indicating cardiac pathology) and functional (“innocent” murmurs). Organic heart murmurs are murmurs caused by a defect (congenital or acquired) or other heart disease.
Most often the cause
organic noise is a valve or septal defect (ventricular or atrial septal defect). In terms of timbre, organic noises are hard, rough, persistent; by intensity – loud, sharp; long in duration, carried out beyond the borders of the heart, into the interscapular or axillary region; persist and intensify after physical activity; are equally audible in any body position and are associated with heart sounds.
Functional noise
in the heart were called “innocent”, because are not associated with the presence of heart disease, can be heard in other diseases not related to heart pathology.
In terms of timbre, functional noises are soft, musical, inconsistent, of low intensity, short, not carried out beyond the heart, weaken after physical activity, their character changes depending on the position of the body, and are not associated with heart sounds.
A more detailed classification of heart murmurs is represented by the following types of murmurs:
Systolic murmurs
- Holosystolic (pansystolic) murmurs.
- Midsystolic (systolic ejection) murmurs.
- Early systolic murmurs.
- Mid-late systolic murmurs.
Diastolic murmurs
- Early high-frequency diastolic murmurs.
- Mid-diastolic murmurs.
- Presystolic murmurs.
Continuous (systole-diastolic) murmurs
Causes of heart murmurs
The following causes of heart murmurs are identified:
- High blood flow speed.
- The flow of blood through a narrowed or deformed opening into the dilated chamber of the heart.
- Regurgitation of blood (return flow) through an incompetent valve.
heart murmurs in children
may occur due to minor anomalies in the development of the heart (additional trabeculae, chords, open oval window, elongated Eustachian valve, septal aneurysm, etc.), which do not affect the development of the child and do not cause harm to his health. Sometimes a functional heart murmur occurs in a child due to intense, rapid and uneven growth of the child (growth murmur).
If a child has a functional heart murmur
may be truly “innocent”, then in adults it may indicate the presence of some pathology, for example, the presence of a heart defect.
In any case, if you have a heart murmur
, it is better to immediately contact a cardiologist for an examination.
When should you see a doctor for tinnitus?
You should consult a doctor if you have persistently disturbing tinnitus that disrupts your usual lifestyle and affects your daily activities. Do not ignore the appearance of tinnitus after an upper respiratory tract infection, especially if the symptom has been bothering you for more than one week. Consult a doctor if tinnitus is accompanied by neurological symptoms (dizziness, loss of coordination), hearing loss, and if tinnitus affects your psycho-emotional state (stress, anxiety, sleep disturbances, poor concentration and memory, irritability, depression).
Diagnosis of tinnitus includes a medical history (the doctor will ask about the nature of the tinnitus, neurological symptoms, episodes of exposure to loud sounds, medications taken), laboratory tests (to determine the underlying disease provoking the symptom), otoscopy, audiometry, tympanometry, tuning fork tests, visual tests ( CT, MRI), magnetic resonance angiography of blood vessels.
There is no effective cure for tinnitus. Typically, a management (symptom control) strategy for tinnitus is used to minimize its negative impact on a person's quality of life. It includes drug therapy (to treat the underlying condition causing the tinnitus, treating anxiety or depression), cognitive behavioral therapy (the patient learns to ignore the tinnitus, better copes with the stress, anxiety, depression caused by his condition), sound therapy, wearing a hearing aid, treatment of TMJ diseases. In some cases, the patient is referred for surgical treatment (Meniere's disease, otosclerosis).
Diagnosis of heart murmurs
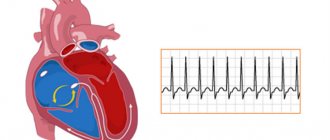
- Auscultation is a highly informative method for diagnosing diseases of the cardiovascular system, based on listening to sound phenomena associated with the activity of the cardiovascular system.
- Angiography.
- Chest X-ray.
- Echocardiography (ECG).
- Cardiac catheterization.
- Load tests.
Samples used to measure heart murmur intensity:
- Breathing (increased sounds from the right side of the heart on inspiration, increased sounds from the left side of the heart on exhalation).
- Valsalva maneuver (forced exhalation with the nose and mouth closed).
- Physical activity (isotonic, isometric, wrist dynamometry).
- Positional changes (changing the patient’s body position, squats, raising legs from a lying position).
- Extrasystole or atrial fibrillation.
- Pharmacological interventions (inhaled drugs).
- Temporary arterial occlusion (external compression of both arms with a bilateral air cuff).
If any pathologies of the cardiovascular system
It is recommended to carry out treatment depending on the etiology of the disease.
GBOU "NIKIO im. L.I. Sverzhevsky" of the Moscow Department of Health
The feeling of constant noise in one or both ears is a very painful feeling, leading some patients to exhaustion and despair. It can also be weak, felt only in silence. By its nature (timbre), the noise can be very diverse: monophonic in the form of a bell or squeak, or multi-toned in the form of the noise of the wind, forest, waterfall, boiling samovar, etc. Less often, the noise is pulsating. Sometimes noise in the ear is combined with noise in the head. The noise in the ear may weaken or intensify at times, especially when the weather changes, with rapid changes in atmospheric pressure. All these ear noises are called subjective, that is, felt only by patients, in contrast to objective noise, which can be heard by an outsider (usually through a tube). Objective ear noises, as a rule, are either pulsating, when noise pulsations in the ear coincide with the heartbeat, with the pulse, or in the form of an aperiodically repeating crackling sound in the ear.
Subjective ear noise is a very common symptom of various diseases of the hearing organ, ranging from the external auditory canal to the auditory zone of the cerebral cortex. It very rarely occurs with normal hearing; more often it appears simultaneously with hearing loss or develops against the background of existing hearing loss - of a sound-conductive nature (conductive), as, for example, with otitis media or otosclerosis, or neurosensory, i.e. with cochlear neuritis.
In patients with otosclerosis and inflammatory pathology of the middle ear, the mechanism of tinnitus is associated with immobility of the stapes or the entry of toxic inflammatory products into the inner ear and irritation of hair cells. The mechanism of ear noise in cochlear neuritis is closely related to the genesis of the underlying disease of the hearing organ or any part of it, which causes nonspecific irritation of the nerve elements of the auditory analyzer.
The most debilitating and difficult to treat tinnitus is observed with cochlear neuritis, which itself can develop under the influence of various causes: exposure to intense environmental noise and vibration (for example, industrial noise, musical cacaphony in clubs and concerts), taking toxic drugs (for example, aminoglycoside antibiotics and loop diuretics), previous general infections (influenza, malaria, etc.), with long-term diabetes, atherosclerosis and hypertension, cervical osteochondrosis, Meniere's disease, etc.
Ear noises of low pitch are more characteristic of middle ear pathology, which is usually accompanied by conductive hearing loss; high tone - damage to the inner ear (with sensorineural hearing loss); mixed tonality - Meniere's disease, various forms of cochlear neuritis, up to damage to the cortical part of the auditory analyzer. A monotonous high-pitched noise is often observed after shooting indoors, after a mechanical injury to the ear (for example, a blow to the ear with the palm of your hand). This noise is caused by local damage to a group of nerve cells in the inner ear.
The effectiveness of treatment of subjective tinnitus in many cases depends on the effectiveness of treatment of the underlying disease. For example, tinnitus due to otosclerosis usually disappears or decreases after hearing-improving surgery. The noise often disappears or decreases after the patient is cured of chronic suppurative otitis media. According to our data, subjective ear noise caused by pathology of the middle ear disappears completely or significantly decreases after successful conservative or surgical treatment in 85% of patients. However, getting rid of tinnitus in patients with cochlear neuritis is very difficult and is much less successful due to irreversible changes in the auditory nerve cells, auditory nerve and cerebral cortex. But, at the same time, treatment can reduce the intensity of the noise, and sometimes remove it for a certain period of time.
In the treatment of ear noise, it should be borne in mind that noise, like pain with appendicitis, flu, etc., is a symptom of a disease in some segment of the auditory analyzer. The intensity of the noise, like the headache, can often be reduced by symptomatic means. A more lasting positive result can be obtained by treating the underlying disease, i.e. pathogenetic treatment. In case of inflammatory pathology of the middle ear, this means eliminating the inflammatory process by conservative or surgical means. With cochlear neuritis that develops in workers in noisy production, the noise sometimes disappears after switching to quiet work, and in the early stages of the development of occupational neuritis, the noise may disappear after rest. In cochlear neuritis of vascular origin, the noise noticeably subsides after a course of vascular therapy (primarily vasodilating and improving venous outflow), reflexology, and health-improving physical exercises. In case of age-related hearing impairment, often accompanied by vascular insufficiency of the brain, noise can be reduced by physical exercises that improve general blood circulation, the prescription of vasodilators, massage of biologically active points, and treatment of cervical osteochondrosis. If the noise is debilitating, it is useful to take a sedative or sleeping pill at night; You can listen to quiet, pleasant music. You should sleep on a raised headboard. Some people find that warmth on the head or ear (dry or wet compress) helps. In some cases, hospital treatment with a protective regime and a course of intensive therapy is indicated.
Drug therapy should be carried out strictly as directed by the doctor, who, based on the examination of the patient, can more correctly choose a complex of drug therapy. At the same time, physical exercise will always be useful, distracting the patient from his own noise and improving blood circulation in the brain and ear, as well as a normal work and rest schedule, good nutrition with a predominance of vegetables, fruits, berries, and dairy products. If you have tinnitus, smoking and drinking alcohol are strictly prohibited.
Using a variety of treatments depending on the general condition of the patient and the cause of hearing loss and tinnitus, unfortunately, not all patients can achieve a good effect; More often it is only possible to reduce the noise and very rarely get rid of it completely in case of cochlear neuritis. The best results were obtained with pathology of the middle ear. In connection with the above, it is necessary for all healthy people to avoid conditions for the development of diseases of the middle and inner ear; first of all, it is necessary to harden the body, avoid noise, give up bad habits, and lead a healthy lifestyle.