Signs of a stroke
The manifestations of hemorrhagic and ischemic strokes differ. In ischemic stroke, focal manifestations predominate - signs of loss of function in damaged areas of the brain.
Common focal manifestations:
- speech disorders;
- lack of understanding of spoken speech;
- paresis (weakness in the limbs, to the complete absence of movement in them);
- loss of visual fields - a person cannot see the right or left half in front of him;
- asymmetry of the lower half of the face - a “crooked” smile;
- decreased sensitivity on the right or left half of the body, face.
Usually the general condition is stable, headaches are often absent, and disturbances of consciousness are rare. The increase in blood pressure (blood pressure) is often moderate. Ischemic stroke most often develops at rest.
In hemorrhagic stroke, cerebral manifestations come to the fore:
Get to know our boarding houses with a short video:
- sharp, severe headache;
- nausea and vomiting;
- disturbances of consciousness up to coma.
Blood pressure is often elevated. Hemorrhagic stroke often develops during periods of vigorous activity and excitement.
First aid in hospital
Upon arrival at the hospital, it is first necessary to conduct a high-quality diagnosis that will confirm or deny the presence of a stroke and identify its type. Depending on the results, resuscitation measures are prescribed. The location of the lesion is important: for example, an ischemic stroke of the cerebellum can also cause hemorrhage in the brain.
- Diagnostics . A computed tomography scan of the brain is urgently performed. Doppler ultrasound may also be required to assess the speed of blood movement through the vessels. Additionally, an ECG, a chest X-ray, a blood test for platelets and glucose, and a biochemical blood test are performed.
- Resuscitation measures. The following measures are common to both types of stroke: maintaining the patient’s breathing, monitoring blood pressure and the functioning of the cardiovascular system, monitoring swallowing function, maintaining the functioning of the bladder and gastrointestinal tract, eliminating cerebral edema. Medicines for ischemic stroke include euphilin, trental, and heparin. For hemorrhagic - gordox, trasylol, vikasol. Also, with this type of stroke, surgical removal of the hematoma may be indicated if it compresses the brain. However, such operations are not prescribed for elderly patients.
After a few days, depending on the patient’s condition, he is transferred from the intensive care unit to the intensive care unit, where he usually spends two to three weeks. However, stroke treatment does not end there; long-term rehabilitation (six months to a year) is required.
Secondary stroke prevention is especially important during this period to prevent another attack. Here you should be patient and methodically follow the recommendations of specialists; rushing during rehabilitation is inappropriate. The best solution is to place the patient in a rehabilitation center, where a whole team of professionals will work with him.
Risk factors
Among the risk factors for stroke, the leading positions are occupied by cardiovascular diseases:
- atherosclerosis;
- rhythm disturbances;
- arterial hypertension;
Rarer causes include:
- blood diseases (polycythemia, essential thrombocytosis, sickle cell anemia, coagulopathies);
- vascular lesions (vasculitis, angiopathy, intoxication);
- malformations and aneurysms of cerebral vessels;
Ischemic stroke may be preceded by transient cerebrovascular accidents (TCI). PNMK is a type of stroke in which focal neurological disorders also appear, but they completely disappear within 24 hours.
Hemorrhagic stroke is often preceded by a series of hypertensive crises, one of which may result in hemorrhage. A hypertensive crisis can provoke rupture of an existing aneurysm.
First aid for a stroke: what to do before the doctor arrives
October 29 is World Stroke Day. For this reason, together with the doctor, we have compiled a detailed guide to first aid for a stroke and found out what should not be done under any circumstances
What is a stroke and why is it dangerous?
A stroke is a disorder of blood circulation in the brain. It can occur due to a ruptured vessel or blockage by a blood clot. In this case, the nerve cells do not receive the required amount of oxygen, glucose and other nutrients, which can lead to their death.
There are several factors that increase the risk of stroke, including: excess weight, high cholesterol, diabetes, hypertension, alcohol and drug use, and smoking. In addition, doctors take into account genetic predisposition and age: the disease most often affects those over 45 years old.
Stroke can be ischemic or hemorrhagic. Subarachnoid hemorrhage is also isolated, which is rare, but in 50% of cases is accompanied by death. He is characterized by acute pain in the back of the head, convulsions, vomiting and loss of consciousness are possible.
Ischemic stroke, or cerebral infarction, is the most common type of cerebrovascular accident. The immediate cause of ischemic stroke is blockage of a vessel supplying the brain. This may occur due to the formation of a blood clot or its entry into the lumen of the vessel. People with atherosclerosis, cardiac arrhythmias, or heart valve disease have an increased risk of developing blood clots. Ischemic stroke can occur when you take medications on your own without a doctor's prescription (for example, diuretics or combined oral contraceptives).
Symptoms of an ischemic stroke develop over a short period of time and are not accompanied by headaches, since there are no pain receptors in the brain. Most often this happens at night when a person is sleeping, and in the morning when waking up he discovers that an arm or leg is not working or speech is impaired.
In a hemorrhagic stroke, the wall of a vessel ruptures and blood permeates the brain tissue. Frequent causes of hemorrhagic stroke are increased blood pressure, taking drugs that reduce blood clotting, disruption of the structure of the vessel wall (aneurysm) or congenital anomalies of the vascular bed - arteriovenous malformations. Hemorrhagic stroke develops quickly and is often accompanied by headache. If blood soaks into the choroid of the brain, where there are pain receptors, a person may lose consciousness. This subtype of stroke has a high rate of death, but if the person survives, he recovers well.
First aid for stroke
It is advisable that a person with a stroke be taken to hospital as soon as possible - within three hours of the onset of the first symptoms. Therefore, it is important to properly organize assistance for a person with suspected stroke.
Call an ambulance. If you experience symptoms of a stroke, ask for help and have someone else call the doctor. Provide brief information about the patient (age, what happened). Leave your contact information so we can contact you. Be prepared to meet the physician and provide access to the patient.
Help the patient find a safe position: it is best to lie on his side with his head slightly elevated.
While you are waiting for an ambulance, try to find out from the patient when the symptoms began, what chronic diseases does he suffer from and what medications does he take? This information will save doctors time and allow them to quickly make decisions.
If a person is unconscious and not breathing, cardiopulmonary resuscitation must be performed. However, in order to provide it correctly, it is necessary to undergo specialized training courses.
If the patient has difficulty breathing, remove restrictive clothing (tight collar, tie or scarf) and open the windows.
— If a person is cold, cover him with a warm blanket.
— While the ambulance is traveling, do not under any circumstances try to give the patient something to drink, feed, or force him to stand up. The person may have difficulty swallowing and may choke. And when trying to stand up due to high blood pressure or lack of coordination, there is a high risk of falling and receiving additional injuries.
- Monitor the person closely for any changes in their condition. Be prepared to tell the emergency operator or doctor about their symptoms and when they started. Be sure to indicate whether the person fell or hit their head.
— In some cases, it is advisable to transport the patient to the nearest hospital yourself if you are not confident in the efficiency of the team.
— Discuss this decision with the emergency operator.
It is good if several people provide assistance. For example, one will be responsible for resuscitation, the second will monitor pulse and blood pressure, and the third will talk on the phone with doctors. Call neighbors and others for help if the sick person is on the street or in a public institution.
Signs and symptoms of stroke
Depending on the severity of the stroke, symptoms may be mild or severe. You need to know what to look for. To check for warning signs of a stroke, you can use the Western mnemonic FAST, which means [4]:
F - face - “face”
A - arm - “hand”
S - speech - “speech”
T - time - “time”
The first symptom is facial asymmetry. If you ask a person to smile, he will not be able to do it; one corner of his mouth will remain downturned. When the patient sticks out his tongue, it may deviate to one side. As soon as you have performed a small operational test, you must immediately call an ambulance. Often the victim does not respond to requests, cannot speak coherently and cannot raise both hands at the same time; sometimes he is in a state of disorientation, the pupils are dilated or there is no reaction to light.
Transient ischemic attack can be difficult to identify based on symptoms alone [5]. They resolve completely within 24 hours and often last less than five minutes. The attack causes temporary circulatory failure and may be followed by a more severe stroke, so it is important to see a doctor as soon as possible.
However, it is worth remembering that only a small part of the brain is responsible for movement and sensitivity, therefore, if blood circulation is disrupted in other parts of the brain, a variety of symptoms may occur: impaired speech, swallowing, vision, dizziness, lack of coordination, confusion and loss of consciousness, epileptic seizures, sudden memory loss or inappropriate behavior of the patient and others. The main task is to call a doctor if someone feels unwell: unusual symptoms appear that were not there before. It’s better to be on the safe side than to miss time, which is the most important factor determining the prognosis for a stroke.
First aid for a stroke before the ambulance arrives
At home, you can carry out a set of measures to support the patient, but in any case you cannot do without professional doctors. If blood pressure rises, it does not need to be lowered; this is an adaptive reaction of the body. Thus, the body tries to improve blood supply to the brain through special “backup pathways” of blood circulation - collaterals. You should not give the patient any medications because you do not know whether the patient has a stroke or other illness. In addition, ischemic and hemorrhagic strokes are treated completely differently. It is the doctors’ task to make a diagnosis within 3 hours, deliver to a specialized center for the treatment of stroke and prescribe appropriate treatment. It is important to understand that nerve cells die within 5 minutes if they do not receive sufficient blood supply. Therefore, the infarction zone can no longer be saved, but around the zone of cell death a border region is formed (the so-called “penumbra” - penumbra), where nerve cells are on the verge of death. If left untreated, the penumbra area increases and more and more cells die, which is manifested by worsening stroke symptoms and a poor prognosis for life and subsequent recovery.
Self-help for stroke
If the symptoms are minor and the victim remains conscious and able to move, he can administer first aid to himself. But only after an ambulance is called. In case of a stroke it is worth:
- Tell someone other than doctors that you feel unwell. Call neighbors and relatives who are nearby.
— Take a horizontal position with your head raised or in a position lying on your side.
- Free your neck and chest from constricting jewelry, shirt collar, tie and other clothing.
- Do not get up until the ambulance arrives.
What will doctors do?
Diagnosis and treatment of the patient is carried out in the neurology department. If a little time has passed since the onset of the attack, the patient has a chance to fully recover.
At the hospital, he undergoes a CT scan and thrombolytic therapy: a drug that dissolves blood clots is injected. In some cases, doctors choose thromboextraction - mechanical removal of blood clots from blood vessels.
Recovery after a stroke
Until the person’s condition stabilizes, he or she must remain in an intensive care unit (resuscitation unit). After his condition improves, he is transferred to a regular ward and prescribed medications to prevent a recurrent stroke. In addition to doctors, rehabilitation therapists, speech therapists, and clinical psychologists work with the patient. The first days and weeks are very important for subsequent recovery. The rehabilitation process depends on many factors, including the speed of first aid and treatment provided, and the presence of chronic diseases.
The first stage of recovery takes place in the hospital: the patient's condition is assessed and stabilized. After treatment, a person can remain in the hospital or be discharged home, but in any case, the doctor’s recommendations must be strictly followed. If stroke symptoms are mild, rehabilitation can be done on an outpatient basis. First of all, it is important to relieve muscle tension, strengthen the mobility of the limbs, and stimulate their mobility with simple physiotherapeutic exercises [6].
If you are caring for someone who has had a stroke, write down your doctor's instructions for further treatment [7]. The patient may need systematic transportation to a rehabilitation specialist or organization of medical care at home.
Stroke Prevention
To reduce the risk of stroke, you need to follow the basic rules of a healthy lifestyle: eat a varied and high-quality diet, exercise, spend time outdoors, relax, and eliminate bad habits. Patients over 40 years of age should undergo periodic medical examinations (dispensary examinations or check-up programs). It is important to carry out timely treatment of chronic diseases that can increase the risk of stroke.
Doctor's comment
Sergey Makarov, neurologist, otoneurologist at GMS Clinic, assistant at the department of nervous diseases at the Institute of Professional Education of the First Moscow State Medical University named after. THEM. Sechenov
– What drugs can be used safely?
– Strange as it may sound, no medications should be given to a patient suspected of having a stroke. Even medications to lower blood pressure can worsen the prognosis, since increased blood pressure is the body’s protective reaction to blockage of the vessel. Unfortunately, there are currently no drugs with proven effectiveness that can clinically significantly change the course of stroke. You need to call a doctor, and then specialists will decide what medications are needed and in what doses.
– How does the lack of first aid affect further treatment?
– The main principle of medical ethics is primum non nocere. “First of all, do no harm.” Therefore, the main help is to ensure the safety of the patient while he waits for emergency medical help. This is what this article is about. Currently, many specialized vascular centers have been created in Russia for the treatment of heart attacks and strokes. If the patient is delivered within this time frame during the “therapeutic window” - the time when the blood clot can be dissolved or removed - then the person has a good chance of recovery, although this process is individual. However, often the duration of the stroke cannot be determined or the patient has contraindications to thrombolytic therapy. In such cases, doctors are forced to limit themselves to symptomatic therapy. The patient is ensured that vital functions are maintained and medications are prescribed to prevent a recurrent stroke.
– If you take a patient to the hospital yourself, do you need to call in advance what to take with you, how justified is this, or is it better to wait for an ambulance?
– This issue should be discussed with the emergency operator. In the vast majority of cases, transportation of patients is carried out by an ambulance team. In large cities, emergency services work very quickly. When transporting a patient by ambulance, the patient is already waiting at the hospital, so many patients receive effective treatment for acute cerebrovascular accident. When transporting a patient to the hospital, you do not need to take anything with you, since the patient will go straight to the intensive care unit, where you cannot take personal items.
Link to publication: RBC
Prevention
Prevention should be aimed at identifying and correcting the main risk factors.
Atherosclerosis
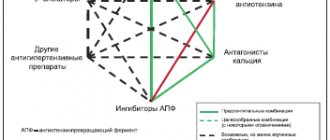
It is necessary to constantly monitor the level of blood lipids - total cholesterol, LDL, HDL, VLDL, TG, CA. If you are prone to high cholesterol, you must follow the prescribed diet. If following a diet does not provide the desired reduction in cholesterol levels, statins are prescribed - drugs that lower blood lipid levels.
Arterial hypertension
If a diagnosis of “Arterial hypertension” is made, you should take all prescribed medications without skipping, even with normal blood pressure values. You need to keep a blood pressure diary, where you should enter your blood pressure and pulse readings. If blood pressure is unstable, there is a tendency to crises, the diary should be filled out 2 times a day - morning and evening. Such a diary will help the doctor choose the optimal therapy.
Rhythm disorders
Rhythm disturbances can be the result of many heart diseases, incl. myocardial infarction. If there are rhythm disturbances in the atria, most often atrial fibrillation, a person may not feel anything; these disturbances can be detected by taking an ECG. Atrial fibrillation causes the formation of thrombi - blood clots that can cause not only strokes, but also heart attacks of other internal organs.
If atrial fibrillation is detected, anticoagulants are prescribed - drugs that prevent thrombus formation. Taking anticoagulants increases the risk of bleeding. Anticoagulants should not be interrupted, and the drug or dose should not be changed without the doctor's permission.
When PMI or stroke occurs in people under 45 years of age without cardiovascular disease, rarer causes should be excluded.
Stroke is easier to prevent than to treat its consequences. In severe cases, patients remain bedridden despite all the efforts of doctors and relatives. In other cases, rehabilitation can take months or years. The network of boarding houses has created special programs for recovery after a stroke in boarding houses, which are aimed at speedy recovery under the supervision of specialists.
Stroke - symptoms, stages of stroke development
Among the stages of a stroke, it is worth highlighting the following stages:
- Transient ischemic attack;
- The second stage is a small stroke;
- The third is a completed stroke.
At the first stage of ischemic stroke, periodic disturbances associated with ischemia of areas of the brain appear. At the same time, there are also clinical signs that manifest such a stroke: the symptoms are mainly caused by an acute reversible disturbance of blood flow, as well as concomitant pathologies. These include:
- Hypertension;
- Hypertensive crisis;
- Thrombophilia;
- Varicose veins of the lower extremities and pelvis;
- Infectious endocarditis.
As a rule, stroke associated with thrombosis or embolism manifests itself without the stage of transient ischemic attack, while hypertensive variants have signs of reversible ischemia. Among them, headaches, a feeling of heat and facial flushing, nausea and vomiting, tachycardia, disturbances in the perception of auditory or visual information, and sweating are especially common. These signs are common to a large number of diseases, especially the circulatory system. Therefore, the importance of treatment at the stage of transient ischemic attacks is enormous.
Content
Minor stroke stage
In a condition such as a minor stroke, the symptoms are caused by ischemia of a region(s) of the brain. This is provoked either by thrombosis, or by the same arterial hypertension during a crisis. The predisposing factor is atherosclerosis of cerebral vessels and autoimmune lesions of the arterial wall.
At this stage, clinical symptoms become especially pronounced. Early signs of a stroke include:
- Speech disorders;
- Impaired motor function (hemiparesis, monoparesis or tetraparesis);
- Visual impairment, loss of visual function;
- Nausea and headache, vomiting;
- Loss of sensation in some areas of the body;
- Nonspecific symptoms listed above.
These disorders should be explained as follows: stroke and cerebral infarction provoke the death of nerve tissue cells, therefore the performance of functions of higher nervous activity is limited. Ischemia or hemorrhage most severely affects the cortex. It is divided into zones, the death of neurons in which causes so-called focal symptoms. It includes loss of sensitivity and motor function. If the size of the damage is small, then monoparesis may develop, that is, the inability to perform motor acts with one limb.
The wider size of the defect causes the development of hemiparesis - a violation of motor function in one half of the body. If the lesion affects a large area, then complete paralysis occurs. At the same time, the amount of damage to the somato-sensory areas of the cortex responsible for sensitivity and movement in each clinical case is separate.
Another sign is pain during a stroke. At the same time, the brain and spinal cord itself do not have pain receptors, therefore this sensation occurs due to damage to the soft tissues of the head and bones of the skull (hemorrhagic traumatic form), as well as due to a hypertensive crisis (ischemic form). At the same time, hypertension also causes a hemorrhagic form, which is characterized by pain in the crown and back of the head. They should be associated specifically with an increase in pressure, and not with the generation of brain tissue itself. Thrombosis of cerebral vessels occurs without pain, and therefore patients often do not seek help, especially if it is impossible to take the person to the hospital. In practice, any cases of impairment of motor function, speech, vision and hearing should be observed in a medical facility, because these signs can help establish a diagnosis of stroke.
Nausea and vomiting are characteristic signs of compression that characterizes the disease stroke. Moreover, these symptoms are characteristic of different locations of damage. Nausea is accompanied by dizziness, weakness and leads to vomiting. It does not bring relief and may occur several times.
Impaired consciousness during a stroke is an early sign. This is observed due to brain damage and disruption of the nutrition of areas of nervous tissue. They can manifest themselves as usual drowsiness, lethargy and coma. It is worth understanding that there is no such disorder of consciousness as drowsiness: here it is used for a correct analysis of the concepts and symptoms by which it is worth diagnosing the pathology at the initial stage. Sudden drowsiness is a sign that characterizes the development of precoma or coma. During precoma, the patient may respond to stimuli and speech, while coma is a complete loss of consciousness. If possible, it should not be allowed, trying to keep the patient conscious. This is needed to track new signs that will indicate the development of the process. Therefore, with a pathology such as stroke, treatment should be based not only on protocol manipulations and components of pharmacological therapy: it is important to take into account new symptoms, changing the tactics for correcting the condition and maintaining vitality.
Accomplished stroke
At this stage, the above signs are no longer important, because, as a rule, they are characteristic of an inpatient department. By this time, the patient has already been taken to a medical facility by ambulance and is in the intensive care unit. What is most important here is the tendency for the old signs of stroke to remain the most important and progress to disturb the condition. New symptoms do not appear except for those that characterize complications. With a pathology such as a stroke, the consequences of this clinical stage are far-reaching, because, in fact, there is no way to eliminate brain damage.
Long-term symptoms of stroke
This category of stroke symptoms is not particularly important for diagnosis and is provided only as an informational guide to complications and their development. Brain function should recover over several weeks or months. The patient continues to have difficulty fully controlling movement, speech, memory, vision, or hearing. It is also possible that these signs will last a year after the stroke, or will remain forever. Since the damage is localized at the level of the most highly differentiated cells, it is impossible to restore or replace them with new neurons (by the way, this does not happen in the body). Therefore, after a stroke, the patient has a set of symptoms that cannot be corrected. Based on this, it is worth understanding that recovery after a stroke is not complete, and therefore some functions will be lost forever.