Previously, when counting platelets according to Fonio, a laboratory diagnostic doctor measured only the diameter of these cells, distinguishing 4 groups of blood platelets (or Bizzocero plaques). Now there is no need to devote so much time to such calculations, if automatic hematological systems with software are put into the service of laboratory work, which will count the number of all formed elements separately, including platelets (PLT).
The device will not ignore the particular characteristics of blood cells - erythrocyte (MCV, RDW, HCT) and platelet indices: MPV (mean platelet volume), PDW (platelet distribution width), PCT ( platelet crit - thrombocrit). Upon completion of the work, the machine itself will draw a histogram curve in order to guide the doctor along the true path in the diagnostic search.
In this publication we will try to understand in detail what the MPV platelet index is.
Different characteristics of platelets
Fragments of megakaryocytes, giant bone marrow cells, anucleate blood plates - platelets (PLT - platelet), circulating in the blood, look like biconvex disks with a diameter of 1.8 microns to 4 microns. Young blood platelets are larger in size than mature cells, aged platelets are the smallest. In blood smears, platelets appear pale blue or lilac in color and are often collected in groups.
In an inactive state, platelets have a round or oval shape, but as soon as they “sense” a violation of the integrity of blood vessels and bleeding, they almost instantly change shape, increase up to 10 times in size, “acquire” pseudopodia and begin to stick together (platelet aggregation) . The blood platelets perform all these actions in order to rush in the form of a conglomerate to the scene of the accident, where the platelets that arrived earlier are already waiting.
Therefore, platelets are very prone to change their size
, since they have a very important function in the human body - participation in vascular-platelet hemostasis or, more simply, these blood platelets help blood clotting in case of various injuries in the microcirculation zone.
Red blood cells and their function in the body
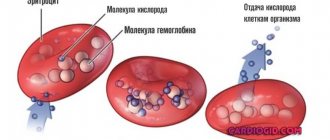
Red blood cells are a cellular unit of blood, the main purpose of which is to saturate the body with all components of the inhaled air. They carry oxygen molecules from lung tissue to internal organs, as well as other parts of the body.
In the opposite direction, red cells remove carbon dioxide from the body, formed after absorbing air. Oxygen delivery is carried out by hemoglobin proteins, which make up 98% of the total mass of protein compounds in red blood cells.
When hemoglobin concentration decreases, the transport function of blood cells is disrupted. Therefore, these indicators must be constantly monitored.
What does the MPV index mean?
When automatically processing blood samples, platelets are counted in the same channel with red blood cells - erythrocytes, so the hematology analyzer can separate particles by signal height in accordance with volume, which allows the device to immediately differentiate them:
- Macroplatelet cells (this group includes elements from 1.8 to 30 femtoliters - in principle, these are the cells that are currently interesting to us);
- Microerythrocytes;
- Fragments of red blood cells - schizocytes;
- Remains of the cytoplasm of white cells - leukocytes or, as it is called, cellular debris.
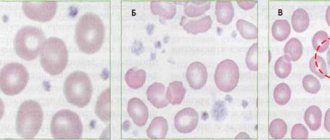
a – normal platelets b – platelets of different volumes (pronounced anisocytosis) c – huge macroplatelets
Meanwhile, this information alone is very little to characterize the state of platelets. At other times they would have been seen on a stained slide, but now most automated hematology analysis systems provide the various indicators present in the hemogram - mean platelet volume (MPV) and other platelet indices. The average volume of blood platelets is calculated by the automatic hemoanalyzer program using the formula:
MPV = [PCT,% x 1000] /
In addition, the device also includes a histogram for its calculations, which is subsequently studied by the doctor when deciphering the results.
MCHC increased
The hemoglobin concentration in red blood cells may be increased in the following cases:
- hyperchromic anemia (ovalocytosis, folate deficiency, B12 deficiency, spherocytosis, including congenital);
- water-electrolyte metabolism is impaired;
- may be high in newborns, which is considered normal.
Elevated concentrations of iron-containing protein are quite rare. If MCHC has increased to 380 grams per liter and continues to rise, hemoglobin may begin to crystallize.
The result is obtained using modern hematology analyzers
Most often, a significant increase in MCHC is not associated with any disease, but indicates an error during a laboratory test, since a high concentration of hemoglobin in red blood cells will lead to morphological changes in red cells and their complete destruction. There is only one disease in which this indicator is increased. This is a hereditary pathology - spherocytosis. Refers to hemolytic anemia and is characterized by a defect in the cell membrane of red cells.
In most cases, the following technical errors are the basis for increased MCHM:
- incorrect determination of hematocrit and hemoglobin;
- violation of the conditions for blood collection and storage, which is why partial disintegration of red blood cells occurred.
MPV norm in general blood test
The average platelet volume - MPV is expressed in femtoliters - fl, fl (1 femtoliter = 1 cubic micron - µm2), depends on the age of the person (data are given in the table below) and normally ranges between 7.0 - 10.0 femtoliters.
And in children from one to three years of age (on average), MPV in a general blood test performed by an automatic device gives higher values.
Table: Normal intervals for the MCV platelet index depending on age
| Age, years | Norm MPV, fl |
| Infants up to one year | 7,1 – 8,0 |
| Children from 1 year to 5 years | 8,1 – 8,9 |
| Children, teenagers and adults from 5 to 60 years old | 7,4 – 12,0 |
| Over 60 years old | 9,5 – 12,0 |
Meanwhile, all these norms and the table are very conditional. The reader can verify this for himself by looking for the boundaries of normal values in other sources. The whole point, as always, is in the reference intervals, which vary noticeably in different laboratories, where the norm falls within the range of 6.0 - 13 femtoliters, somewhere narrows its limits (7.4 - 10.4), so before you start worrying Regarding your own analyses, it is useful to ask what values are used by the CDL, which calculated these indicators.
Preparing for analysis
In most cases, blood for analysis is taken from a vein. It is permissible to take capillary blood from children under 3 years of age and from adults for special indications. The analysis is taken in the morning, on an empty stomach; the fasting period should be at least 8 hours.
Before blood sampling, it is forbidden to eat food or any drinks; you can drink plain water. There is no need to follow a diet a few days before the test, but you should exclude alcoholic drinks and fatty foods. It is undesirable to be exposed to high physical and psycho-emotional stress, which may affect the reliability of the analysis results.
In the process of preparing for the blood sampling procedure, the patient should be warned about possible unpleasant sensations when applying a tourniquet and during vein puncture.
What will the doctor think?
Having familiarized himself with the first results (calculation of platelet indices), the doctor can already imagine different situations regarding the behavior of representatives of the platelet unit in the bloodstream, the state of hemostasis and bone marrow hematopoiesis, taking into account only one indicator - the average platelet volume:
- MPV is within normal limits. In the circulating blood: cells that have not changed in volume, mature, but not old, full-fledged cells capable of performing their functional tasks at the proper level. The coagulation system and bone marrow are functioning normally.
- MPV increased. In the bloodstream, along with normal platelets, circulate young blood platelets, increased in size, and giant platelets, which, although they try, but, not having the qualities of full-fledged mature cells, have not acquired their capabilities, and therefore are not able to fully take assume the responsibilities of “healthy” elements of the platelet unit. There is a rush in the bone marrow, blood clotting is impaired.
- MPV is below normal. In the blood: there are practically no cells of normal size; the platelet link in the bloodstream is represented by small aged platelets that have lost their functions. There are obvious deviations from the norm in hemostasis, bone marrow hematopoiesis is suppressed. Thrombopathy?
Based on studies of the morphological features of blood platelets, as well as on calculations of an automatic analyzer and a histogram, it is possible to discover the relationship between their volume and functional abilities (the adhesive-aggregation function of platelets, due to the content of biologically active substances in their granules).
With “growing up and aging,” the volume of plates decreases, which can be seen in the histogram recording. The presence of the overwhelming majority of young forms in the circulating blood causes the histogram to shift to the right, and the predominant distribution of old blood platelets in the bloodstream shifts to the left.
Average platelet volume is increased
An increased average platelet volume can be a diagnostic sign of various (usually hematological) pathologies or act as a laboratory symptom accompanying certain diseases. For example, MPV is increased when:
- Idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura (an autoimmune process that leads to massive death of blood platelets and intense bone marrow hematopoiesis) and other autoimmune diseases (SLE - systemic lupus erythematosus);
- Myeloproliferative processes;
- Hemorrhagic thrombocytodystrophy or Bernard-Soulier syndrome (rare hereditary disease, autosomal recessive transmission);
- Hereditary large-platelet thrombopathy (a disease characterized by large platelets, but their function is not impaired);
- May-Hegglin anomalies (familial thrombocytopenia, autosomal dominant inheritance);
- Anemic syndrome caused by acute blood loss;
- Thalassemia;
- Diabetes mellitus;
- Hypersplenism and enlargement of the spleen, which can be either isolated (rarely) or accompany various hematological pathologies, for example, myeloproliferative processes (massive death of blood platelets occurs in the spleen, and the bone marrow at this time works in emergency mode, releasing young cells into the bloodstream large sizes);
- Removal of the spleen (however, the MPV indicator in this case changes its values for a short time; soon after the operation it returns to normal);
- The first signs of the formation of a neoplastic process;
- Development of inflammatory reactions;
- Development and progression of the atherosclerotic process (especially in smokers);
- Thyrotoxicosis (high functional activity of the thyroid gland and an increase in the level of its hormones as a result).
An increased MPV is not always associated with the development of some pathology, for example, in people who actively puff on a cigarette, as well as on holidays and weekdays who drink strong drinks, the average volume of blood platelets is always increased.
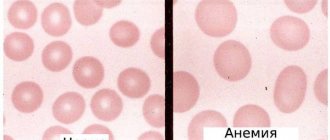
MCV reduced
A decrease in the average volume of red blood cells most often occurs with the development of iron deficiency anemia. They can develop as a result of exposure to various factors, such as:
- Chronic blood loss.
- Lack of iron in the diet.
- Impaired absorption of iron in the intestines.
A decrease in the volume of red blood cells is observed in a variety of chronic diseases - long-term infections, oncological pathologies. Rarely, a congenital decrease in mcv is possible, for example, with thalassemia. This is a group of genetic pathologies that occur when the synthesis of hemoglobin globin chains is disrupted.
If the synthesis of the alpha chain is impaired, alpha thalassemia develops. This is a relatively mild pathology, characterized by a decrease in hemoglobin to 70-90 g/l and a decrease in the mcv index. This form of the disease often does not manifest itself in any way and is detected by chance, when studying laboratory blood parameters.
Beta thalassemia, which occurs when the synthesis of the hemoglobin beta chain is impaired, is much more severe. If defective genes were inherited from one of the parents, it is manifested by a decrease in the mcv index and hemoglobin level. When defective genes are passed on from both parents, Cooley's anemia develops. It is characterized by an extremely severe course; red blood cells not only sharply decrease in volume, but are also quickly destroyed. This leads to enlargement of the liver and spleen and disruption of their functions. To maintain life, such patients require regular blood transfusions, and a complete cure is possible with a bone marrow transplant.
Slightly low or low mean platelet volume?
A slightly reduced or even low average platelet volume is characteristic of a number of conditions that occur with inhibition of bone marrow hematopoiesis:
- Hypoplasia of the megalocaryocyte lineage (congenital pathology and acquired disease (this group of megalocarycytic hypoplasias also includes aplastic anemia);
- X-linked recessive thrombocytopenia with platelet microcytosis (Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome);
- Thrombocytopenia caused by septic conditions caused by various infectious agents (for example, thrombocytopenia in septic endocarditis);
- Myelodysplastic syndrome;
- Malignant processes localized in the bone marrow;
- Inflammatory diseases;
- Children have infectious diseases (measles, rubella, influenza), however, if adults are “lucky enough” to catch such an infection, then the MPV platelet index will react in a similar way;
- Myocardial infarction;
- Some kidney diseases;
- Severe damage to the liver parenchyma (cirrhosis).
The MPV indicator may also be reduced when carrying out various types of therapeutic measures affecting neoplastic processes:
- Chemotherapy treatment;
- Irradiation;
- Cytostatic therapy.
A low average platelet volume may be a sign of pregnancy pathology and, if in this situation the content of blood platelets is simultaneously reduced, then the threat of miscarriage should be suspected. In addition, a reduced average platelet volume is observed when using certain medications.
Platelets are very sensitive
Blood platelets are very sensitive to changes in external conditions (atmospheric pressure, weather) and the state of the body, so their average volume can be increased or decreased not due to disease, but due to certain circumstances. This should not be forgotten when going to the laboratory. Therefore, you should not just drop in and donate blood, but prepare properly:
- Do not drink, eat or smoke in the morning;
- Avoid heavy physical work and mental stress the day before;
- Avoid taking various medications (you can take them after the test);
- If an R-graphy is prescribed on the day of testing, then it is better to reschedule it and do it later, and the same should be done with physiotherapeutic treatment.
In addition, it will be useful for patients to know that there are situations when MPV is lowered or increased by 1-2% of the upper or lower limit, but this is not a platelet pathology, evidence of a blood coagulation disorder, and does not indicate a failure of hematopoietic processes in the bone marrow.
For example:
- In children of the younger age group, MPV sometimes leaves the normal range due to the fact that the hematopoietic system has not yet completed its development;
- Deviations from the norm may be the result of surgical operations, injuries or acute blood loss;
- The average platelet volume may leave the normal range in women before and/or after menstruation.
All this can be explained simply: the body turns on compensatory mechanisms, active production of new blood platelets begins in the bone marrow, and young, large platelets appear in the bloodstream.
How the research is carried out
To obtain data on MSI in a blood test, blood is drawn from a vein. In rare cases, it is possible to use finger capillaries (nowadays they are practically not used, as they are less accurate and informative). This procedure is performed by a nurse or laboratory worker who has the appropriate education and license to carry out this activity. Its duration is no more than 5 minutes and is accompanied by slight pain and discomfort at the puncture site. However, the discomfort quickly disappears, and a small bruise may remain at the puncture site. Persons who are afraid of the sight of blood are strongly advised to turn away and not look at the hand until the end of the procedure. But to prevent loss of consciousness and quickly restore consciousness, a cotton pad and ammonia are always present in the office. Blood sampling is carried out in several successive stages:
- Applying a rubber or fabric tourniquet with clamps to the forearm of the patient, who must work his fists a little (clench and unclench his hand several times to better fill the vessels).
- The technician or nurse selects the most appropriate vein and cleans the skin with an alcohol swab.
- Inserting a needle into a vein, through which blood flows into a syringe or special tube. Often, no more than 5 ml is collected.
- Remove the needle and apply cotton wool soaked in alcohol to the puncture site.
To prevent bruising or bruising, the patient is asked to press his forearm to his shoulder for a few minutes. At this point, the procedure ends and the medical worker signs the tube, after which the resulting material is placed in the analyzer. Its use makes it possible to automatically count all types of blood cells, including red blood cells. The obtained data is sent to the attending physician, after which the MCH blood test begins to be deciphered.