A general analysis is carried out in most cases. This is a standard routine test. It is aimed at identifying possible pathological processes. It is also prescribed as part of a standard preventive examination. Gives a lot of information, but most often non-specific.
That is, it is impossible to make a diagnosis based on the results. Additional measures will be required: more accurate and sensitive, narrowly targeted.
The blood color index is a laboratory reflection of the concentration of hemoglobin in one red blood cell; on average, there are about 33 picograms of the substance per red cell. To make it more convenient to count, this number was conventionally taken as one.
The color indicator is used to diagnose anemic diseases and other pathological processes associated with disorders of the bone marrow. And not only.
A comprehensive diagnosis of diseases of internal organs: liver, kidneys and the entire excretory system is possible.
Based on the results of the examination, specific treatment can begin. Often, narrow diagnostic measures are prescribed to obtain additional information.
What does the indicator mean and when do they resort to analysis?
The technique allows you to estimate how much hemoglobin is contained in one conventional red blood cell. The results can be transferred to all red blood cells as a whole. This is an accurate diagnostic method, therefore it provides informative information.
Red blood cells transport oxygen and carbon dioxide. This is the key element that makes cellular respiration itself possible. A substance known as hemoglobin is responsible for the functional properties of red blood cells. Hemoglobin norms by age and the causes of deviations in women are described here, in men - here.
If it is not enough (and when the color index drops, this is the case), problems with tissue and cellular respiration begin. Consequently, the analysis allows you to find out how consistent the function of red blood cells is.
As for specific indications for conducting research, there are quite a few.
Reasons to prescribe a diagnosis include:
- Pain in the right side under the ribs. May indicate liver disease. Not always, but most often. A blood test will shed more light on the situation.
- Discomfortable sensations in the lumbar region. Indicate pathologies of the kidneys and excretory tract. Medical assistance required.
- Paleness of the skin.
- Feeling of constant weakness, drowsiness.
- Brokenness.
- Decreased performance.
- Violation of taste preferences. Gastronomic perversions.
- Also respiratory and cardiac disorders. Separately or together.
- Long period of fasting. It is almost guaranteed that there will be disturbances from all organs and systems of the body. Therefore, it makes sense to carefully check the patient. Assess the damage that has been caused to structures and systems.
- Stool disorders, pain in the abdomen. Symptoms that clearly indicate disorders of the digestive tract.
- Preventative examination. It would be a good idea to check the color indicator as part of preventive diagnostics.
Very often, diseases at an early stage do not make themselves felt at all. Therefore, a pathological process can only be detected through an objective study.
If there is even a suspicion of diseases of the digestive system or hematopoietic structures, a full diagnosis is necessary. Including the mentioned study.
References
- Nazarenko G.I., Kishkun A.A. Clinical assessment of laboratory research results // M.: Medicine - 2006. - 544 p.
- Tatkov O.V., Stupin F.P. General blood test. Information collection // M.: Publishing solutions. — 2021. — 72 p.
- Fauci, Braunwald, Kasper, Hauser, Longo, Jameson, Loscalzo Harrison's principles of internal medicine, 17th edition, 2009
- Mosby's Diagnostic and Laboratory Test Reference 14th Edition, 3251 Riverport Lane
- St. Louis, Missouri 63043: Elsevier Publishing Hall 2019
Standard tables
Values are dimensionless. As already mentioned, 33 pg is taken as a unit (U). This is what we need to build on.
The formula for calculation is quite simple: the mass of hemoglobin in grams per liter must be multiplied by 3 and the resulting amount divided by the first three digits of the number of red blood cells in the blood.
For example: 125 g/l of hemoglobin and 4.10 million/μl of red blood cells were determined. Therefore, 125*3/410=0.91 Units. This will be the current color indicator.
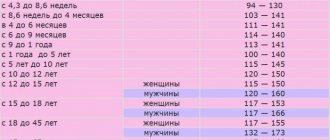
Age data is presented in the table.
Among women
| Age (years) | Indicator (in units) |
| 15-25 | 0.8-1.03 |
| 25-50 | 0.8-1.03 |
| 50 years and older | 0.85-1.05 |
In men
The normal blood color index is 0.8-1.05 units, and is almost the same for both men and women.
| Age (years) | Normal value (U) |
| 15-25 | 0.8-1.02 |
| 25-50 | 0.8-1.03 |
| 50 years and after | 0.85-1.05 |
In children
| Life period | Level in Units |
| Up to 5 days | 0.9-1.3 |
| Up to 15 years | 0.85-1 |
Important Notes
Material for research
Children under 7 years of age: venous blood/capillary blood (for special indications).
Children over 7 years of age and adults: venous blood.
Capillary blood collection for research is carried out only for children under 7 years of age (for special indications).
According to GOST R 53079.4-2008, indications for taking capillary blood are possible in newborns, in patients with very small or hard-to-reach veins, with large-area burns, and in severely obese patients.
Reasons for the increase
The concentration of hemoglobin in red blood cells increases, as a rule, when the number of red blood cells itself decreases. This is a kind of attempt to compensate for the insufficient number of functional active units so that the body does not feel changes.
The factors for the development of the pathological condition will be as follows.
Stomach diseases
Disorders of the digestive tract are the main cause of the disorder. A characteristic feature in the context of the topic is the poor absorption of vitamins that enter the body with food.
Formally, their concentration is sufficient. Another thing is that the body is not able to cope with the task of storing, depositing compounds.
Among the particularly common diseases in which this happens are:
- Gastritis. Acute or chronic inflammation of the gastric mucosa. It occurs in almost 40% of the world's population in one form or another. It is not always accompanied by characteristic symptoms. Perhaps a sluggish, silent course. And most often this is what happens. At least in the early stages of the disease.
- Stomach ulcer. Complex pathological process. It is typically characterized by the development of a defect in the wall of the mucous membrane. Sooner or later, perforation is possible.
That is, the formation of a hole, but this is a relatively long-term prospect. The disease gives a pronounced clinical picture; it is quite difficult not to notice it. Especially if you listen to your body at least sometimes.
- Cancer processes. Tumor formation. Even at an early stage, neoplasia already interferes with the normal absorption of the substance.
Symptoms depend on the disease. But there are some common features:
- Discomfortable sensations in the epigastric region. In the stomach in general. Just above the navel - most often.
- Disorders of normal digestion.
- Dyspeptic phenomena. Among them are belching and heartburn.
- Flatulence. Increased intestinal gas formation. Creates a lot of discomfort for the patient.
There are also more specific symptoms. It all depends on the diagnosis. Treatment is determined by the condition. For gastritis and ulcers, antacids are prescribed to keep the acidity of the juice normal.
A special diet is also prescribed. As for cancer, prompt treatment is necessary. This is a priority. Radiation and chemotherapy are prescribed as needed.
Insufficient intake of vitamin B12
Occurs as a result of the influence of nutritional factors. Simply put, the patient eats incorrectly, not as he should. Hence the problem.
A large amount of useful substances is found in legumes, meat, and fish. Animal products are needed to keep the body normal. People who follow a vegetarian diet are especially at risk. This is a direct path to pathological processes.
The nutritional factor also affects it in a more complex way. Chronic disorders may develop. Be it gastritis, intestinal disorders, liver or pancreas damage. It all depends on the duration of the violation and the timing of following a strict diet.
The treatment is quite simple. It is necessary to enrich the menu with useful ingredients. It is necessary to consume a sufficient amount of animal (40%) and plant (60%) products. This is quite enough to maintain body tone. Products that increase hemoglobin are described here.
As a last resort, you can contact a nutritionist or nutrition specialist. It will help you plan your diet.
Intestinal pathologies
Diseases that affect the thin or thick sections. Most often, the middle and end areas are affected.
Specific diseases that may occur include:
- Colitis. An acute or chronic condition that develops as a result of exposure to an infectious, or less commonly, toxic irritant.
It begins suddenly and is characterized by inflammation and pronounced changes in the mucous membrane. Gradually turns into a relapsing course if sufficient measures are not taken for therapy. Affects any part of the intestine.
- Duodenitis. Inflammation of the duodenum. As a rule, it occurs in combination with gastritis. The reason for this is the anatomical proximity of the digestive tract organs. The disease does not go away on its own; it constantly gets worse. Special treatment is needed.
- Duodenal ulcer. A logical continuation of duodenitis. Changes in the structure of the mucous membrane.
Symptoms, if we talk about the average clinical picture:
- Severe pain. Severe discomfort.
- Nausea.
- Vomit.
- Weakness.
- Heartburn, belching and other dyspeptic symptoms.
- Increased body temperature.
- Diarrhea or constipation. Alternating bowel movements.
The color value of the blood changes as a result of insufficient absorption of vitamin B12. Anemia develops, which is considered a key deviation.
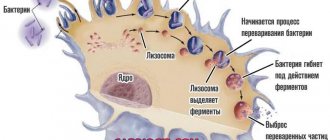
Worm infestations
Parasitic lesions are one of the most common causes of the development of the pathological process.
Helminths are located in the large intestine. They stick to the mucous membranes and consume nutrients that are intended for storage. Assimilation. Accordingly, competition develops between the organism and the parasites.
The disorder is accompanied by a characteristic clinical picture. True, for a long time it remains unnoticed.
Symptoms are represented by the following points:
- Stomach ache.
- Rash. Unexplained red spots on the skin or small papules, vesicles. This is the result of an allergic reaction that develops to the helminth and its waste products. In particularly difficult cases, even anaphylactic shock is possible.
- Increased body temperature.
- Stool disorders. Diarrhea, constipation. More often - the first.
- Disorders of the digestive tract.
- Dyspeptic phenomena.
Helminths are not always located in the large intestine. There are parasites that prefer the liver and are carried throughout the body through the bloodstream. The result will be approximately the same.
Treatment is urgent. The faster the threat is destroyed, the sooner the body will recover. Special antihelminthic drugs are used. Once or in a course.
Liver diseases
Pathologies of the largest gland are represented by several diagnoses:
- Hepatitis. Acute or chronic inflammatory process. Viral, toxic or medicinal origin. Doesn't really matter since the outcome is almost always the same. Especially if you do not receive the necessary treatment.
- Cirrhosis of the liver. Acute or chronic death of organ cells. Necrosis. An extremely dangerous condition that quickly leads to the death of the patient. As a result of the disease, the body cannot normally absorb nutrients. The result is quite clear.
Treatment under the supervision of a hepatologist is necessary. Or, at worst, a gastroenterologist. The task is not the easiest. Hepatoprotectors are used to cover the organ.
Attention:
For early or mid-stage cirrhosis, transplantation is necessary. Liver transplant. This is the only way to save the patient.
A high color index is the result of diseases of the digestive tract. Ultimately, all factors come down to one thing. So-called megaloblastic anemia develops.
This is the result of insufficient intake or absorption of vitamin B12. Red blood cells become defective. Such altered forms in the bloodstream are not able to function normally.
The body increases the concentration of hemoglobin in healthy cells. And so it continues. Increasingly. Quality treatment is required.
A reliable sign of hypochromic anemia
So, hypochromia is a reliable sign of hypochromic anemia, which, differing from each other in other laboratory indicators and their origin, also have their own forms. Thus, the group of hypochromic anemias consists of the following anemic conditions:
Iron deficiency anemia (IDA)
IDA is a typical representative of hypochromic microcytic anemia, and also the most common. Diagnostic criteria:
- Hypochromia and microcytosis;
- Decreased CP and serum iron (Fe) levels;
- Drugs intended to treat such conditions have a positive effect.
Iron-saturated anemia (sideroachrestic)
This form is characterized by a normal iron content in the serum, but due to poor absorption it cannot reach the site where heme synthesis occurs (erythroblasts), therefore, the hemoglobin level drops. This form is most often the result of prolonged intoxication with aggressive chemicals or industrial poisons. In addition, the body is pushed towards the development of chronic hypochromic anemia by long-term use of drugs of various pharmacological groups (affecting the components of red blood).
Diagnostic criteria:
- Hypochromia of erythrocytes;
- Decreased hemoglobin levels;
- Iron concentrations are usually normal;
- There is no effect when treated with ferrum-containing drugs.
Iron redistribution anemia
The cause of the development of this form is excessive destruction of red cells (hemolysis), as well as purulent infections or pathological processes localized in the heart (endocarditis) or lungs (tuberculosis). However, all types of hemolytic anemia (HA) are not suitable as an example of chronic hypochromic anemia, although the destruction of red blood cells (and, accordingly, hemolysis) underlies this pathology. Many forms of HA are normochromic, but quantitative thalassemia corresponds to the definition of hypochromic microcytic anemia.
Indicators used for diagnosis:
- Hypochromia of erythrocytes;
- Decreased hemoglobin levels;
- The serum iron content does not leave the normal range;
- Ferrotherapy does not produce a positive effect.
In other cases (in the presence of signs that can be attributed to different types), the form of hypochromic anemia is classified as mixed
.
Meanwhile, each of the forms has its own origin, that is, the reasons for their formation are different.
Reasons for the decline
Falls are somewhat more common. This is the result of insufficient hemoglobin. It's becoming scarce. Accordingly, in each red blood cell the concentration of the substance decreases. This is reflected in the analysis.
The color index of the blood can be reduced as a result of several diseases.
Nutritional factor
Simply put, poor nutrition. A huge amount of iron is found in meat products, liver, and some plant components.
If the body does not receive enough of this substance, anemia occurs - this is the main cause of low blood color index in adults. Products that increase hemoglobin in the blood are described here.
The symptoms of the pathological process are quite characteristic. The following manifestations are typical for the disease:
- Weakness.
- Drowsiness.
- Insufficient performance.
- Mental and behavioral disorders. At the level of neuroses and depression.
- Headache.
- Nausea.
- Vomit.
- Paleness of the skin.
- Violation of gastronomic preferences. The desire to eat something that is basically impossible to eat. Earth, chalk, etc.
- Brittle hair and nails.
- Delayed wound healing.
Recovery is carried out under the supervision of a hematology specialist. It is enough to change your diet for everything to fall into place. The consumption of animal products, nuts, and chocolate is shown. The menu is prepared by the doctor.
Unfavorable pregnancy
It is characteristic that in this case the consequences are observed both for the mother and for the child himself.
On the one hand, a woman’s body requires more iron during pregnancy. This is necessary because the unborn person, his body, uses a huge amount of the substance. This is how the basic systems of the body need to develop.
Accordingly, you have to consume much more food to cover the needs of two people at once. It is not so easy. If there are diseases of the digestive tract, this is completely impossible. Health problems are guaranteed to begin. Doctor's help required.
The child himself suffers. His body does not receive the normal amount of iron. The problem continues after birth. Since the body is not yet able to independently absorb the substance, and its sources are extremely limited.
This can continue for up to 3 years. Until the body stabilizes functionally.
There are only two correction methods:
- Eat well, taking into account your own needs and the needs of the unborn child.
- If there are diseases, they need to be treated. For iron to be absorbed.
In extreme cases, it is possible to introduce a connection from the outside.
Bleeding
Systematic loss of liquid tissue leads to the release of hemoglobin along with red blood cells.
While the body restores balance, it will take some time, so a decrease in the color index cannot be avoided. This is quite natural.
The same thing is observed with systematic, albeit not so severe, bleeding. For example, nasal. Or with increased fragility of blood vessels. Correction is prescribed if necessary.
Diseases of the digestive tract
They have already been mentioned. Pathological processes in this case lead to slow absorption of iron.
Treatment of the underlying disorder is necessary. If this is not the fastest process, correction is needed here and now. In such a situation, external administration of iron supplements is prescribed. In a adjusted dosage.
Kidney disorders
The paired organ synthesizes a very important substance - erythropoietin. It ensures normal maturation of red blood cells.
The color value of the blood is reduced if the filtering structures stop working properly.
Correction of the underlying pathological process is required.
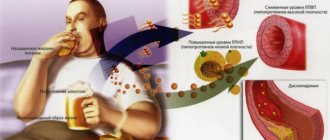
Alcoholism
With systematic consumption of alcohol, red blood cells are destroyed. This is an inevitable phenomenon. At the same time, hemoglobin synthesis slows down. A dual process occurs that ends in severe anemia.
The only way to get back to normal is to give up alcohol.
There are other factors too. For example, poisoning with lead, metal salts and vapors of chemicals and acids. But the bottom line comes down to iron deficiency anemia. She is the root of trouble.
Degree of hypochromia. Relation to microcytosis
Thus, it is clear that hypochromia of erythrocytes means weak staining of the cells (a sign of hypochromia is the median clearing increasing in diameter) as a result of their insufficient saturation with red blood pigment.
hypochromia with microcytosis in the blood
Hypochromia, being a decisive sign of the development of hypochromic anemia, has different degrees of severity:
- 1st degree - the cell is well colored on the periphery, but the clearing zone in the center shows slight hypochromia;
- 2nd degree - the clearing in the center expands, tending closer to the membrane, but the area filled with paint is clearly visible, which indicates moderate hypochromia;
- 3rd degree - the color is located only at the membrane itself, it is actually not visible, so it seems that this is not an erythrocyte at all, but... some kind of pale ring. A similar situation occurs with advanced forms of anemia and indicates its severe course.
Hypochromia of erythrocytes is evidence of the development of hypochromic anemia, but for some reason at the beginning of our work we talked about another characteristic of red blood cells - their size? So, in the vast majority of cases, hypochromia and microcytosis are inseparable; they are the main symptom of hypochromic microcytic anemia. In addition, the importance of these two indicators increases if there is a need to differentiate hypochromic microcytic anemia from other conditions or among themselves.
Platelet link
The next abbreviation in a complete blood count refers to cells called platelets or platelets. Studying platelets without a hematology analyzer is quite labor-intensive; the cells require a special approach to staining, so without an analytical system this test is performed as needed and is not a default analysis.
The analyzer, distributing cells like red blood cells, calculates the total number of blood platelets and platelet indices (MPV, PDW, PCT):
- PLT
is an indicator indicating the number of blood platelets (platelets). An increase in platelet levels in the blood is called thrombocytosis, a reduced level is classified as thrombocytopenia. - MPV
– average platelet volume, uniformity of platelet population sizes, expressed in femtoliters; - PDW
– width of distribution of these cells by volume – %, quantitatively – degree of platelet anisocytosis; - PCT
(thrombocrit) is an analogue of hematocrit, expressed as a percentage and indicates the proportion of platelets in whole blood.
An increased level of platelets and a change in platelet indices in one direction or another may indicate the presence of a rather serious pathology: myeloproliferative diseases, inflammatory processes of an infectious nature localized in various organs, as well as the development of a malignant neoplasm. Meanwhile, the number of platelets can increase: physical activity, childbirth, surgical interventions.
A decrease in the content of these cells is observed in autoimmune processes, thrombocytopenic purpura, atherosclerosis, angiopathy, infections, and massive transfusions. A slight drop in platelet levels is observed before menstruation and during pregnancy, but a decrease in their number to 140.0 x 109/l and below should already be a cause for concern.