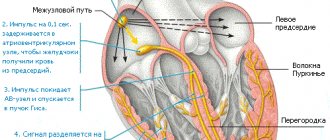
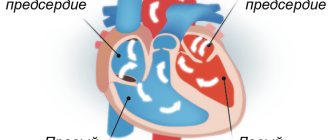
Dextrocardia is a congenital anomaly that involves the location of the heart on the right side. This feature is extremely rare. With this disorder, the main vital functions of the cardiovascular system are not affected.
An ultrasound diagnostician can detect such a deviation even during the intrauterine development of the embryo. The anomaly occurs due to pathology of the heart tube in the fetus, which occurs in the first months of pregnancy. It bends to the right, but this in no way affects the overall development of the cardiovascular system. People with a mirror heart are not sick, and if dextrocardia is not accompanied by functional pathologies, then this anomaly remains only a feature that requires observation by a doctor.
The etiology of displacement of the heart tube to the right side during intrauterine development of the fetus is unclear, and therefore the disorder cannot be prevented. In very rare cases, a child is born with a mirror arrangement of all organs.
Reasons for originality
Until now, the reasons why “mirroring” of human organs occurs are not precisely known. But doctors have a number of theories about this. For example, some doctors are sure that twins first developed in the womb, but then they “merged” into one fetus. And it turns out that a person gets it for two. True, this version is often called unconvincing.
Article on the topic Congenital heart disease in children - are genetics and ecology to blame?
The second scenario is that changes occur under the influence of a woman’s hormonal fluctuations in the early stages of pregnancy. For example, the catalyst may be severe stress experienced by the expectant mother, as a result of which there was a rapid surge of hormones, and the organs were out of place.
There are also those experts who believe that the mirror arrangement of organs is caused by infectious diseases suffered by the mother. Ecology and heredity are also blamed.
Mitral valve prolapse
Prolapse refers to an anatomical defect in the mitral heart valve. It is located between the left ventricle and the atrium. When the atrium contracts, it opens, which ensures the free flow of blood into the ventricle - and further, through the general blood flow. If a serious pathology of the mitral valve develops, its leaflets “bend”. In the worst case, the blood partially remains in the left atrium, which is fraught with unpleasant symptoms:
- heart pain;
- dizziness and shortness of breath;
- fainting;
- interruptions in heart function.
Typically, such symptoms are the exception to the rule, and minor mitral valve prolapse does not pose a threat to the life and health of the child. Severe prolapse is dangerous. It is manifested by severe deflection of the valves and more serious disturbances of cardiac activity (in the second and third degrees).
How to recognize
If there are no additional serious deviations in the state of human health - no external manifestations that the organs are located incorrectly, this may not be visible. The only thing that doctors say is that such children immediately experience bluish skin after birth. In addition, due to the transposition of internal organs, the baby may periodically choke, eat poorly and slowly gain weight. In all other cases, the child will develop like any other, without showing any characteristics. Moreover, often they do not even need surgical correction of the organ’s location.
We'll fix everything! What to do if your baby is born with a heart defect
More details
What does ultrasound reveal?
Our clinic uses modern 4D equipment with Doppler mode. With its help, you can obtain an image of 3 main vessels - the superior vena cava, the pulmonary trunk and the ascending aorta. During the examination, not only the location of the vessels is revealed, but also their diameter and other parameters.
The following fetal pathologies will be visible on the monitor screen:
- A decrease in the diameter of the aorta with expansion of the pulmonary trunk can indicate hypoplasia (underdevelopment) of the left parts of the baby’s heart, which are responsible for the onset of blood circulation;
- A decrease in the size of the pulmonary artery trunk while maintaining normal diameters of the aorta and superior vena cava indicates stenosis (narrowing) of the pulmonary artery. In the fetus, only pronounced forms are detected;
- The small diameter of the aorta with a normal 4-chamber structure of the heart is a consequence of coarctation of the aorta (narrowing of the aorta of the heart in a certain segment);
- Visualization of 2 vessels instead of 3 may be a consequence of the connection of the vessels into a common arterial trunk;
- Displacement of the aorta forward or to the right of the pulmonary artery is observed during transposition of the great vessels;
- The diameter of the aorta is expanded, but the diameter of the pulmonary artery is narrowed, and the aorta is displaced forward. This may be tetralogy of Fallot (a very severe combined cardiac anomaly). The problem includes stenosis or hypertrophy of the right ventricular outflow tract, ventricular septal defect, and dextroposition of the aorta (outflow to the right side). Diagnosis of the fetus is extremely difficult, so the Doppler mode comes to the rescue, helping to visualize the flow of blood into the aorta from both ventricles;
- Hypoplasia (underdevelopment) of the right chambers of the heart is determined by a decrease in their size relative to the left chambers. This pathology is usually accompanied by dysplasia (sagging or bulging) of the mitral valve;
- The common atrioventricular canal is seen as a cardiac septal defect with splitting of the atrioventricular valve;
- Hypoplastic syndrome of the left heart is manifested in the form of underdevelopment of the ventricle and mitral and aortic valves;
- A single ventricle is also not normal, because there should be two of them and they are clearly visible in a four-chamber section;
- When the tricuspid valve is underdeveloped, blood from the right atrium does not enter the left atrium, which is clearly visible during Doppler examination;
- From the 2nd trimester, endocardial fibroelastosis is visualized as thickening of the myocardium and worsening of its contraction;
- Underdevelopment of the myocardium of one of the ventricles (Uhl's anomaly) is noticeable in the 2nd trimester.
What problems arise
A person whose organs are mirrored will feel the symptoms of common diseases differently, which naturally complicates the work of doctors. So, for example, when appendicitis develops, all the characteristic signs will be felt, but not on the right, but on the left, or even practically not felt at all, since the appendix is often located slightly posteriorly. If the spleen hurts, the doctor, without additional research, can attribute such manifestations to the liver or gall bladder. As a result, the wrong treatment will be prescribed.
The issues of transplantology in patients with mirror placement of organs stand apart. After all, donors, as a rule, are people with the usual variant of internal development. Replacing an organ in the presence of a reverse arrangement is a rather complex process and requires special qualifications and experience from the doctor, since it is necessary to correctly position the vessels so that they do not reject the organ and take root well.
Article on the topic
Surgery in the womb: doctors operated on the heart of an unborn child
Pain or heaviness in the right hypochondrium
Hepatitis
Jaundice
Vomit
46707 05 April
IMPORTANT!
The information in this section cannot be used for self-diagnosis and self-treatment.
In case of pain or other exacerbation of the disease, diagnostic tests should be prescribed only by the attending physician. To make a diagnosis and properly prescribe treatment, you should contact your doctor. Pain or heaviness in the right hypochondrium: causes of occurrence, what diseases it occurs with, diagnosis and treatment methods.
Definition
The right hypochondrium is one of nine areas into which the anterior abdominal wall is conventionally divided. This area belongs to the so-called “upper floor” of the abdominal cavity.
In the right hypochondrium there are the liver, gallbladder, hepatic angle of the colon, and swollen loops of the small intestine can also be projected into this area. The organs listed above belong to the digestive system.
The liver is a parenchymal (spongy) organ with a very good blood supply. The outside of the liver is covered with a capsule in which nerve endings are located. The liver is involved in the metabolism of proteins, fats, carbohydrates, vitamins, and plays a vital role in detoxification of the body.
Harmful substances that enter the liver are subjected to “chemical” processing, which makes them less toxic to the body and promotes faster elimination through the gastrointestinal tract and urine.
In addition, liver cells produce bile necessary for digesting food, primarily fats. Bile enters the gallbladder, located on the lower surface of the liver, where bile accumulates, which is released from it into the duodenum during the next meal.
From above, the liver is adjacent to the diaphragm - a kind of muscular partition between the abdominal and thoracic cavities. From below, from the side of the abdominal cavity, the diaphragm is lined with peritoneum (which covers the entire abdominal cavity and organs located in it from the inside), and from above, from the side of the lungs, by the pleura, which lines the pleural cavity from the inside and covers the lungs from the outside. Both the pleura and peritoneum have good innervation, which is important to know to understand the causes of pain and heaviness in the right hypochondrium. The peritoneum also covers the gallbladder and intestinal loops.
Types of pain or heaviness in the right hypochondrium
The pain in the right hypochondrium can be acute, sometimes “dagger-like”, which makes you think about a serious illness. This pain is characteristic of hepatic colic and is often accompanied by nausea, vomiting, increased sweating, increased heart rate and a drop in blood pressure.
In chronic diseases and the gradual development of acute diseases, the pain is often dull, bursting in nature, or is described by the patient as “heaviness, discomfort” in the area of the right hypochondrium.
Pain syndrome can be spontaneous, or it can be provoked by food intake, alcohol, physical activity, change in body position, etc.
Possible causes of pain or heaviness in the right hypochondrium
There is only one mechanism for the development of pain: stimulation of pain receptors. As mentioned above, the peritoneum has good innervation. Also, a large number of nerve endings are localized in the wall of hollow organs (intestines, gall bladder). Therefore, inflammatory processes in these organs naturally manifest themselves as pain.
Pain also occurs when the liver capsule is stretched. This can occur due to an increase in the volume of the organ (which in most cases is associated with tissue swelling), due to the accumulation of any fluid (most often blood) under the capsule (with a traumatic rupture of the liver), or damage to the capsule.
Unpleasant sensations in the area of the right hypochondrium are caused by excessive distension of the intestinal loops by intestinal contents or gases. In addition, since the organs of the chest are located close to the right hypochondrium, in case of development of pleurisy (inflammation of the pleura), the pain syndrome can also be localized in the right hypochondrium and imitate diseases of the abdominal organs.
Diseases that cause pain or heaviness in the right hypochondrium
Among acute diseases accompanied by pain in the right hypochondrium, it is worth mentioning first of all those that require emergency surgical intervention.
These include
acute calculous cholecystitis
and
hepatic colic
.
Both conditions are a consequence of cholelithiasis
. Inflammation of the gallbladder (cholecystitis) develops against the background of an already advanced process of stone formation or, conversely, is the cause of the formation of stones. With hepatic colic, a calculus (stone) becomes wedged into narrow segments of the biliary tract, which is accompanied by severe pain, impaired outflow of bile, and in more severe cases – jaundice (yellowing of the sclera and skin).
Other diseases of the biliary tract, such as
biliary dyskinesia
,
chronic cholecystitis
, cause recurrent pain in the right hypochondrium, usually associated with an error in diet.
Another disease classified as an “acute abdomen” that can cause pain in the right hypochondrium is appendicitis.
(inflammation of the appendix).
Despite the fact that the classic position of the appendix corresponds to the right iliac region, an abnormal position of the appendix in the right hypochondrium is quite common, especially in children.
Overdistension of intestinal loops can develop as part of
intestinal obstruction
.
Swelling of the liver tissue is characteristic of hepatitis (inflammation of the liver parenchyma). Hepatitis can have a variety of origins: viral hepatitis A, B, C, etc., autoimmune, toxic, incl. alcoholic. These diseases are usually accompanied by pain, as well as weakness, nausea and vomiting, yellowing of the skin and sclera, change in the color of urine and feces.
Subcapsular hematomas of the liver (accumulation of blood between the liver tissue and its capsule), as well as ruptures of the liver capsule, are usually traumatic in nature.
Among the diseases of the chest that can cause pain in the right hypochondrium, it is worth mentioning pleuropneumonia (inflammation of the lung tissue and pleura), heart failure, intercostal neuralgia and herpes zoster. The latter is characterized by the appearance of blistering-type skin rashes, which are preceded by severe pain.
Which doctors should you contact if you experience pain or heaviness in the right hypochondrium?
If sudden, progressively increasing pain appears in the area of the right hypochondrium, you should contact a doctor to exclude acute surgical pathology. If the pain is not acute, the examination can begin at or. If necessary, the patient can get advice from a hepatologist (a specialist in liver diseases) and other specialized specialists.
Diagnostics and examinations for pain or heaviness in the right hypochondrium
After a detailed survey and comprehensive clinical examination, the doctor, as a rule, needs laboratory and instrumental confirmation of the diagnosis. For this purpose, the following studies are used:
- A clinical blood test with determination of the leukocyte formula, based on the results of which one can suspect the presence of an inflammatory process in the body and determine its severity.
Myths and speculation
Naturally, like everything unusual, people with “incorrectly” located organs cause a lot of speculation and gossip. For example, they are often credited with psychic abilities and the ability to read minds.
In addition, it is believed that such babies will get sick more. In fact, there is no scientific basis for this. It’s just that such people must have a note about their particularity in their medical record, and also exercise certain caution when actively engaging in physical education.