Heart rhythm disturbances are a group of cardiovascular diseases that doctors call the most common. Therefore, today we will talk about the factors that provoke such heart problems and ways to combat them. We will also get acquainted with the main treatment methods.
Why is the heart rhythm disrupted?
The normal heart rate is between 70-80 beats per minute at rest. It can increase with physical activity, various emotional experiences, exposure to medications, and alcohol.
A slowdown in heart rate is observed with general weakness, severe fatigue, in old age, in athletes or during sleep. In addition, various types of disorders can be caused by side effects of medications or diseases of internal organs (for example, pathologies of the nervous system).
Also, arrhythmias can occur due to cardiovascular diseases, among which the main role is played by:
- myocardial damage caused by atherosclerosis of the coronary arteries, inflammatory processes, injuries and other factors;
- lesions of the sinus node in the heart caused by congenital or acquired factors;
- tumors of the heart muscle;
- pericardial lesions. We are talking about pericarditis, adhesions, metastases and other problems;
- disturbed balance of electrolytes (deficiency of Mg, K, Ca and Na);
- catheterization, angiography, surgical interventions that irritate the heart.
In addition, the problem in question can also occur in completely healthy people. For example, the loss of one or more beats - in other words, extrasystole - happens to any person from time to time.
Such cardiac failures do not cause inconvenience and are not accompanied by a risk to life and health, unless they become permanent.
First aid for an arrhythmia attack
Defibrillators are devices that restart blocked heart muscles by delivering electricity to the chest. Defibrillators are effective in stopping the heart from ventricular fibrillation, but because ventricular fibrillation can be fatal in less than 4 minutes, they should be used as soon as possible. Most defibrillators are external devices, but there are now automated implantable cardioverter/defibrillators (AICDs). These devices can be as large as pacemakers. They can detect dangerous fibrillation and return the heart to normal before any damage is done.
Article sources:
- "New Theory of Arrhythmia" clarifies the causes of arrhythmia. Ermoshkin V.I. Educational bulletin “Consciousness”, 2015. p. 22-30
- Innovations in the treatment of cardiac arrhythmia. Zh.A. Arzykulov, A.A. Omarov, B.B. Kituev, F.A. Tursunova, A.A. Yeshtay, N.G. Pavlova. Bulletin of Surgery of Kazakhstan, 2012. p. 4-5
- On the issue of classification of cardiac arrhythmias. Batyanov I.S., Batyanova E.I. Cardiovascular therapy and prevention, 2005
- A look from the inside focuses on a patient with arrhythmia. Boqueria O.L. Annals of Arrhythmology, 2014. p. 196-199
- Cardiac arrhythmias from the point of view of their dimension. Ubiennykh A.G. Measurement. Monitoring. Control. Control, 2021. p. 70-76
- Epidemiology of arrhythmias (review of literature data). Zatonskaya E.V., Matyushin G.V., Gogolashvili N.G., Novgorodtseva N.N. Siberian Medical Review, 2021. p. 5-16
What is arrhythmia?
There are several types of the problem, each of which has its own characteristics and symptoms. Tachycardia is an increase in the number of heart contractions over 90 beats per minute. It can occur in various parts of the heart, therefore it is divided into ventricular and supraventricular.
Bradycardia is a decrease in heart rate below 60 beats. Pathology can occur with heart blockades, as well as weakness of the sinus node. Paroxysmal rhythm disturbance is a problem manifested by a sharp increase in heart rate up to 200 beats. At the same time, the person is outwardly healthy. A person’s condition at this moment can vary from mild weakness and general malaise to loss of consciousness. In most cases, the attack goes away on its own within a few minutes, but with severe paroxysms, emergency medical attention is required.
Extrasystole is a condition in which the normal rhythm of the heart is interrupted by a single premature contraction of the myocardium. Subjectively, it feels like a short interruption of the heart. Each person experiences an average of one and a half thousand extrasystoles per day. If they do not cause discomfort, treatment is not required.
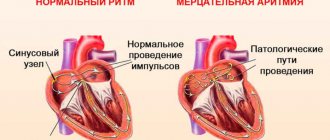
Atrial fibrillation - with this disease, one of the phases of the normal heart rhythm disappears: atrial contraction. As a result, instead of a full contraction, the muscle fibers only twitch - flicker. Because of this, the functioning of the ventricles of the heart is disrupted: they begin to contract irregularly. In severe cases, atrial fibrillation can develop into atrial fibrillation, a condition that threatens a person’s life and requires immediate medical attention. Any disturbances in heart rhythm should not be ignored; if they appear, you should visit a cardiologist as soon as possible.
The main reasons for the development of MA are:
1. diseases of the cardiovascular system:
- hypertonic disease
- heart defects
- previous heart attacks
- previous myocarditis (inflammatory heart disease)
- toxic (alcoholic) cardiomyopathy
2. diseases of the bronchopulmonary system:
- bronchial asthma
- chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
- pneumonia
3. diseases of the gastrointestinal tract:
- peptic ulcer
- erosive gastroduodenitis
- HP infection (Helicobacter pylori gastroduodenitis)
- cholelithiasis
- chronic pancreatitis
- inflammatory bowel diseases
4.endocrine disorders:
- thyroid disease (thyrotoxicosis)
- diabetes
5. infections (ARVI, influenza, sepsis)
6. bad habits:
- alcohol abuse
- drug use
- heavy smoking
7.violation of the work and rest regime (work without days off and holidays, frequent business trips)
8.exacerbation of any concomitant pathology
9.oncological diseases, especially after courses of radiation and chemotherapy
10. combination of factors
AF can be detected when recording an electrocardiogram, when measuring blood pressure (the “arrhythmia” icon flashes on the tonometer screen), or the patient himself feels an unusual heartbeat.
If AF is detected, the patient should immediately contact an arrhythmologist or cardiologist. He will be offered an outpatient examination or, if necessary, hospitalization.
The optimal time to seek medical help is within 48 hours from the moment of the development of MA, since in this case it is possible to restore the rhythm as quickly, effectively and safely as possible.
In the latter case, artificial restoration of sinus rhythm with the help of drugs is called drug cardioversion. In the case when the heart rhythm is restored using an electric current (defibrillator), we talk about electrical cardioversion
One way or another, any form of this disease needs treatment. The global cardiological community has long developed a strategy for the management of such patients and identified the main goals of treating patients with atrial fibrillation.
How do arrhythmias manifest?
Different types of arrhythmias have their own manifestations. Only extrasystoles can be asymptomatic. With tachycardia, a person complains of rapid heartbeat, discomfort or chest pain, dizziness, sudden general weakness and fatigue, and shortness of breath. Also, with this pathology, blood pressure often decreases, which can cause a person to faint.
Some of these symptoms can also manifest themselves with bradycardia, in particular: dizziness, weakness, chest pain, fainting and fainting conditions. Also, with a decrease in the number of heart contractions, difficulty breathing, short-term visual disturbances, deterioration in concentration and memory, and episodes of confused thinking are observed. They arise due to the fact that the brain experiences oxygen starvation as a result of bradycardia.
The main sign of paroxysmal rhythm disturbance is a sharp deterioration in the condition. The duration of the attack is from two to three minutes to several days. During a paroxysm, a person feels a frequent and strong heartbeat, complains of general weakness, dizziness, tinnitus, sweating, nausea and flatulence.
Atrial fibrillation is accompanied by unreasonable fear (panic attack), and is also manifested by irregular heartbeat, intense sweating, shortness of breath, and severe general weakness. He even reaches the point of fainting. Different arrhythmias are similar in their symptoms. Therefore, making an accurate diagnosis is only possible in a medical institution.
Symptoms
When the heart beats faster than normal, it is called tachycardia . Symptoms and signs of arrhythmia include:
- chest discomfort
- cardiopalmus,
- dizziness,
- sometimes fainting.
When the heart beats slower than normal, it is called bradycardia . It can cause fatigue, dizziness, lightheadedness and fainting as it usually causes low blood pressure.
Almost everyone's heart will flutter from time to time, and it usually doesn't mean anything. More often, symptoms of cardiac arrhythmia occur in men and treatment is not always necessary. But if a person has chest pain, feels weak, or notices that the pulse is irregular, either very fast or very slow for a long period, it is time to see a doctor. Source: Insider's View Focus on the Arrhythmia Patient. Boqueria O.L. Annals of Arrhythmology, 2014. p. 196-199.
Symptoms of this disease may not appear. Arrhythmia can be detected by a specialist during a routine clinical examination: before any of its signs appear. But predominantly, heart rhythm disturbances are characterized by the following symptoms:
- pain in the chest;
- increased feeling of heartbeat;
- accelerated heartbeat;
- slow heartbeat;
- dyspnea;
- loss of consciousness or fainting.
In most cases, in a person who has a certain type of arrhythmia, such arrhythmia occurs repeatedly.
Some types of arrhythmias are initially asymptomatic or with few symptoms. Other types of arrhythmias, on the contrary, manifest themselves in pronounced symptoms, but do not have serious consequences. Typically, the nature and severity of the underlying heart disease that causes the arrhythmia are more important than the arrhythmia itself.
Diagnosis of arrhythmias
Diagnostic techniques: general (history collection, examination) and specific (non-invasive and invasive) techniques. Non-invasive research methods include:
- ECG;
- ergometry (physical stress tests);
- surface ECG mapping;
- echocardiography;
- magnetic resonance imaging.
Invasive diagnostics is an electrophysiological study in which special sensors are inserted into the heart cavity, which record the frequency and regularity of contractions of different parts of the myocardium.
Diagnostics
The stethoscope is still a valuable tool for identifying arrhythmias, but there are modern tests that can pinpoint the problem and signs of cardiac arrhythmias in women or men. An electrocardiogram (ECG) displays a graph of the heart's electrical activity using small electrodes attached to the chest. The curve on these graphs shows the type of arrhythmia. Since the arrhythmia may not occur in the hospital, there are portable ECGs that the patient wears at home. Some are turned on continuously over a period of time (called a Holter monitor), while others turn on when a person senses an arrhythmia (called an event monitor or loop recorder).
Certain arrhythmias may be associated with exercise, so patients may be asked to walk on a treadmill or ride an exercise bike while connected to an ECG machine.
Electrophysiological study (EPS) is a more complex test. Thin tubes are inserted into a blood vessel in the leg and directed toward the heart. They hold electrodes that can find muscle tissue that may be causing abnormal electrical activity.
What is arrhythmia?
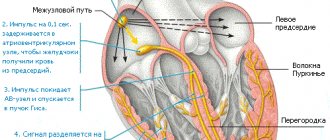
The heart works like a pump and ensures continuous blood circulation.
This is necessary to deliver blood enriched with oxygen and nutrients to every cell of the body. In the right atrium of the heart there is the sinus node (SU), the “commander-in-chief” of the heart rhythm. The sinus node generates electrical impulses, under the influence of which the right and left atria first contract, then the right and left ventricles. Other parts of the myocardium can also generate electrical impulses, but in a healthy heart they are suppressed by the sinus node and do not disturb the heart rhythm.
The correct heart rhythm is considered to be sinus rhythm, in which the heart rate (heart rate) is from 60 to 80 beats/min. An arrhythmia is any heart rhythm that differs from normal sinus rhythm.
Heart rate is determined in a state of physical and emotional rest, since this indicator may increase during sports or excitement. It should also be noted that the normal heart rate is a relative value and depends on the individual characteristics of a person. For example, a rapid heart rate can be observed during pregnancy, a slow heart rate in athletes.
Complications of arrhythmia
.
A number of heart rhythm disorders can increase the risk of developing conditions and diseases such as:
- Stroke
. When the atria fibrillate, they are unable to adequately pump blood to the ventricles. Slowing blood flow in the atria leads to the formation of clots. If a small piece breaks off from the clot, it can enter the bloodstream, spread throughout the body and clog the cerebral arteries, causing the development of ischemic stroke, i.e. damage or death of part of the brain, and sometimes leads to death. - Congestive heart failure
. Due to a prolonged period of bradycardia or tachycardia, such as atrial fibrillation, the heart may not pump efficiently. By controlling your heart rate, you can improve left ventricular contractility and reduce signs of heart failure.
How to get treatment at the Scientific Center named after.
A.N. Bakuleva? Online consultations
How to stop arrhythmia
Some types of arrhythmias (ventricular and atrial extrasystole) may not be treated at all if the number of extrasystoles per day is small. But in most cases, arrhythmia still needs to be treated. For this purpose, there are special antiarrhythmic drugs that a cardiologist can select for you. In case of severe cases of some types of arrhythmias, it will be necessary to prescribe droppers or treatment with electric current - electric pulse therapy. In the most difficult cases, surgical intervention is performed. Folk remedies for arrhythmia should not be used; treatment should be trusted exclusively to a cardiologist. It is very important to monitor the dynamics of the disease and adjust therapy in a timely manner.
Possible complications and prognosis
First of all, the prognosis of the disease depends on the type of arrhythmia. If the rhythm disturbance is not associated with organic damage to the heart, then it may not cause any particular harm to health. For example, such arrhythmias include supraventricular extrasystoles.
However, there are also very dangerous types of arrhythmias. One of them is atrial fibrillation, which can cause myocardial infarction and heart failure.
How to treat cardiac arrhythmia
To determine the treatment method, it is necessary to establish the cause of the disease. The selection of therapy and medications is carried out under systematic ECG control. Depending on the degree of arrhythmia, the doctor may prescribe a conservative treatment method using medications or cardiac surgery.
Only highly qualified doctors will be able to determine the diagnosis and prescribe the correct surgical treatment. Contact the Federal Scientific and Clinical Center FMBA, our specialists will select the treatment method that is suitable for you:
- electrocardiostimulation;
- implantation of a cardioverter-defibrillator;
- radiofrequency ablation.
According to the observations of doctors, heart diseases are actively growing younger; it is often possible to meet a young man or girl with various heart diseases. What can we say about the older generation, for whom arrhythmia is a common occurrence. But this symptom cannot be neglected. Arrhythmia not only signals serious malfunctions in the body, it can lead to short-term or complete cardiac arrest. Arrhythmia is a disturbance in the functioning of the heart muscle. With arrhythmia, the heart beats differently; there is no strict rhythm or specific frequency. Normally, a healthy heart beats in a certain sequence, the time interval between heartbeats is observed. If your heart beats chaotically, it means you have an arrhythmia.
First aid for arrhythmia at home
Attacks of unstable heart function are characterized by suddenness. The patient may complain of general weakness, nausea, rapid heartbeat and dizziness.
If primary symptomatic manifestations appear, you must call an ambulance. A number of step-by-step actions will help relieve an attack of arrhythmia at home:
- help the victim find a position that is comfortable for him - half sitting or lying down; if the patient experiences severe shortness of breath, he is allowed to half sit - in a horizontal position his condition will worsen significantly;
- ensure a flow of fresh air - open the windows or put them in for ventilation;
- remove disturbing clothes, unbutton your collar, loosen your tie;
- try to persuade the patient to take one of the sedatives - Valocordin, Corvalol, tincture of valerian root or motherwort;
- ask the victim to take a series of deep breaths, and after a pause - slow exhalations;
- at the same time, try to calm the patient down - excessive nervousness will provoke a sharp release of adrenaline, the hormone responsible for accelerating contractions of the heart muscle;
- try to make him vomit - to ease his general well-being.
How to prevent arrhythmia attacks
If you have experienced one attack, there is no need to wait for the next one - consult a doctor immediately! You will be prescribed diagnostic measures that will help identify the cause of the arrhythmia. Often these are heart diseases, although sometimes arrhythmia can be a normal variant. Heartbeat disturbances can occur due to strong experiences, stress, fear, and anxiety. Such arrhythmia usually goes away quickly on its own or while taking mild sedatives.
In addition to adequate treatment, lifestyle changes can help prevent arrhythmia attacks. You need to give up alcohol and cigarettes - these toxic poisons impair the normal functioning of the heart. It is important to remove stress and strong feelings from life. Moderate physical activity will help improve heart function. Walking in the fresh air is very beneficial.
Often an attack of arrhythmia occurs due to a deficiency of vitamins such as calcium, magnesium, and potassium. If you do not take cardio medications that contain them, you need to eat honey, beets, corn, seeds, potatoes, parsley, and cabbage. These products are high in heart vitamins. It is very important to exclude animal fats and, in general, all fatty and salty foods that contribute to the development of atherosclerosis and the formation of blood clots. If you have frequent attacks of arrhythmia, you should stop drinking coffee and chocolate - caffeine increases your heart rate.
There are several ways to treat arrhythmia. The choice of method is made by a cardiologist after carefully studying the results of the studies, but first of all the patient should consult a general practitioner.
Causes of arrhythmia
Unstable heartbeat in most cases is characteristic of people with cardiovascular diseases. Arrhythmia can be provoked by a previous heart attack or other cardiac pathology.
The most common causes of cardiac arrhythmia:
- inflammation of the heart muscle (myocarditis);
- myocardial ischemia, angina pectoris and atherosclerosis;
- defective functioning of the heart valves;
- prolonged stress, increased anxiety;
- autoimmune diseases, etc.
There are a number of other factors that increase the risk of developing chronic arrhythmia. Timely prevention and diagnosis can eliminate pathology at an early stage and avoid surgery.