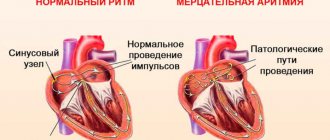
Arrhythmia is a violation of cardiac conduction, in which there is a change in the frequency, rhythm and regularity of contractions of the heart muscle. The heart may beat faster or, conversely, slower, or simply irregular.
Arrhythmia can be provoked by:
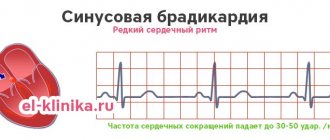
- disturbances in the formation of an electrical impulse in the sinus node (sinus tachycardia, bradycardia);
- violations of intracardiac impulse conduction. Occur as a result of a decrease or cessation of impulse transmission through the conduction system (blockade, premature excitation of the ventricles of the heart);
- combined rhythm disturbances. Combine disturbances in the conduction of electrical impulses and heartbeat rhythm.
Causes of cardiac arrhythmia
The causes can be divided into several blocks:
Extracardiac causes - not related to the heart itself:
- disorders of the thyroid gland;
- disruption of the cardiovascular and/or respiratory system;
- renal and/or liver failure;
- increased intracranial pressure;
- bad habits.
Intracardiac – organic or functional heart disorders:
- associated with the development of the conduction system of the heart
- SVC syndrome, nodular,
- atrial and ventricular extrasystole,
- some types of atrial and ventricular tachycardias.
atrioventricular tachycardia,
- heart failure;
myocardial infarction;
Physiological:
- heavy and prolonged physical activity;
- emotional overstrain.
Causes of ischemic disease. Warning the heart
If we consider organic lesions of the cardiovascular system, arrhythmias most often occur with ischemic heart disease, myocarditis, cardiomyopathies, heart defects, pathologies of large vessels (pulmonary embolism, aortic aneurysms), hypertension, pericarditis and heart tumors. Arrhythmias can also be observed in endocrinopathies (pheochromocytoma, thyrotoxicosis), drug intoxication (glycosides, catecholamines), acute infectious diseases, anemia, in violation of the body's electrolyte balance (especially potassium, calcium and magnesium) and other pathological conditions.
Sometimes heart rhythm disturbances also occur under the influence of exogenous factors: excessive consumption of coffee, alcohol, tobacco. Some types of arrhythmias can also develop in healthy people in response to physical activity or nervous tension.
The arrhythmic variant of IHD is spoken of only in cases where cardiac arrhythmias are the only symptom of this disease. The diagnosis of coronary artery disease remains presumptive until ECG, Holter monitoring and coronary angiography are performed, which reveal various heart lesions. However, in most patients, arrhythmias are combined with other clinical forms of IHD. Rhythm disturbances are also a common symptom of atherosclerotic cardiosclerosis, especially with angina pectoris or heart failure. However, despite the many reasons that can cause rhythm disturbances, all arrhythmias can be divided into three main groups: those associated with impaired impulse formation, those associated with impaired impulse conduction, and combined arrhythmias. Table 1 presents the classification of arrhythmias depending on the mechanism of their occurrence.
Table 1.
Classification of arrhythmias depending on the mechanism of occurrence
| Mechanism of occurrence | Impulse formation disorders | Impulse conduction disorders | Combined disorders |
| Types of rhythm disturbances | Sinus tachy- and bradyarrhythmias, sick sinus syndrome, ectopic rhythms (non-paroxysmal tachycardias), extrasystoles, ventricular tachycardias, fibrillation and flutter of the atria and ventricles | Blockades: sinoatrial, intraatrial, atrioventricular; premature ventricular excitation syndrome | Atrioventricular dissociations, ectopic rhythms with block, parasystoles* |
* Rarely encountered
The diagnosis of “cardiac arrhythmia” is always based on clinical and electrocardiographic data, and treatment includes therapy for the underlying disease and antiarrhythmic measures themselves.
Symptoms of arrhythmia
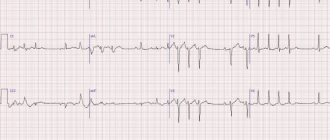
The main symptom of arrhythmia is a change in the frequency or rhythm of the pulse, which is accompanied by a change in the patient’s well-being. However, a number of arrhythmias are hidden and may not be felt by the patient. Such arrhythmias are detected during preventive examinations or during diagnostic studies for another disease. The main method for diagnosing arrhythmia is an ECG.
There are “classic” manifestations of this disease, these include:
- heartbeat;
- heart sinking;
- feeling of “heart somersault” in the chest
- discomfort in the chest area;
- weakness;
- suffocation;
- dizziness;
- loss of consciousness.
A number of diseases can cause quite serious complications. They can lead to the development of life-threatening arrhythmias (ventricular fibrillation and flutter), which threatens an unfavorable prognosis for the patient. If you notice any symptoms, contact a specialist immediately. At the Cardiology Center of the Federal Scientific and Clinical Center of the Federal Medical and Biological Agency, doctors with many years of experience will help identify the cause of your symptoms and conduct a full examination of your heart. The examination program of our center can be found here
How to treat to stabilize the heart
The easiest way to restore the pulse rhythm is at a reduced frequency - bradycardia is corrected by drinking a cup of strong coffee or applying mustard plaster to the chest area. But it is strictly forbidden to use mustard plaster on the area of the anatomical location of the heart - this is fraught with a sharp increase in heart rate and ventricular fibrillation.
An increase in heart rate can be adjusted independently only if it happened spontaneously and literally for the first time. You can stop an attack of arrhythmia:
- tincture of peony, valerian or motherwort;
- breathing exercises;
- neck massage on both sides in the area where the carotid arteries are located;
- by relaxing in a lying position with your eyes closed.
In case of repeated attacks of arrhythmia, regular occurrences, it is necessary to undergo examination by a cardiologist and receive medication prescriptions. Most often, doctors recommend taking Bisoprolol or Cordarone as a course, but these drugs are strictly contraindicated for self-administration.
There are different types of arrhythmia, not all of them are dangerous to human health and life. Bradycardia is considered the most harmless, and tachycardia and atrial flutter must be monitored by specialists and treated.
Diagnosis of arrhythmia
Even a healthy person can experience arrhythmia. To prevent the disease, it is necessary to undergo an annual examination and check the functioning of the cardiovascular system, especially for older people.
At the initial appointment with a physician or cardiologist, the patient undergoes a physical examination. The doctor listens to the heart, examines the pulse, asks for complaints, studies the medical record and pays attention to what medications are prescribed.
After collecting anamnesis, the specialist prescribes an instrumental examination - ECG, ultrasound of the heart.
The most accurate method for diagnosing arrhythmia is considered to be Holter monitoring - an electrocardiographic study that is carried out throughout the day. In this case, the patient must record all his actions hourly. This is necessary to identify external influences that affected changes in heartbeat (physical activity, emotional stress). When interpreting the ECG, doctors will be able to assess the heart rhythm, its frequency and regularity. Afterwards the conductivity of electrical impulses is assessed.
Also used in diagnosis:
- treadmill test (step test) – conducting an ECG with physical activity. Used in the absence of constant attacks in order to correct the course of treatment;
- tilt test (passive orthostatic test) – is carried out on a special rotary table in the presence of doctors in compliance with full safety precautions. The patient is placed on the table in a horizontal position, pulse and blood pressure are measured. Then the table is raised up at an angle of 60 degrees and the patient’s pulse and blood pressure continue to be monitored;
- invasive examination - surgical examination of the heart, during which special radiopaque catheters (probes) are inserted into the blood vessels;
- transesophageal electrophysiological study (TEPS) - performed through the esophagus to electrically stimulate the heart. A sterile electrode is inserted through the nose or nasopharynx to a depth of 40 cm, to the location of the esophagus closest to the heart. Weak electrical impulses begin to be sent.
The Cardiology Center of the Federal Scientific and Clinical Center of the Federal Medical and Biological Agency has a therapeutic department where they will help you determine the type of heart test and prescribe medication.
How many beats per minute should the heart beat normally?
A slow heart rate is a good sign. This indicates the ability of the heart to pump the required amount of blood in the minimum number of contractions. This also happens to a sleeping person, who consumes less nutrients and oxygen during sleep. With each passing year, the heart wears out, the muscles weaken, and the pulse increases. Usually its indicator corresponds to the person’s age. For example, upon reaching eighty years of age, a pulse corresponding to eighty beats per minute is considered normal.
Research into heart tonality using computer technology has enabled scientists to delve deeper into the secrets of the heart. It was found that the heartbeat of a healthy person is either accelerated or with some delay, while the heart rate of a patient with a pre-infarction condition is ideal. This discovery makes it possible to identify predisposition to cardiovascular diseases at earlier stages.
In infants, the pulse is twice as high as the pulse of an adult and is up to 140 beats per minute. But already during the first year of life, the pulse gradually decreases and by the age of six it is equal to one hundred beats per minute. By the age of 18-20 years, the pulse levels out and acquires its normal state - from 60 to 80 beats per minute.
How to treat cardiac arrhythmia
To determine the treatment method, it is necessary to establish the cause of the disease. The selection of therapy and medications is carried out under systematic ECG control. Depending on the degree of arrhythmia, the doctor may prescribe a conservative treatment method using medications or cardiac surgery.
Only highly qualified doctors will be able to determine the diagnosis and prescribe the correct surgical treatment. Contact the Federal Scientific and Clinical Center FMBA, our specialists will select the treatment method that is suitable for you:
- electrocardiostimulation;
- implantation of a cardioverter-defibrillator;
- radiofrequency ablation.
Measurement Rules
You can measure the pulse rate and detect arrhythmia using an ECG or tonometer, but the easiest way to do this is as follows:
- Find the point on the inside of the wrist where the pulse beats are especially pronounced.
- Press the 2nd and 3rd fingers of your free hand to this place, wrap your thumb around the hand.
- Count the number of beats in 60 seconds.
Measurements must be taken taking into account the following nuances:
- After eating, at least an hour and a half should pass;
- the person must be in a sitting or lying position;
- you need to relax and restore your breathing;
- any physical activity (even walking) is excluded 30-40 minutes before measurements.
Causes of heart rhythm disturbances
As a rule, arrhythmia is not the main pathology, but a consequence of other diseases. Causes of heart rhythm disturbances may include:
- sleep apnea syndrome is a disorder of the respiratory system, which is accompanied by temporary cessation of breathing at night, followed by the release of adrenaline and an increase in heart rate;
- arterial hypertension - syndrome of high blood pressure;
- coronary heart disease - a discrepancy between the myocardial need for oxygen and its delivery;
- heart failure - weakening of the pumping function of the heart;
- congenital and acquired heart defects.
- cardiomyopathies - pathologies of the myocardium associated with its mechanical or electrical dysfunction;
- myocarditis - inflammation of the heart muscle;
- myocardial surgery;
- previous heart attack;
- hyperthyroidism - hyperfunction of the thyroid gland;
- lung diseases;
- diabetes;
- infections.
There are arrhythmias that are based on genetic pathologies. For example, the arrhythmia can be caused by congenital long QT syndrome, which leads to ventricular tachycardia.
Risk factors for arrhythmia include:
- physical inactivity or, conversely, excessive physical activity;
- obesity;
- smoking, alcohol abuse;
- chronic lack of sleep;
- hormonal changes in the body. For example, in women, arrhythmia is often diagnosed after the onset of menopause;
- uncontrolled use of drugs that have an arrhythmogenic effect.
Treatment of arrhythmia
Treatment depends on the type and severity of the diagnosis. In some cases it is not required. Treatment is necessary if the disease causes significant symptoms, thereby increasing the risk of complications or development of a more severe form.
For the treatment of tachycardia the following is used:
| Anticoagulants | Antiarrhythmic drugs | Cardioversion | Catheter ablation |
| These drugs are prescribed for atrial fibrillation to prevent blood clots and stroke. | May be prescribed to prevent arrhythmia or restore normal heart rhythm. | It can be done either with an electric current or with medications to restore normal sinus rhythm. | This method is one of the most modern minimally invasive surgical methods aimed at eliminating arrhythmia using special catheters inserted into the heart cavity through punctures in the vessels. |
A pacemaker is used to treat bradycardia. To date, there are no medications that can reliably speed up the heart. If the pulse is too slow or disappears altogether, the device sends electrical impulses that stimulate the heart to work at the required frequency.
It is important to know that some arrhythmias can be dangerous and potentially fatal. The danger is that even in the absence of pronounced clinical manifestations and symptoms, without the necessary treatment, the disease can progress and lead to serious complications. In particular, a complication of atrial fibrillation is a cerebrovascular accident (stroke). Early diagnosis and treatment help reduce the risk of arrhythmia complications.
Average reading time is
6 minutes.