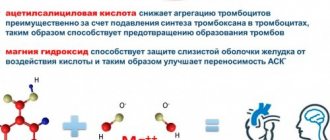
The drugs are similar to each other except that the main active ingredient is acetylsalicylic acid . Cardiomagnyl additionally contains another active component - magnesium hydroxide. Magnesium, which is part of the structure of Cardiomagnyl, ensures the normal functioning of the heart muscle, blood vessels and veins. Cardiomagnyl prevents platelet aggregation, blocking this process. Therefore, taking this drug is most appropriate for the prevention and treatment of thrombosis, heart attacks, and cardiovascular failure. The product is also used for patients at risk: smokers, overweight, elderly patients, diabetics. It contains a special antacid that protects the sensitive gastric mucosa from the negative effects of acid.
Cardio aspirin provides analgesic and antipyretic effects, and Cardiomagnyl prevents platelet aggregation (sticking together). Unlike regular Aspirin, the tablets have a protective coating, which significantly reduces the adverse effect on the gastrointestinal tract.
Comparison of the effectiveness of Aspirin Cardia and Cardiomagnyl
Aspirin Cardia is more effective than Cardiomagnyl - this means that the ability of the drug substance to provide the maximum possible effect is different.
For example, if the therapeutic effect of Aspirin Cardia is more pronounced, then with Cardiomagnyl it is impossible to achieve this effect even in large doses.
Also, the speed of therapy is an indicator of the speed of therapeutic action; Aspirin Cardia and Cardiomagnyl are also different, as is bioavailability - the amount of a drug substance reaching the site of its action in the body. The higher the bioavailability, the less it will be lost during absorption and use by the body.
Comparison of the safety of Aspirin Cardia and Cardiomagnyl
The safety of a drug includes many factors.
At the same time, it is higher for Cardiomagnyl than for Aspirin Cardia. It is important where the drug is metabolized: drugs are excreted from the body either unchanged or in the form of products of their biochemical transformations. Metabolism occurs spontaneously, but most often involves major organs such as the liver, kidneys, lungs, skin, brain and others. When assessing the metabolism of Cardiomagnyl, as well as of Aspirin Cardia, we look at which organ is the metabolizing organ and how critical the effect on it is.
The risk-benefit ratio is when the prescription of a drug is undesirable, but justified under certain conditions and circumstances, with the obligatory observance of caution in use. At the same time, Cardiomagnyl has fewer risks when used than Aspirin Cardia.
Also, when calculating safety, it is taken into account whether only allergic reactions occur or possible dysfunction of the main organs. In other matters, as well as the reversibility of the consequences of using Cardiomagnyl and Aspirin Cardia.
Aspirin? Not so simple!
– Many older people often ask for aspirin at the pharmacy. The drug has been around for over a century and is still being discussed. Why?
– Indeed, humanity has been turning to salicylates for many centuries. Initially, plants containing salicylic acid were intuitively used to treat feverish conditions and joint pain. Then salicylates began to be actively used to treat rheumatism, and they served as the basis for the creation of the drug acetylsalicylic acid - aspirin. However, at the end of the twentieth century, this medicine found a new life: acetylsalicylic acid began to be used in patients with cardiovascular diseases. Aspirin helps prevent many cases of myocardial infarction and stroke.
– Heart attack and stroke: different diseases, but the cause is the same – a blood clot!
– These cardiovascular diseases are complications of atherosclerosis, a pathological process that changes the wall of the artery, leading to the formation of changes on its inner surface and in the underlying tissue, which are called atherosclerotic plaques. They are based on deposits of lipids, cholesterol crystals and overgrown tissue cells of the vessel wall.
Atherosclerotic plaques, or atheromas, usually grow for years, are often found in practically healthy elderly people and sometimes do not cause any clinical symptoms during their gradual growth - unless they lead to a narrowing of the lumen of the artery, preventing blood supply to the heart, brain or other organs. A sharp decrease in the lumen of the vessel can sometimes occur due to hemorrhage inside the plaque, the development of inflammation and its rupture, which entails the formation of a blood clot at this site. This leads to a catastrophic decrease in the supply of oxygen with blood through the vessel supplying blood to the tissues of the organ. The stable course of the disease is disrupted. It is to prevent thrombus formation inside the artery - a key point in the development of an acute disease - that the main effect of aspirin is directed.
– What is aspirin used for and what is a platelet?
– One of the main pharmacological effects of aspirin - preventing the formation of a blood clot - is a consequence of its influence on the excessive activity of platelets that occurs in pathology, accompanied by an increased tendency to thrombus formation. Aspirin in such cases turns out to be an effective remedy.
A platelet is one of the amazing blood cells that normally participates, as its name suggests, in the process of forming a blood clot to stop bleeding when a vessel is damaged. Together with strands of fibrin protein and other blood cells, it forms the basis of a blood clot. In addition, platelets fight microbes found in the bloodstream, are involved in immune processes, and influence the course of inflammation and atherosclerosis. Their membranes contain numerous receptors designed to transmit signals into the cell and create extracellular contacts. Thanks to receptors, a huge number of biochemical transformations occur in our body, the transfer of information from one cell to another is realized, and various processes in the cell are regulated.
Platelets are capable of synthesizing a number of substances. Increased platelet activity can create a threat of thrombus formation in the arterial bed, up to its complete blockage. Acetylsalicylic acid (ASA) in low doses (75–100 mg) can suppress the synthesis of thromboxane A2 and thereby prevent the initiation of platelet activation. As a result of this pharmacological effect of aspirin, the likelihood of developing serious vascular accidents, leading to such serious diseases as myocardial infarction and stroke, is reduced. The platelet in this case acts as the main initiator of the formation of a blood clot clogging the vessel.
Research in recent years has shown that the use of plain and buffer forms of aspirin ensures maximum effectiveness of the drug due to its high bioavailability.
– Aspirin is available in various dosage forms. What is their difference?
– Drugs called “aspirin” can be divided into plain (uncoated), buffered and enteric (enteric) forms of release. Buffer forms, for example, include the drug Cardiomagnil® in the form of film-coated tablets containing ASA, which dissolves in the stomach, as well as magnesium hydroxide. Cardiomagnyl® is a drug with a long history and successful experience in use in millions of patients. Currently, there are many generics of the drug on the market, such as Trombital®, Fazostabil®, Trombomag®, etc. Enteric-soluble forms also contain ASA, but due to the presence of an acid-resistant coating, the tablet dissolves in the intestines. Enteric-soluble aspirins are represented on the Russian market by the following drugs: Thrombo ACC®, Acecardol®, Aspirin Cardio®, CardiAsk®, Ask-Cardio®, etc. It is worth noting that gastrosoluble and enteric forms of ASA have different pharmacokinetic parameters. Thus, as a result of the fact that ASA is better absorbed in an acidic environment, gastrosoluble forms are significantly superior to enteric forms in terms of bioavailability1. Also, gastro-soluble forms provide a faster and more pronounced antiplatelet effect than enteric-soluble forms, and the risk of bleeding in the latter is no lower than that of gastro-soluble forms. Moreover, after taking gastrosoluble ASA, the drug remains in the blood for a significantly shorter time, which can reduce the damaging effect on the gastrointestinal tract2.
– More and more new drugs are appearing on the shelves of pharmacies, which indicate that they are acetylsalicylic acid. Generic aspirin: are they equivalent and absolutely interchangeable - or not always?
– It is believed that copies of drugs - generics - are equivalent to the original if they contain the same substance, have the same release form with the same indications for taking the medication1.
Are all emerging generic aspirin products the same? On the one hand, they all contain equal amounts of the same active ingredient - acetylsalicylic acid, and on the other hand, they may differ in the composition of excipients. It is known that the presence of bioequivalence is not always confirmed by therapeutic equivalence, which is discovered when the drug is changed due to a decrease in clinical effectiveness or the occurrence of side effects.
One of the possible reasons for this may be differences in the content of excipients included in the tablet product, even with the same activity of the pharmaceutical substance3. Inconsistencies in the effect of the drug, unless the case is associated with the use of an obvious falsification, are usually not easy to identify: this requires a long period of observation, careful analysis of the patient's complaints, and evidence is difficult to obtain.
Research in recent years has shown that the use of plain and buffer forms of aspirin ensures maximum effectiveness of the drug due to its high bioavailability. On the other hand, the use of enteric forms leads to a decrease in bioavailability4,5. These provisions are reflected in modern clinical guidelines6.
– Moscow doctors in the SPHIROS study compared laboratory indicators of the effectiveness of the original and two generic aspirin. Tell us about it.
– The study aimed to compare the laboratory effectiveness of two generic buffer preparations of acetylsalicylic acid: Fazostabil® produced by Ozon LLC, Russia (ASK 75 mg + magnesium hydroxide 15.2 mg) and Trombital®, Pharmstandard-Leksredstva OJSC, Russia ( ASA 75 mg + magnesium hydroxide 15.2 mg) – with the original drug Cardiomagnyl® produced in Germany/Takeda Pharmaceuticals LLC Russia (ASA 75 mg + magnesium hydroxide 15.2 mg)7. The method of administration and dosage regimen of the drugs corresponded to the information provided in the approved instructions for medical use. Although the active pharmaceutical substance is the same, the drugs have different compositions of excipients. For example, Fasostabil has 4 times more weight of excipients, 7.5 times more insoluble sorbent substances, and 5 times more shell than the original Cardiomagnyl.
Patients who had indications for taking aspirin, at the discretion of the attending physician, upon admission to the hospital received one of the three drugs available at the time of the study. As a result, three groups of 25 patients each received one of the drugs were formed. Before taking the first dose and after 1 hour, 2 hours, 4 hours, 72 hours and on the 7th day of the study, blood was drawn. Treatment was carried out under the control of laboratory parameters, which included assessment of the functional activity of platelets, measurement of the concentration of salicylic acid metabolite and the level of thromboxane B2 in the blood of patients while taking drugs. In addition, a study was carried out on the comparative kinetics of dissolution of these three drugs and the release of acetylsalicylic acid into a solution simulating the acidic environment of gastric juice.
The average release profile of acetylsalicylic acid from the drug Cardiomagnil® was higher compared to Trombital and Fasostabil, for which it was not equivalent to the branded form. Cardiomagnyl® already after 5 minutes shows superiority in the ability to dissolve in an acidic environment, which was maintained throughout the entire study period. This may be due to differences in the composition and weight of excipients.
In addition, the calculation of the so-called similarity factor (f2) based on data from a study of the kinetics of the dissolution of drugs and the release of ASA from them showed that they are not equivalent to the reference drug. Thus, for the drugs Trombital® and Fasostabil®, in comparison with Cardiomagnyl, the similarity factor was less than 40, which is a low indicator and indicates that it is not identical to the original drug.
Absorption of ASA into the blood from gastro-soluble forms occurs within 30 minutes after taking the medicine. It is known that it is present in the bloodstream for no more than 12–15 minutes, exerting its effect on platelets and the endothelium of the vascular wall, after which it is rapidly hydrolyzed under the action of blood esterases to salicylic acid8. The further effect of aspirin is due to the irreversible blockade of platelet receptors. The effective concentration of salicylic acid can remain in the blood for up to 12–14 hours, so it is by its level that the likely entry of acetylsalicylic acid into the bloodstream is judged. In our study, the concentration of salicylic acid 2 hours after taking the first dose of Cardiomagnyl was significantly higher compared to generics, and this difference persisted throughout the entire study period, indicating a higher bioavailability of the original drug. It demonstrated the highest release ability. By the third day of administration, Cardiomagnyl® led to a significantly greater decrease in the functional activity of platelets and the level of thromboxane B2 compared to generic drugs. Throughout the entire observation period, Cardiomagnyl® significantly suppressed the synthesis of thromboxane B2 to a greater extent and exhibited a disaggregation activity that other drugs did not fully achieve only on the 7th day. This circumstance may be especially important in acute situations - for example, in acute coronary syndrome or in the acute period of stroke, when active antiplatelet therapy is necessary at the earliest stages of treatment.
The results obtained in this study give reason to believe that the composition of excipients, production technology, and, possibly, the characteristics of the active substance may influence the effectiveness of therapy.
Let there be no heart attacks and strokes!
1. Sagar K., Smyth M. A comparative bioavailability study of different aspirin formulations using on-line multidimensional chromatography. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 1999 Nov;21(2):383-92. 2. Cox D., Maree AO, Dooley M. et al. Effect of enteric coating on antiplatelet activity of low-dose aspirin in healthy volunteers. Stroke. 2006;37:2153-2158 3. Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use. Guideline on the investigation of bioequivalence. London: European Medicines Agency. (2010). Available from: https://www.ema.europa.eu/pdfs/human/qwp/140198enrev1fin.pdf 4. Karha J., Rajagopal V., Kottke-Marchant K., et al. Lack of effect of enteric coating on aspirin-induced inhibition of platelet aggregation in healthy volunteers. Amer Heart J. 2006;151(5): 976.e7-976.e11. 5. Leonards JR, Levy G. Absorption and metabolism of aspirin administered in enteric-coated tablets. JAMA. 1965;193(2):99-104. 6. Roffi M., Patrono C., Collet JP, et al. 2015 ESC Guidelines for the management of acute coronary syndromes in patients presenting without persistent ST-segment elevation: Task Force for the Management of Acute Coronary Syndromes in Patients Presenting without Persistent ST-Segment Elevation of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). Eur Heart J 2016;37(3):267-315. 7. Lomakin N.V., Buryachkovskaya L.I., Zolin D.A., Kazei V.I. A prospective, initiative, single-center, open-label, post-registration comparative study of the laboratory effectiveness of various forms of acetylsalicylic acid in a cardioprotective dose with a different composition of excipients: results of the SPYROS study. Rational pharmacotherapy in cardiology. 2020; (in the press). 8. Patrono C., García Rodríguez L., Landolfi R., et al. Low-dose aspirin for the prevention of atherothrombosis. N Engl J Med. 2005;353(22):2373-2383.
Comparison of addiction between Aspirin Cardia and Cardiomagnyl
Like safety, addiction also involves many factors that must be considered when evaluating a drug.
So, the totality of the values of such parameters as “syndrome o” in Aspirin cardia is quite similar to the similar values in Cardiomagnyl. Withdrawal syndrome is a pathological condition that occurs after the cessation of intake of addictive or dependent substances into the body. And resistance is understood as initial immunity to a drug; in this it differs from addiction, when immunity to a drug develops over a certain period of time. The presence of resistance can only be stated if an attempt has been made to increase the dose of the drug to the maximum possible. At the same time, Aspirin Cardia has a fairly low “syndrome” value, just like Cardiomagnyl.
Indications for use
Indications for the use of this drug are:
- risk of stroke;
- the presence of hypertension and the risk of heart attack;
- increased risk of thromboembolism;
- the threat of blood clots in the veins;
- presence of angina pectoris;
- inflammatory diseases in joints and soft tissues;
- after operations;
- suspicion that an acute heart attack has begun;
- the presence of atherosclerosis;
- fever.
Usually for preventive purposes it is prescribed 1 time per day or 2 times. It all depends on the patient’s condition and the presence of various diseases. Before taking the drug, you should definitely consult your doctor. It is the doctor who decides which drug to choose and in what dose it should be used.
You need to understand that such a remedy allows you to very effectively combat blood viscosity and its thickness. Helps in the treatment of hypertension, it reduces the likelihood of heart attack and stroke. Despite the fact that the active component of the two types of aspirin is the same, Aspirin Cardio is more modern and safer. When taking this medication, the walls of the stomach will be protected from the negative effects of acid. A simple analogue does not have any protective shell and dissolves immediately in the stomach, which can lead to various digestive problems and even cause ulcers, gastritis and bleeding. And if you were prescribed Aspirin Cardio, you should not replace it with a cheaper analogue. In our pharmacy you will find various forms of aspirin.
Comparison of side effects of Aspirin Cardia and Cardiomagnyl
Side effects or adverse events are any adverse medical event that occurs in a subject after administration of a drug.
Aspirin Cardia has almost the same adverse events as Cardiomagnyl. They both have few side effects. This implies that the frequency of their occurrence is low, that is, the indicator of how many cases of an undesirable effect of treatment are possible and registered is low. The undesirable effect on the body, the strength of influence and the toxic effect of Aspirin Cardia are similar to Cardiomagnyl: how quickly the body recovers after taking it and whether it recovers at all.
conclusions
The use of Aspirin Cardio as a preventive and therapeutic agent has certain limitations. Considering the risk of bleeding and disruption of the hemostasis system, the drug should be taken only as prescribed by a doctor - a cardiologist or therapist. Antiplatelet therapy is indicated for patients with cardiovascular and cerebral diseases and a high risk of thrombosis. To prevent the development of adverse reactions or progression of the underlying pathology, before taking acetylsalicylic acid, you should read the instructions and consult with your doctor.
Comparison of ease of use of Aspirin Cardia and Cardiomagnyl
This includes dose selection taking into account various conditions and frequency of doses. At the same time, it is important not to forget about the release form of the drug; it is also important to take it into account when making an assessment.
The ease of use of Aspirin Cardia is approximately the same as Cardiomagnyl. However, they are not convenient enough to use.
The drug ratings were compiled by experienced pharmacists who studied international research. The report is generated automatically.
Last update date: 2020-12-04 13:44:58