Increased blood pressure (BP) is the most common reason for calling emergency medical services (EMS). Deterioration of the condition associated with increased blood pressure accounts for 20-25% of calls for emergency medical services, which amounts to about 9,000,000 calls per year [1-3]. Studies conducted in Moscow showed that the number of emergency calls due to increased blood pressure increases annually [4]. The increase in calls for emergency medical services occurs mainly due to multiple calls to the same patients with a moderate, non-life-threatening increase in blood pressure without the development of a hypertensive crisis (HC) [5]. In most of these cases, the administration of tableted antihypertensive drugs orally or sublingually is usually sufficient to provide EMS [5].
D. Papadopoulos et al. [6] believe that in 76% of cases HA is not life-threatening. The results of the EPOCHA epidemiological study [7] showed that 42.5 million people suffer from arterial hypertension in Russia, and the effectiveness of treatment is 23%, so the incidence of emergency conditions associated with increased blood pressure will remain very high.
It is possible to reduce the number of calls to emergency medical services due to increased blood pressure by prescribing individual self-help programs. Drugs prescribed for self-help must be effective, safe, not cause a large number of undesirable effects, have a method of administration accessible to the patient and an affordable price. By analogy with the planned treatment of arterial hypertension, it can be assumed that combinations of drugs in emergency care are more effective than monotherapy. Self-help drugs should be selected during emergency medical care, so that both the doctor and the patient can be convinced of the effectiveness and good tolerability of the drugs.
Of course, one of the main means for providing emergency medical care and self-help for elevated blood pressure is the imidazoline receptor agonist, moxonidine (physiotens) [8]. The obvious advantages of moxonidine include not only high antihypertensive activity, safety, good tolerability and affordable cost, but also good stability (predictability) of the resulting clinical effect. The second basic drug is captopril (Capoten), which is slightly inferior to moxonidine in duration of action.
The purpose of the study is to improve the results of emergency medical care in cases of high blood pressure and optimize the use of healthcare resources.
Research objectives:
1. To compare the effectiveness of a single sublingual application of combinations of captopril with nifedipine or furosemide and combinations of moxonidine with nifedipine or furosemide when providing emergency medical care to patients with non-life-threatening elevated blood pressure.
2. To compare the frequency of adverse events after a single use of combinations of captopril with nifedipine or furosemide, moxonidine with nifedipine or furosemide when providing emergency medical care to patients with increased blood pressure.
3. Assess the impact of self-help recommendations on the use of emergency medical services in connection with increased blood pressure.
Material and methods
A study of the effectiveness and safety of combinations of antihypertensive drugs was carried out in the emergency department of polyclinic No. 17 - the clinical base of the department of emergency medical care of Northwestern State Medical University named after. I.I. Mechnikov.
The study included patients who applied for emergency medical care due to increased blood pressure without the development of hypertension and patients with uncomplicated hypertension.
The study did not include patients under 18 years of age, patients with life-threatening emergencies, patients with contraindications to any of the 4 medications used, and patients who, before the arrival of the EMS team, took any medications that affect blood pressure.
The study used moxonidine (Physiotens, Abbott), furosemide (Lasix, Aventis, Sanofi), captopril (Capoten, Akrihinn), nifedipine (Cardoflex, Egis).
The effectiveness and safety of combinations of 0.4 mg moxonidine with 10 mg nifedipine were compared; 0.4 mg moxonidine with 40 mg furosemide; 25 mg captopril with 10 mg nifedipine; 25 mg captopril with 40 mg furosemide.
Combinations of drugs were prescribed using a table
Table 1. Characteristics of patients Note: AH—arterial hypertension, HF—heart failure, AMI—acute myocardial infarction, ACVA—acute cerebrovascular accident. random numbers.
A total of 389 patients were included in the study. The vast majority of patients were women (78%). Average age: 70.4±0.6 years. Duration A.G. — 21.5±0.5 years. Initial systolic blood pressure (SBP) was 197.4±0.9 mmHg, diastolic blood pressure (DBP) was 107.5±0.6 mmHg.
Depending on the prescribed combinations of antihypertensive drugs, patients were divided into four groups. The characteristics of patients in the groups are presented in Table. 1.
As can be seen from table. 1, there were no significant differences between the groups for all of the listed characteristics. Blood pressure was measured using the Korotkoff method. In each case, measurements were carried out 2 times, taking into account the minimum values. Registration of A.D. were carried out before prescribing medications and after taking medications every 10 minutes during the first 30 minutes of the study, and longer if indicated.
A reduction in blood pressure of no less than 15%, but no more than 25% of the initial value was considered effective and safe, subject to complete disappearance or significant reduction in the severity of complaints [9, 10].
For the primary assessment of the effectiveness of self-help, we compared the annual number of calls for emergency medical services due to increased blood pressure before patients received self-help recommendations and one year after these recommendations were received. To do this, we conducted a continuous sample of emergency medical service call cards for 500 patients with increased blood pressure. Due to the fact that information about 2 patients was incomplete, these cards were excluded from further processing.
Statistical processing of the results was carried out using the application package Statistica for Windows 8.0.550. Checking the empirical law of distribution of variables showed agreement with the theoretical law of normal distribution according to Shapiro-Wilks ( p
>0.05), therefore, to describe numerical characteristics and quantitative characteristics, the arithmetic mean and the mean square error of the mean were used.
P
was taken as the threshold level of statistical significance [11].
All about the dosage form
Unfortunately, not all people carefully study the instructions for the drug when purchasing medications. But in vain. Even when products have the same active substance, their indications and method of use can be very different. And a clear example of this is the drug Glycine, which is produced by the company BIOTICS. The peculiarity of the amino acid is that it is poorly absorbed by the digestive system. If you take the drug by swallowing it with water, it will not have any effect. Glycine, which is produced by the BIOTICS company, is significantly different from other products. It's all about microencapsulation technology, which was developed and patented by the company (the RF patent number is indicated on each package).
Results and discussion
The effectiveness of combinations of antihypertensive drugs is presented in table. 2.
Table 2. Efficacy of antihypertensive drugs
As can be seen from table. 2, combinations of moxonidine with nifedipine, moxonidine with furosemide, and captopril with furosemide were very highly effective. In contrast, the addition of nifedipine to captopril resulted in a sharp decrease in antihypertensive activity.
The absence of increased antihypertensive activity when adding amlodipine to captopril is also indicated by P. Kotruchin et al. [12].
Changes in blood pressure 30 minutes after taking the studied combinations of antihypertensive drugs are presented in the figure.
Decrease in systolic (a) and diastolic blood pressure (b) after taking antihypertensive drugs. 1 — moxonidine with nifedipine; 2 — moxonidine with furosemide; 3 — captopril with nifedipine; 4 — captopril with furosemide.
Combinations of moxonidine with nifedipine, moxonidine with furosemide and captopril with furosemide have pronounced antihypertensive activity (see figure). SBP is more significantly reduced by the combination of moxonidine with furosemide, and DBP by the combination of moxonidine or captopril with furosemide.
The combination of captopril with nifedipine for emergency antihypertensive therapy is ineffective.
In table 3 presented
Table 3. Adverse events of antihypertensive drugs - undesirable effects of the studied combinations of antihypertensive drugs.
As can be seen from table. 3, the least number of adverse events occurred when using a combination of moxonidine with furosemide, the maximum number of side effects was noted when captopril was prescribed with nifedipine.
As a result of the analysis of 498 emergency medical service call cards for patients with elevated blood pressure, it was found that initially during the year they called for emergency medical services 1724 times, i.e., there were 3.5 calls per patient per year. After receiving recommendations for self-help, more than half (279 out of 498) of patients with increased blood pressure did not call for emergency medical services within a year. The remaining 219 patients visited the emergency room for this issue 656 times during the year, i.e., the number of calls per patient decreased from 3.5 to 3.0 per year.
On average, the introduction of individual recommendations for self-help reduced the use of emergency medical services in connection with an increase in blood pressure from 1724 to 656 per year, i.e. by 2.6 times, without requiring additional funding.
The high incidence of arterial hypertension, the low effectiveness of its treatment, the round-the-clock availability of emergency medical services, together with the dependent attitude of patients towards their disease, are realized by the very high demand for emergency medical services at the slightest increase in blood pressure.
The increasing number of calls depletes the resources of the ambulance service and healthcare in general, not improving the course and outcome of the disease, but contributing to the transformation of a medical problem into a social problem.
Solving this problem is impossible without the cooperation of the doctor and the patient with arterial hypertension, in particular without the active use of self-help. Combinations of drugs for self-help should be selected during emergency medical care, so that both the doctor and the patient can be convinced of the effectiveness and good tolerability of the drugs.
When using self-help, you should adhere to the rules, the main ones of which are presented below.
Basic rules of self-help
1. Self-help is indicated for a typical deterioration of the patient’s condition, in particular for a typical increase in blood pressure.
2. The doctor must make sure that the patient correctly understands the content of self-help and is able to correctly follow the specified recommendations.
3. If, after taking the recommended medications, your health and condition do not improve or worsen, it is necessary, without wasting time, to call an ambulance.
4. Self-help should not replace planned therapy.
5. Self-help should not be prescribed to patients who are unable to adequately assess and control their condition.
What is high blood pressure, causes and symptoms
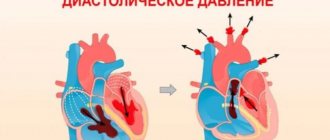
High blood pressure is when the readings exceed 140 (upper, systolic) by 90 (lower, diastolic). These indicators are considered average, since each person has his own individual working pressure, which may deviate from the standard value of 120 to 80. With a systematic increase in pressure numbers, we can talk about hypertension. It affects more than half of people over 50 years of age. If the pressure jumps sharply to numbers of 180 to 120 and above, we are already talking about a hypertensive crisis, which is also one of the complications of hypertension. Such a dangerous condition must be quickly stopped, as it can lead to heart attack, stroke, and so on.
Free consultation right now!
Online consultation with a specialist on your issue!
License number: LO-77-01-019036
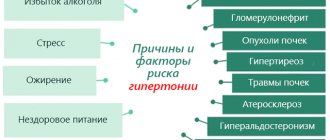
The development of hypertension is influenced by a sedentary lifestyle, smoking, alcohol consumption, poor diet, as well as certain diseases, including diabetes mellitus and kidney disease.
Symptoms of high blood pressure include:
- compressive headache (most often in the occipital part, or encircling the entire head);
- dizziness;
- weakness and fatigue;
- blurred vision (floaters before the eyes);
- depressed state;
- heartache.
The condition may also be accompanied by a feeling of fear, panic attacks, rapid heartbeat, redness of the skin, and sweating.
Write to WhatsApp
COST OF TREATMENT
Capoten or captopril. Captopril or Capoten?
To treat arterial hypertension and heart failure, doctors prescribe the drugs Capoten and Captopril. The patient immediately has questions - what is the difference between the tablets, which is stronger? After all, the principle of operation is the same, but the price is so different. The drugs are similar in structure, effects, dosage, contraindications. But there are also factors that distinguish them.
Characteristics of drugs
"Captopril" and "Capoten" are tablets that are available in 25 mg and 50 mg doses. Therefore, it is easy to choose the right dosage. The active substance quickly dissolves in the digestive tract and is then absorbed into the blood. Half an hour after taking it, the person feels better. For effectiveness, it is recommended to place the tablet under the tongue and dissolve slowly. Both drugs belong to ACE inhibitors. Responsible for improving well-being and normalizing blood pressure.
Active components and mechanism of action
The active substance is captopril. The mechanism of action is to reduce the synthesis of angiotensin, prevent vasoconstriction, sodium and water retention in the human body. The active ingredient helps:
- lowering blood pressure;
- increasing cardiac output;
- vasodilation;
- improving heart function.
What is the difference between the drugs "Capoten" and "Captopril"?
The drug contains additional ingredients that minimize the occurrence of side effects.
The products are similar in many details, but the difference lies in the composition. The active substance is found in almost pure form. The number of additional elements is minimal, while Kapoten contains excipients that minimize side effects. Microscopic cellulose, which is contained in Kapoten, helps the substance to be absorbed into the blood faster.
To produce “Capoten” you need more funds and preparations, which is why its price is higher. Although Captopril is cheaper, it is not inferior in effectiveness. Based on these characteristics, Captopril is considered stronger than Capoten. The difference is also in the countries that produce. - a patented company in the USA and Russia. Captopril is produced in many countries of the former CIS.
When are the tablets prescribed?
The drugs are interchangeable, so doctors prescribe one or the other. The use of one drug constantly becomes addictive, and the effectiveness decreases. To prevent addiction, doctors usually alternate medications. The tablets are recommended to be taken before meals with water. Do not chew. The indications for which both drugs are prescribed are summarized in the table below.
| Indications for use | |
| Problem | Action |
| Hypertension and hypertension | When blood pressure rises, both types of tablets help. Doctors prescribe drugs both as a single medicine and as part of complex therapy. |
| Changes in left ventricular function | After a heart attack, parts of the heart may malfunction. Both remedies are effective in improving cardiac activity. |
| Heart failure | To stabilize the heart, both drugs are prescribed in a therapeutic complex. To prevent the body from becoming addicted, medications are alternated, since the treatment is long-term. |
| Nephropathy | Treatment of diabetes is a complex process that consists of different stages. One of them is to combat kidney complications that are affected by strong drugs. "Capoten" or "Captopril" help normalize kidney function and reduce harm to health. |