The only way to know if you have high or low blood pressure is to measure your blood pressure. Understanding your results is key to controlling your blood pressure.
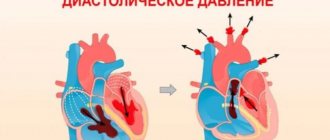
- Systolic blood pressure (First or top number) is the maximum pressure in the arteries when the heart contracts and pushes blood into the arteries.
- Diastolic blood pressure (Second or lower number) - shows the pressure in the arteries at the moment the heart muscle relaxes, it reflects the resistance of peripheral vessels.
general information
As a general rule, any primary medical examination begins with checking the basic indicators of the normal functioning of the human body. The doctor examines the skin, palpates the lymph nodes, palpates certain areas of the body in order to assess the condition of the joints or identify superficial changes in the blood vessels, listens to the lungs and heart with a stethoscope, and also measures temperature and pressure .
The listed manipulations allow the specialist to collect the necessary minimum information about the patient’s health status (make an anamnesis) and indicators of arterial or blood pressure play an important role in the diagnosis of many different diseases. What is blood pressure, and what are its norms for people of different ages?
For what reasons does blood pressure increase or, conversely, decrease, and how do such fluctuations affect a person’s health? We will try to answer these and other important questions on the topic in this material. We will start with general, but extremely important aspects.
Benefits of Journaling
Thanks to regular data collection, the effectiveness of taking antihypertensive drugs increases, since timely detection of deviations makes it possible to accurately correct the treatment regimen.
How to measure blood pressure with a manual tonometer
- Regularity of blood pressure determination.
- Possibility of daily self-monitoring at home.
- Identification of situations that provoke an increase in values.
- Reducing the risk of developing cardiac and vascular complications.
- Allows you to evaluate the effectiveness of therapeutic measures.
- Improving quality of life.
What is upper and lower blood pressure?
Blood or arterial (hereinafter referred to as blood pressure) is the pressure of blood on the walls of blood vessels. In other words, this is the pressure of the fluid of the circulatory system, exceeding atmospheric pressure, which in turn “presses” (impacts) everything that is on the surface of the Earth, including people. Millimeters of mercury (hereinafter referred to as mmHg) is a unit of measurement for blood pressure.
The following types of blood pressure are distinguished:
- Intracardiac or cardiac , occurring in the cavities of the heart during its rhythmic contraction. For each part of the heart, separate normative indicators have been established, which vary depending on the cardiac cycle, as well as on the physiological characteristics of the body.
- Central venous (abbreviated as CVP), i.e. blood pressure of the right atrium, which is directly related to the amount of venous blood returned to the heart. CVP indicators are of utmost importance for diagnosing certain diseases.
- Capillary is a value that characterizes the level of liquid pressure in the capillaries and depends on the curvature of the surface and its tension.
- Blood pressure is the first and, perhaps, the most significant factor, by studying which a specialist makes a conclusion about whether the body’s circulatory system is functioning normally or whether there are deviations. The value of blood pressure indicates the volume of blood that the heart pumps in a certain unit of time. In addition, this physiological parameter characterizes the resistance of the vascular bed.
Since it is the heart that is the driving force (a kind of pump) of blood in the human body, the highest blood pressure values are recorded at the blood outlet from the heart, namely from its left stomach. When blood enters the arteries, the pressure level becomes lower, in the capillaries it decreases even more, and it becomes minimal in the veins, as well as at the entrance to the heart, i.e. in the right atrium.
Three main indicators of blood pressure are taken into account:
- heart rate (abbreviated HR) or pulse;
- systolic , i.e. upper pressure;
- diastolic , i.e. lower.
What does a person's upper and lower blood pressure mean?
Upper and lower pressure indicators - what are they and what do they influence? When the right and left ventricles of the heart contract (i.e., the process of heartbeat occurs), blood is pushed out in the systole phase (the stage of the heart muscle) into the aorta.
The indicator in this phase is called systolic and is recorded first, i.e. is essentially the first number. For this reason, systolic pressure is called upper. This value is influenced by vascular resistance, as well as the frequency and strength of heart contractions.
In the diastole phase, i.e. in the interval between contractions (systole phase), when the heart is in a relaxed state and filled with blood, the value of diastolic or lower blood pressure is recorded. This value depends solely on vascular resistance.
Let's summarize all of the above using a simple example. It is known that 120/70 or 120/80 are the optimal blood pressure values for a healthy person (“like astronauts”), where the first number 120 is the upper or systolic pressure, and 70 or 80 is the diastolic or lower pressure.
Human blood pressure norms by age
Let's be honest, while we are young and healthy, we rarely worry about our blood pressure levels. We feel good and therefore there is no reason to worry. However, the human body ages and wears out. Unfortunately, this is a completely natural process from a physiological point of view, affecting not only the appearance of a person’s skin, but also all of his internal organs and systems, including blood pressure.
So, what should be the normal blood pressure in an adult and in children? How does age affect blood pressure? And at what age should you start monitoring this vital indicator?
To begin with, it should be noted that such an indicator as blood pressure actually depends on many individual factors (mental-emotional state of a person, time of day, taking certain medications, food or drinks, and so on).
Modern doctors are wary of all previously compiled tables with average blood pressure standards based on the patient’s age. The thing is that the latest research speaks in favor of an individual approach in each specific case. As a general rule, normal blood pressure in an adult of any age, no matter in men or women, should not exceed the threshold of 140/90 mm Hg. Art.
This means that if a person is 30 years old or at 50-60 years old the indicators are 130/80, then he does not have problems with the functioning of the heart. If the upper or systolic pressure exceeds 140/90 mm Hg, then the person is diagnosed with arterial hypertension . Drug treatment is carried out when the patient’s blood pressure “goes off scale” beyond 160/90 mm Hg.
When blood pressure is elevated, a person experiences the following symptoms:
- increased fatigue;
- noise in ears;
- swelling of the legs;
- dizziness;
- vision problems;
- decreased performance;
- nosebleed.
According to statistics, high upper blood pressure is most common in women, and low blood pressure is most common in older people of both sexes or in men. When the lower or diastolic blood pressure drops below 110/65 mm Hg, irreversible changes in internal organs and tissues occur, as blood supply deteriorates, and, consequently, oxygen saturation of the body.
If your blood pressure remains at 80 to 50 mm Hg, then you should immediately seek help from a specialist. Low lower blood pressure leads to oxygen starvation of the brain, which negatively affects the entire human body as a whole. This condition is as dangerous as high blood pressure. It is believed that the normal diastolic pressure of a person aged 60 years and older should not be more than 85-89 mmHg. Art.
Otherwise, hypotension or vegetative-vascular dystonia . With low blood pressure, symptoms such as:
- muscle weakness;
- headache;
- darkening of the eyes;
- dyspnea;
- lethargy;
- increased fatigue;
- photosensitivity , as well as discomfort from loud sounds;
- feeling of chills and coldness in the extremities.
Causes of low blood pressure may include:
- stressful situations;
- weather conditions, for example, stuffiness or sweltering heat;
- fatigue due to high loads;
- chronic lack of sleep;
- allergic reaction;
- certain medications, such as heart medications, pain medications, antibiotics , or antispasmodics .
However, there are examples where people live quietly throughout their lives with a lower blood pressure of 50 mmHg. Art. and, for example, former athletes whose heart muscles are hypertrophied due to constant physical activity feel great. That is why each individual person may have his own normal blood pressure readings, at which he feels great and lives a full life.
Causes of changes in blood pressure
High diastolic pressure indicates the presence of kidney, thyroid, or adrenal disease.
An increase in blood pressure can be caused by the following reasons:
- overweight;
- stress;
- atherosclerosis and some other diseases ;
- smoking and other bad habits;
- diabetes;
- unbalanced diet;
- sedentary lifestyle;
- weather changes.
Another important point regarding human blood pressure. To correctly determine all three indicators (upper, lower pressure and pulse), you need to follow simple measurement rules. Firstly, the optimal time to measure blood pressure is in the morning. Moreover, it is better to place the tonometer at the level of the heart, so the measurement will be the most accurate.
Secondly, the pressure may “jump” due to a sudden change in the person’s body posture. That is why you need to measure it after waking up, without getting out of bed. The arm with the tonometer cuff should be horizontal and motionless. Otherwise, the indicators produced by the device will have an error.
It is noteworthy that the difference between the indicators on both hands should not be more than 5 mm. The ideal situation is when the data does not differ depending on whether the pressure was measured on the right or left hand. If the indicators differ by 10 mm, then the risk of developing atherosclerosis , and a difference of 15-20 mm indicates abnormalities in the development of blood vessels or their stenosis .
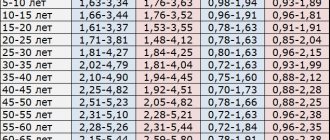
What are the blood pressure standards for a person, table
Let us repeat once again that the table below with blood pressure norms by age is just reference material. Blood pressure is not a constant value and can fluctuate depending on many factors.
Pressure rate table:
| Age, years | Pressure (minimum value), mmHg. | Pressure (average), mmHg. | Pressure (maximum value), mmHg. |
| Up to a year | 75/50 | 90/60 | 100/75 |
| 1-5 | 80/55 | 95/65 | 110/79 |
| 6-13 | 90/60 | 105/70 | 115/80 |
| 14-19 | 105/73 | 117/77 | 120/81 |
| 20-24 | 108/75 | 120/79 | 132/83 |
| 25-29 | 109/76 | 121/80 | 133/84 |
| 30-34 | 110/77 | 122/81 | 134/85 |
| 35-39 | 111/78 | 123/82 | 135/86 |
| 40-44 | 112/79 | 125/83 | 137/87 |
| 45-49 | 115/80 | 127/84 | 139/88 |
| 50-54 | 116/81 | 129/85 | 142/89 |
| 55-59 | 118/82 | 131/86 | 144/90 |
| 60-64 | 121/83 | 134/87 | 147/91 |
In addition, in some categories of patients, for example, pregnant women , whose body, including the circulatory system, undergoes a number of changes during the period of bearing a child, the indicators may differ, and this will not be considered a dangerous deviation. However, as a guide, these blood pressure norms for adults can be useful for comparing your indicators with average numbers.
Table of blood pressure in children by age
Let's talk more about children's blood pressure. To begin with, it should be noted that in medicine, separate norms for blood pressure have been established for children from 0 to 10 years old and for adolescents, i.e. from 11 years and older. This is due, first of all, to the structure of the child’s heart at different ages, as well as to some changes in hormonal levels that occur during puberty.
It is important to emphasize that children’s blood pressure will be higher the older the child is; this is due to the greater elasticity of blood vessels in newborns and preschool children. However, with age, not only the elasticity of blood vessels changes, but also other parameters of the cardiovascular system, for example, the width of the lumen of veins and arteries, the area of the capillary network, and so on, which also affects blood pressure.
In addition, blood pressure indicators are influenced not only by the characteristics of the cardiovascular system (the structure and boundaries of the heart in children, the elasticity of blood vessels), but also by the presence of congenital developmental pathologies ( heart defects ) and the state of the nervous system.
Normal blood pressure for people of different ages:
| Age | Blood pressure (mm Hg) | |||
| Systolic | Diastolic | |||
| min | max | min | max | |
| Up to 2 weeks | 60 | 96 | 40 | 50 |
| 2-4 weeks | 80 | 112 | 40 | 74 |
| 2-12 months | 90 | 112 | 50 | 74 |
| 2-3 years | 100 | 112 | 60 | 74 |
| 3-5 years | 100 | 116 | 60 | 76 |
| 6-9 years | 100 | 122 | 60 | 78 |
| 10-12 years | 110 | 126 | 70 | 82 |
| 13-15 years old | 110 | 136 | 70 | 86 |
As can be seen from the table, the norm for newborn children (60-96 per 40-50 mmHg) is considered to be low blood pressure compared to older age. This is due to a dense network of capillaries and high vascular elasticity.
By the end of the first year of a child’s life, the indicators (90-112 by 50-74 mm Hg) increase noticeably, due to the development of the cardiovascular system (the tone of the vascular walls increases) and the whole organism as a whole. However, after a year, the growth of indicators slows down significantly and blood pressure is considered normal at a level of 100-112 at 60-74 mm Hg. These indicators gradually increase by 5 years to 100-116 by 60-76 mmHg.
Many parents of younger schoolchildren worry about what normal blood pressure is for a child aged 9 years and older. When a child goes to school, his life changes dramatically - there are more loads and responsibilities, and less free time. Therefore, the child’s body reacts differently to such a rapid change in usual life.
In principle, blood pressure indicators in children 6-9 years old differ slightly from the previous age period, only their maximum permissible limits expand (100-122 by 60-78 mm Hg). Pediatricians warn parents that at this age, children's blood pressure may deviate from the norm due to increased physical and psycho-emotional stress associated with entering school.
There is no reason to worry if the child is still feeling well. However, if you notice that your little schoolchild is too tired, often complains of headaches, is lethargic and in no mood, then this is a reason to be wary and check your blood pressure readings.
Normal blood pressure in a teenager
According to the table, blood pressure is normal in children 10-16 years old, if its levels do not exceed 110-136 per 70-86 mmHg. It is believed that at the age of 12 the so-called “transitional age” begins. Many parents are afraid of this period, since a child from an affectionate and obedient baby under the influence of hormones can turn into an emotionally unstable, touchy and rebellious teenager.
Unfortunately, this period is dangerous not only for sudden changes in mood, but also for the changes that occur in the child’s body. Hormones that are produced in larger quantities affect all vital human systems, including the cardiovascular system.
Therefore, pressure indicators during adolescence may deviate slightly from the above norms. The key word in this phrase is insignificant. This means that if a teenager feels unwell and has symptoms of high or low blood pressure, he needs to urgently contact a specialist who will examine the child and prescribe appropriate treatment.
A healthy body can adjust itself and prepare for adult life. At 13-15 years old, blood pressure will stop “jumping” and return to normal. However, in the presence of deviations and certain diseases, medical intervention and drug adjustment are required.
High blood pressure may be a symptom of:
- arterial hypertension (140/90 mmHg), which without appropriate treatment can lead to a severe hypertensive crisis ;
- symptomatic hypertension , which is characteristic of renal vascular diseases and adrenal tumors;
- vegetative-vascular dystonia , a disease characterized by surges in blood pressure within the range of 140/90 mmHg;
- lower blood pressure may increase due to pathologies in the kidneys ( stenosis , glomerulonephritis , atherosclerosis , developmental abnormalities );
- Upper blood pressure increases due to defects in the development of the cardiovascular system, diseases of the thyroid gland, and also in patients with anemia .
If blood pressure is low, there is a risk of developing:
- hypotension;
- myocardial infarction;
- vegetative-vascular dystonia;
- anemia;
- myocardiopathy;
- hypothyroidism;
- adrenal insufficiency;
- diseases of the hypothalamic-pituitary system.
Controlling your blood pressure levels is really very important, and not only at 40 or after fifty. A tonometer, like a thermometer, should be in the home medicine cabinet of everyone who wants to live a healthy and fulfilling life. Spending five minutes of your time on a simple procedure for measuring blood pressure is actually not difficult, and your body will thank you very much for it.
What is pulse pressure
As we mentioned above, in addition to systolic and diastolic blood pressure, a person’s pulse is considered an important indicator for assessing heart function. What is pulse pressure and what does this indicator reflect?
Correct finger position when measuring pulse
So, it is known that the normal pressure of a healthy person should be within 120/80, where the first number is the upper pressure, and the second is the lower.
So, pulse pressure is the difference between systolic and diastolic pressure , i.e. top and bottom.
Normal pulse pressure is 40 mmHg. Thanks to this indicator, the doctor can draw a conclusion about the condition of the patient’s blood vessels, and also determine:
- degree of wear of arterial walls;
- patency of the vascular bed and their elasticity;
- the condition of the myocardium, as well as the aortic valves;
- development of stenosis , sclerosis , as well as inflammatory processes.
It is important to note that a pulse pressure of 35 mm Hg plus or minus 10 points, and the ideal is 40 mm Hg. The value of pulse pressure varies depending on the age of the person, as well as on his state of health. In addition, other factors, such as weather conditions or psycho-emotional state, also influence the value of pulse pressure.
Low pulse pressure (less than 30 mm Hg), at which a person may lose consciousness, feel severe weakness, headaches , drowsiness and dizziness, indicates the development of:
- vegetative-vascular dystonia;
- aortic stenosis;
- hypovolemic shock;
- anemia;
- heart sclerosis;
- myocardial inflammation;
- ischemic kidney disease.
Low pulse pressure is a kind of signal from the body that the heart is not working correctly, namely, it is weakly “pumping” blood, which leads to oxygen starvation of our organs and tissues. Of course, there is no reason to panic if the drop in this indicator was isolated, however, when this becomes a frequent occurrence, you need to urgently take action and seek medical help.
High pulse pressure, as well as low, can be caused by both momentary deviations, for example, a stressful situation or increased physical activity, and the development of pathologies of the cardiovascular system.
Increased pulse pressure (more than 60 mmHg) is observed with:
- pathologies of the aortic valve;
- iron deficiency;
- congenital heart defects;
- thyrotoxicosis;
- renal failure;
- coronary disease;
- inflammation of the endocardium;
- atherosclerosis;
- hypertension;
- feverish conditions;
- when the level of intracranial pressure .
What can PD tell you?
At the moment of contraction, the heart pushes a certain volume of blood into the vascular system (stroke volume), which causes stretching of the blood vessels. During diastole, the vessels, due to the elasticity of their walls, return to their original volume. Under the influence of certain diseases, as well as age-related changes, a person’s blood vessels lose their natural elasticity and firmness. As a result, they become rigid and unable to adequately respond to the pulse wave, which leads to an increase in PP.
Based on the PD value, the doctor judges the condition of the vascular walls, vascular patency, and the presence of vascular spasm.