Coagulation, manifested by clots during menstruation, is a fairly common symptom, in most cases not the result of a disease. However, if there are a lot of bloody clots, menstruation is accompanied by severe pain and excessively heavy and prolonged bleeding, this means a deviation from the norm and the need for diagnosis and treatment by a gynecologist.
Common causes of clot formation are hormonal imbalances, bleeding disorders, as well as pathologies such as endometriosis, polyps and fibroids in the uterus.
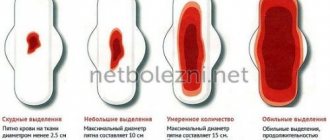
Monthly vaginal bleeding occurs as a result of detachment of the epithelial layer of the uterus, so it is natural that the discharge is heterogeneous. Most women experience clots during menstruation.
What should the menstrual period be like?
Every woman's period is different. Usually the period lasts 3-7 days, and its main symptom is dark bloody discharge. The first two days are characterized by more active bleeding, and in subsequent days blood secretion decreases.
Blood clots in menstrual flow should not be a concern if there are few of them, menstruation lasts less than a week and is not accompanied by severe pain.
Blood clots in menstrual flow
Heavy periods in teenagers
Teenagers often experience heavy periods. They occur quite often, in 37% of cases. Girls aged 13-16 years have unstable hormonal levels, the balance between the amount of estrogen and progesterone is disrupted. But there are other reasons why girls may have heavy periods with clots:
- enlarged thyroid gland;
- poor blood clotting;
- genital tract infections;
- lack of vitamins;
- stressful situations, mental overload, mental trauma;
- Infectious diseases (sore throat, flu) can also affect this.
If a child develops such disorders, you should immediately consult a doctor. The doctor must find out the cause of the deviation and prescribe treatment. If the girl does not complete the course of therapy, there is a high probability that she will later develop polycystic ovary syndrome (diagnosed in 30% of patients).
Causes of blood clots during menstruation
One of the reasons for the formation of clots is hormonal imbalance. This condition occurs in young girls with their first menstruation, and in women immediately after childbirth. This is usually a harmless symptom that disappears as hormonal levels normalize.
Women who have very heavy periods often notice blood clots. This is due to a lack of iron, which is required for the formation of anticoagulants. During normal bleeding, anticoagulants prevent blood from clotting, allowing the uterus to empty freely in preparation for a new cycle. In case of heavy bleeding, the coagulant is quickly consumed, so the blood coagulates, forming clots.
Menstrual blood with clots is also a sign of endometriosis - wandering endometrial syndrome. This condition is accompanied by a number of symptoms:
- pain;
- severe bleeding;
- painful sexual intercourse;
- problems with conception;
- increased fatigue.
Pathology occurs when the mucous membrane - the endometrium of the uterus - grows into the tissues of other organs, not even always reproductive ones. Endometriosis can affect: ovaries, peritoneum, bladder, intestines and other organs. The disease is asymptomatic, hiding for several years. Endometriosis is a serious pathology and poses a threat to life if left untreated.
Uterine bleeding - symptoms and treatment
Treatment of uterine bleeding is divided into surgical and medical. Drug treatment can be hormonal and non-hormonal [11][20].
In case of acute uterine bleeding and for women over 35 years of age, surgical treatment is preferable:
- Hysteroscopy with biopsy. Insertion of a hysteroscope into the uterine cavity to visualize it, identify and remove a pathological focus in the uterus. At the same time, it is also a diagnostic research method. The operation is effective for polyps, submucosal uterine fibroids and endometrial hyperplasia.
- Separate diagnostic curettage of the uterine cavity and cervical canal. Recommended for premenopausal, postmenopausal women and for acute bleeding. The disadvantage of this method is the formation of adhesions in the pelvic cavity and Asherman's syndrome, which lead to infertility [11][20].
- Endometrial ablation is the complete destruction of the endometrium. Effective in eliminating uterine bleeding, but leads to amenorrhea, scarring in the uterine cavity (which will complicate biopsy taking) and infertility. Therefore, it is performed only in premenopausal and postmenopausal women [15][17].
- Hysterectomy - removal of the uterus via laparotomy (an incision in the lower abdomen along the hairline). It may be recommended for patients who refuse hormonal therapy and for those who experience symptomatic anemia or a significantly reduced quality of life due to bleeding [11][20].
- Emergency measures are required extremely rarely, only in case of heavy bleeding. Hemodynamics (blood movement through the vessels) is stabilized by intravenous administration of crystalloid solutions, blood products and other measures. If the bleeding does not stop, uterine tamponade is performed - a urinary catheter balloon is inserted into the uterine cavity, expanding it with the introduction of 30-60 ml of water. In this way, the vessels in the uterus are mechanically compressed, and bleeding stops [20].
Non-hormonal drug treatment (for young girls under 35 years old) includes:
- Taking NSAIDs (non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs) reduces bleeding by 25-35% and eliminates pain due to a decrease in the production of prostaglandins [5][18].
- Antifibrinolytics - tranexamic acid, which inhibits the production of enzymes that dissolve blood clots. Stop bleeding, reducing blood loss by 40–60%. They also have anti-allergic and anti-inflammatory effects. Take no more than five days. Allowed for pregnant women [2].
Hormone therapy suppresses endometrial growth and reduces menstrual bleeding. Treatment usually lasts six months or more [11][12][20]. Hormone therapy treatments include:
- combined oral contraceptives;
- vaginal rings;
- gestagens;
- progestin-releasing intrauterine systems.
Combined oral contraceptives:
- contains at least 30 mcg ethinyl estradiol;
- contain levonorgestrel 150 mcg or gestodene 75 mcg - as an analogue of progesterone, which is produced by the corpus luteum after ovulation.
Take one tablet every 3-4 hours (up to six tablets per day) until bleeding stops completely. Then the intake should be continued, reducing the number of tablets by one per day. When one tablet per day remains, you should take them until 21 days from the start of treatment. Then take a break of 7 days (bloody menstrual-like discharge will appear). Then continue one tablet a day for 21 days, then break again for 7 days. The course is six months or more.
The ethinyl estradiol and etonogestrel vaginal ring can be used instead of the pill after bleeding has stopped if this method is more convenient than taking the pill every day. The vaginal ring is an elastic ring that conforms to the anatomical shape of the vagina, from which ethinyl estradiol is released daily. It is installed deep in the vagina from the first day of menstruation (or immediately, without a break after taking hormonal pills) on the 21st day (similar to taking combined oral contraceptives). Then it is removed for 7 days (similar to a break when using hormonal pills). It is recommended to use for at least six months [12][14][20].
Progestin drugs:
- dydrogesterone - 30 mg per day;
- micronized progesterone - 300 mg per day;
- norethisterone - 5-10 mg per day.
Taking gestagens continues for at least six months. Approved for use during pregnancy [11][20].
Levonorgestrel-releasing intrauterine systems. Under the influence of body temperature, a daily dose of a hormone is released that acts on progesterone and estrogen receptors in the uterus, thereby inhibiting the growth of the endometrium. Intrauterine systems are effective for 97% of patients. They are used for from 6 months to 5 years, providing contraception (hormonal effect on the endometrium and mechanical effect like a spiral) [11][19].
Gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonists (GnRH) - These drugs suppress the production of hormones by the ovaries, leading to amenorrhea. They are used to reduce the size of leiomyomas or before surgical treatment. However, their side effects (eg osteoporosis) limit their use to six months [11][16].
Summarizing:
- for uterine bleeding in juvenile age, hormonal drugs should be used;
- for bleeding in pregnant women, gestagens (dydrogesterone or micronized progesterone) and fibrinolysis inhibitors (tranexamic acid) should be used;
- in perimenopausal and postmenopausal age, surgical methods are used (hysteroscopy and curettage of the uterine cavity).
If, after a histological examination of a biopsy sample from the uterus, malignant changes are detected, then hysterectomy (removal of the uterus) is used with possible removal of the appendages and regional lymph nodes. If there is a question about a woman’s reproductive function, and the ovaries cannot be preserved, cryopreservation of oocytes is recommended.
Diagnosis of the problem
At the appointment, the doctor should ask you about your cycle, at what age it began, whether there have been pregnancies or abortions, how long the cycle lasts, how heavy your periods are and whether there are any clots. How much discomfort do you experience? Before your visit, it makes sense to count the number of hygiene products you use per day and over the entire period. After consultation, a number of tests are prescribed:
- blood test for hormones, iron and coagulation;
- Pap test - a painless smear from the cervix to check for cell changes. In serious cases, an intrauterine biopsy is prescribed (the procedure takes about 15 minutes and is well tolerated);
- Ultrasound.
Based on these initial examinations, additional examinations may be prescribed, for example hysteroscopy (a minimally invasive method using an optical tube).
How to feel about “grandmothers’ recipes”?
In preparing this article, we conducted a survey and found out that, without exaggeration, a huge number of women are trying to cope with the situation of uterine bleeding on their own - using traditional medicine recipes. Naturally, in this case we are talking about moderate or scanty bleeding. The reasons for this state of affairs most likely lie in the absence of a certain culture of treatment and constant monitoring of one’s health. On the other hand, many books and brochures with various folk recipes can now be bought at any bookstore. It is also not difficult to find such information on the Internet. Recipes based on nettle, yarrow, St. John's wort, and viburnum are presented there as safe, effective, affordable, and, moreover, tested by several generations of women.
Without criticizing traditional medicine and recognizing its merits, we would like to focus your attention, first of all, on the inadmissibility of self-medication in case of uterine bleeding. As noted above, the causes of bleeding can be different. Bleeding is only a consequence, a symptom of the disease. You need to treat what caused it: tumor, dysfunction, uterine fibroids, endometriosis, etc. Therefore, it is extremely important to consult a doctor in a timely manner and correctly diagnose the causes of bleeding. And only then, in the treatment regimen, in some cases folk remedies can be used.
Heavy periods after a cleanse, abortion or miscarriage
If a woman has had an abortion or miscarriage, her body has experienced severe stress, and also a major hormonal change. According to statistics, approximately 12% of women have irregular menstrual cycles after an abortion; they may also have heavy periods after an abortion. If it was a medical abortion, then uterine bleeding very often appears. To avoid serious complications, it is better to immediately seek help from a doctor.
After curettage, a woman may have bleeding similar to menstrual bleeding. This is how it should be, there is no need to be afraid. After a few days, the discharge will change color (turn brown) and gradually dry up. But real menstruation should begin in 26-35 days (this depends on the length of the cycle), it proceeds as usual. But if heavy periods appeared after cleansing, i.e. a woman has to change pads every 2-3 hours, she needs to consult a doctor. An unpleasant feeling in the lower abdomen and elevated temperature may indicate inflammation.
Bleeding due to uterine fibroids, adenomyosis, endometrial and cervical canal polyps
Uterine fibroids, endometriosis and polyps and endometrial hyperplasia are diseases associated with benign growth of uterine tissue. They appear most often during reproductive age.
All this pathology is easily diagnosed using ultrasound. As a rule, no additional examination methods are required. You can read about possible treatment options for uterine fibroids in the corresponding section of the website www. ya-zdorova.ru. In the presence of pathology of the uterine cavity, hysteroscopy with the appropriate amount of surgical intervention is indicated to eliminate the cause of bleeding.
Obstetric hemorrhage
This term refers to intense bleeding that occurs immediately after childbirth. Their cause is a violation of the contractility of the uterus (atony or hypotension of the uterus), or a pathology associated with the blood coagulation system. Hypotony is a decrease in the tone of the uterus, which leads to its inability to actively contract. Atony is a complete loss of the ability to contract and respond adequately to medications and other types of stimulation. Obstetric hemorrhage is very dangerous because it leads to a large loss of blood in a short time. Very often the question is literally about saving a woman’s life - and then doctors decide on a hysterectomy, that is, removal of the uterus.
What symptoms may occur?
You need to visit a gynecologist if you have the following symptoms:
- You have noticed that your periods have become heavier than before. A woman may notice that she begins to spend more hygiene products and has to choose more “drops”.
- During your period, you begin to feel worse, and pain occurs. Worried about weakness, increased fatigue.
- The duration of menstruation has increased.
- There is pressure, discomfort, pain in the pelvis.
- Enlargement of the abdomen, something dense can be felt in it. If the fibroid is large enough, it protrudes and is noticeable when the woman lies on her back.
- I am worried about pain in the pelvis and legs.
- Urination has become frequent or difficulty occurs during urination.
- Constipation occurs constantly.
- Your vagina leaks blood when you don't have your period.
These signs may indicate not only fibroids; they occur in various diseases. An accurate diagnosis will be made by a gynecologist after examination and ultrasound.
Bleeding in cancer
One of the first manifestations of uterine and cervical cancer is uterine bleeding, although, as a rule, the process may not be at such early stages. It may not cause the woman any painful sensations, be scanty and short-lived. If such bleeding occurs during a regular menstrual cycle, you should immediately consult a doctor.
A timely visit to a gynecologist allows you to detect a tumor at an early stage and significantly increases the chances of a successful cure. The diagnosis can be made based on a gynecological examination, ultrasound and a number of tests.