Initial appointment with a THERAPIST with 25 years of experience
ONLY 1800 rubles!
(more about prices below)
To study the state of the blood coagulation system, a prothrombin test is used. In this article we will talk about what a blood test for prothrombin is and what the norm of this substance is. The study of prothrombin is one of the most important components of a coagulogram.
Get tested
If you are in doubt about the choice of laboratory testing, make an appointment with a therapist or consult by phone
+7
Price of a blood test for prothrombin
| Service | Price |
| Prothrombin (according to Quick) + INR | 250 rub. |
| APTT | 190 rub. |
| Thrombin time | 200 rub. |
| Fibrinogen | 190 rub. |
| Antithrombin III | 350 rub. |
| D-dimer | 1100 rub. |
| Protein S | 1700 rub. |
| Protein C Lupus anticoagulant | 1320 rub. |
Where to take a prothrombin test in St. Petersburg?
You can get tested for antibodies to prothrombin in St. Petersburg at our MRI center and RIORIT clinic. You can make an appointment and find out the cost of the examination by phone..
MRI and ultrasound center RIORIT
Area:
Kalininsky
Metro:
metro station Grazhdansky Prospekt, metro station Devyatkino, metro station Prospekt Prosveshcheniya
Address:
St. Petersburg, Kalininsky district, st. Rustaveli, 66 lit. G
Telephone:
Equipment:
Siemens, open type
Schedule:
Around the clock
What is important to know about registering for tests
Do I need to make an appointment: It is better to make an appointment for blood tests and smears to avoid waiting in the treatment room.
Opening hours of the treatment room: Mon - Fri from 8:00 to 12:00
Form of payment: cash, credit cards
Doctor's referral: not required
Minimum patient age: Urinalysis, stool test - any age, blood test - from 10 years
How quickly the results are ready: Average time 1-2 business days. Ready results can be received by email or during a second visit to the clinic
Indications for prescribing prothrombin time analysis
- detailed examination of the whole body;
- pre- and postoperative examination;
- suspicion of impaired hemostasis;
- suspicion of hidden bleeding;
- suspicion or presence of thrombosis;
- control of hemostasis functions during treatment with direct and indirect anticoagulants;
- diagnosis of liver diseases;
- a history of cardiovascular diseases and their complications, as well as thromboembolism of various organs;
- diagnosis of nosebleeds and hemorrhages in various organs and tissues;
- diagnosis of chronic anemia.
Preparing for a blood test for prothrombin time:
- do not eat 12 hours before taking a blood test;
- do not smoke 30-60 minutes before the test;
- limit physical and psycho-emotional stress;
- if possible, discontinue medications that affect coagulation or prescribe a study before starting therapy;
- follow a diet excluding fried and very fatty foods.
Prothrombin - what is it?
Prothrombin is a complex type of protein structure that is responsible for the state of the blood coagulation system and its ability to thicken. The human body needs blood in a liquid state: it transports useful substances to organs and tissues, protects against infections, and also maintains the desired body temperature. But, if some area of the external or internal tissues is injured, bleeding occurs. To stop it, a blood clot is created - a kind of plug that clogs the damaged area. The ability of blood to clot is used by the body precisely for the purpose of thrombus formation, and the most important participant in this process is prothrombin. A study of the prothrombin norm is performed in the following cases:
- Before surgery.
- During rehabilitation after injury or surgery.
- Before labor begins
- To diagnose the presence of diseases associated with blood clotting.
Prothrombin is formed in the liver; its synthesis is due to the presence of vitamin K in the body. By examining the prothrombin rate, the doctor can not only assess the functioning of the blood coagulation system, but also diagnose diseases of the digestive system and liver. It is possible to determine whether the level of prothrombin in the blood is normal by performing a test for the prothrombin index, also known as PTI. This parameter is calculated as a percentage of the normal time required for the blood clotting process to the actual plasma clotting time.
Blood clotting process
If we briefly describe the coagulation process, it will consist of the following phases:
- prephase or vascular-platelet hemostasis;
- prothrombinase;
- thrombin;
- fibrin;
- postphase, which consists of two parallel processes: retraction (reduction and thickening of the blood clot) and fibrinolysis (dissolution of the blood clot).
Thus, for the formation of a blood clot, several components are necessary: the vessel wall, blood elements, and the plasma blood coagulation system.
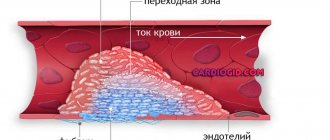
This process looks like this: damage to the vascular endothelium causes activation of enzymes of the coagulation system, which, in turn, forms fibrin threads, which are the framework for the formation of a blood clot.
The coagulation system is activated in two ways:
1. External - when coagulation factors come into contact with damaged tissues outside the vessel.
2. Internal - associated with destroyed blood cells and damage to the endothelium, that is, the process starts inside the vessel itself.
When is laboratory testing performed?
Prothrombin analysis is prescribed in the presence of the following conditions:
- Atherosclerotic changes.
- Varicose veins.
- Liver dysfunction.
- Changes in the coagulation system.
- With vitamin K deficiency.
- For antiphospholipid diseases.
- In case of autoimmune diseases.
- To monitor the process of treatment with anticoagulant drugs.
Complexes with this research
Pregnancy planning.
Clinical indicators 3,890 ₽ Composition For those at risk of COVID-19 Diagnosis of diseases complicating the course of coronavirus infection 2,570 ₽ Composition
Examination during pregnancy. 3rd trimester 5,820 ₽ Composition
IN OTHER COMPLEXES
- Miscarriage RUB 28,220
- Expanded hospital complex RUB 4,390
- Joining IVF RUB 15,090
- Examination during pregnancy. 1st trimester 10,260 RUR
- Female infertility RUB 9,760
How to prepare for the analysis?
Prothrombin levels and its normal levels in the blood may vary depending on various factors. In order for the prothrombin test to give the most accurate results, it must be taken in compliance with certain rules, in particular:
- Come to the clinic on an empty stomach (at least four hours must pass after your last meal).
- Tell your doctor if you are taking any medications. If you are taking medications that affect blood clotting, notify your doctor about this before issuing a referral for testing.
When testing for prothrombin, the blood is placed in a special container filled with sodium citrate. After this, the substances are mixed and sent to a centrifuge, which allows the plasma to be separated from the blood cells. Then, when the process is completed, a tissue substance is placed in the container, on which the resulting solution is tested.
Coagulogram. What is this?
You can take a coagulogram test on any day (except Saturday and Sunday) in the laboratory of the National Health Institution “Nodal Hospital at the station. Vyborg. The result is issued on the same day. (office no. 4)
Coagulogram (syn.: hemostasiogram) is a set of blood indicators that characterize its ability to clot. Blood clotting is one of many protective functions that maintain the normal functioning of the body by preventing excessive blood loss.
The coagulogram can be basic or extended. Typically, a baseline study is ordered first. It helps to understand where in the system the deviation from the norm occurred. And if a pathology is detected, a detailed study is carried out, as a result of which not only qualitative changes are determined, but also quantitative ones.
Material for taking a coagulogram: Venous blood Indications for a coagulogram:
- monitoring the state of the hemostasis system;
- routine examination before surgery;
- pregnancy;
- gestosis (complication of a normal pregnancy);
- monitoring of anticoagulation therapy; (for example, taking heparin)
- monitoring of antiplatelet therapy;
- hematological diseases;
- varicose veins Moscow
- atrial fibrillation;
- Coronary heart disease (CHD);
- stroke;
- Pulmonary embolism (PE);
- DIC syndrome; (impaired blood clotting due to massive release of thromboplastic substances from tissues)
- taking medications (oral contraceptives, glucocorticosteroids, anabolic steroids);
- cirrhosis of the liver.
Basic coagulogram parameters:
- Fibrinogen . The most important test of the state of the coagulation system.
- Prothrombin index (PTI), INR (international normalized ratio), PTT (prothrombin time) . Usually one of these tests is performed, based on the equipment available in the laboratory. The most universal test is INR. All of these studies show an extrinsic clotting pathway.
- Activated partial thromboplastin time . In the test you can find the abbreviation APTT.
- Thrombin time.
Additional coagulogram parameters:
- Protein C. An insufficient amount of this parameter leads to thrombosis.
- Antithrombin . Like protein C, it is a factor in the anticoagulation system.
- D-dimer . Formed as a result of the destruction of a blood clot.
- Lupus anticoagulant.
- Plasma tolerance to heparin.
- AVR (Activated Recalcification Time).
- RFMC (soluble fibrin-monomer complexes).
- Plasma recalcification time.
Coagulogram norms (Table):
| Clotting time | ||
|
| |
| Bleeding time | ||
|
| |
| Analysis indicator | Designation | Norm |
| Prothrombin time according to Quick | PV | 11-15 sec |
| INR (International Normalized Ratio) | INR | 0,82-1,18 |
| Activated Partial Thromboplastin Time | APTT | 22.5-35.5 sec |
| Activated Recalcification Time | AVR | 81-127 sec |
| Prothrombin index | PTI | 73-122% |
| Thrombin time | TV | 14-21 sec |
| Soluble fibrin-monomer complexes | RFMK | 0.355-0.479 units |
| Antithrombin III | AT III | 75,8-125,6% |
| D-dimer | 250.10-500.55 ng/ml | |
| Fibrinogen | 2.7-4.013 g | |
Preparing for a coagulogram:
- This analysis is carried out in vitro (in vitro - outside the body). Blood is taken from a vein.
- Blood is donated on an empty stomach. The last meal should be no later than 8-12 hours before the test.
- You cannot drink any drinks (coffee, tea, and especially alcohol). Only clean water is allowed.
- When taking a coagulogram, it is necessary to indicate the medications you are taking - especially those that affect the blood clotting process Moscow
- The emotional state of the patient is very important. You need to try not to be nervous, to be calm and balanced. Muscle overstrain also negatively affects the results of the study.
- It is useful to drink an additional glass of cold water right before taking the test.
- Interpretation of the results is carried out only (!) by a specialist.
Coagulogram during menstruation:
A coagulogram during menstruation is not able to give clear results. The fact is that during this period the blood is diluted and it is not possible to test its clotting abilities. Therefore, to carry out the procedure, it is advisable to wait until the end of the critical days, but not to take the test immediately.
During this period, the body, on the contrary, is interested in removing excess blood from the uterus, so coagulation is somehow impaired. After the critical days, everything returns to full normality, and the woman can easily get tested. Again, it is also not worth carrying out the procedure just before your period; the body is preparing for the withdrawal process and the blood gradually thins out. In this case, the coagulogram will be unreliable and will have to be taken again
Factors influencing the result of a coagulogram?
Factors distorting the result of the analysis:
- violation of the technique of taking and storing material;
- blood sample hemolysis;
- the presence of fat drops in the material;
- ingress of tissue thromboplastin from the patient’s capillary blood;
- the presence of a lupus anticoagulant in the patient’s blood (directly inhibits coagulation factors);
- sharply increased or decreased hematocrit;
- anticoagulants entering the blood sample;
- transfusion of donor blood components in the last month (distorts the fibrinogen indicator, APTT).
Factors that increase INR and PT and reduce PI:
- drinking alcohol, fatty foods;
- medications: antibiotics, anabolic steroids, aspirin (in large doses), acetaminophen, allopurinol, warfarin, vitamin A, heparin, glucagon, diuretics, MAO inhibitors, indomethacin, kanamycin, clofibrate, corticotropin, levothyroxine, mercaptopurine, methyldopa, mefenamic acid, mithramycin, nalidixic acid, neomycin, nortriptyline, propylthiouracil, reserpine, streptomycin, sulfonamides, tamoxifen, tetracyclines, tolbutamide, phenylbutazone, phenytoin, quinidine, quinine, chloral hydrate, chloramphenicol, cholestyramine, cimetidine, ethanol.
Factors that reduce INR and PT and increase PI:
- excess intake of vitamin K from food (found in beef or pork liver, green tea, broccoli, chickpeas, cabbage, turnips, soy, green leafy vegetables);
- diarrhea and vomiting (due to dehydration and increased blood viscosity);
- medications: vikasol (vitamin K analogue), antacids, antihistamines, ascorbic acid, barbiturates, griseofulvin, digitalis, diuretics, colchicine, corticosteroids, caffeine, xanthines, meprobamate, oral contraceptives, rifampicin, theophylline, phenobarbital, chloral hydrate.
Factors that increase APTT:
- antibiotics, asparaginase, aspirin, warfarin, heparin, thrombolytic drugs (streptokinase, urokinase), quinine, cholestyramine, cyclophosphamide, enoxaparin.
Factors that increase fibrinogen content:
- estrogens, oral contraceptives.
Drugs that reduce fibrinogen levels:
- atenolol, valproic acid, lipid-lowering drugs, corticosteroids, progesterone, thrombolytic drugs (streptokinase, urokinase), fluorouracil, estrogens, fibrin degradation products, nicotine.
Prothrombin according to Quick
The Quick prothrombin test is the most accurate way to analyze the activity of this protein, which leaves the prothrombin index test far behind. This is not the most common type of analysis. As a rule, it is performed during screening tests, in the presence of blood diseases, and also as a monitoring measure when the patient is using anticoagulant drugs. Normally, the Quick prothrombin percentage of 30-40% corresponds to 50-60% of the prothrombin index.
Prothrombin time indicators
Prothrombin time is a special laboratory indicator that reflects the external pathway of activation of the blood coagulation system.
Often, prothrombin time is determined with activated partial thromboplastin time (aPTT), which evaluates the intrinsic activation pathway. Taken together, these two indicators reflect the coagulation and anticoagulation systems as a whole and its changes in the pathology of internal organs.
The normal prothrombin time is 11-16 seconds.
Also, to determine the functions of the coagulation system, other indicators are determined - prothrombin index and international normalized ratio (INR).
Prothrombin index (PTI) is a percentage indicator determined by the ratio of the prothrombin time of control plasma to the PTI of the test human plasma. Normally it should be 95-105%.
International Normalized Ratio (INR) – This test compares blood taken from a patient to internationally normalized plasma.
The norm value can range from 0.85-1.25.
It should be borne in mind that during warfarin therapy, indicators may change, so it is necessary to take into account medical history.
Decoding and norm
The normal level of this substance in the blood can vary from 70 to 140%. Such a large difference between the upper and lower limits of the norm may be due to the influence of various factors - age and gender, pregnancy, taking certain medications. For example, the norm for prothrombin during pregnancy differs from the normal level for a woman who is not in an “interesting situation.” Also, for women, the prothrombin rate may vary depending on factors such as the day of the menstrual cycle. A general practitioner will help you make a competent interpretation of the prothrombin test in St. Petersburg
or a specialized specialist.
Prothrombin index during pregnancy
A hemostasiogram (coagulogram) during pregnancy is mandatory, since the prothrombin index of a pregnant woman is an important indicator that makes it possible to prevent severe bleeding during childbirth or prevent the formation of blood clots.
If a woman’s prothrombin index is reduced (less than 80%), then there is a risk of bleeding, and it makes sense to prescribe coagulants to the patient. If the prothrombin index is elevated, that is, it is about 100%, the pregnant woman is prescribed drugs that prevent increased blood clotting.
An important indicator for a pregnant woman is the prothrombin time. A doctor who knows the clotting time of a woman in labor can prevent bleeding or, if it does begin, the development of hemolytic shock, which in most cases is the cause of death of a woman during childbirth.
Pregnant women have different attitudes towards the need to register with an antenatal clinic. Some people follow all the doctor’s recommendations, while others believe that a large number of tests only harms their health and family budget.
The main thing that a pregnant woman should remember is that if the doctor does not know that her prothrombin index is low, he will not be able to prevent placental abruption or bleeding after childbirth, and vice versa, a high prothrombin index will be able to promptly indicate to the doctor the danger of developing placental vascular thrombosis.
Prothrombin according to Quick is reduced
Prothrombin will show a value below normal if the patient has the following diseases or conditions:
- lack of fibrinogen in the blood;
- liver diseases characterized by changes in the process of synthesis of blood clotting factors;
- congenital deficiency of certain blood clotting factors;
- hypoprothrombinemia;
- lack of vitamin K;
- taking anticoagulant drugs, coumarins, steroids, thyroxine and other substances that weaken the effect of vitamin K.
Quick prothrombin below normal is also one of the signs of leukemia. Low prothrombin may indirectly indicate the presence of hepatitis and a disease such as cirrhosis.
If the test results show a prothrombin level below normal, do not rush to get upset. Low prothrombin is not the only indicator by which the state of the blood coagulation system is determined. Contact a competent and experienced specialist who, after reading the transcript, will give comprehensive advice on your health.
Methodology for studying prothrombin time
To determine the prothrombin time, fresh plasma from the patient being studied is used. The blood is collected in a tube containing sodium citrate to bind blood calcium. Next, the sample is mixed, centrifuged, and an excess amount of calcium is added at a temperature of 37C to restore the blood’s ability to clot. After this, tissue coagulation factor (better known as factor III) is added and the time of blood clot formation is noted.
It should be taken into account that in some pathologies the prothrombin time may be increased or decreased.
Prothrombin time is increased with:
1. Congenital deficiency of certain blood coagulation factors such as II (prothrombin), V (Proaccelerin), VII (Proconvertin), X (Stewart-Prower factor).
2. Acquired deficiency of blood coagulation factors resulting from diseases (chronic liver and kidney diseases, amyloidosis, autoimmune diseases).
3. Disseminated intravascular coagulation syndrome (DIC syndrome), which develops in blood diseases, including cancer.
4. The use of indirect anticoagulants (warfarin) in the main therapy.
5. Developmental hypovitaminosis K (for diseases of the pancreas and gall bladder, dysbacteriosis, malassorption syndrome).
6. An increase in the level of antithrombin in the blood.
The use of certain drugs also leads to an increase in prothrombin time (some antibiotics, steroid hormones, laxatives, acetylsalicylic acid in doses exceeding therapeutic ones).
Prothrombin time is reduced with:
1. Polycythemia.
2. Pregnancy in the last trimester.
3. Thrombosis of deep veins of the lower extremities.
4. Use of acetylsalicylic acid in small doses.
5. Taking oral contraceptives.