Coagulation, manifested by clots during menstruation, is a fairly common symptom, in most cases not the result of a disease. However, if there are a lot of bloody clots, menstruation is accompanied by severe pain and excessively heavy and prolonged bleeding, this means a deviation from the norm and the need for diagnosis and treatment by a gynecologist.
Common causes of clot formation are hormonal imbalances, bleeding disorders, as well as pathologies such as endometriosis, polyps and fibroids in the uterus.
Monthly vaginal bleeding occurs as a result of detachment of the epithelial layer of the uterus, so it is natural that the discharge is heterogeneous. Most women experience clots during menstruation.
What is a clot
During menstruation, each woman has a different intensity of bleeding, and the color of the spotting is also different. The amount of blood lost and its thickness also vary from person to person, but in all women, without exception, anticoagulants are secreted during menstruation, which slow down clotting. If these substances do not do their job, small lumps may form, which are normal and not dangerous.
Treatment will most likely not be required if:
- the woman is not yet 18 years old, her periods have recently started and her cycle is sometimes “strange”;
- if a woman has recently given birth or undergone surgery;
- if the pregnancy was terminated in the near future or curettage was performed;
- the uterus is not located naturally and the woman knows about it;
- woman uses a spiral.
A large blood clot may be released in the morning; it is formed due to the fact that the woman has been lying in one position for a long time and the discharge has had time to coagulate. Menstruation with lumps is normally not accompanied by pain, fever, or poor general health. The discharge itself looks like pieces of jelly with veins.
Content
- Why do clots come out during menstruation?
- Menstruation with clots: reasons
- Menstruation with clots: reasons
- Brown periods with clots: treatment
Some women experience brown periods with clots.
Often they are not a sign of serious illness. But still, if you find blood clots during your period, consult your doctor and undergo an examination to determine the cause of their occurrence. We will try to understand the main reasons why periods come in clots further in the article.
When to suspect pathology
There are a number of signs that can indicate to a woman that something is going wrong in her body. A woman doesn’t need her period to miss out on life for a week. This is a natural process that should be easy and painless.
- Bleeding lasts longer than normal. The normal duration is 3 to 5 days.
- Blood is lost profusely, a woman uses more than 2 packs of sanitary pads (100-150 ml of blood loss).
- Strong, unpleasant odor of discharge.
- Severe pain. It hurts to touch the stomach; every movement increases the pain.
- The cycle is not stable.
- Menstruation comes either too often or late. Normally, the duration of the cycle from 1 day of menstruation is 26-30 days.
If there is at least one point that matches, this is a reason to visit your gynecologist and share the problem.
If a woman is bothered by spotting with blood for several days before her period, the beginning of the cycle is considered from the first day of the appearance of this discharge.
Only a detailed study, including tests, smears, ultrasound and examination, will help the doctor draw conclusions about women’s health.
When to see a doctor?
If large clots appear during menstruation, you should consult a gynecologist, especially if the discharge is heavy, prolonged and accompanied by pain.
You should not worry if your periods come regularly and there is no or moderate pain.
It is necessary to go to the gynecologist about clots during menstruation in the following situations:
- Menstruation lasts more than a week, the discharge is heavy.
- Pregnancy is planned and attempts are made to conceive. In this case, the discharge may indicate that the egg has been rejected and a miscarriage has occurred.
- Discharge during menstruation contains large clots with an unpleasant odor.
- A woman experiences severe pain during her period. This may be a sign of inflammation or hormonal disorders.
Can hormonal imbalance cause the formation of lumps?
Young teenage girls often experience minor hormonal imbalances. After all, the cycle is not established immediately and lumps of menstruation are not uncommon. It’s a completely different matter when an adult woman faces hormonal imbalances, the causes of which can be very different.
- Constant stress
. Many diseases are triggered due to trivial problems at work, quarrels, and tension in the family. Including hormonal problems. - Abortion
. The body experiences enormous stress after termination of pregnancy for personal or medical reasons. In this case, the restructuring of hormones occurs quickly, menstruation comes, although it was not planned. This can cause even very large lumps to appear. - Changing the method of birth control
. Causes a hormonal imbalance, the nature, duration and amount of discharge may change. Much depends on how well this or that method was chosen. - Climax
. A very common cause of large lumps during menstruation is age. At risk are women who are 45 years of age or older, whose bodies are slowly preparing for menopause.
A woman's hormonal levels can be unstable for many reasons. The main ones are in the list, each of them can disrupt the cycle to one degree or another. Blood clots are the most common manifestation.
Discharge with clots like liver during menopause
Natural bleeding during menopause is due to age-related reasons - they are associated with hormonal changes in the whole body, the decline of reproductive function (childbearing period), and are a transition to the elderly phase.
Pathological changes accompanied by excessive bleeding with clots occur for various reasons:
- Use of contraceptives.
- Menopausal changes that are not characteristic of real age. May begin at the age of 30–34 years. The reason may be early menstruation, absence of pregnancies or a long gap between births, diseases of the reproductive organs, abortion, or refusal of breastfeeding. Lately they are becoming more common.
- Hereditary factors.
- Complications after infectious diseases and surgical interventions.
- Age-related changes in blood clotting, tendency to blood clots. As a result, a lot of blood accumulates in the uterine cavity and clumping occurs.
- Constant use of medications for chronic diseases (endocrine system, diabetes) that affect the overall hormonal balance of the body.
- Inflammatory processes and tumor-like pathologies in the lower spine, genitourinary system, and intestines.
Endometriosis and adenomyosis as a cause of lumpy discharge
Endometriosis is a disease characterized by the growth of the uterine lining outside its confines. The disease is common and is accompanied by very painful and prolonged menstruation. Also, failures up and down (less often) are not uncommon. Menstruation is heavy, blood loss is often greater than in healthy women. Clotted blood is a common symptom that identifies endometriosis.
Adenomyosis, in turn, affects not only the uterus, but also nearby organs. The appearance of these diseases still does not have specific causes; it is generally accepted that because of it the uterine mucosa can resemble a honeycomb. Possible reasons may include:
- surgical operations in the body of the uterus;
- abortion;
- cauterization of erosion;
- curettage of the uterus;
- C-section.
Over time, untreated diseases affect the contractile function of the uterus, then it is no longer the coagulated blood that comes out as clots, but the sloughed uterine mucosa.
Lumps with endometriosis are denser, often larger, this is due to cycle disorders, over time the walls thicken unevenly.
Pathological discharge
Scarlet bloody.
When they appear a few days before menstruation, they indicate erosion of the cervix, after sexual intercourse - about trauma to the vagina, and during pregnancy - about the threat of termination2. In some cases, such discharge is associated with endometriosis, uterine fibroids, and endometritis4,5.
Smearing brown.
They are a sign of hormonal disorders2,3 and/or endometrial hyperplasia6.
Foamy, abundant, yellow-green2,7.
Indicate infection of the vagina, fallopian tubes, ovaries or other organs of the reproductive system. May be one of the symptoms of sexually transmitted diseases.
Thick purulent3.
They are a sign of purulent cervicitis and can worsen with stress or during bowel movements. Unlike normal white discharge after menstruation, it has a more viscous consistency.
Pinkish with an unpleasant odor2.7
. May indicate the development of endometritis. Usually appear before menstruation.
Watery, dirty gray color 2.7
. This is a symptom of diseases such as endocervicitis, endometritis. They are observed both before and after menstruation. Dirty gray mucus with a strong fishy odor may indicate vaginal dysbiosis.
Curdled white 2.7.
Heavy white discharge after menstruation and during other phases of the cycle may be a sign of vaginal candidiasis (thrush). They may be accompanied by the appearance of a white coating on the external genitalia, itching, and burning.
Up to contents
Polyposis can cause clots to form
Women over 30 years of age are at risk for this disease. The main way to identify polyps is through clots in menstrual fluid. The endometrium grows, filling the uterus, and during menstrual bleeding, parts of it are also released.
- Menstruation becomes irregular and painful. A woman temporarily loses her legal capacity and finds it difficult to do household chores and work.
- Clots may come out in chunks. Patients characterize them as “scraps” of tissue.
- The cycle is not regular, sometimes menstruation occurs every other time.
It is also interesting that at the beginning of the disease, the blood clots are not large and resemble coagulated blood.
Polyposis is a benign disease, with the exception of the only cancerous form - adenomatous.
However, from cycle to cycle they increase, often becoming denser. If not all of the remnants of the old endometrium have come out, this can trigger inflammation. Ultrasound will help identify polyposis.
What happens during menstruation?
Every month, regardless of a woman’s wishes, her uterus prepares to receive a fertilized egg. Under the influence of hormones, the inner layer of the uterus, the endometrium, begins to thicken. If pregnancy does not occur, the level of hormones decreases, the blood supply to the mucous membrane of the inner surface of the uterus stops, the endometrium is rejected and excreted through the genital tract. Thus, menstrual discharge is a complex mixture consisting of blood, mucus, endometrial particles, and vaginal cells.
What other causes of lump formation
The cause of lumpy discharge does not always lie in the uterus. Sometimes, even the most unexpected illnesses affect women's health.
- Inflammation in the genitals. Various infections of both internal and external parts of organs can cause strange menstruation with lumps. Your period may be dark, thick, or excessively thin.
- Obesity. Excess weight affects all body systems, including the level of estrogen in the blood. The level affects the rate of endometrial growth.
- Thyroid diseases, diabetes, blood pressure. These diseases disrupt the body's metabolism, which can lead to heavy menstruation with lumps of clotted blood.
- Taking medications. Some medications can affect the course of your cycle.
- Excess vitamin B. Causes the formation of dark-colored blood clots during menstruation. Before critical days and in the middle of the cycle, mucus with blood streaks appears.
- Temperature. Heavy menstruation with lumps can be caused by commonplace acute respiratory infections. An increase in temperature most often affects only one cycle, but it frightens the woman no less.
- Active sports, loads before the start of the cycle. They increase blood flow to the pelvic organs, due to which menstrual periods become abundant and blood clots faster.
Each of these reasons or their combination can affect the quality of the cycle once or affect the overall health of the female reproductive system. If lumps of blood appear constantly, it is better to find out why this is happening from your gynecologist and whether this is normal.
Possible reasons for the violation
Only a qualified specialist can give an accurate diagnosis of the cause of menstrual periods; on your own, you can only guess what happened to you. Often, heavy discharge with pieces of meat during menstruation is a sign of illness. Do not delay your visit to the gynecologist and do not self-medicate, following the advice on women's forums.
Gynecological diseases can also cause liver clots.
Bacterial vaginosis
When there is no menstruation and white or yellow vaginal discharge appears with a specific odor, vaginosis is suspected. The disease develops when the microflora is disrupted. Vaginosis can also manifest itself during menstruation: it becomes abundant, flows like a river, and clots with pieces of meat fall out.
Factors causing vaginosis:
- Washing your genitals too often.
- Insufficient washing of the genitals.
- Use of hormonal drugs.
- Frequent change of sexual partners.
Endometriosis
The reason for this is hormonal imbalance. The uterus produces too much endometrium, which extends beyond its boundaries. The endometrium begins to peel off and large blood clots can be seen on the pad. Pain occurs before, during and after menstruation. The disease causes discomfort during sexual intercourse. If left untreated, endometriosis can cause infertility. A gynecologist will help you find the answer to the question of how to stop heavy periods with blood clots due to endometriosis.
Uterine fibroids
Myoma is a benign formation, but in severe cases it can become malignant. The cause of fibroids is hormonal imbalance. Often women before menopause can catch the disease. Myoma has no symptoms. The girl does not notice anything except incomprehensible discharge during menstruation. The tumor may either disappear over time or increase in size. In the latter case, it is necessary to remove the fibroid surgically. Myoma prevents blood from flowing freely, so it clots in the vagina.
- Joint pain before menstruation
Uterine polyp
Polyp occurs due to hormonal imbalance. This is a benign formation. Too much estrogen is produced, and the inner walls of the uterus build up layers of endometrium. The result is growths called endometrial polyps. The disease is accompanied by the release of large clots, pain in the lower abdomen, pain during sexual intercourse, and uterine bleeding after menstruation. A characteristic symptom of polyps is infertility.
Iron-deficiency anemia
These strange words mean that your body simply does not have enough iron. During menstruation, girls lose a lot of this substance, as it comes out along with the blood. Blood clots are accompanied by loss of strength, dizziness, weakness, and pallor.
Even if the product is rich in iron, it is not always absorbed. Heme (ferrous) iron is found in foods of animal origin and is absorbed by 25%, while non-heme (ferric) iron is found in foods of plant origin. It is absorbed by a maximum of 10%. Therefore, a vegetarian girl may experience iron deficiency and develop iron deficiency anemia.
Eat the following foods:
- pork liver;
- beef liver;
- hard cheese;
- eggs;
- mackerel;
- pork;
- chicken;
- cottage cheese.
Thrush
Thrush can also cause unpleasant sensations and menstruation with pieces of “something incomprehensible.” It causes itching and burning, inflammation of the genital organs. It also makes itself felt during a woman’s absence of menstruation – white sticky discharge in the form of lumps, an unpleasant odor, pain during sexual intercourse and urination. Your periods will be heavy with clots.
Endometritis
Endometritis is a disease of the uterus that is accompanied by dark discharge after childbirth. The cause is a change in the vaginal microflora and the proliferation of pathogenic bacteria. The disease could be caused by cesarean section, damage to the walls of the uterus during childbirth, accumulation of blood in the uterine cavity due to decreased muscle tone, decreased immunity during pregnancy, and blood loss during childbirth.
The woman’s temperature rises to 38°, pus comes out of the vagina, her stomach hurts, her head hurts, her skin becomes dry, and tachycardia is observed - increased heart rate. Your stomach may even swell. With endometritis, large pieces of blood similar to the liver come out during menstruation.
If you notice these symptoms, immediately run to the doctor. He will prescribe you antibacterial drugs, conduct anti-inflammatory therapy, and uterotonic therapy.
Pathological changes in female organs
There are serious problems that affect a woman's overall health, including the possibility of blood clots during her period.
- Myoma
. This is a serious benign neoplasm that disrupts the “standard” process of expelling the obsolete layer of the endometrium. The clots come out more than once, but over several days. - Hyperplasia
. The disease affects many women and is always accompanied by the release of dark lumps. - Cancerous changes
. Due to the tumor, the removal of the rejected unnecessary layer is difficult. The blood coagulates and causes fear. The lumps can be really huge, there are a lot of them, and menstruation causes severe pain. - Polycystic
. Ovarian cysts trigger hormonal problems. Bleeding in the middle of the cycle is not uncommon, and menstruation itself causes excruciating pain.
Pathological diseases can be life-threatening for a woman. Most of them cause pain during sexual relations, and contact may result in bleeding. Heavy periods and bleeding between periods can activate or worsen anemia.
When to ask for help
You should consult a doctor during menstruation in chunks if the clots are accompanied by the following unpleasant phenomena:
- Menstruation is heavy and lasts more than seven days.
- A lot of clots are released at once.
- Huge discharge.
- You can't get up from the pain.
- You feel an unpleasant, specific smell.
IMPORTANT! If you have no health problems, your menstrual bleeding will smell faintly like raw meat or iron. If there is a violation, you will smell rotten meat or fish.
Photo of menstruation with pieces of endometrium:
Diagnostics
The examination involves the use of laboratory, hardware and instrumental techniques. The most informative:
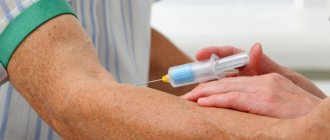
- Blood test (clinical, biochemical), general urine test. They help detect the inflammatory and infectious process, hormonal imbalance, and anemia. The determination of blood clotting is valuable.
- Ultrasound of the uterus and appendages.
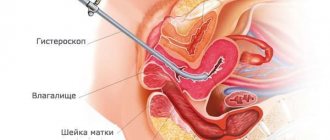
- Hysteroscopy.
- Laparoscopic examination (in 90% of cases accompanied by a biopsy).
- MRI. The method of complex radiation imaging is used to confirm the presence of a tumor process.
Diagnostic measures are prescribed taking into account the expected type of disorder and the cause of its development.