What is D-dimer
D-dimer is the part of the protein that remains after the blood clot breaks down. It is a breakdown product of fibrin, the fibers of which form a blood clot. D-dimer consists of two D-particles of fibrinogen contained in blood plasma.
The amount of D-dimer in the blood can be determined using a test. If this indicator is excessively high, then the patient has a high risk of thrombosis.
This analysis is not included in the mandatory laboratory tests. It is prescribed only to those who are at risk for thrombosis.
Decoding the results
Increased D-dimer levels
When the level of D-dimer in the blood increases, it is necessary to search for a probable cause, since some conditions accompanied by an increase in its concentration require immediate medical attention.
An increased level of D-dimer as a physiological norm occurs in old age (after eighty years), as well as during pregnancy (gradually increasing in proportion to the gestational age).
- Outside of pregnancy, a high D-dimer may indicate the presence of thrombosis in the veins or arteries. This is usually accompanied by complaints characteristic of thrombosis (pain in the limb, swelling, redness or pallor) or thromboembolism (shortness of breath, chest pain, hemoptysis). In this case, help must be urgent. But in approximately 20-30% of cases, thrombosis is asymptomatic. In this case, your doctor will help you draw up an examination plan and decide on tactics.
- D-dimer often increases in people suffering from obesity, autoimmune diseases (rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus, etc.), as well as liver disease and cancer. In this case, the increase is most likely secondary, and if there are no signs of thrombosis, observation by your doctor is sufficient.
- Often, D-dimer is elevated in older people (also without signs of thrombosis). Prescribing thinning drugs in this situation is not always necessary, since the risk of bleeding must also be taken into account.
- Since D-dimers are breakdown products of already formed blood clots, their concentration may increase after bleeding or during the period of hematoma resorption.
- The most difficult thing to interpret is the increase in D-dimer due to thrombosis during pregnancy. The same level of D-dimer can be observed both in a patient with thrombosis and in a healthy pregnant woman. Therefore, complaints and the likelihood of thrombosis (the degree of risk, which is calculated on a special scale) are always assessed in parallel.
Normal D-dimer levels
A normal test result indicates that the patient is not at risk of thrombosis. However, in rare cases (no more than 2 per hundred) in the presence of thrombosis, the level of D-dimer remains normal. As a rule, this is due either to the very small size of the blood clot, or to improper storage of the material for the study. Thus, the diagnostic value of the D-dimer test is quite high (98%) and allows its active use to exclude the process of thrombus formation.
Low D-dimer levels
A low D-dimer should not be a concern. If the value is below the lower limit (although most laboratories indicate only the upper limit, which is correct), this can reliably indicate only one thing: you definitely do not have thrombosis.
It makes no difference whether to take a D-dimer test before or after taking thinning drugs, since this indicator is cumulative and reflects the activity of the coagulation and anticoagulation systems retrospectively.
What does D-dimer show in a blood test?
A blood test for D-dimer (also called dedimer) shows whether there are small blood clots in the bloodstream. These clots can clog blood vessels and cause life-threatening conditions:
- deep vein thrombosis;
- heart attack;
- stroke;
- pulmonary embolism.
To assess the risk of such serious diseases, doctors prescribe patients to do a D-dimer test.
Blood from a vein is donated on an empty stomach in the morning. You must not eat 8 hours or smoke 2 hours before the test. You are allowed to drink only water; tea, coffee, juices and other drinks, especially sweetened ones, should be avoided. The result is ready within 2 days.
Sports and medicine
It has been established that among marathon athletes, increased levels of inflammatory and hemostatic markers of cardiovascular risk increase the likelihood of developing acute coronary pathology. There was a twofold increase in the levels of CRP, von Willebrandt factor, D-dimer, leukocyte count, and fibrinolytic activity, which persisted for 4 hours after the end of the competition. The level of fibrinogen decreased immediately after stopping running, but the content of its breakdown product, D-dimer, increased. Consequently, blood clots formed, although this was not clinically evident.
D-dimer: what kind of analysis is it?
Checking the condition of the blood and the possible presence of clots in it is carried out using a blood test. There are two types of tests:
- Quantitative - reveals whether the D-dimer level is elevated or within the normal range. The results show o (increased) or “no” (normal).
- Qualitative - the exact number of D-dimer is indicated in numbers.
Quantitative analysis is more informative and provides doctors with more information about the condition of the patient's bloodstream. During the treatment of hemostasis, the analysis is carried out several times. If the indicator decreases, it means that the blood clot is dissolving and the patient is recovering. But high-quality analysis is cheaper and therefore more accessible to patients.
The test result will allow the doctor to accurately determine the risk of cardiovascular and cancer diseases in a particular patient.
Orthopedics and traumatology for the elderly
Elderly individuals (over 60 years of age) are characterized by changes in the ratio of coagulation, anticoagulation and fibrinolytic systems. Most often they are expressed by shifts towards hypercoagulation. Such patients pose a great risk in terms of endoprosthetics of large joints. In all groups of patients after hip replacement surgery during anticoagulant therapy, the data obtained indicate the development of changes towards hypercoagulation.
Assessment of plasma D-dimer level is one of the sensitive and informative tests for determining the degree of risk of developing thrombotic complications and the effectiveness of anticoagulant therapy.
Indications for analysis
Doctors order a D-dimer blood test for a variety of symptoms and medical history. The test result will allow you to monitor the patient’s condition and prescribe appropriate treatment.
List of indications:
- tendency to thrombosis, disseminated intravascular coagulation syndrome;
- chest pain;
- rapid heartbeat;
- sudden shortness of breath, breathing problems;
- hemoptysis;
- cough;
- cyanosis of the skin and mucous membranes;
- abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting;
- muscle pain;
- sharp pain in the leg or arm;
- change in color of an arm or leg (pallor, blueness, blackening);
- swelling of the limb;
- varicose veins of the legs;
- decrease in daily urine output;
- bleeding from gums;
- pregnancy;
- after injury;
- coronavirus infection COVID-19;
- control during treatment with anticoagulants.
During pregnancy, the risk of blood clots increases, so to monitor a woman’s health, she periodically undergoes a D-dimer test.
With these diseases and conditions, the patient should carefully monitor his well-being and consult a doctor in case of any ailments.
Problems caused by thromboembolism
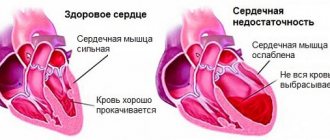
Thromboembolism kills hundreds of thousands of people every year. If a blood clot enters the blood vessels of the brain, an ischemic stroke occurs. A blood clot in the coronary vessels of the heart causes an acute heart attack. Pulmonary embolism leads to acute respiratory and heart failure. Acute attention to these diseases is due to their high mortality rate.
When a blood clot forms, a process called fibrinolysis immediately begins. This process is much slower. A substance called plasmin breaks down fibrin into fragments. D-dimer is a fibrin degradation product and is one of these debris. Consequently, d-dimer will be elevated if there is a blood clot in the body.
What should the normal indicator be?
The normal level of D-dimer in blood plasma is 250 ng/ml. this indicator confirms that the patient is not at risk of thrombosis. In pregnant women, this figure can reach 1000 ng/ml or more, i.e. grow 3–4 times.
Normal D-dimer levels in pregnant women:
- up to 450–500 ng/ml in the 1st trimester;
- up to 900–920 ng/ml in the 2nd trimester;
- up to 1450–1500 ng/ml in the 3rd trimester.
If a pregnant woman, on the contrary, has a low level, she is urgently referred to a hematologist, who will prescribe medications. A decrease in dedimer during pregnancy is a sign of long-standing problems with blood clotting that arose long before pregnancy. With good treatment, childbirth proceeds normally.
Normal indicators during pregnancy
Regardless of how pregnancy occurs, the dimer concentration in a woman expecting a child will be slightly higher than in the general population. In the first three months of embryo development, it is considered normal to exceed the norm by one and a half times. By the end of the second trimester, the figure can exceed the norm by three times. In the future the level may be even higher. All options considered are the norm both for women whose pregnancy occurred naturally and for patients after IVF. These conditions do not require specialized treatment. On the contrary, drug-induced reduction in indicators is often accompanied by excessive blood thinning and severe bleeding, especially during or after childbirth.
What does elevated D-dimer mean?
Even a slight increase in this indicator may indicate probable thrombosis. If the D-dimer reaches 273 ng/ml or higher, it is deadly.
D-dimer is elevated in many diseases:
- cardiac ischemia;
- acute coronary syndrome;
- thrombosis of the pulmonary artery (PE) or deep veins;
- DIC syndrome;
- acute or chronic heart failure;
- infections, injuries;
- sepsis;
- hematomas;
- kidney disease;
- preeclampsia and gestosis in pregnant women;
- coronavirus COVID-19;
- old age (over 80 years);
- malignant neoplasms.
The D-dimer level depends on the size of the clot, as well as the time and duration of taking thrombolytic drugs or anticoagulants.
With a decreased D-dimer level, the patient's risk of bleeding increases, so the patient needs to consult a hematologist and other specialists. Doctors conduct additional examinations and laboratory tests and prescribe an appropriate course of treatment.
Blood donation
Externally, donating blood is no different from a regular intravenous injection. The prepared patient is placed on a couch or asked to sit in a special chair. Then the woman needs to expose her arm above the elbow. A nurse applies a venous tourniquet just above the elbow, and the woman is asked to clench and unclench her fist several times. The injection site is treated with alcohol twice, after which an injection is given and the required amount of blood is collected. At this point, the patient may experience minor discomfort. After completing the set, a cotton ball moistened with alcohol is applied to the injection site and asked to hold the arm in a bent position. The resulting material is sent to the laboratory for further research.
Increasing values
- The presence of arterial and venous blood clots;
- Acute inflammatory or infectious process;
- Sepsis (severe infection of the body);
- Liver and kidney diseases;
- Oncological processes;
- Extensive hematomas (for example, as a result of a fall, compression, etc.).
Physiological increase in D-dimer concentration:
- normal pregnancy (moderate increase from the 1st trimester);
- pathological pregnancy (critical level of indicator);
- old age (from 80 years);
- recent surgery;
- thrombolytic treatment.