Blood pressure during a heart attack
Blood pressure is the force with which blood is pumped in the circulatory system. When blood flow is restricted or completely blocked, the heart muscle lacks oxygen - leading to a heart attack.
.
During a heart attack, blood pressure can rise, fall, or remain constant, depending on how the body responds.
Increased blood pressure
Blood pressure may rise during a heart attack as hormones such as adrenaline
. Hormones are released when the fight-or-flight response is triggered during times of extreme stress or danger. This automatic reaction can make the heart beat faster and stronger.
Lower blood pressure
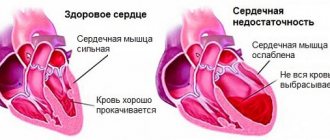
Blood pressure may drop if a person has a heart attack and the heart is too weak to support it because the muscles may be damaged. The intense pain a person may feel during a heart attack can also trigger an automatic reaction that can lead to low blood pressure and fainting.
What will happen if you are taken to the hospital?
Firstly, they will connect you to all the necessary devices and monitors and conduct an ECG test. It will help measure the heart's electrical impulses and detect any abnormal heart rhythms or other abnormalities that indicate a heart attack. Nurses will take the necessary tests, checking your blood to measure the level of an enzyme called troponin. It is released into the bloodstream if the heart muscle is damaged or dies.
Depending on your condition, doctors may keep you in the hospital until you feel better.
Blood pressure and heart attacks
If high blood pressure is left unregulated, it can increase the risk of a heart attack. High blood pressure can be an indicator of how hard the heart has to work to pump blood throughout the body through the arteries, so doctors keep an eye on it. The accumulation of fat, cholesterol and other substances in the arteries is called plaque. Over time, the plaque hardens, causing the arteries to narrow. This narrowing means that more pressure is required to push blood through the network of blood vessels. When plaque breaks away from the artery wall, a blood clot forms around it. Heart attacks can occur because plaques or blood clots disrupt or block the blood supply to the heart.
However, high blood pressure is not always a serious health problem. Even healthy people can experience high blood pressure from time to time due to exercise or stress.
Signs and symptoms of a heart attack
The most common symptoms of a heart attack are:
- chest pain
- discomfort in the upper body
- dyspnea
Other signs and symptoms include:
- sweating
- nausea
- anxiety
- swelling in the legs
Symptoms may vary by gender, but the most common heart attack symptom for both women and men is chest pain or discomfort.
Doctors believe women may experience different symptoms. For example, they may experience shortness of breath, nausea, and back and jaw pain.
Heart disease is the leading cause of death in women. Despite this, many women believe their symptoms are caused by less serious illnesses, including acid reflux, the flu, or simply aging.
Why does my heart hurt with normal or low blood pressure?
Heart pain occurs in patients with normal or low blood pressure for the simple reason that hypertension is neither the only nor even the main cause of chest pain. Any person can have heart pain, as there are a huge number of causes for this symptom.
We have already said that the chest contains not only the heart. Accordingly, at a doctor’s appointment it often turns out that another organ (stomach, esophagus, spine, etc.) is hurting. But if it is determined that it is the heart, then in 80% of cases the cause is coronary syndrome. Other diseases are less common: these may be myocarditis, cardiomyopathy, heart defects (usually mitral valve prolapse), aortic stenosis, pulmonary hypertension.
What is a silent heart attack?
An asymptomatic heart attack, as the name suggests, may have few or no obvious symptoms. In some cases, people may feel tired, have flu-like symptoms, or experience indigestion or discomfort in the chest, back, arms, or jaw. This type of heart attack can sometimes be worse than a normal one, as people who have it may not receive any treatment.
An asymptomatic heart attack can only be diagnosed using an electrocardiogram.
Is it possible to exercise after a heart attack?
Exercise actually reduces the risk of another heart attack, but this decision is up to your doctor. An individual exercise program will be selected for you, which will be, first and foremost, safe. Your doctor may also recommend brisk walking, cycling, or swimming, all of which help strengthen your heart muscle and prevent future complications.
Not only treatment, but primarily competent prevention of cardiovascular diseases will help reduce the risk of heart problems.
You can make an appointment with a cardiologist in our clinic by phone
When to see a doctor
People should see a doctor if they experience chest pain, discomfort, or the following symptoms:
- pain in one or both arms
- pain in the back, neck, jaw or stomach
- dyspnea
- sweating
- nausea
- dizziness
If your blood pressure rises, when the systolic pressure is above 180 and the diastolic pressure reaches 110 or more, you should consult a doctor. Blood pressure in this range puts people at greater risk of heart attack.
Related article: High blood pressure and low pulse - what could be the reason?
Heart attack and stroke: signs, emergency care, prevention
Myocardial infarction is a disease in which, due to blockage of the coronary artery, the full blood supply to an area of the heart muscle (myocardium) suddenly and abruptly stops, which leads to a severe lack of oxygen (ischemia), nutrients and death of myocardial cells. This area can no longer take part in heart contractions, so the heart cannot provide blood flow to the body. All organs and tissues begin to experience oxygen starvation, which leads to disruption of their function. The main cause of heart attack is elevated levels of cholesterol and certain lipids in the blood.
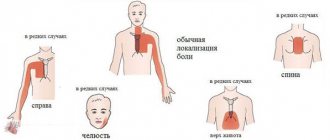
Typical manifestations of myocardial infarction are a feeling of severe pressure or pain behind the sternum, or slightly to the left or right of it. The pain is most often squeezing, pressing, tearing (feeling of a stake in the chest), sometimes burning. Irradiation of pain to the left shoulder girdle, shoulder, arm, less often to the neck and lower jaw, sometimes to the right half of the shoulder girdle is typical. Occasionally, the pain is localized in the epigastric region. Unlike angina, pain during myocardial infarction lasts more than half an hour, usually several hours. Nitroglycerin taken brings only minor and short-term relief. Severe weakness and cold sweat are often noted. Often in the acute stage of myocardial infarction, patients experience nausea, vomiting, hiccups, and bloating, which are of a reflex nature. In some cases, myocardial infarction is practically asymptomatic.
During the period of pain, the patient's face has a suffering appearance, the skin is usually pale, sometimes with a cyanotic tint. Breathing is rapid. Blood pressure may rise when pain occurs, but soon drops to an unusually low level for the patient. The pulse is frequent, heart sounds are weakened. In most patients, various cardiac arrhythmias can be detected.
If you or someone else suddenly has the above characteristic signs of a heart attack, even with weak or moderate intensity, which last more than 5 minutes, do not hesitate, immediately call an ambulance team. Do not wait more than 10 minutes - in such a situation it is life-threatening.
The recovery period after a myocardial infarction lasts 4-6 weeks. It occurs differently in different patients. Most often, during this period, patients remain able to work, but they sometimes experience angina attacks. In rare cases, the course of the post-infarction period is interrupted by the onset of a second infarction.
The results of large-scale international studies, in particular the INTERHEART study, showed that the following factors have a decisive influence on the risk of developing myocardial infarction: dyslipidemia, smoking, hypertension, abdominal obesity, psychosocial factors (stress, social isolation, depression), diabetes mellitus, reduce the risk : eating enough vegetables and fruits, regular physical activity.
Emergency self-help and mutual assistance measures in case of a heart attack (myocardial infarction).
In our country, up to 80% of deaths occur outside of medical organizations - at home, at work, in the country, in public and other places. Most of them occur suddenly or by the mechanism of sudden death. However, with knowledge of simple first aid techniques on the part of people surrounding a person who finds himself in such a critical condition, as well as everyone’s knowledge of first self-help measures, can in most cases save the patient’s life.
Characteristic signs (symptoms) of a heart attack (myocardial infarction)
• sudden (paroxysmal) pressing, squeezing, burning, aching pain in the chest (behind the sternum) lasting more than 5 minutes;
• similar pains are often observed in the left shoulder (forearm), left shoulder blade, left half of the neck and lower jaw, both shoulders, both arms, the lower part of the sternum along with the upper abdomen;
• lack of air, shortness of breath, severe weakness, cold sweat, nausea often occur together and sometimes follow or precede discomfort/pain in the chest
• often these manifestations of the disease develop against the background of physical or psycho-emotional stress, but more often with some interval after them.
Algorithm of urgent actions:
• Call an emergency medical team.
• Sit (preferably in a chair with armrests) or lie in bed with the head of the bed raised, take 0.25 g of acetylsalicylic acid (aspirin) (chew the tablet, swallow) and 0.5 mg of nitroglycerin (put the tablet/capsule under the tongue, first bite the capsule , do not swallow); free your neck and provide fresh air (open the vents or windows).
• If after 5-7 min. After taking acetylsalicylic acid (aspirin) and nitroglycerin, pain persists, you need to take nitroglycerin a second time.
• If pain persists 10 minutes after taking the second dose of nitroglycerin, it is necessary to take nitroglycerin a third time.
• If after the first or subsequent doses of nitroglycerin there is severe weakness, sweating, shortness of breath, you need to lie down, raise your legs (on a bolster, etc.), drink 1 glass of water and then, as with a severe headache, do not take nitroglycerin.
• If the patient has previously taken cholesterol-lowering medications, give the patient his usual daily dose and take the drug with you to the hospital.
Attention! A patient with a heart attack is strictly forbidden to get up, walk, smoke or eat until the doctor’s special permission;
You should not take aspirin (acetylsalicylic acid) if you are intolerant to it (allergic reactions), as well as with obvious or worsening peptic ulcers of the stomach and duodenum;
Nitroglycerin should not be taken if there is severe weakness, sweating, or if there is severe headache, dizziness, or acute impairment of vision, speech, or coordination of movements.
Prevention of myocardial infarction.
As for the prevention of atherosclerosis, everyone who has become familiar with the factors contributing to its occurrence knows what to do. The one who sharply reduces the consumption of animal fats and develops a rational attitude to nutrition will do the right thing. You should eat low-fat cottage cheese and low-fat kefir. More fiber-rich vegetables should be included in the menu - raw and sauerkraut, beets, carrots (at least 500 g per day). Fiber helps remove excess cholesterol from the body. When the first cases of increased pressure are detected, for which you need to regularly, at least once every one to two months, measure blood pressure and, by contacting a doctor, take the necessary measures, it is quite possible to stop the development of hypertension (blood pressure should not be higher than 140/90 mm Hg. Art.). If elevated cholesterol levels are determined, then by resorting to dietary and drug treatment, the progression of atherosclerosis can be delayed (the maximum permissible level of cholesterol in the blood is 5 mmol/l). The most important preventive measure is to stop smoking. Harmful substances in cigarette smoke contribute to the development and progression of atherosclerosis, cause fluctuations in blood pressure, thicken the blood and provoke thrombosis. The danger is posed by so-called passive smoking, so it is important not only to quit smoking, but also not to be in areas where smoking is allowed and in the company of smokers. Smoking significantly reduces the effect of physical training, so the desire to achieve the maximum effect from exercise and lead an active lifestyle is another reason to stop smoking.
In order to timely identify initial disturbances in the activity of the cardiovascular system and, if necessary, prescribe optimal drug treatment that can prevent the development of myocardial infarction, experts strongly advise regular medical examinations or preventive medical examinations at the clinic at the place of residence.
Finally, it is important to remember that only a doctor prescribes treatment for a heart attack, and the patient and his relatives strictly follow the instructions. Self-medication of a heart attack, no matter how easy it may be, is unacceptable!
Stroke: causes, symptoms, prevention.
In the modern world, people suffer from such a disease as “stroke” more often than from “myocardial infarction”. Residents of large cities are most susceptible to this disease, where life is full of stress and anxiety, and there is also an unfavorable environmental situation. Stroke accounts for approximately 6 million deaths per year worldwide and is second only to coronary heart disease as a cause of death.
A stroke is a terrible blow, which often divides not only the life of the patient, but also the life of his family into two parts: “Before” and “After”. Everything can change overnight: an active, active person can become a helpless disabled person in need of constant outside help, caring for which places a heavy burden on his loved ones, creating considerable socio-economic difficulties for society. What kind of life are people forced to lead after suffering a severe stroke? This is a real genuine tragedy and tears invisible to the world, since for many of them even leaving the apartment is an insoluble problem, and it is not so rare that the disease is bedridden, making the patient completely dependent on others.
A stroke is an acute disorder of cerebral circulation, leading to damage to the brain substance and disruption of its functions. There are two types of this disease: ischemic stroke and hemorrhagic stroke. Ischemic stroke occurs when the lumen of a vessel is blocked by a thrombus or embolus. The cause of a hemorrhagic stroke is a rupture of the vessel wall and blood entering the brain.
Many risk factors for stroke are common to other cardiovascular diseases. They are divided into two large groups: internal - high blood pressure, age, family history (stroke, myocardial infarction, hypertension in close relatives), high blood cholesterol, obesity; external – emotional stress, sedentary lifestyle, bad habits, environmental features. In addition, stroke has risk factors unique to it: initial manifestations of insufficient blood supply to the brain, dyscirculatory encephalopathy, transient cerebrovascular accidents, and previous strokes.
The onset of a stroke can vary. Hemorrhagic stroke occurs suddenly. Subsequently, patients can even indicate at what hour and even minute they began to experience symptoms of the disease: severe headache, vomiting, dizziness, weakness, malaise. There may be a deterioration in a person’s orientation in the surrounding space, difficulty speaking, loss of consciousness, and the development of paralysis. With ischemic stroke, the onset may be slow. Often patients note increasing sensations of weakness in one half of the body, a gradual deterioration in speech, swallowing, facial distortion, and unsteady gait.
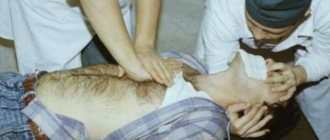
When the first such signs appear, the most correct thing is to immediately call an ambulance and hospitalize the patient in the neurological department. If a person’s stroke has developed acutely, with loss of consciousness and signs of paralysis, before the ambulance arrives, the patient must be turned on his side and a pillow placed under his head (if this happened at home); rolled up clothes or a bag (if this happened outside the home). To make breathing easier, unfasten your collar and, holding your head with your hands, constantly wipe away the foam with a handkerchief so that it does not get into your respiratory tract. To prevent the patient from biting his tongue, a comb or stick wrapped in a scarf can be inserted between the teeth. You cannot hold your arms and legs with force, trying to unclench your cramped fingers, much less lean on the patient with your whole body. This may make the seizure worse. The patient's arms and legs should only be held lightly so that he does not injure himself and others. And no ammonia! It may cause respiratory arrest. You cannot move a patient during an attack. If the patient’s pulse cannot be felt, the heart has stopped, and breathing has stopped, an indirect cardiac massage and mouth-to-mouth artificial respiration must be performed. Everything else is the task of the ambulance team.
Stroke prevention is based on the basic principles of a healthy lifestyle.
· Know and control your blood pressure - it should not be more than 140/90 mmHg.
· Do not start smoking or stop smoking as soon as possible.
· Add as little salt as possible to your food and avoid canned and processed foods that contain it in excess.
· Control your blood cholesterol levels – the maximum allowable level is 5 mmol/l.
· Follow the basic principles of a healthy diet - eat more vegetables and fruits (at least 500 g per day), avoid added sugar and saturated animal fat.
· Don't drink alcohol. The risk of stroke is highest in the first hours after drinking alcohol.
· Exercise regularly. Even moderate physical activity (walking outdoors for 30 minutes a day) reduces the risk of developing cardiovascular diseases, including stroke.
Preventative medical examinations and consultations that you can undergo:
— in a clinic at your place of residence, where you can undergo medical examination or in-depth preventive examination;
— at the Health Center (in Krasnodar at Tramvaynaya str., 5), where your blood pressure will be measured, your blood glucose and cholesterol levels will be determined, and your body mass index will be calculated. Knowing your risk for developing heart disease can help you develop a specific action plan to improve your heart health.