Physical inactivity is a pathological condition in which, due to low physical activity, muscle strength decreases and muscle atrophy occurs. Physical inactivity is not a disease. It is considered a risk factor that provokes the development of diseases of all systems and organs, but primarily the heart, blood vessels and musculoskeletal system.
We will talk about the causes of physical inactivity, consequences and comprehensive restoration of the body, including osteopathic methods.
Physical inactivity - what is it?
Physical inactivity is a condition characterized by insufficient physical activity and decreased muscle strength. It is not an independent disease. The main symptoms of physical inactivity: constant fatigue and decreased performance, excess weight, insomnia and emotional lability. Diagnosis is based on medical history and objective examination; laboratory and instrumental methods are used to identify concomitant pathologies. Treatment consists of gradually increasing the volume of physical activity and eliminating the etiological factors of physical inactivity. If there are indications, drug correction is carried out.
Signs of physical inactivity
They can be identified by the discrepancy between mobility and physical activity standards.
- For infants up to one year old, physical activity consists of developing gymnastics, massage, water treatments, and active games with adults.
- Children 1 to 2 years old should be active every day for 3 hours straight. This can be walking for a distance of up to 200 m with a gradual increase in distance, playing on a sports ground, etc. It is possible to conduct planned activities.
- At the age of three, a scooter and a bicycle are added to the games.
- From the age of five until the age of 18, daily one-hour sports activities are required in the form of physical education, visiting sports clubs, active games, and walks. The optimal frequency of strength training is three times a week.
- For healthy adults aged 18-50 years, moderate physical activity of one hour per day is necessary to maintain good health. Intense training, strength, coordination exercises, and stretching are required twice a week for 45-60 minutes.
- People aged 50-65 years are recommended to do moderate physical exercise daily for 25-40 minutes. in the form of walking, swimming, gymnastics, sports games, etc. Mandatory ten-minute daily aerobic exercises. Performing strength exercises is necessary twice a week.
If the above physical minimum is observed, physical inactivity has no chance.
Causes and risk factors
Physical inactivity can be caused by objective reasons, for example, disability, severe and long-term illness. But in most cases it is associated with improper lifestyle organization or sedentary work. The main risk factors for the development of physical inactivity include:
- insufficient physical activity;
- excess body weight;
- psychological disorders;
- somatic diseases;
- genetic factors;
- intrauterine fetal hypoxia;
- birth injuries;
- bad habits.
Symptoms of physical inactivity
Physical inactivity is characterized by gradual development, that is, the symptoms of the pathology do not appear in the patient immediately, but periodically. The disease of an immobile lifestyle begins to manifest itself in the form of an increasing feeling of apathy, rapid fatigue, a noticeable decrease in performance, disturbances in the quality of sleep, the appearance of nervousness, irritability, and aggressiveness. As the disease progresses, symptoms become aggravated - periodic headaches begin, the risk of fractures increases, weight increases, shortness of breath occurs, and back pain worsens. In some women, physical inactivity provokes the development of anorgasmia, and in men, erectile dysfunction.
Symptoms
Physical inactivity is not a disease, so there are no exact characteristic signs. As a rule, it leads to the following conditions.
- Constant feeling of fatigue and weakness. Rest does not restore a person’s energy potential.
- Lack of desire to adhere to a healthy diet. After all, playing computer games is more interesting with chips than with a bowl of soup.
- Psycho-emotional disorders. With a sedentary lifestyle, a person becomes irritable and aggressive.
- Insomnia or, conversely, drowsiness.
- A gradual decrease in performance, which goes unnoticed by a person.
- I'm constipated.
- Headaches.
- Decreased libido, lack of satisfaction from sexual intimacy.
- Shortness of breath even with slight exertion or at rest.
- Obesity.
Symptoms do not appear immediately but develop over time. Subsequently, complications of physical inactivity appear, which have their own specific symptoms. One of the most striking is lethargy and crackling joints at the slightest movement.
Features of the course in children
In children and adolescents, it develops due to limited mobility at school and at home.
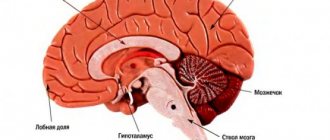
When a child spends most of the day at school, stagnation of blood and lymph occurs in the lower extremities, but the brain and other organs are less well supplied with blood. Oxygen starvation occurs, attention, memory, ability to think and concentrate deteriorate.
Weakness of the muscular frame, especially the anti-gravity muscles of the back, provokes poor posture and curvature of the spine.
In children, an inactive lifestyle leads to the development of diseases much faster, because their skeleton and muscular system are not yet fully formed and do not have a sufficient reserve of resistance.
What are the dangers of body immobility and physical inactivity?
- Since there is no physical activity, the patient’s muscles begin to flabby, weaken, and their elasticity and firmness are lost. This condition is dangerous due to the development of atrophy.
- The patient's strength and endurance decrease, and pathologies of the nervous system are observed (nervous disorders, depression).
- A prolonged course of the disease threatens the development of osteoporosis, as the bones stop absorbing calcium. Pathology can cause the development of osteoarthritis, as well as osteochondrosis.
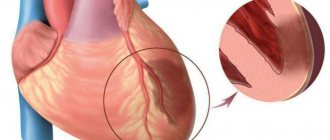
- Passivity is a direct path to the development of cardiac pathologies (coronary disease, hypertension, arrhythmia).
- The functionality of the respiratory system is impaired, which leads to congestion and obstruction.
- The pathology provokes a malfunction of the digestive system - intestinal motility is disrupted, constipation and colitis appear.
All of the above negative conditions lead to a decrease in the patient’s life expectancy.
Complications of physical inactivity
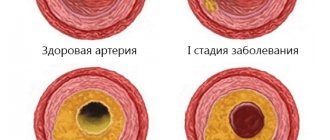
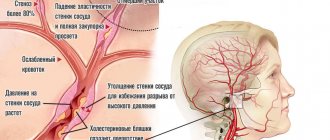
The main “target” of physical inactivity is the cardiovascular system. Patients experience dyslipidemia and atherosclerotic vascular lesions, which contribute to the development of coronary artery disease. Due to calcification and rigidity of the vascular wall, arterial hypertension occurs. The mortality rate from cardiac causes (heart attack, heart failure) in patients with physical inactivity is 20-30% higher than the population average.
The musculoskeletal system is affected. Osteoporosis develops and the incidence of bone fractures increases. The function of the joints (osteoarthrosis) and the spinal column (osteochondrosis) suffers. A connection between physical inactivity and aging has been established: in older women who devote less than 40 minutes to physical activity per day, their biological age is 8-10 years higher than their passport age. Ultimately, all these complications reduce life expectancy.
What happens to the body during physical inactivity?
Human muscles must contract, which is facilitated by physical activity. Ideally, this is at least 2.5 hours a week of aerobic (cardio) exercise and 1.5 hours of strength training.
If a person moves little, his muscular strength decreases and the conductivity of neuromuscular impulses deteriorates, that is, the muscle fibers practically stop contracting.
Hence the main danger of physical inactivity - consequences that sooner or later make themselves known, and well, if not all at once:
Among the severe consequences of physical inactivity are heart failure, heart attacks, osteoporosis, osteoarthritis, that is, degenerative changes in bones and joints. Thus, not only a person’s quality of life decreases, but also its duration.
Treatment of physical inactivity
If symptoms of pathology appear, you need to visit a competent specialist for diagnosis. This is necessary, since the symptoms of physical inactivity are not specific and may indicate the progression of other ailments. The course of treatment is developed based on the degree of development of the disease, as well as the general condition of the patient.
Before treating the disease, it is necessary to eliminate the true cause, which led to physical inactivity. The treatment plan is usually aimed at eliminating the consequences of the pathology (obesity, increased blood pressure, sexual dysfunction, etc.).
Correction of the pathological condition, in addition to a gradual increase in physical activity, includes physiotherapeutic methods, massage, and diet therapy. To restore the functions of organs and body systems during physical inactivity, the following are recommended:
- physical therapy – you should start with it, especially with physical inactivity that has developed against the background of somatic diseases;
- aerobic physical activity (fast walking, running, badminton, tennis, skiing);
- strength exercises;
- exercises to stretch muscles and ligaments.
For physical inactivity that has developed against the background of psychological problems, it is recommended to work with a psychologist or psychotherapist. Children, as well as adults, are recommended to play outdoor games, play sports or dance, and travel.
11.08.2021
Physical inactivity: symptoms, its consequences and prevention
Physical inactivity is one of the most pressing problems in the modern world. The disease called by this term does not exist in medicine, but this condition can lead to disruption of the functions of many organs and systems. That is why doctors around the world are paying more and more attention to physical inactivity among the population every year. It’s not difficult to guess the meaning of this term; “hypodynamia” means “reduced activity.” Regular physical activity is necessary for all people, regardless of age and gender. Systematic training strengthens the muscular system, including the myocardium, prevents congestion in the lungs, and improves blood circulation in the vessels. People who exercise regularly have good memory, high performance and good immune status.
Symptoms of physical inactivity
The main reason for physical inactivity in people in the modern world is obvious. Achievements of technological progress make human life more comfortable, but few people think that a decrease in physical activity, for example, when using a personal car, has a negative impact on health. In addition, physical inactivity is a constant companion for people in so-called sedentary professions (programmers, managers, etc.). This problem does not bypass children, especially of school age, who after classes (during which they also sit) prefer to spend their free time at home on the computer rather than on the street. Of course, there are reasons why a person is forced to limit his movement, for example, due to serious illness or as a result of injury. But even in such cases, patients need movement. It’s not for nothing that ancient healers said: “Movement is life.” Physical inactivity is a condition that is accompanied by a huge number of symptoms, most of which are a consequence of insufficient physical activity. The following main symptoms can be identified: lethargy, drowsiness; bad mood, irritability; general malaise, fatigue; decreased appetite; sleep disturbance, decreased performance. Almost every person can periodically feel such symptoms, but few people associate them with physical inactivity. Therefore, when such signs appear, you should think about whether you are devoting enough time to physical training. A long-term decrease in physical activity leads to atrophic changes in muscles and bone tissue, metabolism is disrupted, and protein synthesis decreases. Physical inactivity has an extremely adverse effect on the functioning of the brain, causing headaches, insomnia, and people becoming emotionally unbalanced. Another sign of physical inactivity is an increase in appetite, which results in an increase in the amount of food consumed. Reduced physical activity and excessive nutrition can quickly lead to the development of obesity, which contributes to the occurrence of lipid metabolism disorders and atherosclerosis. It is known that the presence of atherosclerosis significantly increases the risk of cardiovascular diseases. This is also facilitated by increased fragility of blood vessels, which is also a consequence of metabolic disorders. Considerable attention should be paid to physical activity in children, especially of school age. When sitting at a desk for a long time, blood stagnates in the vessels of the lower extremities, which leads to depletion of the blood supply to other organs, including the brain. As a result, thought processes, memory and concentration deteriorate. In addition, sedentary children have a weak muscular system. Due to the weakness of the back muscles, they develop poor posture. As we see, the consequences of physical inactivity can be expressed in dysfunction of many organs and systems, and often such disorders are associated with low physical activity in the last place, although in fact this is not the case.
Prevention of physical inactivity
Obviously, prevention measures should be aimed at increasing physical activity in each person. Children need to be taught from early childhood to do daily morning exercises, active games in the fresh air, compulsory attendance at physical education classes at school, and attendance at sports sections is very useful. Recently, sports centers and fitness clubs have become widespread, regular visits to which are an excellent prevention of physical inactivity. However, the inability to attend sports centers should not be the reason for insufficient physical activity. Every person can take daily walks and jogs in the fresh air. In addition, it is useful to have any exercise machine at home, not necessarily expensive and large; in every home there is a place for a simple jump rope, expander or dumbbells.
GP GUZ "City Clinic No. 4 of Grodno" Badak E. A.
Prognosis and prevention
By normalizing the level of physical activity, the risk of cardiovascular complications and critical conditions is significantly reduced. Patients who follow all medical recommendations increase their life expectancy and improve their quality of life. Primary prevention of physical inactivity involves combating risk factors (sedentary work, obesity, etc.), moderate but regular physical activity.
The main measures to prevent physical inactivity include:
- sufficient physical activity;
- long walks in the fresh air;
- alternating mental and physical activity;
- timely treatment of somatic diseases;
- correction of excess weight;
- balanced diet;
- rejection of bad habits.
Causes of physical inactivity
Despite the global promotion of an active lifestyle and the cult of the body, according to WHO, at least a quarter of the world's population suffers from physical inactivity. Pathology ranks fourth in the list of causes of early mortality from cardiovascular diseases.
The main reason for physical inactivity is urbanization and a sedentary lifestyle, hence its fair name - “a disease of civilization.”
The main risk factors that predetermine the development of physical inactivity:
- prolonged inactivity after a serious illness or surgery;
- specific work that forces a person to spend the working day in a sitting or standing position. With the transition to remote work during the pandemic, the situation did not get better;
- due to fatigue, muscle and back pain caused by forced body position, people refuse to play sports;
- personal transport leaves many people no chance to walk even short distances;
- obesity can be both a cause and a consequence of physical inactivity;
- passion for social networks and computer games among adults and children. According to statistics, about 80% of teenagers remain indifferent to sports for this reason.
People work five days a week, and on weekends they try to sleep and relax on the couch, but rest does not bring relief. Today you don’t even need to go to the store; any food and non-food products are brought home, which further aggravates the pathological condition.