© Author: Sazykina Oksana Yuryevna, cardiologist, especially for SosudInfo.ru (about the authors)
Doctors teach many patients with attacks of paroxysmal tachycardia to independently perform so-called vagal tests. These are the simplest manipulations aimed at a reflex effect on the cardiovascular system. This includes the Aschner test with pressure on the eyeballs, the test with straining and coughing, and massage of the carotid sinus. Each of these manipulations is based on mechanical stimulation of receptors associated with the neurohumoral regulation of the heart muscle. This irritation leads to a decrease in heart rate, which in the case of palpitations plays a positive role in restoring normal heart rhythm. But some may develop adverse consequences due to such tests, so such tests are currently contraindicated for the patient to perform independently without medical supervision. In particular, we are talking about massage of the carotid sinus.
Anatomical and physiological features
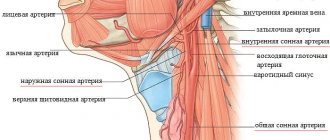
The sinocarotid zone is a small formation at the site of the branch of the internal carotid artery from the common carotid artery, in the inner membrane of which there is a high density of baroreceptors. The carotid sinus itself is located in the inner lining of the artery (in the intima).
These receptors are represented by protein complexes that detect fluctuations in blood pressure in the vascular bed. From the receptors, electrical impulses are transmitted along the nerve fibers of the vagus nerve to the brain, and then, through the centers of the autonomic nervous system, an inhibitory effect is exerted on the sinus node, located deep in the myocardium of the right atrium. Thus, the heart muscle contracts less frequently, cardiac output becomes less, resulting in a decrease in overall peripheral vascular resistance.
Elderly patients suffering from atherosclerosis of the carotid arteries must remember that the slightest mechanical irritation of the neck area (tight collar, scarf, strong tilting of the head back) can have an irritating effect specifically on the sinocarotid zone, which, in the presence of hypersensitivity of the carotid sinus, can cause hemodynamically significant a decrease in heart rate and a decrease in blood pressure below critical.
Vagal stimulation to relieve reciprocal tachycardia involving the AV junction (AVRT, AVNRT)
The first step to stop tachycardia
there must be vagal stimulation. An increase in vagal tone can temporarily block conduction through the AV node and thereby interrupt the cycle of tachycardia.
Best methods
are the Valsalva maneuver and carotid sinus massage (if possible, they are performed on patients in a supine position). The first technique is carried out by attempting forced exhalation with the nose and mouth closed for 10-15 s, after which the patient breathes normally.
test is based on
there is an increase in intrathoracic pressure and the resulting arterial hypotension, which triggers the autonomic reflex. The patient should be instructed to try to exhale until he feels dizzy, a sign of hypotension.
Carotid sinus massage
is performed by pressing firmly with a finger for 5 seconds on the left or right (but not both at the same time!) carotid artery at the level of the upper edge of the thyroid cartilage. This technique should not be used if carotid artery disease is known or if there is a bruit over the carotid arteries.
Pressing on the eyeballs
is a well-known method of vagal stimulation, but it is very painful and should not be used.
Relief of reciprocal tachycardia involving the AV junction: by massage of the carotid sinus.
Drugs for intravenous administration to relieve reciprocal tachycardia involving the AV junction (AVRT, AVNRT)
If vagal stimulation is ineffective, the tachycardia can almost certainly be controlled with an intravenous injection of one of the following drugs. In this case, the drug of choice is adenosine.
Adenosine
Adenosine
is a powerful means of blocking conduction through the AV node and has a very short period of action - less than 20 s. It is very effective in reversing AVNRT and AVRT.
The drug is administered intravenously as a stream very quickly (in 2 seconds), after which the needle or catheter is washed with saline. The recommended starting dose for adults and children is 3 mg and 0.05 mg/kg, respectively.
If there is no effect, you can additionally administer 6 mg (0.10 mg/kg) and 12 mg at intervals of 1 minute to achieve a maximum dose of 12 mg (0.20 mg/kg).
For adults, a dose of 3 mg is rarely effective and it is better to start with 6 mg.
There is evidence of the possibility of administering up to 18 mg of the drug without significant adverse effects. If the patient has received adenosine in the past, it is prudent to start with the dose that has previously been found to be effective.
After heart bypass surgery, how long do they stay in intensive care?
Many patients report chest tightness, shortness of breath, and a feeling of heat after administration of adenosine. Although these symptoms last less than 30 seconds, some patients find them very unpleasant. After cessation of tachycardia, complete AV block may develop, lasting several seconds. Several ectopic ventricular complexes may appear.
Adenosine
may cause bronchospasm, so it is recommended to avoid its use in patients with bronchial asthma.
Two variants of the mechanism of reentrant tachycardia involving the AV junction: atrioventricular reentrant (re-entry) tachycardia (AVRT) due to the presence of an additional AV conduction pathway and AVNRT due to the presence of a double conduction pathway in the AV node itself.
In both cases, tachycardia occurs with a high heart rate and narrow QRS, which can be stopped with adenosine. DPP – additional pathway. *Diagram illustrating supraventricular tachycardia (SVT), caused by frequent abnormal electrical activity within the atria. The AV node is not an integral part of the arrhythmia mechanism, but only conducts (partially or completely) atrial impulses to the ventricles.
Relief of reciprocal tachycardia involving the AV junction: with the help of adenosine (after its administration, as often happens, a short episode of complete AV block is observed).
Verapamil
Intravenous administration of verapamil (5-10 mg over 30 s) usually leads to restoration of sinus rhythm within a couple of minutes. Verapamil should not be prescribed to patients who have recently received beta blockers orally or intravenously, and the drug should never be used unless VT is excluded: in this case, dangerous arterial hypotension may develop.
Other medicines. Other drugs such as sotalol, disopyramide, and flecainide may also be effective.
Electrical methods for stopping reciprocal tachycardia involving the AV junction (AVRT, AVNRT)
Electrocardiostimulation
. AVRT and AVNRT can be terminated using various pacemaker techniques. The simplest of them is stimulation of the RA (for several seconds) through a transvenous electrode with a frequency exceeding the frequency of tachycardia by 10-20%. After abrupt cessation of stimulation, sinus rhythm is often restored. If this does not happen, stimulation can be repeated.
There is a small risk of transformation of tachycardia into AF, which usually does not last long and is stopped with the restoration of sinus rhythm. However, in patients with WPW syndrome, AF can occur at a very high ventricular rate.
More complex methods require the use of a programmable pacemaker, which allows the application of extrastimuli at precisely calculated coupling intervals. The use of these methods for long-term treatment requires implantation of a pacemaker, but currently this approach is losing its position to catheter RFA.
Cardioversion
. If attempts at medical management are ineffective or clinical circumstances require immediate restoration of sinus rhythm, electrical cardioversion should be performed.
a – Relief of reciprocal tachycardia involving the AV junction using frequent atrial stimulation.
b - Termination of AVRT using a pair of precisely synchronized atrial stimuli, which are best seen in lead V1. After restoration of sinus rhythm, signs of WPW syndrome are revealed. The carotid sinus is the most important node that supplies the brain and the entire central nervous system. It is a concentration of nerve cells and also contains receptor zones that regulate the functioning of the heart. Carotid sinus massage is often used in medicine to diagnose a variety of diseases of the nervous system.
Where is the carotid sinus located?
Before you begin the massage procedure, you need to figure out where the necessary point is. To do this, you should consider the structure of the carotid artery.
The carotid sinus is located between the internal and external parts of the carotid artery in the neck. It is a small bulge. You can feel it if you place your fingers under the larynx in the area of the Adam's apple and raise your palm higher.
Under no circumstances should you search for the carotid sinus by applying strong pressure to the area of the carotid artery. Even short-term compression of an artery can lead to dire consequences.
Effect on the carotid sinus
Pressing this area can stimulate the vagus nerve, which connects the organs and tissues of the head, neck, chest and abdominal cavities with nerves, thereby ensuring their connection with the central nervous system. In addition, a certain effect on the carotid sinus helps to treat certain diseases and eliminate their symptoms.
Indications for carotid sinus massage
Previously, this procedure could be recommended by a doctor to a patient as a treatment procedure during an attack of tachycardia. But, due to the fact that massage can neutralize an attack exclusively of sinus or supraventricular tachycardia, and is ineffective for other types of tachyarrhythmias (atrial fibrillation, ventricular tachycardia), and the patient is not able to independently interpret this or that type of rhythm disturbance, then perform this procedure not only pointless, but also dangerous. It is dangerous precisely because excessive stimulation of the sinocarotid zone and irritation of the carotid sinus can provoke a sharp decrease in pressure, up to a syncope with loss of consciousness.
Currently, massage of the sinocarotid zone is performed only under medical supervision, with a cardiogram recorded and blood pressure measured. This manipulation is used exclusively for diagnostic purposes, if the presence of carotid syndrome is suspected.
How is massage of the neck and collar area useful?
Massage of the collar zone of the cervical spine is not only a relaxing, but also a therapeutic procedure.
When the neck muscles are relaxed, blood and lymph flow improves, and brain cells quickly receive the oxygen and microelements they need. In just a few sessions, you can relieve spasms in the neck-collar area and get rid of pain in the upper back and discomfort from muscle stiffness. When brain cells for many years do not receive enough oxygen and the elements they need, carried throughout the body by blood, headaches, dizziness, frequent fainting, and darkening of the eyes appear. All these symptoms can be eliminated with the help of a course of therapeutic massage of the cervical-collar area. The procedure will also help get rid of pain in the cervical spine, which often occurs due to a sedentary lifestyle and lack of physical activity.
How does carotid syndrome occur and why is it dangerous?
This syndrome occurs in elderly patients due to the lack of elasticity of blood vessels affected by atherosclerotic plaques in the area of the branching of the carotid arteries. An increased sensitivity of baroreceptors is formed in the sinocarotid zone, from where inhibitory signals arrive to the conduction system of the heart. As a result, the heart rate decreases, and as a result, cardiac output decreases. Since these processes lead to a decrease in blood supply to the brain, the patient loses consciousness (usually lasting no more than one minute). Such attacks can be repeated quite often.
Bath and sauna
Restrictions on visiting baths and saunas after stenting are associated with the underlying disease, which led to stenting. You can wash in the bathhouse. A temperature that is comfortable for the patient is recommended. It's not worth worrying about . Fluid loss and overheating can cause increased blood clotting and stent thrombosis. Problems with the stent decrease after its endothelialization (fouling of the “vessel skin” - endothelium). The timing of this process depends on the type of stent. If before stenting you regularly steamed in a bathhouse or sauna, then over time you can return to this habit, but with caution.
Technique for carotid sinus massage
A doctor can perform massage of the sinocarotid area. The test is carried out as follows. The patient is in a supine position, with a tonometer cuff on the shoulder, and with the electrodes of the ECG machine applied.
The doctor stands at the head of the patient, feels a small rounded formation on the neck behind the angle of the lower jaw on the right (in some cases, bilateral stimulation is required), and then stimulates the sinocarotid zone with circular movements for 3-5 minutes.
After a short stimulation of the sinocarotid zone, the patient's blood pressure is measured and an electrocardiogram is recorded. Even if loss of consciousness does not occur, but the patient experiences an episode of bradycardia lasting more than three seconds, or there is a sharp decrease in blood pressure by more than 50 mm Hg, the result is regarded as positive.
Carrying out procedures for heart diseases
In case of IHD (coronary heart disease), massaging of the carotid sinus is performed when an attack occurs. It is recommended to carry out the procedure immediately. The patient is placed on his back, the neck is straightened and gentle pressing movements are made. Massaging is carried out once, the doctor adjusts the duration and frequency of pressing depending on the improvement or deterioration of the patient’s condition.
Massage for vegetative-vascular dystonia is the most frequently prescribed procedure, because... VSD requires long-term treatment, and massage is the optimal means of therapy, less toxic compared to drug treatment. Massage for VSD helps relieve rapid heartbeat and headaches. This improves the patient’s condition and relieves the uncomfortable symptoms of VSD. In this case, the doctor prescribes 3 procedures lasting 6-8 minutes.
Massage for arrhythmia is prescribed with caution, because... the procedure slows down the heart, which helps eliminate the threat of cardiac arrhythmia, but can provoke ventricular arrhythmia in older patients. During its implementation, the doctor monitors the patient especially closely and adjusts the duration of the massage and pressure. To improve heart function, 3-4 procedures lasting no more than 10 minutes are performed.
Massage for angina pectoris is intensively performed alternately on the right and left sides to achieve a quick effect when attacks occur or when testing the patient’s condition. But there are contraindications that the doctor must pay attention to: hypertension and thromboembolic complications. The procedure is carried out 2-3 times lasting from 5 to 10 minutes. The technique is adjusted, the time of exposure to the sinus changes depending on the pathology.
Contraindications for carotid sinus massage
This manipulation is strictly contraindicated if the patient has such unfavorable symptoms as:
- Severe shortness of breath, especially worse when lying down (a sign of congestion in the pulmonary vessels),
- A suddenly developed cough, dry in nature or with sputum, especially foamy pink ones (may be a sign of acute left ventricular failure).
- Intense pain or even mild pressing discomfort in the chest (a symptom of probable acute coronary pathology and pre-infarction condition),
- Very frequent pulse (more than 150 per minute), especially in combination with loss of consciousness, since such rhythm disturbances are accompanied by disturbances in intracardiac and general hemodynamics.
Carotid sinus massage is strictly contraindicated for diseases such as:
- acute and exacerbation of chronic heart diseases (heart attack, chronic heart failure, heart rhythm disturbances),
- exacerbation and decompensation of other chronic diseases (bronchial asthma, diabetes mellitus),
- acute infections,
- general poor health of the patient,
- low blood pressure and low pulse.
So, massage of the carotid sinus is not only a therapeutic, but also a diagnostic procedure that allows one to differentiate the nature of fainting, especially in older age. If we talk about massage as a therapeutic procedure, then patients need to clearly understand that it is unacceptable to perform massage in this area on their own.