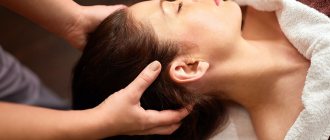
Scalp massage for high blood pressure
Head massage for hypertension is performed as follows (including in the video below):
| Patient position | Types of massage techniques | How to do it |
| Lying on your stomach, head resting on your hands folded in front of you | Stroking | Using the pads of your fingers, stroking movements are made from the crown to the back of the head, then from the crown to the temples, from the crown to the forehead |
| Trituration | Using the fingertips, rubbing movements are made from the forehead to the neck. At first, rubbing is done in zigzags, then in circles, then in beak-shaped | |
| On the back, under the head there is a cushion | Stroking | Using finger pads, stroke from the center of the forehead to the temples |
| Trituration | From the forehead to the temples, rubbing is carried out in zigzag, then circular lines. | |
| Tingling | Light tingling from the center of the forehead along the hairline towards the temples | |
| Stroking | Again you need to make light strokes along the same trajectory as before |
Absolute contraindications
If there are contraindications from the list below, massage is harmful, as it increases blood circulation and lymph flow, which will only harm the body
Massage taboo:
- — Flu, ARVI, tonsillitis, any acute inflammatory processes
- — Blood diseases, internal bleeding
- — Malignant neoplasms and tumors
- — Purulent processes of any localization
- — Scurvy
- — Osteomyelitis
- — Complicated forms of varicose veins: thrombosis, thrombophlebitis and trophic ulcers, any acute inflammation of blood and lymphatic vessels
- — Aneurysm of the aorta and heart, acute myocardial ischemia
- — Pulmonary heart failure of the third degree
- — Hyper- and hypotonic crisis
- — Diseases of the abdominal organs with a tendency to bleeding
- — Active form of tuberculosis
- — Kidney and liver failure
- - Venereal diseases
- - Mental illness with excessive agitation and significantly altered psyche.
More detailed information is in the following video:
Massage of the collar area for high blood pressure
Massage of the collar area for hypertension is performed in a sitting position. The massage therapist's fingers do not apply strong, but light pressure, moving only from top to bottom (in the direction of blood outflow from the cranial cavity). The stages of this massage for hypertension are as follows (including watch the video):
- Superficial light stroking with palms, directed from the ears, along the back of the neck, to the middle of the shoulder blades, and then upward, to the lymph nodes under the chin.
- Deep (that is, with pressure) stroking along the trajectory described in point 1. The hands do not leave the body.
- Trituration. First one, then the second part of the back is rubbed from the shoulders to the lower corners of the shoulder blades.
- Deep stroking is performed from the shoulders to the bottom of the shoulder blades.
- From the shoulders to the shoulder blades, rubbing is done in a spiral.
- Sawing is performed along the same trajectory: with the edge of the hand, which is a continuation of the little finger, sawing movements are performed back and forth with one or two hands. In this case, the tissues shift and stretch.
- Light stroking in the same trajectory.
DISEASES OF PERIPHERAL BLOOD VESSELS Indications. Obliterating atherosclerosis and endarteritis, varicose symptom complex, postthrombophlebitis syndrome (depending on the stage of the disease), phlebitis, thrombophlebitis without a tendency to relapse and erysipelas. Contraindications. Thrombobliterating diseases of peripheral arteries in the stage of gangrene; pronounced phenomena of atherosclerosis of cerebral vessels and a tendency to cerebrovascular accidents, phlebitis, thrombophlebitis, vascular aneurysms. Diseases of the arteries of the lower extremities. Methodology (Fig. 137). The patient's position is lying down. The impact begins with treatment of the paravertebral zones of the spinal segments S5-1, L5-1, D12-10 (planar stroking, rubbing, kneading, vibration, shaking, patting). Then massage the lumbosacral region (stroking, rubbing), massage the buttocks area (stroking, rubbing, kneading, shaking). After this, the iliac crests and costal arches are massaged (rubbing), the lower extremities (selectively) - stroking (soles, shins, joints), rubbing, special attention to the soles. At the end they shake the pelvis. The procedure is completed with passive movements, breathing exercises, and chest stretching. The duration of the procedure is 12-15 minutes, the course is 10-15 procedures. Diseases of the arteries of the upper extremities. Methodology. The patient sits, resting his head on his hands, a bolster or a pillow. They begin with a massage of the paravertebral zones D7-1, C7-3 (stroking, rubbing). Then the trapezius muscles and latissimus dorsi muscles are massaged (stroking, rubbing, kneading, special attention is paid to the sternocleidomastoid muscle). After this, the scapular and subscapular areas are massaged (stroking, rubbing), the upper limbs (stroking, starting with the hands, forearm, shoulder, affecting the joints); massage of the deltoid muscles (stroking, rubbing, kneading). Finally, passive movements are performed.
Rice. 137. Scheme of reflex changes in diseases of the blood vessels of the upper and lower extremities. The designations are the same as in Fig. 121
The duration of the procedure is 10-15 minutes, the course is 12 procedures, every other day (the same as with the previous disease). Diseases of the veins of the lower extremities. Indications. Varicose veins of the lower extremities, the presence of trophic changes in the skin and minor trophic ulcers, previous phlebitis, thrombophlebitis without a tendency to relapse and erysipelas. Methodology. The patient lies on his stomach. The massage begins with the paravertebral zones L5-D10. Then I massage the buttocks, lower edges of the chest, iliac crests and lower limbs (from the feet). Stroking, rubbing, kneading, vibration with puncturing, patting, chopping in the gluteal region, shaking the pelvis, massage of the joints, and passive movements are used. Finish the procedure with breathing exercises. Time - 12-15 minutes, course - 12 procedures, every other day. Will add), hydromassage. Methodical instructions 1. For unilateral lesions, lie on your back, leg slightly bent at the knee joint and elevated at an angle of 45°; stroking, rubbing the thigh, very gentle vibration. Do not perform striking techniques or kneading! This is followed by a massage of the lower leg, then the massage is carried out, bypassing the varicose nodes: gentle stroking, rubbing and pinching according to Nikolsky is performed, first on the skin, and then on the subcutaneous layer. 2. For bilateral lesions, massage of both limbs is used. 3. If there are open ulcers, reflex-segmental massage should be used in the lumbar region. During surgical treatment, massage is done after 2 months, starting with the suction technique. Lymphostasis (elephantiasis) is manifested by swelling of the soft tissues of the extremities. Methodology. The massage session lasts 3 minutes (stroking, light, then deep). If the patient feels better, then rubbing can be done like a suction massage. If severe pain occurs, then massage is not done. Paget-Schroetter disease. Paget-Schroetter disease is a thrombosis of the subclavian or jugular vein, which is caused by sudden lifting of heavy objects or sudden movement or compression. It manifests itself as swelling of the upper limb with a pronounced venous pattern, a feeling of heaviness, and cyanosis. The treatment complex includes a suction-type massage of the limbs. Raynaud's disease. Objectives of massage: improving blood circulation in the upper extremities, improving tissue trophism. Methodology. The patient is sitting. The procedure begins with a massage of the paravertebral zones from D7 to NW. Then they massage the collar area (all techniques), the deltoid muscle, the entire limb (stroking), rubbing the hands and fingers, the wrist joint and the elbow joint. Finish the procedure with passive movements. Course - 15-25 procedures, 15-20 minutes each, every other day. Phlebeurysm. Etiology: heavy physical labor, pregnancy, heredity, infectious diseases and complications after them. Clinical picture: varicose veins, increased fatigue; slight swelling towards the end of the day. Objectives of massage: 1) help improve venous outflow, improve lymphatic drainage; 2) improvement of tissue trophism in the lower extremities. Massage plan. First, the healthy leg is massaged, and then the patient, taking into account the source of the disorder, using the suction method. Segmental massage for vascular diseases. In all vascular diseases, even in the presence of clinical manifestations only on the lower or upper extremities, there are tensions in all segments on both sides of the spine, especially pronounced in the area of the cervical and upper thoracic segments when the upper extremities are affected and in the lumbar and sacral segments when the lower extremities are affected. limbs. Methodology: Start by influencing all segments from the bottom up. Then the thigh or shoulder area is massaged from proximal to distal sections, in sequence. Having eliminated the tension, move on to massage the lower leg or forearm. They mainly use stroking techniques. Segmental massage is indicated for organic changes in the walls of blood vessels and their blockage. Do not perform local massage of venous nodes or areas of thrombophlebitis! Reflex displacement. When massaging in the area of the shoulder blades above and below its spine along the back of the deltoid muscle, numbness, itching, and tingling in the hands may occur. This is eliminated by intensive massage of the armpit. When massaging the left armpit, there may be complaints of pain in the heart (relieved by massage of the left half of the chest). When massaging the back of the head and cervical segments, headaches and loss of consciousness may occur, and rapid falling asleep (can be eliminated by rubbing the eyelids and massaging the forehead along the frontal muscle). When acting on the lower thoracic and lumbar segments, a feeling of pressure and pain in the bladder area may occur (they are eliminated by affecting the tissues of the lower abdomen, the anterior edges of the pubic bones). HEART DISEASES Main indications. Congenital heart defects, hypertension, hypotensive crises, myocardial dystrophy, angina pectoris in the interictal period, after myocardial infarction, neuroses with impaired cardiac function, even when it stops. Objectives of massage. Improve blood circulation in the heart muscle, increase blood flow to the heart, eliminate congestion, regulate blood pressure in general, improve the condition of the contractile elements of blood vessels, and promote, if necessary, the development of collateral circulation. Heart defects. Methodology. The patient sits with support on the headrest. The procedure begins with stroking along the spine from L1-D12 to D5-2 and from C7 to C3. The following techniques are also used: straight-line rubbing, circular rubbing, pressing, sawing, vibration with fingers from bottom to top. Then stroking, rubbing, kneading the lateral surfaces of the back, the area of the latissimus muscles, then the shoulder girdle (trapezius muscles) are carried out. They influence the intercostal spaces, rub the costal arches with an emphasis on the left side, light striking techniques, and shake the entire chest. A massage is performed on the anterior surface of the chest with an emphasis on the sternum area (stroking, rubbing, kneading, light vibration). When massaging the areas of the heart and the left half of the anterior surface of the chest, the following techniques are used: stroking, rubbing, kneading, continuous and intermittent labile vibration and breathing movements. The massage is completed on the lower and upper extremities with the patient lying on his back, using stroking and kneading techniques with passive and active movements in various joints. Massage on the limbs is done for up to 3-5 minutes. The duration of the procedure is 15-20 minutes, per course - up to 12 procedures, preferably every other day. Myocardial dystrophy. Methodology. The patient sits or lies on his stomach, then on his back (while massaging the anterior surface of the chest). The massage begins by affecting the tissue along the spine at the level of segments L1-D5-8, C7-4. Varieties of stroking, rubbing (linear, circular), sawing, kneading - pressing, stretching, forceps-like shifting, labile continuous vibration, massage of the collar area (all techniques) are used. Next, during the massage, the VII cervical vertebra (da-zhui point) is isolated - rubbing, pressing, vibration is done; when massaging the intercostal spaces - stroking, rubbing, kneading, vibration, shaking and compression of the entire chest. The procedure is completed with a massage of the lower and upper extremities, without highlighting local effects on individual joints, small muscle groups, with an emphasis on large muscle groups, using the following techniques: grasping stroking, rubbing with the base of the palms, kneading (felting, longitudinal, transverse multidirectional), vibration (shaking , shaking). The duration of the procedure is 20-25 minutes, per course - from 10 to 15 procedures, depending on the patient’s response; massage can be performed every other day or daily. Angina pectoris. Methodology. The massage begins with exposure along the spinal column from bottom to top at the level of segments L1-D12, O6-2, C6-2, using all techniques along the lines along the spine. When massaging the back, large muscle groups (the latissimus dorsi muscle), the area of the left shoulder blade, the shoulder girdle, especially the left one are separately massaged, then the upper and anterior surface of the chest is massaged, especially paying attention to the left half, the sternum area, the intercostal space and the left shoulder. Massage of the lower and upper extremities can be performed with the patient lying on his back with his limbs bent. In this case, special attention is paid to the left hand, emphasizing the impact on the ulnar line and the Shao Chun, Shen Men, Shao Hai points. The duration of the procedure is 15-20 minutes, per course - 10-12 procedures, preferably every other day; in this case, the technique should be differentiated depending on the patient’s condition, and should not use sharp, energetic techniques in the first procedures. Cardiac ischemia. The clinical picture and basic treatment methods are described quite fully [Belaya N.A., 1983; Kunichev L.A., 1985, etc.]. The issue of starting procedures is decided individually depending on the patient’s condition. Methodology. Massage is carried out strictly depending on the stages of treatment (the period of treatment in a hospital, the post-hospital period, the sanatorium-resort). Period of treatment in hospital. Features of the massage are associated with the patient being in a lying position. The massage begins with impact on the lower extremities (feet, legs, thighs). Do stroking, gentle rubbing with fingertips, kneading - shallow felting, longitudinal. When massaging the upper extremities, all techniques are carried out taking into account the patient’s condition. If there is a positive reaction to massage manipulations, the technique is gradually expanded, complemented by massage of the back and gluteal muscles with the patient positioned on the right side. The duration of the procedures is 3-10 minutes, daily. Post-hospital period. The patient sits or lies on his stomach. The massage begins from the back area, emphasizing the effect along the spine from bottom to top, from the pelvis to the cervical region. Then massage the large muscle groups in the back (latissimus, trapezius, intercostal). They affect the peri-scapular areas and the collar zone. When massaging the lower extremities, begin the massage with the feet, using all techniques and passive movements in the joints. The procedure is completed with a massage of the anterior chest wall with an emphasis on the left pectoralis major muscle, sternum, and left shoulder. If the patient's response is positive, the technique is expanded to include massage of the abdomen and upper extremities, with an emphasis on massage of the left arm. The duration of the procedure is 10-20 minutes, daily or every other day. Constant monitoring by a doctor is required. Period of sanatorium-resort treatment. Usually, 2-4 months after hospital treatment, patients are sent to sanatorium-resort treatment, where types of massage are widely used in the rehabilitation complex. The massage is carried out with the patient lying on his stomach. They begin with exposure in the back area from the underlying segments to the cervical spine along the spine, using all techniques. Then a massage is applied to large muscle groups on the back and in the collar area, using all techniques, with the exception of intermittent vibration. After this, the intercostal spaces are massaged, ending with light shaking. A massage is performed on the anterior surface of the chest with an emphasis on the left half, then on the abdominal area using vibration effects, especially for atony and constipation. The procedure is completed with a massage of the lower and upper limbs, without separately highlighting the effects on the joints, but using passive movements, emphasizing techniques that widely cover the entire surface of the limb. You should not rush to use intermittent vibration techniques. Autonomic responses must be taken into account. The duration of the procedure is 15-20 minutes, per course - 2-15 procedures, daily or every other day, combining or combining with other types of treatment. Segmental massage. Indications. Functional disorders, heart disease, vasomotor angina, cardiosclerosis, neurosis, chronic heart failure (Fig. 138).
Rice. 138. Scheme of reflex changes in heart diseases. The designations are the same as in Fig. 121
Methodology. The patient usually sits, the massage therapist sits or stands behind him. The procedure begins with exposure to the paravertebral areas. Planar stroking is done from L2 to N3 and waist segmental stroking (3-4 passes each movement); classical rubbing of the left half of the back (2-3 times); flat stroking on both sides of the back (3-4 times); drilling technique 1-2 ways on the left (2-3 times); stroking along the spine (2-3 times); massage of the spinous processes of the spine (2-3 times); flat stroking along the spine (2-3 times); “saw” technique on the left (2 times, alternating with stroking); stroking and rubbing the left edge of the lower chest (2-3 times to reduce the displacement of the reflex). After this, the area of the left shoulder blade is affected. Stroking is carried out along the boundaries of the scapula - outer, inner - and spine (3-4 times); rubbing all edges of the shoulder blade with an emphasis on the lower left corner (2-3 times); rubbing, pressing on the subscapularis muscles (2-3 passes). After this, they penetrate into the subscapular region at the bottom I on the left between O6 and D4, rubbing, pressing, and finally stroking along the contour of the entire scapula. Then the intercostal spaces are massaged from the sternum to the spine. Apply segmental waist stroking (3-4 times from bottom to top); rubbing the left half of the chest (4-5 times); light vibration effects along the lower edges of the costal arches (3-4 times); stroking from the sternum along the pectoralis major muscle on the left to the spine. The procedure is completed by applying pressure to the left armpit (its muscles). The massage therapist is positioned on the side, the patient fixes his left hand. All movements in the cavity are made from the bottom up along the middle lateral line of the chest, repeating stroking 5-6 times, rubbing 4-5 times. The massage manipulations are completed by influencing the left upper limb, starting from the area of the shoulder, girdle, forearm, hand with an emphasis on the ulnar line and the Shen Men, Shao Chun, Shao Hai points, as well as light stroking movements from the left nipple to the 2nd chest line to the qi-hu point (5-6 movements) (Fig. 139).
Rice. 139. Points used for pain in the heart area
You should pay special attention to the displacement of the reflex and massage the lower left part of the chest. Duration of the procedure - up to 20 minutes, per course - 8-10 sessions, alternate with other types of massage (classical, acupressure, periosteal). HYPERTENSION DISEASE This disease is caused by increased arterial tone. Hypertension is divided into 3 stages. Stage I - increase in blood pressure to 160... ...180/95...105 mm Hg. Art. There are no changes in the myocardium, often short rest and rest completely normalize the person’s condition, however, sleep disturbances, headaches, decreased mental performance, and noise in the head may be observed. Stage II - blood pressure is increased to 180... ...200/105...115 mm Hg. Art. Hypertensive crises occur periodically, and left ventricular hypertrophy is detected by X-ray and ECG. Stage III is the most severe. Blood pressure above 200/115 mmHg. Art. This stage often ends with myocardial infarction or stroke. Massage as a therapeutic method is indicated for stages I and II of hypertension. In stage III hypertension, massage cannot be used! Methodology. The patient is in a sitting position supported by a headrest or pillow. Massage of the interscapular area from the level of the spine T2-7 (D2-?) along the 1st and 2nd lines (1.5-2 cun from the midline), 3-4 passes of each type of technique. All movements are performed from top to bottom: 1) stroking - flat, ironing, comb-shaped, rake-shaped, all techniques with weights; 2) rubbing - straight, circular, spiral, sawing, comb-shaped (with bent fingers, back side); all techniques can be performed with weights, as well as “shading” and “planing” techniques; 3) kneading - pressing, shifting, stretching, forceps; 4) vibration - labile, continuous, with one or two hands, individual fingers. Massage of the collar area in the direction from the Feng Fu point to the Jian Yu points: 1) stroking - grasping, flat, forceps-shaped, comb-shaped, rake-shaped, all techniques are performed unilaterally with weights in the direction from top to bottom towards the shoulder joints; 2) rubbing - straight, circular, sawing, crossing, hatching, pincer-shaped, all techniques can be performed with weights; 3) kneading - transverse, longitudinal, pressing, shifting, stretching, forceps, all techniques with weights; 4) vibration - labile, continuous, with individual fingers, one hand or both, all movements from top to bottom. Head massage. A massage of the occipital region is carried out - influencing the feng fu, feng chi, tian-yu points in 10-15 stages with a sedative method, on all symmetrical points at the same time, and single points with one finger. Then the effect is “shifting”, “pressing” from the occipital protuberance to the crown (from feng fu to bai hui) upward, 8-10 passes. Next, proceed to perform massage manipulations over the scalp, all movements are carried out individually, taking into account the direction of hair growth and the patient’s hairstyle: 1) stroking - plane, grasping, rake-shaped, tong-shaped, ironing; 2) rubbing - circular, straight, spiral, hatching; 3) kneading - pressing, shifting, stretching, forceps; 4) vibration - continuous, labile and stable, puncturing, point effects. Massage of the frontal part of the face. All movements are directed from the midline to the ears or from the superciliary arches to the occipital part of the head: 1) stroking - plane, rake-shaped, comb-shaped, ironing, forceps-shaped; 2) rubbing - step over the frontal part of the face - straight, circular, hatching; 3) kneading - pressing, shifting, stretching, forceps; 4) vibration - continuous, both labile and stable, point impacts (e-zhong, tou-wei). Then, the symmetrically located points of the sy-bai (infraorbital foramen) are simultaneously affected by the techniques of “shading”, “puncturing”, “tapping” for 10-15 s. Sedative effect on BAP. Act on the yin-tang, e-zhong, shen-ting, and bai-hui points for 1.5-2 minutes each. Then repeat the scalp massage in the previously recommended directions. Complete the procedure with a massage of the collar area, as at the beginning of the technique, and a massage of the interscapular area along the 1st-2nd line from top to bottom from D2-7 (T2-7). Perform all previously recommended massage techniques in the same sequence. The duration of the procedure is 10-15 minutes. For headaches, this technique can be used 2 times a day; for the treatment of stage I-II hypertension, the course consists of 20-24 procedures with mandatory instrumental determination of blood pressure. It is carried out in a calm environment (no telephone, loud music or other irritants). Perform only if you have high blood pressure, do not do if you have hypotension! This technique, after influencing the outputs of the infraorbital nerve (Si-Bai points), is expanded by influencing points along the midline of the head in an inhibitory manner for 1.5 to 2 minutes, starting from the Yin-Tang, E-Zhong, Shen-Ting, Bai points -hui (Fig. 140). HYPOTONIC DISEASE The main manifestations of the disease are a pronounced decrease in blood pressure, general weakness, fatigue, headaches, pain in the heart, dizziness, especially when changing body position, decreased ability to work, fatigue. Methodology. The patient's position is lying on his stomach, perform all massage techniques in 4-5 passes.
Rice. 140. Points used for hypertension
Back massage (from L5 to Sz) 1) Stroking - grasping, flat, rake-shaped, comb-shaped, ironing, weighted, forceps-shaped; 2) rubbing - straight, circular, spiral, sawing, crossing, pincer-shaped, hatching, planing, various directions of movements, shuttle; 3) kneading - longitudinal, transverse, rolling, shifting, stretching, pressing, forceps, all kneading with weights and in different directions, shuttle; 4) vibration - continuous and intermittent, both labile and stable, chopping, tapping, patting, puncturing, sparing the projections of the heart and kidneys on the back area. Massage the entire back, lumbar and cervical region. Massage of the gluteal region 1) Stroking - grasping, flat, comb-shaped, rake-shaped, with weights, tong-shaped, ironing; 2) rubbing - straight, circular, spiral, weighted, pincer-shaped, sawing, crossing, hatching, planing; 3) kneading - longitudinal, transverse, pressing, with weights, shifting, stretching, forceps; 4) vibration - continuous and intermittent, both labile and stable, shaking, tapping, patting, chopping, puncturing. Massage of the lower extremities (back surface). If the person being massaged has congestion (varicose veins, hematomas, complaints of swelling, hemarthrosis, poor circulation), massage of the back surface of the legs is carried out in the following sequence: thigh, lower leg, foot; in the absence of these pathological disorders, you can start the massage from the foot and further lower leg, thigh: 1) stroking - grasping, flat, rake-shaped, comb-shaped, ironing, all techniques with weights; 2) rubbing - straight, circular, spiral, weighted, sawing, crossing, pincer-shaped, hatching, planing; 3) kneading - longitudinal, transverse, pressing, with weights, tongs, felting, shifting, stretching; 4) vibration - continuous and intermittent, both labile and stable, chopping, patting, tapping, shaking, puncturing, shaking! Massage of the lower extremities on the front surface (in a position of being massaged while lying on your back) 1) Stroking - all types of techniques and with weights; 2) rubbing - all types of techniques and with weights; 3) kneading - main and auxiliary types of techniques, except for rolling; 4) vibration - continuous and intermittent, both labile and stable, chopping, tapping, patting, puncturing, shaking, shaking; 5) passive movements in all joints of the lower extremities with simultaneous compression of the points corresponding to the joint. Chest massage 1) Stroking - all types of techniques towards the lymph nodes; 2) rubbing - all types of techniques, carried out in different directions on the front of the chest; 3) kneading - longitudinal, transverse, rolling, pressing, shifting, stretching, pincer-like; 4) vibration - labile and stable, both continuous and intermittent (take into account the guidelines for the use of vibration on the anterior surface of the chest). Massage of the abdominal area Perform all massage techniques taking into account intestinal peristalsis, making movements from right to left in a clockwise direction: 1) stroking - main and auxiliary types of technique; 2) rubbing - all types of techniques, carried out in the direction from right to left, also using shading and planing; 3) kneading - all varieties of basic and auxiliary techniques, except felting, the same in a clockwise direction; 4) vibration - variations of the technique, taking into account the state of the person being massaged and his response. Complete the massage with breathing movements. The duration of the procedure is 25-35 minutes, 10-12 procedures per course. Combine with exercise therapy, physiotherapy, balneological and other treatment methods. The technique of acupressure for hypotension is presented in Fig. 141.
Massage of the shoulder girdles (shoulders) for hypertension
The massage is performed in a sitting position. Both hands of the massage therapist are involved, with which he performs actions in the following sequence:
- spiral rubbing of the shoulder joints;
- rubbing, in which spirals are “written out” with your hands. They are carried out from the back of the shoulders to the auricle;
- rubbing in straight lines, running from the neck to the shoulder joints;
- sawing, which is carried out from the neck to the shoulder joints;
- kneading areas from the neck to the shoulder joints with pincer-like movements.
Relaxing massage "Anti-stress"
The effect of stress is associated with an inevitable increase in the level of cortisol in the blood, which slows down the saturation of muscles with amino acids. The general nervous condition also causes muscle fibers to tense, causing physical discomfort. The cervical-collar area spasms the most, which can easily be soothed by a relaxing Anti-Stress massage, which helps a person quickly return to inner peace and harmony.
ANTI-STRESS MASSAGE METHOD SHVZ
When preparing to perform a therapeutic effect, the massage therapist prepares for a more gentle effect than that provided for the treatment of cervical osteochondrosis and other diseases. Relaxing hand contact is associated only with gentle contact of low or medium force. The main effect is on the head area.
Sequence of performing the “Anti-stress” technique:
- Stroking.
Hands clasp your head, then they gradually descend to your shoulders (repeat 5 times). Then the impact is transferred to the neck: movements in a circle, carried out with the pads of the fingers, begin from the location of the first vertebra and reach the skin of the shoulder girdle. - Massage of the back of the head and ears.
The thumbs are placed behind the ears, while the other fingers are bent and slightly further away. The trajectory of the hand movement is from the behind-the-ear space to the center of the back of the head. Then a similar technique is repeated in the opposite direction (3 times). - Temple stimulation.
A similar movement in the CVZ area is performed up to the back of the head, but begins from the temple area. Working out the temporal part is an important part of anti-stress massage: impact on this area helps to quickly relieve headaches, which are often present with nervous tension. It is necessary to repeat the reception until a feeling of lightness appears. - Massage of the parietal area.
The fingers repeat a scratching-like movement directly in the area of the parietal part of the head. - Kneading the forehead.
The fingertips are placed on the area where hair begins to grow (face area), and the little fingers touch the eyebrows. Circular movements are gradually transferred to the right and left. Another option is to use two hands, but massage without moving the fingers. - Impact on the shoulder girdle.
The massage therapist moves his fists from the back of the head to the shoulder joint. The manipulation is repeated 8–10 times. - Finger rain.
A pleasant, relaxing procedure that relieves tension through rhythmic but light tapping of fingers over the entire surface of the head, neck and shoulders.
The recommended duration of massage for the cervical-collar area is 8–10 minutes. To enhance the relaxing effect, you can also use aromatic candles, quiet music and essential oils, which help to quickly distract from unpleasant thoughts and emotions.
Medical fact
Taking a course of relaxing massage helps to significantly increase stress resistance.
CONCLUSIONS
It is recommended to use this type of massage for anyone experiencing excessive mental or physical stress. You can also use anti-stress body massage if necessary occasionally, if you have to deal with exciting situations only occasionally. An additional pleasant effect is a change in a person’s attitude towards a stressful situation after therapeutic stimulation. Relaxation and recuperation help make the problem less significant or find ways to get rid of it faster.
Neck massage along the front surface at high pressure
The patient sits on a chair, the massage therapist stands behind him and performs:
- stroking with palms from the chin to the collarbones and armpits;
- slight tingling of the muscle running from the ear to the collarbone;
- lightly stroking the front of the neck.
With the same movements and in the same sequence, a person can perform self-massage for hypertension.
You can help yourself with hypertension by performing a back massage. To do this, lie on your stomach and place a rolled-up blanket under your feet so that your shins are at an angle of 45-100 degrees. Turn your head as comfortably as possible.
Now use your hands to stroke your back from the pelvis to the neck 7 times. Kneading is then performed in the same direction, which is also performed seven times.
Now proceed to self-massage of the collar area. It is first stroked, then “squeezed” with the pads of the fingers, without touching the neck area, and rubbed in straight lines using the thumbs.
Self-massage
Self-massage is a procedure designed to replace the therapeutic effect provided by a massage therapist. It is also useful to acquire the skill of self-massage of the neck and shoulders to relieve spasms during the working day. Restoring good health may be necessary both during a hike and before performing physical exercises, which sometimes - without warming up the muscles - cause discomfort in the body. Anyone can quickly master the technique performed with their own hands, thanks to relatively simple techniques that are easy to repeat.
SELF-MASSAGE TECHNIQUE SHVZ
The exercise can be performed either sitting or standing - the effectiveness of the effect does not change depending on the position of the body. However, uncomfortable positions that cause muscle tension should be avoided.
Method of neck and shoulder self-massage:
- Neck.
First, you grab it with both hands, which touch the cervical vertebrae with your fingertips, but do not press on them. Then strokes are carried out, descending from top to bottom (amplitude from 1 to 3 cm). Stimulation options: with both hands simultaneously or with each hand alternately. - Shoulder girdle.
Having begun to rub the neck in a circular motion, the person, without leaving the body, moves his hands to his shoulders and rhythmically grasps the skin (the technique of squeezing the fingers is reminiscent of the process of sculpting plasticine). Gradually, the massage area of the neck-collar area shifts to the shoulders. - Upper back.
Together with the shoulder girdle, the adjacent skin areas are kneaded. The maximum amount of time should be devoted to the upper trapezius muscle, which is often very tense. - The entire neck and collar area.
At the end of the massage, any actions are performed that can be repeated with your own hands - patting, tapping, chopping (20 times each technique). Kneading the muscles should be completed by stroking.
If during self-massage you were able to detect trigger points that cause pain when pressed, then you should rub them very carefully.
Only specialists in the field of massage have the knowledge and skills to help bring exceptionally beneficial effects to these areas of the body.
Medical fact.
You can massage the CVZ area even through clothing, so you can provide a therapeutic effect not only at home.
Acupressure for high blood pressure
Acupressure for hypertension can be effective in reducing blood pressure to some extent. It is based on the communication of some vibration to biologically active points, which can be located symmetrically on the body, or can be in a single copy. In the first case, the points are massaged simultaneously, using two index fingers; if there is only one point, only that is massaged. Circular movements are made clockwise.
At the beginning of the massage and at the end, the pressure on the point is less than in the middle. Massage duration is 3-5 minutes. During this procedure, breathing is smooth, calm, and the body is relaxed. To treat hypertension and high blood pressure, the following points are used for massage (see picture):
- Symmetrical point tzu-san-li (massaged on two legs). It can be found in the depression, which is located 4 fingers below the kneecap, if they are positioned transversely (point 1 in the figure) and outward from the edge of the tibia by the width of one finger. Massage for 5 minutes.
- 2 symmetrical points: between the 1st and 2nd toes, between the 2nd and 3rd toes. Massage time – 5 minutes (points 2 and 3 in the picture).
- Symmetrical point. It is found 4 transverse fingers above the inner ankle of the foot (see picture - point 4).
- Symmetrical point. Spread your thumb and index finger apart. The point is located in the resulting space, between two bones (point 5 in the picture).
- Asymmetrical point. It is located at the intersection of the line running along the middle of the head and the one that connects the upper parts of the ears (point 6 in the picture). Massage for 3 minutes.
Contraindications to facial massage
For facial massage, the list of contraindications is shorter:
- — Acute inflammatory processes in the oral cavity and sinuses (acute sinusitis, sinusitis, rhinitis, stomatitis, gingivitis, carious mouth)
- — Herpes
- — Acne above grade 2 (inflammatory elements more than 10 pieces) or furunculosis
- — The period after deep peelings and cleansing (up to 1 month)
- — Oncology.
Facial massage is not recommended after Botox and other injections, and installation of gold threads
Massage at the cellular level at home
For hypertension, massage using the medical method of phonation is especially effective by transferring microvibration energy into the body. This method affects the blood supply and lymph flow of a certain area of the body, affecting the tone of blood vessels and the speed of blood flow through them, activating nerve receptors located in the skin and deeper tissues, thereby:
- improving cell nutrition and oxygen supply;
- promoting metabolism and biochemical reactions that enable life to exist;
- accelerating the cleansing of tissues from dead cells and decay products (poisons, waste);
- providing cell regeneration (restoration).
Phonation is carried out by a special medical device Vitafon, developed in 1992 by Russian physicist V.A. Fedorov.
Considering the mechanics of the device, we can say that it produces massage at the cellular level up to 10 cm deep inside the body. This vibroacoustic massage can be performed independently and at home.
The effectiveness and safety of this medical method, unlike other types of massage, is confirmed by numerous scientific studies and clinical practice.
You can read more about this here.
To summarize, we can say that a positive answer to the question “is it possible to do massage with high blood pressure and hypertension?” will only be a correctly performed medical massage with a focus on the patient’s sensations during its implementation. If, during the process of manual massage, excessive efforts cause damage to the tissues of the body, this can lead to narrowing of the arteries, and accordingly, after the massage, the pressure may rise, since the body cannot allow the blood supply to the brain to deteriorate.
List of used literature:
- Dubrovsky V.I. Massotherapy. Practical guide. – M, GEOTAR-MED, 2005.
- Shapkin V.I. Reflexology: a practical guide for doctors. – M, GEOTAR-MED, 2015.
- Schnorrenberger Klaus K. Acupuncture therapy, 2012.
- Ivanichev G.A. Manual medicine. – M, MEDpress-inform, 2003.
Author of the article: intensive care physician M.S. Krivega (Regional Infectious Diseases Clinical Hospital, Zaporozhye)
You can ask questions (below) on the topic of the article and we will try to answer them competently!
Hypertension
Hypertension is a disease characterized by high blood pressure. Blood pressure is the pressure with which blood presses on the walls of blood vessels. Blood pressure is considered normal if it is 110-120/70-80 mmHg. Arterial hypertension is a condition in which the pressure reaches 140/90 mmHg or higher.
Causes of arterial hypertension
Various factors can contribute to increased blood pressure, such as:
- condition of blood vessels, heart and kidneys,
- level of water and salt in the body,
- level of hormones in the body.
Arterial hypertension can also be caused by obesity, anxiety, nervous disorders, constant stress, age, alcohol abuse, smoking, excess salt in the body, diabetes, hereditary arterial hypertension.
Due to arterial hypertension, there is a risk of developing heart failure, dangerous kidney diseases and the risk of death at a young age.
Arterial hypertension can develop due to long-term use of medications or against the background of current diseases of the body. This arterial hypertension is called secondary, its causes can be:
- diseases of the adrenal glands (Cushing's syndrome or pheochromocytoma),
- chronic kidney disease,
— pregnancy (increased blood pressure during pregnancy is extremely dangerous, preeclampsia may occur),
- renal artery stenosis (narrowing of the artery that carries blood to the kidneys),
- hyperparathyroidism,
- long-term use of contraceptives, diet pills, medications for migraines and colds.
Symptoms of arterial hypertension
In the early stages of the disease, there are usually no symptoms. Increased blood pressure is usually detected during routine medical examinations.
In severe form, arterial hypertension is characterized by headaches, dizziness, nausea and vomiting, blurred vision, nosebleeds, and confusion.
Examination and diagnosis of arterial hypertension
To make a diagnosis of arterial hypertension, it is necessary to measure blood pressure several times a day for several days. The patient needs to acquire a home device for measuring blood pressure and independently chart the results obtained. The doctor will study this graph and take note of the information, and the patient will be able to draw conclusions about changes in pressure during the day and the reasons that cause “jumps” in pressure.
Treatment of arterial hypertension
The goal of treating hypertension is to lower blood pressure and reduce the risk of various complications.
Treatment methods include taking medications, quitting smoking and alcohol, following a diet that excludes fatty and salty foods, playing sports, and losing excess weight.
Patients diagnosed with arterial hypertension should undergo regular preventive examinations, monitor their health, and consult a doctor promptly if their blood pressure increases in order to prevent the development of the disease.
Help of massage of the collar area
Of all the anatomical zones of the human body, the most effective in relation to blood pressure levels is the collar zone. A large number of neurovascular bundles pass through this area, causing reflex effects on blood pressure. That is why neck massage is very effective in treating arterial hypertension.
The method of massage of the collar zone for arterial hypertension is extremely simple and is not difficult even for performing this massage independently. Massage of the collar area includes three main massage techniques: kneading, stroking and rubbing.
Neck massage has no contraindications or side effects. In addition, it can be used not only to treat arterial hypertension, but also to prevent this disease.
History of massage - in both India and China, massage was performed by clergy. In addition, schools were created in these countries that taught massage techniques.
Massage products - for the prevention and treatment of various diseases, special ointments are used that have a positive effect on muscles and tissues due to the components they contain.
Leg massage - massage carried out systematically for 2-3 weeks will help prevent cramps and spasms in the muscles of the lower extremities in the future. Look at all costs: the price in the advice store is leeching!
Neck massage - before moving on to massaging movements, you need to prepare the skin: it needs to be cleaned, warmed and lubricated with a nourishing cream. The cream should be applied with soft stroking movements from bottom to top.
Prostate massage - the causes of inflammation of the prostate gland are infectious diseases, sexual abstinence or sexual excess. It is recommended to carry out a massage, which...
Lower back pain - sets of exercises should be performed only during periods of attenuation of pain and interrupted when it appears.
Massage and metabolism - If you massage immediately after physical activity, the release of nitrogenous substances will increase by 15%. In addition, massage performed after muscular work accelerates the release of lactic acid from the body.
Massage and blood circulation - under the influence of massage, the movement of all body fluids, especially blood and lymph, accelerates, and this happens not only in the massaged area of the body, but also in distant veins and arteries. So, foot massage can cause redness of the scalp.
Features of the procedure
The course may include 10-15 sessions every 2-3 days. If the massage is performed for medical reasons, the doctor will adjust the duration of the course depending on the patient’s well-being.
The massage procedure has several features:
- Not only the professionalism of the massage therapist is important, but also a relaxing environment . Therefore, the room should have a comfortable temperature and pleasant music. Some massage therapists use incense.
- The massage is carried out using oils and creams, which also have a certain effect . For example, lavender in the composition relaxes, peach oil improves skin elasticity, etc.
- The duration of one session is approximately 30 minutes . For a child, the massage should last no more than 15 minutes.
- The specialist is obliged to pay attention to the patient's requests and comments . The procedure should not cause severe pain or discomfort.
- After finishing the massage, you need to get up very smoothly , slowly, without making sudden movements.
It is very important to contact a trusted specialist who knows how to massage a specific area and how hard to apply pressure to the skin and muscles. If the massage was done incorrectly or unprofessionally, migraines may appear or worsen, chronic diseases may worsen, or a sharp increase in blood pressure (hypertensive crisis).
Sometimes a massage therapist, in addition to oil and cream, uses additional products, for example, sea salt. It helps remove edema, reduces the manifestations of osteochondrosis, and breaks down fatty deposits. But you should not use even fine salt for people who have very thin or sensitive skin. This will lead to burning and irritation.
Also, natural honey is often used during massage if the client is not allergic to bee products. Honey improves the condition of the skin, has a good lifting effect, removes excess fluid and toxins, softens, and improves lymph flow. But in its pure form, honey is not applied to the skin; it will stick to your hands and interfere with stroking. It is heated a little to make it more liquid, and then mixed with butter or cream.