Introduction
The great Russian scientist and academician I.P. Pavlov wrote: “Man is the highest product of earthly nature. Man is the most complex and best system. But to enjoy this treasure, a person must be healthy, strong and smart.” He also wrote this: “A person can live up to 100 years. “By our own impudence, by our own confusion, by our own ugly treatment of our own bodies, we reduce this normal period to a much smaller number.”
The average life expectancy of a Russian citizen is 65 years. For comparison, the average life expectancy in the United States is 77 years, in Japan - 78 years. Russia is one of the leading countries in the world in terms of mortality from cardiovascular diseases. Not everyone in our country still understands that a healthy lifestyle is very important. It is much easier to prevent a disease than to treat it. To prevent this, we must refocus our medicine on health. This does not mean that doctors should stop treating patients. But in addition to diseases, it is necessary to know well the characteristics of health in order to be able to give qualified advice to those who want to maintain and strengthen it. And for this you need a psychological reorientation from a doctor. He himself must believe in the power of the body's defense mechanisms if they are properly trained. After all, the main obstacle to the spread of a healthy lifestyle is people’s psychology. Many people tend to resist both restrictions and stress until there is a real need for it. A doctor can and should change a person’s psychological attitude. My dream is to become a doctor and treat people. I would like to be an example of how to promote a healthy lifestyle for my future patients. It's not easy, but I think every doctor should strive for it. And then disease prevention will be the main task of our healthcare.
Cardiovascular diseases
Cardiovascular diseases, along with cancer and diabetes, are at the forefront of the most common and dangerous diseases of the 20th and 21st centuries. The most terrible epidemics of plague, smallpox and typhoid fever are a thing of the past, but their place is not empty. New diseases also correspond to new times. It is not for nothing that the medicine of the future should be called the “era of cardiovascular diseases.” Why are these diseases so common? There are many reasons for this, let's focus on just a few of them.
The human cardiovascular system, created during its biological evolution, has not changed significantly throughout the history of mankind. But our way of life is very different from the way of life of our distant, even not very distant ancestors. At that time, physical exercise, food production, housing and all other activities required constant and large expenditures of muscle strength. And the human circulatory system is initially oriented towards such an intense lifestyle. To function normally, a person must, for example, travel at least 6 km a day, every day! By our modern urban standards, many cannot even walk one or two bus stops to the nearest metro station. In most cases there is no time for this.
Undoubtedly, our ancestors had much more free time than we do, and at the same time, in a mysterious way, much more. Let's give an example from the textbook: The enormous literary heritage of Pushkin and Lermontov was left to us by poets, the first of whom died at the age of 37, the second - 28 years. Until this time, they had written volumes of brilliant works, not to mention the fact that literary creativity did not interfere with their active life in other areas. Our body is precisely tuned to such a detailed, leisurely, but eventful life with great physical activity and a wealth of various emotions. But are there many people today who can still afford to live like this?
It may seem surprising that most cardiovascular disease is caused not by overuse, but by chronic, constant overload. However, this is only surprising at first glance. Of course, everyone knows perfectly well how weakened muscles will become if they do not exercise. And the heart also has a muscle, and it is just as useful under heavy loads as any other muscle in the body. Of course, now we are talking about a healthy heart. Blood vessels also contain muscle tissue, and they also need exercise. Vascular heart disease.
In fact, the importance of cold and contrast techniques and people's favorite baths and saunas is that at first the ambient temperature is very high, and then it changes greatly to very low. The ships are expanding and entering into contracts, which means they are working. This is their training. It is better to start such procedures from an early age. It has been proven that children who are given cold water after a warm bath feel better and get less sick. Unfortunately, many parents who sincerely want to protect their child from diseases create a “pleasant” temperature regime that is the same both in summer and winter, both at home and outside. After the first puff, the child becomes ill, and the first serious infection leads to cardiac complications. Why, he was so well taken care of, right? Precisely because they did not “care” about it - the blood vessels and heart did not learn to respond correctly to the environment.
Therefore, muscle weakness not only makes a person physically weak, but also reduces his natural stamina and hence is just a step away from being exposed to all sorts of diseases, bacterial and viral. By the way, infections can spread in the heart, for example, flu or angina, often with improper treatment of complications in the form of myocarditis - inflammation of the heart muscle, myocardium, which has already been mentioned. People who lead a sedentary lifestyle are more likely than others to suffer from obesity, which is usually caused by the body's excess demand for nutrients and energy. Obesity inevitably leads to respiratory problems (shortness of breath), resulting in pulmonary and heart failure (cardiovascular failure). In addition, overweight people have a significantly increased risk of atherosclerosis, since the blood vessels (as we have already noted, they are usually unprepared) can no longer cope with the increased blood circulation.
An untrained cardiovascular system leads to other types of problems. For most modern people, especially citizens, the global decline in physical activity has led to an increase in excessive nervous and mental stress. This is largely due to the amount of information that comes to us every day through television, newspapers, the Internet and other media. If we consider that most of this information evokes strong negative emotions in us, it becomes clear how overloaded the human nervous system is.
But the nervous and cardiovascular systems are closely interconnected. Every strong emotion causes one or another reaction in the body, and every reaction of the body is associated with at least minimal changes in the blood supply to the organs. For example, we are ashamed, and our faces turn red from the blood flow. We are afraid, trembling and trembling in the body - this is a large amount of the stress hormone adrenaline that has entered the blood. We worry, our heartbeat races. And there are many examples of this. Behind every such, albeit minor, change in blood circulation is the cardiovascular system. Nature has created a way to relieve excess stress from the body: Man has designed it in such a way that the release of nervous tension occurs in the most natural way in the process of increased physical activity. But when the balance between physical and neuropsychic stress is disturbed, the reaction to emotional stress is overly pronounced, prolonged, and acquires pathological features. Thus, diseases such as high blood pressure and atherosclerosis begin to develop in the cardiovascular system, which are usually followed by coronary heart disease and myocardial infarction.
In search of a replacement for the “sensation of muscular pleasure” (as the greatest physiologist of the last century, I.P. Pavlov, called it), some turn to means of artificial jubilation. Thus, people get caught up in bad habits and often forget that the use of alcohol, tobacco and, moreover, drugs can trigger the development of many cardiovascular diseases, especially coronary heart disease.
Cardiovascular diseases and new technologies
Today, the treatment of cardiovascular diseases has become a matter of our national security. Mortality from them in Russia has increased almost 1.5 times over the last decade, and people are increasingly dying at working age. 55.5% of total mortality is caused by diseases of the heart and blood vessels, of which almost half of the cases are caused by coronary heart disease and cerebrovascular diseases. The 12th (LXXV) session of the General Meeting of the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences, held at the end of March in Moscow, was entirely devoted to new biomedical technologies in the prevention, diagnosis and treatment of cardiovascular diseases.The reality and hopes of cardiology
As Academician of the Russian Academy of Sciences and Russian Academy of Medical Sciences Evgeniy Chazov (Russian Cardiology Research and Production Complex of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation) noted in his report, the main contribution to the increase in mortality was made by the most difficult period in the life of the country, the most difficult psychosocial situation, loss of reference points, impoverishment, and unemployment. The most crisis periods clearly correlate with an increase in mortality (the beginning of economic reforms in 1992-1993, the default in 1998). Thus, we can talk about the neurobiology of social processes - a new field in medical science. Psycho-emotional stress is accompanied by changes in a number of organs and systems in the body. For example, the number of neurons in the brain decreases; in severe cases, changes occur in the hippocampus.
Recent studies conducted at the Russian Cardiology Research and Production Complex (RKNOK) made it possible to confirm the hypothesis expressed by A. Myasnikov about the role of the central nervous system in the development of a number of cardiovascular diseases. Moreover, not only changes occur in the brain, but the activity of the immune system is also disrupted: the level of C-reactive protein, pro-inflammatory interleukins, and tumor necrosis factor increases. Experimental studies have shown that blood pressure levels correlate with norepinephrine synthesis.
Scientists' views on the process of atherosclerosis are changing. It turned out that the formation of atherosclerotic plaques and atherothrombosis are associated with inflammatory processes in the vascular wall, both exogenous and endogenous. Cytomegaloviruses play a significant role in this process.
New knowledge is changing diagnostic and treatment methods. For example, a number of proinflammatory cytokines are markers of restenosis. Ultrasound examinations make it possible to study the state of the “intima-media” complex, which is extremely important in diagnosing coronary heart disease. Intravascular ultrasound makes it possible to determine not only the presence of atherosclerosis, but also the consistency of the plaque. And finally, a new method has emerged for studying calcium in blood vessels using electron beam or mainline computed tomography, which allows one to judge the nature of atherosclerotic changes in the coronary vessels without coronary angiography. The amount of calcium determined by this method correlates with the degree of atherosclerosis.
Before the eyes of our generation of doctors, revolutionary changes have occurred in the field of diagnosis and treatment of cardiovascular diseases, noted E. Chazov. Modern methods place the diagnosis of coronary heart disease in the category of student tasks. Unfortunately, primary health care is deprived of instrumental capabilities, and the knowledge of doctors at this level is insufficient to diagnose IHD.
Advances in medicine are most clearly demonstrated in changing the fate of patients with myocardial infarction. In the 60s, at the Institute of Therapy, the best clinic in the country for the treatment of this pathology at that time, the mortality rate exceeded 30%, and now it is about 5%. This happened due to the creation of intensive observation units, thrombolytic therapy, shock control, and a rehabilitation system.
The use of genes for therapeutic purposes also promises wide possibilities - from angiogenesis to the transformation of simple cells into cardiomyocytes. In this regard, much hope is placed on stem cells. In the emergency treatment department of the RKNPK, stem cells were injected intracoronarily to treat a critically ill patient with myocardial infarction, who now feels quite well. For now, this is a clinical experiment, but it has a great future, E. Chazov emphasized.
Cellular technologies
“Why does a heart surgeon devote his report to cellular technologies in cardiology?” — the report of Academician of the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences Yuri Shevchenko (National Pirogov Medical and Surgical Center of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation) began with this question. This is a deeply conscious choice that he and his colleagues came to a long time ago when they were faced with professional dissatisfaction with the results of cardiac surgery. If the myocardium does not have reserves, neither the efforts of surgeons, nor the medical capabilities, nor the achievements of technical progress will help it. The problem of myocardial viability is the main one, and not only in cardiac surgery. The myocardium does not regenerate, only a scar is formed, and heart failure and severe circulatory failure subsequently develop.
Cellular technologies have recently shown themselves to be very attractive in terms of restoring the functions of various organs. The greatest attention is drawn to hematopoietic stem cells, which may be able to replace cardiomyocytes. This technology has been developing over the past 5-7 years, but interesting experimental and clinical experience has already been accumulated. Experimental studies using stem cells in the treatment of myocardial infarction have shown intensive migration of these cells into the infarction zone and their differentiation into cardiomyocytes with the formation of blood vessels.
Yu. Shevchenko reported on his own clinical experience of transplantation of cultured embryonic cardiomyocytes, carried out in compliance with all ethical standards in 1997-1998. in four patients with heart attacks as an addition to conventional coronary artery bypass surgery. However, not a single patient died, all of them quickly recovered after the operation and are currently feeling well, which at least indicates the safety of this method. Previous experimental studies have shown that this procedure improves the function of one’s own cardiomyocytes, stimulates angiogenesis in the affected areas of the myocardium, restoring its function.
Cardiac surgeons increase activity
Academician of the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences Leo Bockeria (Scientific Center for Cardiovascular Surgery named after A.N. Bakulev of the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences) in his report “Cardiovascular and endovascular surgery: the latest technologies and achievements in the aspect of prevention and treatment in adults and children” spoke about successes in surgical treatment of congenital heart defects in Russia over the past 5 years - the number of clinics performing operations with artificial circulation has increased, the number of patients operated on has increased by 25%, and the number of children operated on in the first year of life has increased. Without surgical treatment, more than 70% of children with congenital heart defects die within a year. The situation requires changes in the organization of medical care for such children. On the basis of the Scientific Center for Cardiovascular Surgery named after. A.N. Bakulev created a perinatal center with emergency cardiology departments and two surgical departments.
Minimally invasive surgery is increasingly being used to treat acquired heart defects, as CT scans can now provide three-dimensional images of the chest and accurately determine the location of the incision. Surgeons have a wide range of domestic artificial heart valves in their arsenal, including bicuspid ones, which are not inferior to foreign models. Mortality during such operations is close to zero; 97% of patients do not need valve replacement for 10 years or more.
The problem of surgical care for patients suffering from coronary heart disease is still acute, but there are encouraging trends here too - compared to 1996, the number of angioplasty operations has increased 5.5 times. Today there is a real opportunity to help a patient whose coronary artery bypass surgery may not give the desired effect. The National Center for Cardiovascular Surgery has developed a method for mapping the heart using radionuclide testing, which allows assessing the effectiveness of the intervention. A simultaneous combination of CABG and transmyocardial laser revascularization is widely used, which makes it possible to achieve complete restoration of blood supply to the myocardium.
However, as L. Bokeria emphasized, the potential of the institutes of the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences, including the National Center for Agricultural Sciences, is not used enough. In all areas of cardiovascular surgery, the latest scientific directions are rapidly emerging, requiring organizational decisions. It is necessary to create federal programs for the treatment of congenital heart defects in newborns, life-threatening arrhythmias, and acute coronary circulatory disorders.
On the way to an artificial heart
One of the important areas being developed at the Research Institute of Transplantology and Artificial Organs is the study of the biomechanics of the heart muscle, as noted in the report of Academician of the Russian Academy of Sciences and Russian Academy of Medical Sciences Valery Shumakov and co-authors. Together with the Ural State University, a unique software and hardware complex was created that makes it possible to study the regional mechanical properties of the myocardium - contractile activity and elasticity of the left ventricular wall. This complex allows you to assess the condition of the heart muscle before and after revascularization.
As part of the heart transplantation program and a number of cardiac surgical operations at NIITiTO, a new method for regulating pulmonary hemodynamics based on inhalation of nitric oxide began to be developed for the first time. These studies were based on the recognition of the regulatory role of nitric oxide in numerous physiological processes, including the regulation of vascular tone. In total, inhaled nitric oxide was used in 261 patients to correct pulmonary hypertension, acute right ventricular failure and acute blood injury syndrome during operations with cardiopulmonary bypass. Against the background of continuous medical inotropic support after cardiac surgery, nitric oxide provided an improvement in the pumping function of the heart and cardiac index, a decrease in pulmonary artery pressure and intravascular resistance.
Methods of mechanical circulatory support in patients with heart failure continue to be intensively studied and applied in clinical practice. Over the past three years, the number of operations using intra-aortic counterpulsation has sharply increased at NIITiIO, which significantly improves the results.
Due to the fact that circulatory support systems are used in patients with extremely severe forms of heart failure, which require long-term use (up to several years), special requirements are placed on the design of these systems. Therefore, NIITiIO continues research to improve implantable circulatory support systems. Together with the Moscow Aviation Institute, we are developing an implantable electromechanical drive for a pulsatile ventricular pump. The total size of this drive does not exceed 300 cm, weight - 650 g, it can operate in autonomous mode for more than 2 hours and from the electrical network for more than 1 year. In the last decade, the design of another type of pump has been developed - a rotary one; it differs from a pulsating pump in its smaller size, quiet operation, lower energy consumption, lack of valves and, accordingly, blood trauma.
NIITiIO already has experience in transplanting autologous bone marrow cells for cardiomyoplasty. Using differentiation culture media, in vitro experiments confirmed the possibility of transforming up to 30-40% of mesenchymal stem cells into cardiomyocyte-like ones, some of which began to spontaneously contract. Experiments on animals have shown that these cells live and function in the transplantation zone both when administered intracoronarily and intramyocardially.
Cerebral stroke: problems and solutions
According to RAMS academician Evgeniy Gusev and co-authors (RGMU), about 450 thousand strokes are registered annually in Russia, and 200 thousand patients die. There are more than 1 million stroke survivors in the country. The authors prepared a stroke registry, which is used in many countries. For the first time in the world, a system of step-by-step care for patients with stroke has been created, which is used in 35 regions of Russia. An analysis of the work of the regions showed that the most effective treatment of patients with stroke is when hospitalized in a specialized hospital with a neurosurgical department. CT and MRI play a decisive role in verifying the diagnosis, and the earlier the patient is hospitalized, the lower the mortality rate for stroke.
The dynamics of stroke forms change with age. Up to 40 years of age, the hemorrhagic form dominates, by 45-49 years its frequency is compared with the ischemic one, and in old age the latter predominates. Analyzing the causes of stroke, the authors point to a predisposition to it and the main factors that trigger the pathological process (arterial hypertension, hyperlipidemia, hyperglycemia, hypercholesterolemia, chronic stress, migration, urbanization). If we cannot yet change heredity, then it is necessary to first take measures aimed at reducing the number of risk factors that contribute to the occurrence of stroke. If it has developed, then, if possible, one should strive to prevent complications caused by it. In the future, a system of rehabilitation measures and measures to prevent recurrent stroke are needed.
Among cardiovascular diseases, damage to the cerebral vessels is especially dangerous. Academician of the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences Nikolai Vereshchagin and Professor Zinaida Suslina (Research Institute of Neurology of the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences) in the report “Stroke in the Mirror of Medicine and Society” reported that in 2000 in Moscow more patients were hospitalized with stroke than with myocardial infarction. Hospitalization of patients with stroke is 26 per 10 thousand population, with myocardial infarction - 22 per 10 thousand. Mortality from stroke continues to increase.
Comparison of qualitative indicators of cerebral vascular damage in Russia and Western countries is not in our favor. The mortality rate for men from stroke in Russia is 2 times higher than in Northern European countries and 8 times higher than in the USA. Thanks to modern advances in science, technology and the quality of medical care in 25 European countries, mortality from stroke is reduced annually by 3-5%. With sufficient government attention to this problem, these results could be achieved in Russia, but, unfortunately, positive changes are not visible in our country.
Stroke is a heterogeneous clinical syndrome caused by many factors and various mechanisms, manifested in two forms - hemorrhage (20%) and ischemia (80%). In most cases, the disease can be diagnosed using generally accepted clinical methods, but the diagnosis can only be verified with computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging. Verification is extremely important for choosing the optimal treatment tactics: hemorrhagic stroke is subject to surgical treatment, ischemic stroke is subject to conservative treatment. Moreover, with ischemic stroke, it is important to know its subtypes, which directly determines the effectiveness of treatment and prevention.
When comparing the advantages and merits of a particular method, one must adhere to the principles of evidence-based medicine, and not opinions, even authorities. Taking this into account, modern stroke treatment tactics are based on the following principles: mandatory hospitalization of the patient in a specialized institution with a neurosurgical department; provision of medical care in neuroreanimation conditions. The optimal result for hemorrhagic stroke is achieved by emergency surgery using a stereotactic technique. Postoperative mortality with it is 2 times lower than with the open method of surgery. With the latter, mortality is almost the same as with conservative treatment. An important factor in a positive stroke outcome is competent conservative therapy in the first week of patient management followed by neurorehabilitation.
Stroke prevention is based on generally known facts. First of all, blood pressure control is necessary, which is usually often neglected by patients themselves and which doctors do not always take into account. By reducing high blood pressure, stroke can be prevented in almost 50% of cases and myocardial infarction in up to 20%. The second important control factor is to avoid imbalance of hemorheology. The third important factor is a healthy lifestyle (physical activity, eliminating bad habits, reducing salt intake to 1.5 g/day, etc.).
Different faces of cardiovascular pathology
Academician of the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences Nikolai Mukhin (MMA named after I.M. Sechenov) and corresponding member of the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences Valentin Moiseev (RUDN University) highlighted the problem of cardiorenal relationships, which is one of the key ones in the development of cardiology and nephrology. The most important achievements in one of these areas have always been useful for the other. Today, the relevance of this problem is determined by deciphering the mechanisms of blood pressure regulation, as well as the commonality of risk factors for damage to the cardiovascular system and kidneys. Knowledge of these mechanisms allows you to choose the optimal therapeutic strategy aimed at cardio- and nephroprotection. Its main targets are the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system and generalized endothelial dysfunction. At the same time, along with ACE inhibitors, the use of angiotensin-II receptor blockers, as well as neutral vasopeptidase inhibitors and statins is promising.
The report of Professor Veronika Skvortsova (RUDN University) was devoted to the mechanisms of the damaging effects of acute cerebral ischemia, as well as neuroprotection. The author analyzed the results of clinical and fundamental studies conducted in acute focal cerebral ischemia in different types of ischemic stroke. The modern concept of the damaging effect of ischemia on brain tissue, cellular, biochemical, molecular and genetic mechanisms of the development of cerebral infarction are presented. The main strategies for anti-ischemic brain protection, directions for therapeutic and preventive neuroprotection are proposed.
Professors Yuri Aleksandrovsky and Lyubov Romasenko (State Scientific Center for Social and Forensic Psychiatry named after V.P. Serbsky) in the report “Psychological and psychiatric approaches to the prevention and treatment of cardiovascular diseases” analyzed the psychological characteristics of those suffering from cardiovascular diseases and those noted in them cardiovascular disorders. A parallelism has been established in the increase in the number of patients with myocardial infarction and borderline mental disorders, in particular social stress disorders. In the clinical picture of cardiovascular diseases, doctors have learned to see manifestations of depression, anxiety disorders, panic attacks and successfully use psychopharmacological drugs. An example of the convergence of psychiatry and general medical practice is the successful experience of joint work of a “team” of psychiatrists with clinicians from the MMA named after. I.M. Sechenov and RKNPK.
Corresponding Member of the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences Nikolai Yakhno (MMA named after I.M. Sechenov) reported on modern technologies in the study of the diagnosis of cognitive and motor disorders in chronic cerebrovascular insufficiency. According to his data, chronic ischemia and acute decirculation of the brain often cause multiple lesions of the gray matter of the cortex and subcortex. The latter leads to mental (mnestic-intellectual and emotional disorders) and movement disorders. With significant spread of brain damage, the development of vascular dementia is possible. The doctor is faced with two serious tasks - to prevent stroke and mnestic-intellectual disorders.
Rheumatic fever occupies a significant place in the structure of population morbidity. Academician of the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences Valentina Nasonova (Institute of Rheumatology of the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences) reported that over 230 thousand patients with rheumatic heart disease represent the “gene pool” of this pathology. Hereditary predisposition to it is observed 6 times more often than in the general population (1.4%). At the same time, significant progress has been made in recent years in revealing the pathogenesis and diagnosis of rheumatic diseases. Thus, factor M-5, which can cause an autoimmune process, was found in the lipoproteins of β-hemolytic streptococcus. Post-rheumatic arthritis with a short latent period (3-5 days) has been identified. A correlation has been established between echocardiography parameters and immune signs of valvulitis.
Early diagnosis and prompt treatment of rheumatic fever remain important. Therefore, if we want to prevent its expected surge, we should pay special attention to children from families whose members suffered from rheumatic diseases and provide them with primary prevention. Primary prevention after a sore throat or other streptococcal infection is achieved by a single administration of 1.5 million units of bicillin-5, the activity of which remains for a week. For secondary prevention, benzathine-benzylpenicillin is necessary; its minimum inhibitory concentration lasts 3 weeks.
Academician of the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences Vladimir Petrov and Professor Alexander Spasov (Volgograd State Medical Academy) reported on the development and clinical studies of a new chemical class of antiarrhythmic drugs. Corresponding member of the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences Leonid Rozenshtraukh and co-authors (RKNPK) also reported on the creation of domestic class III antiarrhythmic drugs.
Professor Alexander Gavrilenko (Russian Scientific Center for Chemistry of the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences) gave an interesting report “New technologies in the treatment of critical ischemia of the lower extremities”. It is known that reconstructive vascular surgery has reached a certain limit. In some cases, limb ischemia cannot be eliminated by conventional vascular surgery. For its treatment, a new method has been developed, which consists of arterialization of the venous blood flow in combination with bioengineering technology. Having previously excised the valves of the vein, an anastomosis is performed (in the in situ position) with the artery of the affected limb. At the same time, engineered genes are introduced intraarterially or intramuscularly, which sprout neocapillaries, improving blood supply to tissues in the ischemic zone. The results of the experiments are encouraging, and a new method combining surgery with gene therapy is about to be introduced into the clinic.
Gayas AKZHIGITOV. Fedor SMIRNOV.
Cardiovascular diseases. cardiovascular failure
Cardiovascular diseases are numerous and occur in different ways. Some of them, such as rheumatism or myocarditis, are predominantly heart diseases. Other diseases, such as atherosclerosis or phlebitis, mainly affect the arteries and veins. Finally, the third group of diseases affects the cardiovascular system as a whole. The last class of diseases is mainly hypertension. Although it is often difficult to draw such a clear line between cardiovascular diseases. For example, atherosclerosis is a disease of the arteries, but when it develops in the coronary artery, this type of atherosclerosis is called coronary heart disease and is already classified as a heart disease.
Another note: not all diseases are what we are used to, since cardiovascular diseases are diseases. For example, heart failure is not a disease, but a collection of symptoms that can be associated with various diseases and not necessarily of cardiovascular origin. Angina pectoris or toady blisters are not a disease in itself, but one of the symptoms of coronary heart disease and so on.
The origin of diseases of the cardiovascular system can be different: birth defects, injuries, inflammatory processes, poisoning. In addition, diseases of the cardiovascular system can be caused by disruption of the mechanisms that control the functioning of the heart or blood vessels, or by pathological changes in metabolic processes. Sometimes other causes contribute to the development of the disease, not all of which have been fully investigated. However, despite all the differences, diseases of the cardiovascular system have much in common. They are “united” by manifestations, serious complications and consequences. Therefore, there are some rules that are common to most cardiovascular diseases for identifying them, as well as general preventive measures that help to avoid most diseases of this kind or, if the disease has developed, to avoid complications.
Let us briefly list the most important diseases of the cardiovascular system, their origin and places where they are located. The first to be mentioned are congenital heart defects and large blood vessels that develop before birth and are called congenital heart defects. Typically, the development of the disease begins in the heart valves or chambers, from where it is transmitted to the entire cardiovascular system. Along with congenital heart defects, there are also acquired heart diseases, which in their symptoms resemble congenital heart defects, but develop after birth.
There are diseases of the cardiovascular system that are based on the inflammatory process. Often these are complications of infectious diseases such as influenza or angina. Endocarditis, pericarditis, myocarditis and other diseases are quite numerous, but not common. These diseases are usually located in the heart area. Sometimes, however, the heart muscle, the myocardium, can be affected by toxins and inflammation that develop in other organs. This clinical picture is typical for myocardial dystrophy.
There are also quite a few diseases of the cardiovascular system that arise not in the heart area, but in the vascular system. Depending on their function, blood vessels are divided into arteries and veins. Arteries transport oxygen and nutrient-rich red blood from the heart to the periphery. Dark-colored blood flows through the veins, supplying tissues with oxygen and saturating them with carbon dioxide and metabolic products. After complete circulation, the blood returns to the heart, where it is again saturated with oxygen, and everything begins again. Vascular diseases can also be divided into diseases of the veins and arteries. This division is easily explained by the fact that the load on the veins, through which thicker blood flows, exceeds the load on the arteries. The veins of the lower extremities are especially vulnerable: they must draw blood against gravity. Therefore, it is the veins in the legs that suffer most from varicose veins and inflammatory venous diseases - phlebitis and thrombophlebitis.
As for the arterial canal, it falls into the initial stages of the most common diseases of the cardiovascular system - atherosclerosis and high blood pressure. However, as for hypertension, we can say that it applies equally to both the venous bed and the capillary system, since, of course, not only blood pressure, but also the blood pressure of the entire vascular system increases. Atherosclerosis develops in the arteries, narrows their lumen and impairs the blood supply to the body.
Very often, atherosclerosis develops in the coronary arteries of the heart; this type of atherosclerosis is considered as a separate disease - coronary heart disease. The most common clinical manifestations of coronary heart disease are attacks of angina pectoris of the chest or, as it is also called, angina pain: aches and pains in the heart area caused by stress, and in severe cases, at rest. A complication of coronary heart disease can be as serious as a myocardial infarction due to the development of necrotic lesions in the heart muscle.
Another variant of coronary heart disease is cardiosclerosis, which sometimes manifests itself in various changes in heart rhythm (arrhythmia) and heart failure. Both arrhythmia and heart failure, as already mentioned, are not diseases in the strict sense of the word. The term "arrhythmia" refers to various diseases that have one thing in common - deviations from the normal heartbeat rhythm. Heart failure (cardiovascular failure) is a set of pathological signs (shortness of breath, cyanosis, edema, etc.) indicating that the heart cannot cope with its full load. The causes of heart failure can be different, sometimes they are not even related to cardiovascular diseases, although most often heart failure develops due to atherosclerosis.
Diseases of the cardiovascular system: causes, diagnosis and symptoms
- home
- Diseases of the cardiovascular system
Cardiovascular diseases - diseases of the circulatory system at the beginning of the 20th century accounted for no more than a few percent in the structure of pathology of the population.
Back in the 50s. According to a mass survey in more than 50 cities and rural areas of the Russian Federation, they occupied 10th - 11th place in the ranking of diseases. The situation was approximately the same abroad. Subsequently, the changed lifestyle of the population, industrialization, urbanization with psycho-emotional stress and other risk factors of a civilized society, as well as the improving diagnosis of coronary heart disease, hypertension and other lesions sharply increased the proportion of circulatory diseases. Today, cardiovascular diseases are in first place as causes of disability and mortality among the population of the Russian Federation. Cardiovascular diseases such as hypertension (HTN), atherosclerosis and coronary heart disease (CHD) constitute the so-called group of “social diseases”, i.e. The culprits of these diseases are the achievements of human civilization, and the reasons are:
1.chronic stress;
2. physical inactivity - low mobility;
3.excess body weight due to poor nutrition;
4.tobacco smoking.
Hypertension is a state of persistently elevated blood pressure. According to the WHO nomenclature, the indicator of hypertension (from the Greek hiper + tonos - over + tension) is considered to be 160 mm Hg. Art. and higher for systolic (the highest value during contraction of the heart muscle) and 95 mm Hg. Art. and higher for diastolic (the smallest value during the period of relaxation of the heart) pressure.
The main cause of hypertension is neuropsychic stress. And the dangerous consequences are ruptures in the walls of blood vessels due to high pressure in them. If this occurs in the thickness of the heart muscle, then it is a heart attack, and if it occurs in the substance of the brain, it is a stroke.
Atherosclerosis (from the Greek athere + sclerosis - gruel + compaction, hardening) is a lesion of the arteries (blood vessels through which oxygenated blood moves from the heart to the organs and tissues in the systemic circulation), in which on their inner surface appear numerous yellowish plaques containing large amounts of fatty substances, especially cholesterol and its esters.
The essence of atherosclerosis comes down to the fact that cholesterol is deposited on the inner wall of blood vessels in the form of lipid stains, and then in the form of plaques that protrude into the lumen of the arteries. Over time, the plaques grow with connective tissue (sclerosis), the wall of the vessels above them is damaged and a blood clot can form in this area. Sometimes the plaques themselves can completely clog the lumen of the vessel, which leads to the cessation of nutrition of the cells around it. If this occurs in the thickness of the heart muscle, then it is called a heart attack, if in the substance of the brain, it is ischemic (from the Greek isc + haima - delay, failure + local anemia) stroke (from the Latin insulto - to attack, attack, blow).
Cholesterol is necessary for our body to: build cell membranes, form bile, synthesize sex hormones, produce vitamin D. Only 20% of cholesterol enters the body with food, and 80% is produced by the body itself (in the liver). Coronary heart disease is damage to the heart muscle (myocardium) caused by a disorder of the coronary (within the heart muscle) circulation. The main forms of IHD are angina pectoris (angina pectoris), myocardial infarction (a piece of dead tissue in the heart muscle) and post-infarction cardiosclerosis (a scar that appears on the heart after the healing of an infarction wound).
The first stage of IHD is angina, which manifests itself in the patient with chest pain of a pressing, squeezing or burning nature, which can radiate to the left shoulder, shoulder blade, and resemble heartburn. The sternum is the bone located in the middle of the front surface of the chest, to which the ribs are attached. It covers the heart, located in the middle of the chest, and only a small part of it, the apex, protrudes from behind it to the left. If you feel stabbing pains in the heart area, then they have nothing to do with the cardiovascular system - these are manifestations of neurosis.
Pain during angina pectoris signals to us that the heart muscle does not have enough oxygen. When the heart muscle works, like any other, a breakdown product is formed - lactic acid, which must be washed out of it with a sufficient amount of blood. But if the vessel is affected by an atherosclerotic plaque, and even compressed as a result of a jump in blood pressure, then the amount of blood passing through it decreases and may even stop completely. Any acid acting on nerve endings causes pain and burning.
During myocardial infarction , due to the cessation of oxygen access to the heart tissue, muscle, at the site of occlusion (blockage of a vessel), it dies. But this process does not develop immediately, but after 2-4 hours from the onset of a heart attack.
Stroke, “brain stroke” is an acute disorder of cerebral circulation due to hypertension, atherosclerosis, etc. It manifests itself as headache, vomiting, disturbance of consciousness, paralysis, etc.
Stroke is currently becoming a major socio-medical problem in neurology. Every year, about 6 million people suffer a cerebral stroke in the world, and in Russia - more than 450 thousand, that is, every 1.5 minutes one of the Russians develops this disease. In large Russian cities, the number of acute strokes ranges from 100 to 120 per day. Early 30-day mortality after a stroke is 35%; about 50% of patients die within a year.
Stroke is currently one of the main causes of disability in the population. Less than 20% of cerebral stroke survivors can return to their previous jobs. Among all types of stroke, ischemic brain damage predominates. Ischemic strokes account for 70-85% of cases, cerebral hemorrhages - 20-25. Stroke is the second most common killer after myocardial infarction.
Risk factors for the development of stroke are: genetic predisposition to vascular diseases of the brain, disorders of fat metabolism, hypertension, obesity, lack of physical activity, smoking, age of the patient, repeated stress and prolonged neuropsychic stress.
Strokes can be classified according to the nature of their course. The least dangerous stroke is a transient ischemic stroke, or minor stroke, which is caused by a short-term cerebrovascular accident. A progressive stroke initially causes very small changes in the nervous system, and after 1-2 days deterioration occurs. With a major stroke, the nervous system experiences a strong “blow” from the very beginning. The sooner the patient sees a doctor and begins treatment, the more favorable the prognosis.
Chinese medicine views cardiovascular diseases as disturbances in the passage of energy (excess or deficiency) in the heart meridian, circulatory meridian, and related small intestine meridian, endocrine meridian, liver meridian, spleen/pancreas meridian, kidney meridian and lung meridian. .
The heart meridian belongs to the system of manual Yin meridians, paired. The direction of energy in the meridian is centrifugal. The time of maximum activity of the heart meridian is from 11 to 13 hours (at this time it is recommended to engage in physical work), the time of minimum activity is from 23 to 1 hour.
According to the canons of ancient oriental medicine, the heart meridian is a functional system that mainly affects the functional state of the blood circulation and heart. In addition, the ancient canons claim that mental activity, consciousness and emotions are under the control of the heart. A person remains vigorous and cheerful as long as his heart is healthy. Deterioration of heart function leads to low activity, irritability, lethargy, indecisiveness, etc. In connection with this, the points of the heart meridian are given primary importance in the treatment of various kinds of emotional stress disorders, neuroses, depression and some other functional diseases. In these cases, acupressure “improves a person’s mental state and calms the heart.” Eastern doctors believe that “the tongue is the mirror of the heart, and the face is a reflection of its condition.” The heart also affects the condition of the eyes and ears. A pleasant “fire raging in the heart” makes a person vigilant, and a “decrease in the energy of the heart” is accompanied by deterioration of hearing.
Blood circulation in arteries and veins is the result of the interaction of Yang and Yin energies. The heart pulsations felt in the arteries are caused by the circulatory system itself. All life processes proceed as a rhythmic alternation of tension and relaxation (relaxation). Blood moves from the lungs, where it is enriched with oxygen, acquires a bright red color and is filled with YANG energy, to the small intestine, where it gives off oxygen and is saturated with YIN energy.
The movement of blood flow is controlled by the forces of YANG and YIN, which are associated with two opposing organs - the lungs and small intestine, which represent the two poles of energy. The heart does not beat without blood flow. Both oxygenated and depleted blood move through the heart, causing it to contract and then relax.
The change in heart rhythm is felt by the whole body; it manifests itself in all organic processes, controlling and adjusting their rhythms. This follows the principles of ancient medicine - the heart meridian controls the arteries between the lungs and the small intestine and “the lungs control the heart.”
The meridian of blood circulation (pericardium) and sexual function controls the main circulation of “vital force” (QI energy), which ensures the connection and joint work of internal organs. It also serves as protection against the penetration of pathogenic microbes. Both the meridian itself and its internal organs are closely connected with the heart. Both the meridian and the heart have the same external signs of impending danger, they use similar mechanisms to ensure optimal functioning, and they begin in the same part of the chest. Carrying out general control over the regulation of the circulation of QI energy throughout the vascular system, the meridian also provides energy to the genitals for their satisfactory functioning.
The time of maximum activity of the pericardial meridian is from 19 to 21 hours. By this time, Chinese doctors recommend finishing physical activity and moving on to mental activities.
From the standpoint of Chinese medicine and the theory of the five elements as the basis of all things (including the human body), the heart belongs to the element of Fire. The heart emotion is joy, the color is red.
The heart controls the activities of all organs, and therefore in Chinese medicine it is called “the official who leads the rulers.” If the Spirit of the Heart is disturbed, then a person becomes restless, he suffers from insomnia or difficult dreams, he develops forgetfulness, inattention - even to the point of impaired consciousness.
Pathologies in any organ can lead to heart disease. The most common syndrome of disorders in the cardiovascular system is “heat in the liver and stagnation of blood in the liver.” This heat rises, and this, in turn, leads to an increase in blood pressure, to tachycardia.
Patients with “heat of the liver and stagnation of liver blood” have inflamed red eyes and a red complexion.
Another common syndrome in heart disease is related to the kidneys. Hypertension caused by kidney pathology is also known in European medicine. In the Eastern tradition, this syndrome is called “empty kidney qi.”
We can call Qi the energy of life circulating through the channels of the body. Syndromes of fullness and emptiness of Qi indicate a violation of the harmony of human life and, consequently, a disease.
The syndrome of “emptiness of kidney Qi energy” has a second figurative name: “the water of the kidneys does not flood the fire of the heart.” The kidneys, which in the Chinese medicine system are considered the “first mother of the body,” lack energy and the harmony of life is disrupted. The result is tachycardia, heart rhythm disturbances, and increased blood pressure.
Another common heart disease syndrome is associated with spleen pathology. With poor nutrition, addiction to fatty, sweet, raw and cold foods, and a tendency to drink alcohol, the spleen and stomach are damaged, and dampness accumulates. “The mucus produced by the spleen clogs the heart and brain.”
In addition to other cardiac manifestations of the syndrome, in this case “the window of the brain closes”, the person’s consciousness becomes confused, in severe cases - even to the point of delirium.
The “empty blood” syndrome is close to the European diagnosis of “iron deficiency anemia”.
Thus, diseases of the cardiovascular system can be treated comprehensively, using the methods of oriental medicine and the methods of electropuncture diagnostics based on them according to Voll and the Autonomic Resonance Test. This approach is carried out at the Center for Energy-Information Medicine.
Diagnostics allows us to identify the causes of cardiovascular diseases in a particular person and select an individual health program:
1. balanced nutrition for the treatment of obesity and hypercholesterolemia, drinking regimen;
2. bioresonance therapy, acupuncture, hirudotherapy for the treatment of “causal organs”;
3.elimination of emotional imbalance and increasing stress resistance with the help of psychotherapy and induction programs;
4. solving the problem of physical inactivity with proper physical exercises (physical therapy, bodyflex, oxysize, yoga, qi gong, tai chi).
It must be remembered that the prevention of diseases of the cardiovascular system and their complications lies primarily in a healthy lifestyle and timely consultation with a doctor!
Treatment of cardiovascular diseases
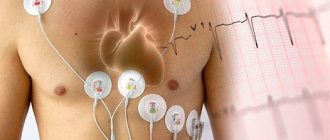
All cardiovascular diseases are treated by a cardiologist; self-medication or self-correction of treatment is completely unacceptable. At the slightest sign of cardiovascular disease, it is necessary to consult a cardiologist, since a common feature of almost all cardiovascular diseases is the progression of the disease. If you suspect that a heart problem cannot wait for visible symptoms to appear, then many diseases of the cardiovascular system begin with the development in the patient of a subjective feeling that “something is wrong.” The earlier the stage of the disease is identified during an examination by a cardiologist, the easier, safer and with fewer medications it can be cured. The disease often develops completely unnoticed by the patient, and deviations from the norm can only be detected during an examination by a cardiologist. Therefore, preventive visits to a cardiologist with a mandatory ECG examination are necessary at least once a year.
The role of genetics in the development of cardiovascular diseases
Today there are practically no diseases left in the formation of which a hereditary component would not be found. And cardiac pathologies are no exception. Cardiovascular diseases such as coronary heart disease, atherosclerosis and hypertension are multifactorial, but both environment and genetics contribute equally to their development.
There are also monogenic diseases, for which a mutation in just one gene is sufficient. These include the following diseases of the cardiovascular system:
- familial hypercholesterolemia (mutations in ARH (1p36-p35), LDLR (19p13.2), USF1 (1q22-q23));
- long QT syndrome (KCNQ1 (11p15.5), KCNJ2 (17q23), ANKB (4q25-27), KCNE1 (21q22), etc.);
- short QT syndrome (KCNH2 (7q3), KCNQ1 (11p15.5));
- Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome (PRAKG2 (7q3));
- hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (MYHCB (14q12), PRKAG2 (7q36), TPM1 (15q22.1), MYL3 (3p), etc.);
- familial forms of sick sinus syndrome (SCN5A (3p21-24)), etc.
Molecular genetic tests help detect causes of cardiovascular disease associated with mutations in genes. DNA tests make it possible to determine a person’s individual risk of contracting a particular disease and help prevent pathology by correcting lifestyle.
Research is identifying mutations that cause monogenic cardiovascular diseases. They also make it possible to detect genetically determined features of drug metabolism in order to draw up the most adequate treatment regimen.
In medical genetics, you can undergo such an examination (panel “Hereditary heart diseases”) and other tests to identify the likelihood of cardiac pathologies.
Prevention of cardiovascular diseases
Prevention of cardiovascular diseases consists of a number of measures common to most of these diseases, but some diseases obviously require a separate approach. We'll focus on some general guidelines. Primarily, cardiovascular disease is caused by neuropsychological stress. Therefore, reducing their number and intensity is the most effective preventive measure against all cardiovascular diseases.
Oddly enough, most people believe that the most explosive place from a neuropsychological point of view is home. When at work, with strangers, we are still trying to suppress the manifestation of negative emotions, we treat the family according to the principle “why with their ceremonies?” and spit out on them all our accumulated irritations during the day. We often get the same answer. This creates mutual dissatisfaction, tension and... cardiovascular disease. We must remember more often that if we do not do everything possible to make our loved ones happy and peaceful, then no one will. If everyone could change their attitude towards the world from demanding to giving, then there would definitely be fewer heart problems. Therefore, cardiologists advise people to treat themselves and others kindly, not try to remember the offense, learn to forgive from the heart and forget what they have forgiven.
Often the main object of a person’s constant dissatisfaction is himself. Everyone has heard words about love, not only for loved ones, but also for oneself, for a long time, and yet they repeat hackneyed truths: in order to love the whole world, you need to start with yourself. Everyone needs positive emotions, so for such powerful preventative measures there are good books, good films, communication with friends, an active and joyful intimate life with a loved one and a loving person.
As we have already said, a necessary part of the prevention of cardiovascular diseases is a physically active lifestyle, namely the “muscle pleasure” that Academician Pavlov spoke about. These are sports activities, long walks in the fresh air, swimming, walking, that is, any physical activity that gives a person pleasure. It’s good to get used to hardening methods: It could be a contrast shower, pouring cold water, walking barefoot in the snow, going to a bathhouse or sauna - the choice is huge, and everyone can find what they like best. Meanwhile, all these activities strengthen the walls of blood vessels and thereby prevent many serious diseases. The rest should also be complete. A normal sleep period should be 8-10 hours a day, and it is better if you have the opportunity to rest during the day.
Of course, we cannot avoid such an important part of our life as nutrition. It has been proven that the abundance of fatty, spicy and salty foods in our diet not only causes obesity, but also negatively affects the elasticity of blood vessels, thereby impairing blood circulation. The problem with salt is especially acute at high blood pressure. In this case, eliminating regular salt from the diet is an essential measure.
But everything else to prevent cardiovascular diseases should never be added to food, and salty delicacies should only be placed on the holiday table. The fact is that excess salt in the body prevents the kidneys from coping with the removal of fluid from the body, thereby causing unnecessary stress on the blood vessels and heart. In addition, there are foods that have a tonic effect on the body and can have a direct effect on the cardiovascular system. These include strong tea, coffee and alcoholic drinks. All this, especially alcohol, should not be abused.
Smoking, of course, has the greatest negative impact on the cardiovascular system. Almost all cardiovascular diseases are much more common in smokers than in non-smokers. And if we can still talk about the proven benefits of a small amount of dry grape wine from the point of view of alcohol (this has been repeatedly confirmed by French scientists), then smoking only harms, which is why we insist so strongly on the need to completely abandon this habit. And to “calm the nerves,” as their dependence on tobacco is often explained, there are more useful and pleasant ways.
So, let's summarize what has been said: physical activity, a psychological attitude towards a friendly approach to yourself and the world around you, proper nutrition, avoidance of bad habits and regular examinations with a cardiologist - this is the minimum necessary to be sure that cardiovascular diseases will pass you by. Let’s hope that the fashion for a healthy lifestyle, which is rapidly conquering the world, will help free the 21st century from the name “the era of cardiovascular diseases.”
Causes of diseases of the cardiovascular system
Cardiovascular disease is caused by a number of reasons, the most common of which are:
- atherosclerosis (formation of cholesterol plaques on the inner wall of blood vessels). This leads to a narrowing of the lumen of the vessel, and sometimes to its blockage, and an increase in blood pressure
- congenital malformations of the heart and blood vessels
- obesity
- lipid metabolism disorder
- disruption of the endocrine system
- infections (streptococcus, enterococcus and others)
- sedentary lifestyle
- stress
- diseases of other organs and systems (for example, diabetes, kidney disease and others)
- heredity
Bibliography
- Islam. Brief reference book, science, M. 1983.
- G.F. Kim, Islam. Ideology, Law, Politics and Economics, Master of Science, 1985.
- Religions of the world. Encyclopedia. Volume 6, M., Avanta, 1996 F. Pavlenkov, Bibliographic Library, Moscow, Republic, 1995.
- Kochetov A.N. List of used literature.
- A.N. Smirnov, A.M. Fraanskaya-Tsvetkova, “Internal Diseases”, Moscow, 1994.
- R. A. Gordienko, A. A. Krylov, “Guide to intensive care”, Leningrad, 1985.
- R.P. Oganov, “Protect the heart...”, Moscow, 1983.
- A. A. Chirkin, A. N. Okorokov, I. I. Goncharik “Therapist’s Diagnostic Manual”, Minsk, 1993.
- IN AND. Pokrovsky, “Medical encyclopedia for home”, Moscow, 1993.
- A.V. Sumarokov, V.S. Moiseev, A.A. Mikhailov “Recognition of heart disease”, Tashkent, 1974.
- N.N. Anosov, J.A. Bendet “Physical activity and the heart”, - Kyiv, 1984... Buddhism. M., political science, 1965.
- Krivelev I.A. History of religions. T. 2, M., “Thoughts”, 1984.