Types of disease
Stroke is a pathology accompanied by impaired blood circulation in certain areas of the brain. The condition is accompanied by oxygen starvation and a severe deficiency of nutrients, which ultimately leads to the death of brain cells. As a result, there is a complete or partial loss of functions for which the affected area was responsible.
Depending on the underlying cause, there are two types of stroke:
- Ischemic (most common). It is a consequence of blockage of the lumens of cerebral vessels. The disease progresses slowly and is not accompanied by hemorrhage, but is accompanied by the death of brain cells.
- Hemorrhagic. Caused by hemorrhage in the brain tissue as a result of rupture of a local vessel. Due to the accumulation of blood and pressure exerted on a certain area of the brain, its functions are impaired.
Important! The cause of a stroke may be cerebrovascular disease.
Symptoms, signs and first aid
Anyone can have a stroke, which is why it is so important to know the primary symptoms of the condition. It is indicated by:
- weakness in the limbs;
- fainting conditions;
- numbness of half the face, distortion of features;
- Strong headache;
- speech impairment, misunderstanding;
- various visual impairments;
- complete or partial paresis;
- impaired coordination of movements up to its complete loss;
- impaired skin sensitivity;
- instability and tension of the pulse.
If we talk about what pressure is possible during a stroke, then its indicators can be both low and high. To make sure that the patient has had a stroke, he must be asked to perform several familiar actions. For example, smile broadly or say a few words. He will not succeed: the affected part of the face will remain motionless, and speech will be unclear, as if the person’s mouth is filled with porridge and he is trying to speak through it.
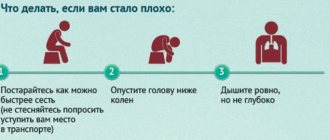
What to do if this happens? First of all, immediately call an ambulance. Lay the patient down so that the head is elevated in relation to the legs, unbutton the collar, and remove the woman’s bra. A person must breathe deeply. Trying to lower blood pressure on your own is strictly prohibited.
What to do if you have a stroke
There are techniques that allow you to identify signs of a stroke yourself. For example, they can be used if someone becomes ill on the street and you suspect a stroke. You need to ask the person to smile, speak, raise both hands. If the victim cannot comply with your request or there is asymmetry, you should immediately call for help and list all the symptoms.
At the same time, you need to provide first aid: lay the victim down, placing a small support under his head, and free him from clothes that are preventing him from breathing. He should not eat or drink or make sudden movements. When vomiting, turn your head to the side.
Further treatment is carried out in a hospital. First, diagnostics are carried out to clarify the diagnosis; computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging, lumbar puncture and EEG (echoencephalography), angiography are prescribed. Then conservative (basic therapy, treatment of neurological complications) or surgical treatment is prescribed.
After the end of the acute period, rehabilitation is prescribed: massage, physical therapy and other activities, depending on the degree and type of disorder. The patient is observed by a neurologist, physiotherapist, speech therapist, and psychotherapist.
The brain has neuroplasticity: with the right approach, you can recover from a stroke, restore brain function and prevent stroke complications. The key factor is timely initiation of treatment, proper rehabilitation and regular exercise.
According to WHO, about 60% of patients do not require assistance by the end of the first year, and 30% of patients of working age can return to work.
What blood pressure can trigger the development of a stroke?
At what blood pressure level can a stroke occur and can the condition develop at normal blood pressure? It is worth noting that most often a stroke occurs in hypertensive patients. The reasons are:
- Stably high blood pressure, which does not decrease even while taking medications;
- sharp jumps in indicators caused by a stressful situation or significant physical activity;
- refusal of treatment for hypertension and heart disease.
Doctors call the physiological level of blood pressure, at which all body systems operate in a natural mode, a level of 120/80 mm. rt. Art. When it increases to 180/120, we can talk about the development of a hypertensive crisis, which can quite easily turn into an apoplexy (stroke).
The danger in terms of the development of pathology is represented by too small a difference between the upper and lower blood pressure readings. If it is less than 40 units, then the likelihood of blockage of the vascular lumen increases significantly. Therefore, a blood pressure of 130/110 is more likely to trigger the development of a stroke than a blood pressure of 160/90.
Acceptable indicators and pressure deviations after impact
What blood pressure should a patient have after a stroke? Everything will depend on the type of pathology.
Ischemic form
During the first few hours after the formation of the condition, almost all patients experience high blood pressure. This is a protective reaction of the brain aimed at stabilizing the work of the myocardium. That is why a specialist should select antihypertensive drugs, taking into account the current condition of the patient.
Incorrectly selected medications can reduce blood pressure too much. The worst outcome in this case may be the death of a person. In addition, recovery after a stroke will be longer and more difficult.
Indications for emergency reduction of blood pressure are:
- increase to 180/220–100/120 mm. rt. st;
- the need to administer an antithrombotic agent;
- development of systemic circulatory failure;
- diagnosing aneurysm/arteriovenous malformation of cerebral vessels;
- disorders of the kidneys.
During the first 48–72 hours after an ischemic stroke has occurred, blood pressure can be reduced by no more than 15% relative to the existing one. At this time, increased blood pressure is normal.
Important! In patients who do not have a history of hypertensive pathology, blood pressure should not fall below 165/95 mm. rt. Art. In the presence of the disease, the minimum level is determined by 185/105 mm. rt. Art.
It is very important to protect the patient from factors that can provoke a sharp increase in blood pressure. These include nervous tension, severe pain, and fluid retention.
Hemorrhagic form
This type of stroke occurs against the background of a significant increase in blood pressure, so antihypertensive therapy should be started as early as possible. Taking medications helps:
- reducing the volume of the hematoma, stopping its spread;
- decrease in intracranial pressure;
- blocking the development of swelling of brain tissue.
The critical level of blood pressure, upon reaching and overcoming which it is necessary to take measures to reduce, is considered to be 140/90 mm. rt. Art. But the decline should be gradual. During the day, it can be lowered only by 20% relative to the current one.
Treatment and rehabilitation
The patient receives treatment in a hospital. All patients with suspected stroke are hospitalized on an emergency basis. The optimal period for providing medical care is the first 3 hours after a brain accident has occurred. The person is placed in the intensive care unit of a neurological hospital. After the acute period has been overcome, he is transferred to the early rehabilitation unit.
Until the diagnosis is established, basic therapy is carried out. The patient’s blood pressure is adjusted, the heart rate is normalized, and the required blood pH level is maintained. To reduce cerebral edema, diuretics and corticosteroids are prescribed. Craniotomy is possible to reduce the degree of compression. If necessary, the patient is connected to an artificial respiration apparatus.
Be sure to direct efforts to eliminate the symptoms of stroke and alleviate the patient’s condition. He is prescribed medications to lower body temperature, anticonvulsants, and antiemetics. Medicines that have a neuroprotective effect are used.
Pathogenetic therapy is based on the type of stroke. In case of ischemic brain damage, it is necessary to restore nutrition to the affected area as quickly as possible. To do this, the patient is prescribed drugs that resolve blood clots. It is possible to remove them mechanically. When thrombolysis fails, the patient is prescribed Acetylsalicylic acid and vasoactive drugs.
In case of a stroke, it is extremely important to provide timely treatment to the damaged areas of the brain. A course of use of the drug accelerates the process of recovery of brain cells after a stroke, even in cases of impaired blood circulation or hypoxia. This allows for rapid restoration of memory, thinking, speech, swallowing reflex and restoration of other functions of daily activities. Gliatilin has a positive effect on the transmission of nerve impulses, protects brain cells from repeated damage, which prevents the risk of recurrent stroke.
The drug is well tolerated by patients; it is contraindicated for use by pregnant, lactating women and people with hypersensitivity to choline alfoscerate.
Courses will need to be taken regularly. You definitely need to do physical therapy, undergo physical therapy, and visit a massage therapist. After a stroke, many patients have to restore motor skills over a long period of time and learn to care for themselves independently.
Relatives and friends should provide support to the patient and not leave him alone with the problem. Psychologists are involved in the work. Sessions with a speech therapist are often required.
Low and high blood pressure
During the first 24 hours after the impact, maintaining high blood pressure is an acceptable norm. The danger is high blood pressure that persists for a week after a stroke. The symptom indicates incorrect treatment. In this case, the patient becomes incapacitated and develops neurological disorders.
Such negative consequences for the patient’s health are due to the continuing increase in cerebral edema, which results in wedging of the brain stem into the occipital part. It is possible that breathing processes may be disrupted until a critical condition develops, as well as heart failure and cardiac arrest.
Complications of hypertensive crisis
If the pressure, despite the therapy, still jumps, then the consequences may be as follows:
- re-strike;
- expansion of the ischemic focus;
- development of encephalopathy;
- hemorrhage in the skull.
Why does a patient have low blood pressure after a stroke and why is this condition considered negative by doctors? A rapid decrease in blood pressure occurs against the background of the following pathological conditions:
- development of a major stroke;
- brain stem damage;
- the formation of cardiogenic shock against the background of a heart attack;
- heart rhythm disturbance;
- dehydration;
- blockage of the pulmonary arteries;
- blood poisoning;
- aneurysm.
Low blood pressure values during the rehabilitation period indicate progression of the pathology. The prognosis in this case is extremely unfavorable, this applies to both recovery and human life. A decrease in blood pressure can occur against the background of regular use of hypertensive drugs that were prescribed to the patient even before the stroke developed.
But if the reason for this is not drug treatment, then this is a signal that the body is unable to independently regulate blood pressure as a result of impaired cerebral blood circulation. Medical statistics show that severe hypotension during the first few days after a stroke causes the death of the patient.
Symptoms and signs
Hypertensive stroke is characterized by all the main signs of acute cerebrovascular accident. There are a number of characteristic symptoms:
- Muscle tone disorders on the opposite side of the lesion;
- Reduction or loss of sensitivity on the side opposite to the lesion;
- Meningeal symptoms;
- Muscle spasm and the formation of contractures, or no muscle tone at all.
The clinical symptom complex also includes general cerebral symptoms:
- Headache;
- Severe nausea and vomiting without relief;
- Depression of consciousness;
- Tinnitus, vestibular disorders;
- Decreased cognitive abilities.
Causes of blood pressure surges
A sharp fluctuation in blood pressure after a stroke occurs when the organs and systems of the body are unable to perform their functions. Most often it is the brain that is affected. Against the background of unstable blood pressure, both cardiac and peripheral circulation worsens, and the destruction of the walls of blood vessels also occurs. The patient develops an acute form of atherosclerosis. The development of recurrent strokes cannot be ruled out.
The main danger lies not in the increase or decrease in pressure, but in its constant fluctuation
The leading causes of sudden changes in blood pressure that occur after a stroke are:
- disturbances in the functioning of the central nervous system;
- low mobility of the vasomotor center;
- high blood sugar levels;
- hormonal imbalance;
- changes in the electrolyte composition of the blood.
Important! With a hemorrhagic stroke, the risk of developing a second stroke is high. This usually happens on the fifth or sixth day after the first blow.
Stroke in hypotensive patients
The development of a stroke is also possible with low blood pressure (in people suffering from hypotension). The formation of pathology is due to the body’s inability to independently eliminate the impending blow. A stroke in hypotensive patients can be triggered by features of a person’s lifestyle, stressful situations, disturbances in the functioning of internal organs and systems as a whole, and the use of antihypertensive medications.
The cause of stroke development against the background of hypotension can be:
- a sharp increase in blood pressure - occurs as a result of severe stress, overwork, as a side effect of the drug;
- rupture of an aneurysm - can be triggered by lifting weights, staying in a prolonged inclined position in hot rooms or under the open sun - a violation of the integrity of the vessel occurs as a result of overstrain;
- bleeding disorder - in this case, the likelihood of blood clots and blockage of blood vessels in the brain increases.
In the chronic form of hypotension, the likelihood of developing an ischemic stroke increases significantly with age. In the presence of cardiovascular pathologies, the risk of hemodynamic stroke increases. This is a subtype of the ischemic form, caused by circulatory decompensation. Its cause may be:
- atrioventricular block;
- myocardial infarction;
- weak sinus syndrome;
- atrial fibrillation.
Parkinson's disease is often accompanied by hypotensive crises, which, in turn, can cause the development of hemodynamic stroke. In hypotensive patients, signs indicating the formation of a hemorrhagic form of stroke are almost completely absent.
The condition is characterized by a slow onset and a long period of persistence of symptoms of brain damage with low blood pressure. The patient does not experience loss of consciousness or headaches. But almost all the precursors are typical for ischemic stroke. Most often, symptoms occur at night or in the morning.
Stroke test
There is a test called BE FAST, which is used in medicine to instantly diagnose a stroke attack. The abbreviation has its own meaning:
- B - balance. You need to watch how a person makes movements. Poor balance indicates an impending blow.
- E - eyes. Check the level of visual acuity - have the patient alternately close/open his eyes and tell what he sees in front of him.
- F - face. Ask to smile and stick out your tongue. During an attack, curvature occurs in one direction.
- A - arms. Have the victim raise both arms or shake their palms - one of the limbs will be weaker or will not rise.
- S - speech. Talk to the victim - if there is a lack of cerebral blood supply, speech is impaired.
- T - time. The patient denies the disorder.
If you discover at least one type of deviation, immediately contact the Yusupov Clinic, where experienced doctors will provide primary medical care, establish an accurate diagnosis, and prescribe therapeutic measures. For this purpose, innovative medical technologies of the European level, powerful equipment, and an individual approach are used. You can ask questions and get tested by calling the numbers provided.