Prevention
To prevent deviation of a nonspecific indicator means to prevent the development of the disease. To do this you will need:
- lead a healthy lifestyle;
- eat properly and nutritiously;
- devote time to sports;
- strengthen the immune system;
- regularly take vitamins (preventive courses of multivitamin preparations);
- undergo annual preventive examinations;
- promptly sanitize foci of chronic infection;
- promptly and completely treat all emerging diseases.
Indicators according to age
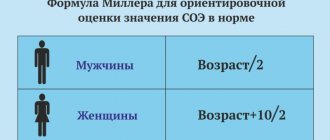
The speed of movement of red blood cells in the bloodstream in men largely depends on age, therefore, when obtaining results, especially if the ESR is elevated, the doctor must take into account the age category of the patient.
The age table takes into account certain age limits and contains the permissible maximum and minimum values of the indicator in accordance with the norm.
| Age | Minimum speed (mm/hour) | Maximum speed (mm/hour) |
| 30–50 | 1.0 | 10.0 |
| 50–60 | 5.0 | 14.0 |
| after 60 years | 18.0 | 35.0 |
The older the man, the higher the level of erythrocyte sedimentation rate . Moreover, even in old age, in the male half of the population, the indicator should not exceed 35. A slight deviation is acceptable, which should be monitored for the timely detection of serious pathology.
What does ESR show?
The erythrocyte sedimentation rate is determined in the laboratory after blood is drawn from the patient. Leave the material for 60 minutes and see how quickly the bodies appear at the bottom of the tube. Measurements are carried out in millimeters per hour.
Let's take a closer look at the process.
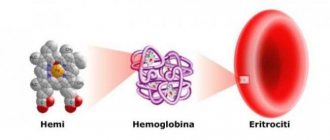
Blood is a fluid that circulates through vessels in the body. It is heterogeneous and consists of the following elements:
- erythrocytes - red cells;
- white leukocytes;
- lymphocytes;
- plasma is a clear liquid with a salty taste in which proteins are dissolved.
We will not analyze the entire composition. Within the framework of the topic, the main thing is the presence of erythrocytes in the liquid - red cells, which carry oxygen throughout the organs and tissues.
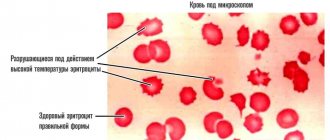
As blood moves through the body, all its components mix. Red blood cells color the composition red. If blood is placed in a tall test tube, the liquid will begin to “stratify.” Leukocytes and red blood cells are relatively heavy, so they sink to the bottom of the vessel in which they are located - they settle. Laboratories measure the speed of the process.
If the body is healthy, then everything happens slowly. In the case of inflammation, for example, the following are produced:
- immunoglobulins;
- fibrinogen is a protein that is involved in the wound healing process.
These substances attach to red blood cells, so the mass of red cells increases. There is an increase in ESR.
It is not necessary that the erythrocyte sedimentation rate increases due to inflammation or coronavirus. But this should be considered as an indication for other tests.
ESR is a nonspecific marker. This means that it is impossible to say exactly what is happening to the body. Doctors have noticed that most often the erythrocyte sedimentation rate becomes higher in rheumatic diseases:
- arthritis;
- lupus;
- vasculitis.
The higher the ESR, the worse the situation. For example, in a normal state, the erythrocyte sedimentation rate may be 25. If the ESR is 40, this is a reason for an extended examination.
Please note that with coronavirus infection, the same thing happens as with rheumatism: the immune system does not work correctly and attacks the body, destroying tissues and organs. An ESR of 80 or 100 can occur with severe suppuration, a cancerous tumor, pneumonia, including that which arose as a complication of COVID-19.
The reasons for the increase in the rate of sedimentation of blood particles may be:
- decay and death of tissues, purulent processes;
- metabolic disorders, diabetes;
- liver pathologies, blood loss, exhaustion;
- anemia;
- hormonal changes in a woman’s body.
The erythrocyte sedimentation rate may be less than normal. The following reasons:
- dysfunction of the circulatory system, weak production of red cells, changes in their shape, etc.;
- heredity;
- psychological and psychiatric problems;
- the effect of medications on the body.
During and after COVID-19, a high ESR or ROE is characteristic - the erythrocyte sedimentation reaction. This is explained by the fact that coronavirus is a disease that affects not only the respiratory system, but also other systems of the body. Covid affects everything at once, causing complications.
What ESR value is considered normal?
A chronic disease can also influence the deviation of the result from the conventional norm, but is not pathological.
The ESR norm differs among people of different genders, ages, and even body types.
For women, due to the characteristics of the body, this norm is higher than for men - it is associated with more frequent blood renewal, as well as a number of hormonal changes that the female body regularly undergoes.
An increase in ESR in pregnant women from 4 months is normal and does not require additional diagnostics.
This table illustrates the normal amount of ESR in the blood of an adult.
- The normal ESR level in a child's blood. Reasons for increased erythrocyte sedimentation rate in children
Men; Women; Pregnant women
| Men | Women | Pregnant women |
| ESR norm | 8 -10 mm/h | 10 – 18 mm/h | The norm is to increase the result to 45 mm/h. This figure is higher if there is a lack of hemoglobin. |
Determination of indicators and their interpretation should also be carried out taking into account the patient’s age.
Floor; Up to 20 years; Range from 20 to 55 years; Over 55 years old
| Floor | Up to 20 years | Range from 20 to 55 years | Over 55 years old |
| Men | 12, mm/h | 14, mm/h | 32, mm/h |
| Women | 20, mm/h | 21, mm/h | 23, mm/h |
In pregnant women, there is a relationship between the acceleration of red blood cells and their body type.
In thin people, in the first half of pregnancy, ROE reaches 21-62 mm/h, in the second - 40-65 mm/h.
For overweight people – 18-48 mm/h and 30-70 mm/h, respectively. The norm is any indicator in the specified range.
Important: In women taking oral hormonal contraceptives, the erythrocyte sedimentation rate is always higher.
A test that evaluates the rate of separation of blood into plasma and red blood cells. The rate of separation is mainly determined by the degree of their aggregation, i.e., the ability to stick together.
Synonyms Russian
Erythrocyte sedimentation reaction, ROE, ESR.
English synonyms
Erythrocyte sedimentation rate, Sed rate, Sedimentation rate, Westergren sedimentation rate.
Research method
Capillary photometry method.
Units
Mm/h (millimeters per hour).
What biomaterial can be used for research?
Venous, capillary blood.
How to properly prepare for research?
- Eliminate alcohol from your diet for 24 hours before the test.
- Do not eat for 2-3 hours before the test (you can drink clean still water).
- Stop taking medications 24 hours before the test (in consultation with your doctor).
- Avoid physical and emotional stress for 30 minutes before the test.
- Do not smoke for 30 minutes before the test.
General information about the study
Determination of erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) is an indirect method for identifying inflammatory, autoimmune or oncological diseases. It is performed on a sample of venous or capillary blood, to which a substance has been added that allows it not to clot (anticoagulant). When analyzing ESR using the Panchenkov method, blood is placed in a thin glass or plastic tube and monitored for an hour. At this time, erythrocytes (red blood cells), as having a large specific gravity, settle, leaving a column of transparent plasma above them. The ESR is calculated based on the distance from the upper boundary of the plasma to the red blood cells. Normally, red blood cells settle slowly, leaving very little pure plasma. For this method, a Panchenkov apparatus is used, consisting of a tripod and capillary pipettes with a 100 mm scale.
For capillary photometry (automatic analyzers ROLLER, TEST1), the kinetic “stopped jet” method is used. At the beginning of the ESR analysis, programmed mixing of the sample occurs in order to disaggregate the red blood cells. Ineffective disaggregation or the presence of microclots can affect the final result, since the analyzer actually measures the kinetics of red blood cell aggregation. In this case, the measurement occurs in the range from 2 to 120 mm/h. The results of measuring ESR by this method have a high correlation with the Westergren method, which is the reference method for determining ESR in the blood, and have identical reference values.
The results obtained using the capillary photometry method in the region of normal values coincide with the results obtained when determining ESR using the Panchenkov method. However, the capillary photometry method is more sensitive to an increase in ESR, and the results in the zone of increased values are higher than the results obtained by the Panchenkov method.
An increase in the level of pathological proteins found in the liquid part of the blood, as well as some other proteins (the so-called acute-phase proteins that appear during inflammation) contributes to the “gluing” of red blood cells. Because of this, they settle faster and the ESR increases. It turns out that any acute or chronic inflammation can lead to an increase in ESR in the blood.
The fewer red blood cells, the faster they settle, which is why women have a higher ESR than men. The ESR rate varies depending on gender and age.
What is the research used for?
- For the diagnosis of diseases associated with acute or chronic inflammation, including infections, cancer and autoimmune diseases. Determining ESR is sensitive, but one of the least specific laboratory tests, since an increase in ESR in the blood itself does not allow determining the source of inflammation, in addition, it can occur not only due to inflammation. That is why analysis of ESR is usually used in combination with other studies.
When is the study scheduled?
- When conducting diagnostics and monitoring: inflammatory diseases,
- infectious diseases,
- oncological diseases,
- autoimmune diseases.
What do the results mean?
Reference values (ESR norm - table)
| Floor | Age | Reference values |
| up to 15 years | 2 - 20 mm/h | |
| Male | from 15 to 50 years | 2 – 15 mm/h |
| over 50 years old | 2 - 20 mm/h | |
| Female | up to 50 years | 2 - 20 mm/h |
| over 50 years old | 2 – 30 mm/h |
The results of this test must be interpreted in light of clinical data, medical history, and other tests.
Reasons for increased ESR in the blood
- Infectious diseases (usually bacterial causes). ESR can increase in both acute and chronic infectious diseases.
- Inflammatory diseases.
- Connective tissue diseases (rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus, systemic scleroderma, vasculitis).
- Inflammatory bowel diseases (Crohn's disease, ulcerative colitis).
- Oncological diseases: Myeloma. As a rule, it is accompanied by a very high level of ESR in the blood, because with it pathological proteins are synthesized in large quantities, which cause the formation of erythrocyte “coin columns”.
- Hodgkin's disease is a malignant disease of the lymph nodes. The ESR indicator is usually used not to make a diagnosis, but to monitor the course and effectiveness of treatment of an already diagnosed disease.
- Cancer of various localizations, especially hemoblastosis. It is believed that an extremely high level of ESR in the blood indicates the spread of the tumor beyond the primary site (i.e., metastases).
- Myocardial infarction. When it occurs, damage to the heart muscle occurs, which causes a systemic inflammatory response and, accordingly, an increase in ESR. After a heart attack, the ESR peaks about a week later.
- Anemia. A decrease in the number of red blood cells can lead to an increase in their sedimentation rate.
- Burns, injuries.
- Amyloidosis is a disease associated with the accumulation of pathological protein in tissues.
Reasons for decreased ESR in the blood
- Diseases accompanied by changes in the shape of red blood cells, such as sickle cell anemia or hereditary spherocytosis (they make it difficult for red blood cells to settle).
- Polycythemia (increased number of red blood cells) and conditions that lead to it, such as, for example, chronic heart failure or lung diseases.
What can influence the result?
- ESR in women usually increases during pregnancy and menstruation.
- Oral contraceptives, theophylline, and vitamin A may increase ESR.
- Taking corticosteroids and administering albumin can reduce ESR in the blood.
Norm of ESR in men and degree of deviation
The normal erythrocyte sedimentation rate in men is from 2 to 10 mm/hour. With age, the ESR indicator in men may change, remaining within the age norm. It is known that 5% of absolutely healthy men have, as a variant of the norm, increased erythrocyte sedimentation rate.
Table 1. Norm ESR in men by age
| Age | ||
| From 18 to 20 years old | 2 — 10 | 2 — 10 |
| From 20 to 50 years | 2 — 12 | 2 — 10 |
| 50 years and older | 5 — 20 | 2 — 12 |
For convenience, deviations from normal ESR parameters are usually classified by degree:
1st degree – a slight deviation from the norm, characterizing changes in blood parameters that are within acceptable limits.
- ESR (erythrocyte sedimentation rate) in the blood: normal for women by age (table)
2nd degree – the indicator differs from the norm by 15-30 units. This signals microcirculatory disorders in the man’s body. For example, about the presence of an infection that slightly changes the normal functioning of the body.
3rd degree – deviation from normal ESR values by 30-60 units, which indicates the presence of a serious inflammatory or necrotic process in the male body.
4th degree - if the ESR norm in men is exceeded by 60 units, which is an indicator of a catastrophically serious condition of the body.
Increasing ESR
If we exclude possible natural causes of an increase in ESR, then in other cases high results may indicate the presence of inflammatory processes in the body. The rate of sedimentation directly depends on the state and changes in the composition of proteins in the blood. The principle of the analysis is the ability of red blood cells to stick together - aggregation. Red blood cells themselves carry the same negative charge and therefore repel each other. The appearance in the plasma of acute phase proteins (fibrinogens, immunoglobulins), formed during inflammatory processes, increases the degree of erythrocyte adhesion and, accordingly, their sedimentation rate increases.
Most often, an increase in this indicator is observed in the case of:
- acute and chronic infections
- immune system diseases
- heart attack
- malignant tumors
- sepsis (60 mm/h or more)
- anemia
- erythrocytosis
- leukocytosis
- DIC syndrome
- taking hormonal medications
- intoxication
- injuries
- postoperative conditions
Thus, deciphering the ESR is only an indirect indicator of the health status of the subject’s body. Using this indicator alone, it is impossible to determine the nature of the disease. Deviation from the norm only signals the presence of possible health problems. And, before you panic, you need to contact a specialized Medical Center, which will provide consultation with qualified specialists who can give an accurate assessment of the patient’s condition, conduct the necessary examinations, determine the diagnosis and prescribe appropriate treatment.
Treatment
There is no specific treatment that would bring the study results into line with healthy parameters. To reduce the erythrocyte sedimentation rate, you will need to establish the correct diagnosis and undergo a course of appropriate treatment. What therapy will be depends on the detected pathology and existing chronic diseases.
Normal ESR in men occurs only in absolute health, but in most patients there are minor deviations up or down. If the changes are not critical and other parameters of the biological fluid are normal, the patient is recommended to undergo a repeat study in two to three weeks.