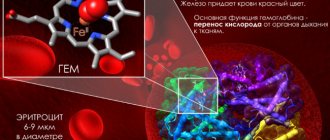
Our expert is nutritionist, candidate of medical sciences Rimma Moisenko .
Compared to sweet fruits, berries contain less fructose, but more pectins and fiber that are beneficial for digestion. Therefore, unlike fruits, berries can be eaten without restrictions. The fact is that recent studies have shown that many of us do not tolerate fruits rich in fructose (usually exotic fruits), since their digestion requires certain enzymes, which not everyone has. If there is a lack of such enzymes, fructose is not absorbed and can harm health: swelling appears, vitality and mood decrease, toxins accumulate in the body, which acidify it from the inside, thereby accelerating the aging process. Moreover, it turned out that fructose contributes to obesity to an even greater extent than glucose. Therefore, you should not get too carried away with fruits; it is better to give preference to berries.
All berries from the middle zone contain a lot of organic acids that improve metabolism. This makes berry sauces an excellent addition to meat dishes, as acids accelerate the breakdown of proteins.
In addition, berries are a great addition to your morning porridge. They will supply the body with useful substances, but will not lead to weight gain, unlike fruits, which, due to the abundance of sugars, do not go well with cereals.
A mixture of dried berries and nuts is suitable as a snack.
Healing jam. What berries did our ancestors use to treat themselves? More details
Blueberry
Composition (per 100 g of product): calorie content – 37 kcal; proteins – 0.4 g, fats – 0.1 g, carbohydrates – 8.7 g; sodium – 10 mg.
Blueberries are rich in anthocyanins - 300-700 mg (per 100 g of product) with a daily requirement of 200 mg. Anthocyanins reduce inflammatory reactions in the body and oxidative stress in the intestines. It is especially beneficial for dental health - anthocyanins reduce gum inflammation.
One study also found that a diet high in blueberries reduced cardiometabolic risk—that is, the risk of developing diabetes and cardiovascular disease.
What berries boost immunity? Which ones are good for the heart and blood vessels?
Berries have a positive effect on cognitive function (speed and accuracy of inferences) and the digestive system (thanks to fiber), help athletes recover from hard training and competitions, maintain moderate blood sugar levels (fiber slows down the absorption of glucose), and also reduce cholesterol levels.
Berries have a positive effect on cognitive function (speed and accuracy of inferences) and the digestive system (thanks to fiber), help athletes recover from hard training and competitions, maintain moderate blood sugar levels (fiber slows down the absorption of glucose), and also reduce cholesterol levels.
Let's figure out the health benefits of each specific type of berry.
Blueberry
Composition (per 100 g of product): calorie content – 37 kcal; proteins – 0.4 g, fats – 0.1 g, carbohydrates – 8.7 g; sodium – 10 mg.
Blueberries are rich in anthocyanins - 300-700 mg (per 100 g of product) with a daily requirement of 200 mg. Anthocyanins reduce inflammatory reactions in the body and oxidative stress in the intestines. It is especially beneficial for dental health - anthocyanins reduce gum inflammation.
One study also found that a diet high in blueberries reduced cardiometabolic risk—that is, the risk of developing diabetes and cardiovascular disease.
Blueberry
Composition (per 100 g of product): calorie content – 84 kcal; proteins – 1 g, fats – 0.5 g, carbohydrates – 21 g; sodium – 1.5 mg.
Blueberries have a positive effect on cognitive function, including supporting mental performance in older people. The berry is rich in flavonoids, which have an anti-inflammatory function, including reducing the risk of cardiovascular diseases. Vitamin C improves immunity and reduces age-related symptoms - blueberries contain 5 times more of it than blueberries (14.4 mg per 100 grams versus 2.8 mg per 100 g in blueberries).
Blackberry
Composition (per 100 g of product): calorie content – 62 kcal; proteins – 2 g, fats – 0.7 g, carbohydrates – 13.8 g; sodium – 1 mg.
Blackberries are also rich in anthocyanins, which reduce inflammatory reactions in the body, thereby slowing down the aging process. Flavonoids (vitamin P), in addition to similar antioxidant properties, also reduce the risk of developing chronic diseases - cardiovascular disease, cancer and diabetes. Eating blackberries reduces the level of “bad cholesterol” (LDL) by 50%, preventing the development of atherosclerosis.
High vitamin K content has a beneficial effect on bone health, which reduces the risk of osteoporosis and osteopenia.
Raspberries
Composition (per 100 g of product): calorie content – 64 kcal; proteins – 1.5 g, fats – 0.8 g, carbohydrates – 14.7 g.
Raspberries contain polyphenols, which improve the functioning of the endothelium (cells of the inner surface of blood vessels and heart cavities) and reduce the risk of developing hypertension (high blood pressure).
The high content of dietary fiber (8 grams per 100 grams of product) reduces cholesterol levels in the blood, which also has a beneficial effect on the cardiovascular system. Raspberries are rich in resveratrol, which increases bone strength - helps in bone formation and prevents age-related bone degradation.
Cranberry
Composition (per 100 g of product) : calorie content – 46 kcal; proteins – 0.5 g, fats – 0.1 g, carbohydrates – 12 g; sodium – 2 mg.
Cranberries contain unique phytonutrients (proanthocyanidins type A) that prevent the development of urinary tract infections. Eating cranberries also helps prevent ulcers.
The polyphenols in cranberries prevent the development of stomach cancer and may inhibit the growth of cancer cells in the mouth, colon and prostate. Drinking cranberry juice reduces the level of “bad” cholesterol and increases “good” cholesterol, reduces the stiffness of blood vessels and blood pressure.
Currant
Composition (per 100 g of product): calorie content – 63 kcal; proteins – 1.6 g, fats – 0.22 g, carbohydrates – 15.5 g; sodium – 1.1 mg.
Gamma-linolenic acid (GLA) in currants reduces inflammation in the body and helps fight some inflammatory diseases.
Some studies show the effectiveness of currants in the treatment of glaucoma.
Black currant seed oil helps maintain normal blood cholesterol levels and reduces the concentration of triglycerides, the bad fats in the blood. Blackcurrant juice improves kidney function and helps in treating kidney stones.
Gooseberry
Composition (per 100 g of product): calorie content – 66 kcal; proteins – 1.3 g, fats – 0.9 g, carbohydrates – 15 g; sodium – 1.5 mg.
The high content of soluble dietary fiber (6.5 g per 100 g) reduces the risk of developing cardiovascular diseases.
Eating gooseberries also reduces the risk of developing type 2 diabetes due to their high magnesium and potassium content, which regulate blood sugar levels. Gooseberries contain about 50% of the daily requirement of vitamin C - 42 mg per 100 grams of product.
Strawberries
Composition (per 100 g of product): calorie content – 41 kcal; proteins – 0.8 g, fats – 0.4 g, carbohydrates – 7.5 g.
Strawberries are rich in vitamin C (60 mg per 100 g of product). It also contains a lot of potassium (161 mg), calcium (40 mg), magnesium (18 mg) and sodium (18 mg), which has a beneficial effect on muscle function and the cardiovascular system in athletes.
Cherry
Composition (per 100 g of product): calorie content – 87 kcal; proteins – 1.4 g, fats – 0.3 g, carbohydrates – 22 g.
Consuming fresh cherries or cherry juice helps treat gout and arthritis. The vitamin composition of cherries and dietary fiber reduce the risk of developing lung and colon cancer.
Cherries also reduce muscle soreness and speed up recovery after workouts. Cherry juice reduces systolic and diastolic blood pressure. The high potassium content allows these berries to be recommended for people with problems with the cardiovascular system.
Strawberry
Composition (per 100 g of product): calorie content – 49 kcal; proteins – 1 g, fats – 0.5 g, carbohydrates – 11.7 g; sodium – 1.5 mg.
Strawberries are a berry with a low sugar concentration and high dietary fiber content. It is great for a diabetic diet and prevents spikes in blood sugar.
Strawberries also relieve symptoms of arthritis, including osteoarthritis of the knee joints. The berry promotes wound healing due to its high concentration of vitamin C (59 mg per 100 g of product). Strawberries reduce the risk of colon cancer.
Grape
Composition (per 100 g of product): calorie content – 62 kcal; proteins – 0.6 g, fats – 0.3 g, carbohydrates – 16 g; sodium – 2 mg.
The high vitamin K content has a beneficial effect on bone strength and helps with blood clotting problems.
The skin of red grapes is high in resveratrol, which reduces the risk of high cholesterol, high blood pressure, blood clots and cardiovascular disease. Eating grapes improves memory and cognitive function in older people.
Source: sports.ru
Share news:
Blueberry
Composition (per 100 g of product): calorie content – 84 kcal; proteins – 1 g, fats – 0.5 g, carbohydrates – 21 g; sodium – 1.5 mg.
Blueberries have a positive effect on cognitive function, including supporting mental performance in older people. The berry is rich in flavonoids, which have an anti-inflammatory function, including reducing the risk of cardiovascular diseases. Vitamin C improves immunity and reduces age-related symptoms - blueberries contain 5 times more of it than blueberries (14.4 mg per 100 grams versus 2.8 mg per 100 g in blueberries).
Rosehip for immunity
Rosehip is the champion among berries in terms of vitamin C content. In rosehip, ascorbic acid is not destroyed during the drying process and is completely preserved until spring. However, in order not to lose a single gram of beneficial substances, the rose hips must be properly dried. It is best to dry the berries at room temperature in a well-ventilated area away from direct sunlight. Under such conditions, drying will take quite a long time - up to three weeks. However, you should not rush into trying to dry rose hips in an oven or electric dryer - under the influence of high temperatures, a significant part of the vitamins and minerals is lost.
A vitamin drink is prepared from dried rose hips, which can be mixed with any juice, thus obtaining even more beneficial substances. To prepare a rosehip infusion, take about 30 berries, crush them in a mortar, pour a liter of hot water at a temperature of about 80 degrees and leave in a thermos for 12 hours. This drink will help strengthen the immune system, restore strength after illness, it is useful for children, adults and the elderly, because most of us are deficient in vitamin C.
Article on the topic
Jam, butter, marmalade. What can be prepared from sea buckthorn
Blackberry
Composition (per 100 g of product): calorie content – 62 kcal; proteins – 2 g, fats – 0.7 g, carbohydrates – 13.8 g; sodium – 1 mg.
Blackberries are also rich in anthocyanins, which reduce inflammatory reactions in the body, thereby slowing down the aging process. Flavonoids (vitamin P), in addition to similar antioxidant properties, also reduce the risk of developing chronic diseases - cardiovascular disease, cancer and diabetes. Eating blackberries reduces the level of “bad cholesterol” (LDL) by 50%, preventing the development of atherosclerosis.
High vitamin K content has a beneficial effect on bone health, which reduces the risk of osteoporosis and osteopenia.
Raspberries
Composition (per 100 g of product): calorie content – 64 kcal; proteins – 1.5 g, fats – 0.8 g, carbohydrates – 14.7 g.
Raspberries contain polyphenols, which improve the functioning of the endothelium (cells of the inner surface of blood vessels and heart cavities) and reduce the risk of developing hypertension (high blood pressure).
The high content of dietary fiber (8 grams per 100 grams of product) reduces cholesterol levels in the blood, which also has a beneficial effect on the cardiovascular system. Raspberries are rich in resveratrol, which increases bone strength - helps in bone formation and prevents age-related bone degradation.
TOP 10 healthiest nuts for the cardiovascular system
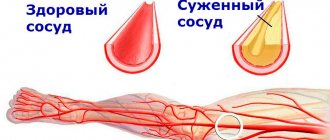
To fully supply the body with oxygen, the arteries and veins must be elastic and the pump strong. Nuts are excellent support for the heart and blood vessels, thanks to the amino acid arginine. Incoming unsaturated fats are important for lowering bad cholesterol.
One handful contains proteins that energize the heart. Eating nuts three times a week reduces the frequency of angina attacks by 30–50%. for the circulatory system .
Cranberry
Composition (per 100 g of product) : calorie content – 46 kcal; proteins – 0.5 g, fats – 0.1 g, carbohydrates – 12 g; sodium – 2 mg.
Cranberries contain unique phytonutrients (proanthocyanidins type A) that prevent the development of urinary tract infections. Eating cranberries also helps prevent ulcers.
The polyphenols in cranberries prevent the development of stomach cancer and may inhibit the growth of cancer cells in the mouth, colon and prostate. Drinking cranberry juice reduces the level of “bad” cholesterol and increases “good” cholesterol, reduces the stiffness of blood vessels and blood pressure.
Different products for different eye diseases
Depending on the problem you are facing, it is recommended to consume different foods first.
- If your work involves a lot of stress and your eyes get tired quickly, then parsley and carrot juice will help.
- The vessels will remain elastic and strong if you enrich your diet with apricots, both fresh and in the form of dried fruits or juice; rose hips will also help.
- For myopia, hawthorn and pumpkin are good remedies.
- For the development of cataracts, glaucoma, and optic nerve disease, parsley juice is very useful; one tablespoon per day is enough.
Why aren't blueberries on the list? In addition to the fact that it has a general supportive effect rather than a specific one, this summer berry, like carrots, has recently begun to give way to the benefits of green and yellow foods. This is explained by the fact that the latter contain more lutein and zeaxanthin - pigments that have a positive effect on eye health.
Currant
Composition (per 100 g of product): calorie content – 63 kcal; proteins – 1.6 g, fats – 0.22 g, carbohydrates – 15.5 g; sodium – 1.1 mg.
Gamma-linolenic acid (GLA) in currants reduces inflammation in the body and helps fight some inflammatory diseases.
Some studies show the effectiveness of currants in the treatment of glaucoma.
Black currant seed oil helps maintain normal blood cholesterol levels and reduces the concentration of triglycerides, the bad fats in the blood. Blackcurrant juice improves kidney function and helps in treating kidney stones.
Walnuts, where do they come from? From Greece?
Walnuts, according to one of the most common versions, originated in Northern India. In the middle of the 15th century. Constantinople, the capital of Byzantium, fell under the onslaught of the Turkish Sultan. Pavel Syutkin: “Trade ties with Russia were interrupted for a long time. Around the 16th-17th centuries, their new name appeared in Rus': “Volosh nuts”. These are the same walnuts, only brought to us from Wallachia (the south of modern Romania).”
In Vladimir Ivanovich Dahl’s we find: “Nut is masculine, a tree fruit in a hard, strong shell. Sometimes they say instead of hazel and hazel, walnut or walnut tree, meaning Voloshsky nut, walnut.” By the end of the 19th century, the name “walnuts” became predominant in the Russian language.
Encyclopedic Dictionary of Brockhaus and Efron : “Walnut, Voloshsky nut (Juglans L.).”
Eggplant rolls with walnuts, see recipe here
Now, as promised, let's talk about the benefits and harms of walnuts.
Gooseberry
Composition (per 100 g of product): calorie content – 66 kcal; proteins – 1.3 g, fats – 0.9 g, carbohydrates – 15 g; sodium – 1.5 mg.
The high content of soluble dietary fiber (6.5 g per 100 g) reduces the risk of developing cardiovascular diseases.
Eating gooseberries also reduces the risk of developing type 2 diabetes due to their high magnesium and potassium content, which regulate blood sugar levels. Gooseberries contain about 50% of the daily requirement of vitamin C - 42 mg per 100 grams of product.
Which nuts are not recommended to eat?
Important! Any nuts in a salty or sweet glaze are food that is harmful to the heart, figure and teeth.
If salt or sugar is added to sodium-rich peanuts and pistachios, a real disaster will occur. Even one handful will provide the body with the daily requirement of salt and sugar. Strong thirst will force you to take a large amount of water, which will lead to swelling of the face and limbs. Blood pressure will rise.
The heart will have to pump a large volume of blood, and arrhythmia will appear. All this causes great harm to the circulatory system. If used in this way, the beneficial nut will only cause harm.
Any peeled grains quickly deteriorate during storage. They breed mold fungi that produce aflatoxin poisons. Before purchasing, feel free to smell the nuts to check for freshness. Your sense of smell will not deceive you. Chop the fruit. If a dry cloud comes out of it, the nut is full of poisonous mold. It is better to buy unpeeled kernels in supermarkets.
Doctors recommend eating nuts in the morning or before lunch. Left in the stomach overnight they will not have time to digest. Excess calories will be deposited on the stomach. Before use, soak for 2-3 hours for better absorption. Combine kernels with fresh and dried fruit.
Strawberries
Composition (per 100 g of product): calorie content – 41 kcal; proteins – 0.8 g, fats – 0.4 g, carbohydrates – 7.5 g.
Strawberries are rich in vitamin C (60 mg per 100 g of product). It also contains a lot of potassium (161 mg), calcium (40 mg), magnesium (18 mg) and sodium (18 mg), which has a beneficial effect on muscle function and the cardiovascular system in athletes.
Cherry
Composition (per 100 g of product): calorie content – 87 kcal; proteins – 1.4 g, fats – 0.3 g, carbohydrates – 22 g.
Consuming fresh cherries or cherry juice helps treat gout and arthritis. The vitamin composition of cherries and dietary fiber reduce the risk of developing lung and colon cancer.
Cherries also reduce muscle soreness and speed up recovery after workouts. Cherry juice reduces systolic and diastolic blood pressure. The high potassium content allows these berries to be recommended for people with problems with the cardiovascular system.
Strawberry
Composition (per 100 g of product): calorie content – 49 kcal; proteins – 1 g, fats – 0.5 g, carbohydrates – 11.7 g; sodium – 1.5 mg.
Strawberries are a berry with a low sugar concentration and high dietary fiber content. It is great for a diabetic diet and prevents spikes in blood sugar.
Strawberries also relieve symptoms of arthritis, including osteoarthritis of the knee joints. The berry promotes wound healing due to its high concentration of vitamin C (59 mg per 100 g of product). Strawberries reduce the risk of colon cancer.
Grape
Composition (per 100 g of product): calorie content – 62 kcal; proteins – 0.6 g, fats – 0.3 g, carbohydrates – 16 g; sodium – 2 mg.
The high vitamin K content has a beneficial effect on bone strength and helps with blood clotting problems.
The skin of red grapes is high in resveratrol, which reduces the risk of high cholesterol, high blood pressure, blood clots and cardiovascular disease. Eating grapes improves memory and cognitive function in older people.
Read also
- What fruits and vegetables to eat in the fall?
- What are isotonics? What types of sports drinks are there? Is it possible to make isotonic water with your own hands?
- Do you need creatine for training? How to take it correctly? Understanding the properties of the additive
- What are the benefits of cherries? Is there any harm? Or is this the perfect berry?
- What are the benefits of watermelon? Is it possible to eat it every day? How to select and store ripe fruits?
- Walnut: how to use it to get the maximum benefit and not harm yourself?
- How are legume products useful and what is it? Why were there nuts among the beans, peas and lentils?