Hemorrhoids are a vascular disease that is characterized by varicose veins of the anus and rectum with the formation of hemorrhoids that are prone to inflammation and prolapse.
The disease is one of the most common vascular pathologies, affecting up to 10% of the world's population, and among proctological diseases, hemorrhoids are the undisputed leader. In its development, the disease goes through several stages. Stage three hemorrhoids are a serious pathology that requires immediate treatment and often leads to serious complications. The transition of the disease to the third stage occurs for several reasons, the main of which are poor-quality therapy for the initial stage of the disease, or its absence.
Reasons for the development of the disease
Hemorrhoids are classified as vascular pathologies, and therefore their occurrence in 90% of cases is due to the adverse effects of various aspects on the blood vessels of the pelvic area. The essence of the disease is a violation of blood circulation in the veins and arteries of the rectum, in which the outflow of venous blood is disrupted. If stage 3 hemorrhoids occur, the patient experiences a strong increase in nodes, which, at the slightest strain, fall out of the anus.
The most common causes of the disease:
- unhealthy diet, which is based on refined, low-fiber foods;
- tendency to constipation;
- lack of movement;
- lack or lack of perineal hygiene;
- pregnancy and childbirth;
- lifting weights;
- bad habits - drinking alcohol and tobacco.
Of course, these phenomena cannot immediately lead to the formation of third-degree hemorrhoids, however, they provoke weakening of the vascular walls, and with a prolonged effect on the body they contribute to the progression of the disease to stage 3.
Hemorrhoids 4 degrees
The patient's condition is rapidly deteriorating. Stage 4 hemorrhoids require immediate surgical intervention and removal of hemorrhoids. The advanced disease is characterized by pain when walking and even while sitting. Reduction of tumors into the anus is impossible.
Bleeding becomes profuse. As a result, anemia or anemia is diagnosed. The patient feels severe weakness, loss of strength, and lack of appetite. Blood clots form in the cavernous veins, which negatively affect the blood circulation process. Hemorrhoids become inflamed, thereby provoking the appearance of suppuration and necrosis, dead areas of soft tissue. Harmful bacteria spread throughout the body and worsen the condition.
Symptoms of hemorrhoids at stage 3
The symptoms that characterize grade 3 hemorrhoids arise due to profound changes in the vascular wall and cavernous bodies in the rectum. Since they weaken, the nodes can no longer be held in their normal position, and fall out of the anus at the slightest strain: when coughing and sneezing, sudden movements (jumping, for example). Evacuation becomes a real torture, since the pain becomes very severe, and it does not subside for several hours after visiting the toilet.
In addition, pain may occur when walking and sitting. This is due to the fact that grade 3 hemorrhoids can be complicated by thrombosis (the pain becomes more intense and prolonged), inflammation of the mucous membrane of the anal canal, the skin of the perianal area or subcutaneous fat. Bleeding at this stage of hemorrhoids occurs very often, since the walls of the blood vessels become thinner more than at previous stages of the disease.
In the absence of therapy, the disease develops into chronic hemorrhoids of the 3rd degree. This form of the disease is characterized by periods of subsidence of symptoms and their resumption. It is important not to miss the moment and consult a doctor, even if the illness has subsided and the symptoms have weakened to the point of discomfort. It is important for patients to understand that hemorrhoids are not a disease that can disappear on their own - it will develop further, which is fraught with many serious complications.
Hemorrhoids 1st degree
The initial stage of hemorrhoids is asymptomatic and does not bother the patient. In some cases, itching and burning appears in the anus. Impurities of blood, pus and mucus form in the stool. Drops of blood are visible on the toilet paper. At the early stage of proctological disease, patients rarely seek medical help. It is extremely important to contact a medical specialist in time to begin treatment at the first stage and avoid complications.
Advanced forms of the disease are much more difficult to cure. At stage 1 of hemorrhoids, the patient is prescribed rectal suppositories or medications. They eliminate the inflammatory process, kill harmful bacteria, and improve blood flow in the vessels. Traditional medicine is used. Potato suppositories will help improve blood circulation in the anus and make bowel movements easier.
Treatment methods for hemorrhoids at stage 3
A disease such as grade 3 hemorrhoids requires complex treatment. It must include symptomatic therapy, treatment of blood vessels and normalization of intestinal functions. In addition, most patients diagnosed with the third stage of hemorrhoids are treated with surgical or minimally invasive treatment using the following methods:
- ligation of the hemorrhoid with latex rings;
- disarterization of hemorrhoids;
- hemorrhoidectomy;
- removal of hemorrhoids with laser or high-frequency currents;
- cryotherapy;
- infrared or electrocoagulation of hemorrhoids (the latter is rarely used).
Each of these procedures has features that allow them to be used in different situations. Thus, the method of removing hemorrhoids with a laser and a high-frequency coagulator is effective and easy to rehabilitate. They can be used for any size of nodes and even for bleeding from hemorrhoidal veins.
Rice. 3 Stage of ligation of the hemorrhoid using latex rings. The simplest, most popular and effective method of treating stage 2–3 hemorrhoids.
Latex ligation and dearterization are also quite effective procedures used to eliminate pathologies such as stage 3 hemorrhoids - treatment with their use ends successfully in most cases, however, they have more contraindications than laser removal of venous plexuses, and also carry the risk of bleeding or inflammation of the mucous membrane.
Coagulation of the vessels feeding the hemorrhoid is another popular method of eliminating the disease, which allows you to eliminate the symptoms of the disease within a few hours after the procedure. Hemorrhoidectomy also has the most radical effect - a radical procedure that consists of removing hemorrhoidal plexuses in the classical way (with a scalpel) or using a laser or high-frequency scalpel.
Rice. The stage of the operation is hemorrhoidectomy, suturing and ligation of the hemorrhoidal artery, the so-called “pedicle of the hemorrhoid.”
It is important to remember that treating grade 3 hemorrhoids without surgery (surgical or minimally invasive) is a myth. No drug can return the vessels in the rectum to their original healthy state. In this case, minimally invasive treatment methods are the least traumatic. If the disease reaches the third stage, the patient will sooner or later have to turn to a proctologist surgeon for help.
Chronic combined hemorrhoids - treatment
Depending on the severity of the pathology, the proctologist determines the treatment tactics. With grades 1 and 2 of hemorrhoidal development, conservative therapy with medications is possible. More severe pathology requires radical therapy. The hospital's first surgical department uses various surgical techniques. Surgery for combined hemorrhoids is preferable, which is performed using gentle techniques to achieve minimal trauma to healthy tissue.
Nutrition for grade 3 hemorrhoids
Normalization of nutrition is an important condition for eliminating grade 3 hemorrhoids. Even if the patient has undergone surgery, nutrition will determine his condition in the near future (in the postoperative) period and for at least 2–3 months after treatment. So, even a small error when drawing up a menu can result in constipation or diarrhea, which will lead to an exacerbation of hemorrhoids or the appearance of new nodes.
To prevent this, it is recommended to adhere to the following nutritional principles:
- give up alcohol, coffee and carbonated drinks - they weaken blood vessels and irritate the intestines;
- do not eat hot and spicy foods - they irritate the intestines and provoke stool disorders;
- enrich your diet with fiber - it is found in fresh fruits, vegetables and dark-colored cereals;
- introduce vegetable oil into the menu - as a dressing for cereals and salads, it will help enhance peristalsis;
- drink at least 2 liters of water per day.
In the postoperative period, the diet should be as strict as possible. Porridges (oatmeal or pearl barley, preferably mucous), weak broths from lean chicken meat (without skin!), stewed or pureed vegetables, juices and tea, and whole grain bread are allowed to be used as food. After a week, the menu can be diversified.
Disease prevention
Even in the absence of symptoms, it is extremely important to follow preventive measures to avoid the appearance of hemorrhoidal cones and an increase in their size. To do this, you should visit a proctologist every six months for diagnostic tests. At home, it is recommended to do baths and microenemas, and use rectal suppositories, which have a positive effect on the microflora and the condition of soft tissues. In a hospital setting, cauterization of blood vessels is performed.
It is important to follow a diet, include fermented milk products, fruits and vegetables in your diet, and drink plenty of clean water. To improve the functioning of the esophagus, avoid excessive consumption of caffeine and alcoholic beverages. Spicy seasonings and sauces irritate the intestinal mucosa.
Every day you need to walk in the fresh air and do physical exercise. This prevention is especially important for people who lead a sedentary lifestyle. Squats will help relax your muscles and improve blood flow in your veins and arteries.
Proctologists advise limiting heavy lifting and excessive physical activity. Try to minimize muscle tension. To activate blood circulation in the anus and avoid enlargement of hemorrhoids, you can rinse the anus with cool water using herbal remedies.
To avoid irritating the soft tissue of the anus, you should purchase damp toilet paper. Only with a timely visit to a proctologist can complications and the development of proctological diseases be avoided. To make an appointment, call the number listed on the official website. An employee of the private medical clinic “Proctologist 81” will call you back and confirm the selected time. Prices for diagnostic tests and procedures are posted on the website. The cost depends on the stage of the disease and the presence of concomitant pathologies.
Haemorrhoids
5280 28 July
IMPORTANT!
The information in this section cannot be used for self-diagnosis and self-treatment.
In case of pain or other exacerbation of the disease, diagnostic tests should be prescribed only by the attending physician. To make a diagnosis and properly prescribe treatment, you should contact your doctor. Hemorrhoids: causes, classification, symptoms, diagnosis and treatment methods.
In world statistics of proctological diseases, hemorrhoids rank first as the most common pathology (up to 41% of cases): more than 75% of people aged 45-65 years are diagnosed with varicose veins of the rectum.
Reasons for the development of hemorrhoids
- The development of varicose veins of the rectum due to compression from the outside (tumors of the pelvic organs or intestines) with impaired outflow through the intestinal veins.
- Impaired outflow of venous blood from the rectum due to pathologies not related to the pelvic and intestinal organs (liver disease).
- Dystrophy of the anatomical structures responsible for the elasticity of the venous wall.
Provoking factors for the development of hemorrhoids include:
- Pregnancy and childbirth.
- Connective tissue dysplasia.
- Hereditary predisposition.
- Physical inactivity, predominantly sedentary lifestyle.
- Impaired intestinal motility with a predominance of constipation.
- Frequent or constant use of laxatives, regular mechanical irritation of the rectal mucosa.
- Activities associated with excessive muscle tension (weightlifting, physically demanding work).
- The predominance of spicy and spicy foods in the diet.
- Diseases of the pelvic organs, leading to compression of the pelvic veins.
- Pathology of the valve apparatus of the intestinal veins (in particular, the rectal plexus).
- Liver pathology (for example, cirrhosis) with the development of portal hypertension.
Classification of the disease By localization:
- interior;
- outer;
- combined.
With the flow:
- Spicy
- without inflammation of hemorrhoids;
- with inflammation of hemorrhoids;
- with the involvement of surrounding tissues in the inflammatory process.
- Chronic
- with bleeding without prolapse of hemorrhoids;
- with bleeding, but the prolapsed nodes are reduced spontaneously;
- reduction of nodes is possible only manually (with or without bleeding);
- the nodes are irreducible (with or without bleeding) or fall out immediately after reduction.
According to etiology, hemorrhoids are divided into:
- congenital (hereditary);
- acquired;
- symptomatic.
Symptoms of hemorrhoids
Acute hemorrhoids, due to the vivid clinical picture, immediately forces you to seek help. In this case, timely treatment prevents the process from becoming chronic.
In acute hemorrhoids, discomfort, itching and pain in the anus are noted, especially aggravated by defecation. Blood appears in the stool, and it covers the feces without mixing with them.
Chronic hemorrhoids are characterized by the same symptoms, but there are periods when the symptoms disappear, appearing again under the influence of provoking factors. With exacerbation of chronic hemorrhoids, its symptoms are similar to those of acute disease.
During the period of remission of chronic hemorrhoids, there are no complaints of specific discomfort.
The clinical picture of hemorrhoids depends on the stage of the disease.
The first stage of hemorrhoids is characterized by minimal manifestations; discomfort during bowel movements and pain in the hemorrhoids are possible. When examined by a specialist, dilation of the capillaries of the rectal mucosa is recorded, which indicates venous stagnation, the appearance of nodes and local inflammation of the mucous membrane. Sometimes blood is released during bowel movements.
The second stage is characterized by prolapse of hemorrhoids during and after defecation with the possibility of their spontaneous reduction. In this case, bleeding and mucus discharge from the rectum occur more often, and itching and discomfort in the anal area are bothersome.
At the third stage, hemorrhoids fall out not only during defecation, but also during straining, coughing and other actions leading to increased intra-abdominal pressure (lifting heavy objects), and do not spontaneously reduce.
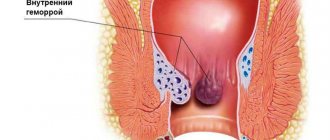
At the fourth stage, repositioning of the nodes is impossible either spontaneously or manually. This stage is the most dangerous in terms of the development of complications: prolonged heavy bleeding is possible, threatening the development of anemia (a decrease in the level of hemoglobin and the number of red blood cells that carry oxygen to all tissues, which, accordingly, will affect all organs), and thrombosis of hemorrhoids. Internal hemorrhoids in the early stages are asymptomatic; there may be a sensation of a foreign body in the rectum or a feeling of empty bowel. The discharge of blood and mucus at this stage is so scanty that it goes unnoticed. Hemorrhoids do not protrude into the lumen of the rectum.
As hemorrhoids enlarge, the intestinal lumen narrows, and therefore the process of fecal excretion is disrupted. Defecation is accompanied by pain and microtrauma of the mucous membrane, which leads to inflammation and aggravation of the symptoms of the disease. At a later stage, the entire symptom complex appears (bleeding, pain, discharge of blood and mucus from the rectum, prolapse of nodes, discomfort in the anal area), the likelihood of complications increases - anemia, thrombosis or the addition of a secondary infection with the development of paraproctitis (inflammatory - often purulent - tissue disease surrounding the rectum).
External hemorrhoids are characterized by the appearance of pain in the anus after exposure to provoking factors (coughing, prolonged sitting, heavy lifting, straining, defecation). With this form of the disease, bleeding occurs much less frequently than with internal hemorrhoids. Blood is visible not on feces, but on linen, toilet paper and personal hygiene products. Upon examination and palpation of the affected area, painful nodes are detected.
If persistent pain occurs in the perineum, not related to the act of defecation, or an increase in the size of the hemorrhoids, the development of thrombosis of the hemorrhoids is most likely, which, if left untreated, can lead to complications and the need for surgical intervention.
Diagnosis of hemorrhoids Diagnosis of hemorrhoids begins with an examination (external and internal) or by a proctologist. With internal hemorrhoids, the nodes are dark cherry in color, have a soft elastic consistency, are painful on palpation, and protrude into the lumen of the rectum. With external hemorrhoids, nodes of a similar type are visible around the anus. Instrumental diagnostic methods are used - anoscopy, sigmoidoscopy, colonoscopy.
Diagnosis of the disease
Diagnosis of combined hemorrhoids is carried out using the same methods that detect individual forms of this disease. Differential diagnosis is carried out with the expectation that the symptoms of this disease may be similar to other pathologies, including cancer. Therefore, only a qualified specialist can diagnose mixed hemorrhoids, based on the symptoms when examining the patient. If necessary, the proctologist may prescribe other examination methods in order to clarify the pathology. Self-medication should not be practiced under any circumstances; a person can unintentionally complicate the course of the disease.
Classification of hemorrhoids
Depending on the form of manifestation:
- Internal hemorrhoids. The affected veins are located in the anal canal and are not visible during normal examination. When defecation or strong tension in the anus, hemorrhoids fall out, which is accompanied by acute pain and often bleeding.
- External hemorrhoids. Hemorrhoids are initially located on the outside. Unlike the internal ones (covered by the mucous membrane), they are covered with skin and do not bleed during bowel movements.
- Combined hemorrhoids. The patient simultaneously has both internal and external hemorrhoids.
Depending on the nature of the course:
- Spicy. Accompanied by severe pain. Inflamed veins first turn blue and then (in the absence of proper treatment) turn black. Tissue necrosis begins.
- Chronic. The pain is mild. The patient first calmly resets the prolapsed nodes on his own. But if nothing is done, then he needs outside help for this procedure, and then it becomes completely impossible to straighten the nodes.
Hemorrhoid excision surgery
It is possible to completely cure hemorrhoids at stage 3 of pathology only with the help of surgical intervention. Minimally invasive techniques in the last stages of the disease turn out to be ineffective, since cavernous formations reach significant sizes. Treatment methods using surgery include hemorrhoidopexy according to the Longo method, hemorrhoidectomy according to Milligan-Morgan. Both methods are quite traumatic and require the patient to be in a hospital and undergo rehabilitation measures.
Indications for surgical intervention are the following patient conditions:
- lack of effect from drug therapy;
- constant prolapse of hemorrhoids;
- development of thrombosis;
- complications in the form of proctitis, paraproctitis, pinched veins, necrosis;
- heavy bleeding;
- constant deterioration of the patient's well-being.
The operation is performed closed or open, involves the complete removal of cones, and can be carried out in several stages. After excision of the nodes, the patient is under the supervision of medical personnel in an inpatient setting. During this period, the patient must limit physical activity and follow a special diet aimed at preventing constipation. To do this, you should avoid strong and gas-forming products, and exclude spicy, fatty, salty, and fried foods. The diet should include boiled cereals, low-fat fermented milk products, vegetables, fruits, and herbal teas. It is necessary to avoid drinking alcohol, carbonated drinks, strong tea, coffee, and chocolate.
Important! The further success of treatment depends on how clearly the patient follows the doctor’s recommendations during the recovery period.
The role of traditional treatment
Traditional medicine gives good results in the treatment of all forms and degrees of varicose veins in the rectal area. Herbs and some natural products can be used as adjuvant therapy or to help restore health after surgery.
Chamomile has an excellent antiseptic, anti-inflammatory and healing effect on hemorrhoids.
Effective folk recipes:
- ice candles. To eliminate pain and inflammation, it is recommended to use suppositories made from ice. To do this, you can use a decoction of chamomile, nettle, calendula or other herbs. In order to make a candle, you need to pour the broth into foil molds, put them in the freezer to harden, after which the suppository is inserted into the anus 1-2 times a day;
- mumiyo. This product helps eliminate most of the symptoms that occur in patients with a delicate problem. For treatment, you need to knead a small amount of mumiyo and lubricate the affected areas with it. For internal hemorrhoids, a piece of the product is inserted into the anus overnight;
- warming with garlic steam. To prepare the decoction, you need to take milk and boil it. After this, you need to add a head of finely chopped garlic to the product, sit over the steam for 15 - 20 minutes;
- natural juice therapy. For hemorrhoids, patients are recommended to drink the juice of rowan berries, beets, and carrots daily. These products help normalize digestion, prevent constipation, and eliminate soreness and inflammation.
When using folk remedies, you should strictly adhere to the recipe and dosage of the medications. The best option is a preliminary consultation with a proctologist.