- Home >
- Clinic services >
- Neurology >
- Cerebral vasospasm
In the human body, the brain is the most important organ, which not only regulates the functioning of all other organs and systems, but is also responsible for our consciousness, perception and memory.
The human brain, like any other organ, must be supplied with blood and receive the required amount of oxygen and metabolic substances. Therefore, the microvasculature of the brain is one of the most complex vascular networks in our body. Indeed, when blood flow to the brain is disrupted, pathological processes occur, many of which are irreversible. One of the common causes of circulatory disorders in various parts of the brain is vascular spasm. Nowadays, cerebral vasospasm is a condition that most often occurs in people over 30 years of age. What is a spasm, how and why does it occur in the vessels of the brain, and how should this condition be treated?
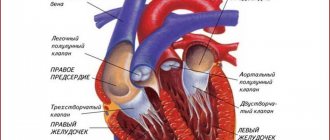
The definition is: a spasm is a case of sudden contraction of smooth or striated muscle. It is known that our vessels have a wall consisting of smooth muscle, when a vessel spasm (angiospasm) occurs, the lumen of the vessel closes, which is always fraught with complications.
Causes of cerebral vascular spasms
Like any disease or pathological condition, spasm of the blood vessels of the brain has its causes. This condition has been studied quite thoroughly, and knowing the etiology (origin) of this disease is extremely necessary, because treatment of vasospasm is always symptomatic.
The causes of vasospasm in the brain (cerebral vasospasm) can be divided into two groups of etiological factors: cerebral and extracerebral.
- Brain: Atherosclerosis. Atherosclerosis is the process of formation of the so-called atherosclerotic “plaque” on the inner vascular wall (endothelium). In essence, a plaque is an accumulation of clumped elements of circulating blood and various salts and fats. As a result of recent studies, it was found that atherosclerosis already affects 90% of adolescents aged 14 to 16 years around the world. This, of course, is due to the dietary habits and lifestyle of modern people, as well as a number of aggressive environmental factors.
- Hemorrhages in the brain. In these conditions, a reflex vasoconstriction occurs. The process takes some time, but ultimately ends with a complete narrowing of the damaged vessel, and as a result, a stoppage of blood supply.
- Osteochondrosis. As a rule, vasospasm occurs with osteochondrosis in the cervical vertebrae. This process entails a narrowing of the lumen of the vessels supplying blood to parts of the brain. Thus, as a result of a decrease in the volume of incoming blood, vasospasm occurs.
- Cerebral aneurysm. These are various changes and defects in the structure of the walls of blood vessels in the brain.
- Vasculitis (angiitis). Pathological changes in blood vessels are based on inflammation, which can be primary (independent) or secondary (as a symptom or complication of certain diseases).
- Vascular embolism. This should include thromboembolism as the most common cause of cerebrovascular accidents. Thromboembolism is a pathological condition in which a blood vessel is blocked by a blood clot. In this condition, spasms in the blood vessels of the brain are also noted.
- Tumors and tumor-like diseases of the head. In such conditions, spasm occurs due to compression of the vessel by the tumor.
- Circulatory disorders in diseases of the cardiovascular system (cardiovascular system). As a rule, vasospasms of the brain occur in diseases such as ischemic heart disease (coronary heart disease), chronic heart failure, and increased vascular stiffness.
- lack of sleep;
—>
At the MART clinic on Vasilyevsky Island
- Evidence-based medicine
- Experienced specialists
- Monitoring of patients for 6 months.
- Diagnostics (MRI, ultrasound, tests)
- Daily 8:00 – 22:00
Make an appointment
Prevention
Preventing any spasm requires adherence to a regimen and dietary restrictions.
According to WHO, abuse is defined as the single consumption of more than 60 ml of alcohol by men (150 ml of vodka, 0.5 liters of wine, 1.3 liters of beer), for women - more than 50 ml (125 ml of vodka, 0.4 liters of wine, 1.1 l beer) even once a month.
And no more
Treatment of hypertension and atherosclerosis helps to avoid the occurrence of additional symptoms that intensify the underlying disease.
Many doctors advise patients over 40 years of age to take a daily dose of a blood thinner (Cardiomagnyl, Cardiasc).
- Why is a study of the blood vessels of the brain and neck performed?
Clinical manifestations of vasospasm
It must be remembered that cerebral vasospasm is a kind of circulatory disorder, and since the brain is associated with the regulation of neuropsychological processes, the main clinical manifestations are associated with a violation of neurological and psychological functions. To describe the symptoms of cerebral vasospasms, it is convenient to identify two groups: neurological and psychological lesions.
I. Neurological lesions in cerebral vasospasms.
- Headache, migraine. One of the early symptoms of vasospasm.
- Dizziness. As a rule, they arise spontaneously. They can occur together with loss of orientation in space.
- Feeling sick or suddenly vomiting.
- Visual, auditory, taste or olfactory disturbances, including hallucinations.
- Sometimes patients experience pain in various parts of the body (although the connection with cerebral vasospasm has not been established).
- Decreased performance.
- Increased fatigue.
II. Psychological disorders:
- The main and most alarming signs are memory impairment and amnestic syndrome.
- Various types of preservation (multiple repetitions of words or actions).
- Violations of psychological orientation. Patients are not able to talk about themselves, their profession, etc. This state is sometimes accompanied by apathy and indifference to the environment.
Raynaud's syndrome: treatment
An integrated approach to eliminating the causes of Raynaud's syndrome allows you to cure the disease without surgery. With the development of secondary Raynaud's syndrome associated with connective tissue pathologies, the patient is prescribed medications to eliminate the symptoms and causes of the disease.
With independent Raynaud's syndrome, drug and surgical treatment is carried out in exceptional cases. Raynaud's syndrome, the symptoms and treatment of which are interrelated, requires the exclusion of provoking factors such as vibrations, stress, smoking, and cold. Rheumatologists at the Yusupov Hospital also include physiotherapeutic procedures in the treatment plan. Professional psychologists with many years of experience teach patients techniques for relieving stress and tension, and relaxation.
The mechanism of cerebral vasospasm
Angiospasm can be considered as an incomplete contraction of vascular muscle tissue. Under normal conditions, the vessels constantly contract and immediately relax. During spasm, the process of relaxation of blood vessels takes much longer, or does not occur at all.
So, there are three mechanisms for the occurrence of spasms:
- disturbances in ion exchange in smooth muscle cells (for example, with an increase in the amount of calcium ions, constant contraction of blood vessels occurs);
- reflex mechanism (for damage to the vascular wall, inflammation and other conditions);
- neurogenic mechanism (has no clinical evidence).
Raynaud's syndrome in women
Raynaud's syndrome symptoms and treatment in women begins at an earlier age. Among people suffering from this disease under the age of 50, there is a fivefold predominance of the disease in women. Common manifestations of Raynaud's syndrome are: pallor, bluishness of the skin and loss of sensation in certain areas of the limbs or face.
Some women ignore the signs of the disease at an early stage, resulting in the development of other serious diseases, the successful treatment of which determines the timely detection of the disorder. Raynaud's syndrome develops in several phases:
- the vasoconstrictor phase is characterized by the appearance of pallor of the skin, which can last up to 15 minutes;
- the cyanotic phase lasts several minutes, pallor during this phase is replaced by cyanosis;
- the phase of reactive hyperemia is characterized by redness of the skin.
This sequence is not observed in all patients during an attack. The duration and order of the phases depends on the course of the disease and the general condition of the body.
Diagnosis of cerebral vasospasm
The diagnosis is made by a specialist based on symptoms, as well as instrumental and hardware research methods. When diagnosing cerebral vascular spasm, the most informative methods are:
- MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) of the head and neck;
- Contrast magnetic resonance imaging of blood vessels (angiography). This method uses the introduction of special contrast agents into the bloodstream.
Can also be used:
- magnetic resonance imaging
- Doppler examination using ultrasound (less informative research method).
Why are cerebral vascular spasms dangerous?
Since spasm of a vessel causes cessation of blood circulation in one or another area of the brain, the most basic complication is the development of ischemia (a dangerous complication is ischemic stroke). Ischemia is a decrease in blood supply to a tissue or organ due to decreased blood flow. A decrease in blood supply can lead to the development of hypoxia, and subsequently to tissue metabolic disorders. It is important to note that with prolonged ischemia, tissue necrosis (death) can occur, which is fraught with serious consequences.
If you have any questions, ask our specialist! Ask a Question
Treatment of Raynaud's syndrome in Moscow
Patients of the Yusupov Hospital receive high-quality medical services, as doctors and staff take a responsible approach to fulfilling their duties. Raynaud's syndrome, the symptoms of which appear unexpectedly in patients, raises many questions and concerns. Rheumatologists at the Yusupov Hospital clearly explain to patients the features of this disease and the most optimal methods of treating it.
The therapy clinics of the Yusupov Hospital, where they provide care to patients with Raynaud's syndrome, have modern equipment to identify circulatory disorders and associated pathologies that can worsen a person's quality of life. When treating the disease, specialists use modern approaches and means that have a minimum number of side effects.
For a comfortable stay for patients, the Yusupov Hospital has a pre-registration system by telephone, so there is no long wait required to visit a specialist.