Cheese with all its varieties is the most popular product. For many peoples it is part of the traditional diet. There are also many culinary recipes where cheese is an integral ingredient. It gives dishes a unique delicate taste and increases their nutritional value. However, is it as useful as is commonly believed? Doesn't it cause harm to the body? Such doubts are caused by some substances that cheese contains, and cholesterol is one of them.
There is an opinion that hypercholesterolemia and eating cheese are incompatible things. Is it really? Should we be so categorical and completely exclude a healthy product from the diet?
What is cheese made of?
- The main component of cheese is fats, including cholesterol - 60%.
- Proteins (about 30%).
- Vitamins necessary for the regulation of vital metabolic processes: A, group B, C, E.
- Potassium, which is indispensable for the full functioning of myocardial cells.
- Calcium is the basis of mineral metabolism in the body.
- Phosphorus, along with calcium, is one of the main components of mineral metabolism.
- Manganese, which takes part as a catalyst in many biochemical reactions.
- Zinc.
- Sodium, which is the main mineral of the intercellular substance.
- Copper.
- Iron, necessary for the transport of oxygen to organ tissues.
Such a composition rich in various useful substances necessary for the formation of cells of bone, nervous and muscle tissue makes cheese an extremely valuable food product. This combination is especially useful for people whose bodies have an increased need for nutrients: children, pregnant women, as well as patients in the recovery period after extensive injuries.
The nutritional value
Many people love cheese for its delicate taste and piquant smell; not a single feast is complete without it; it is an important component of many dishes. The rich composition makes the product especially valuable for children, the elderly, patients with tuberculosis, weakened after serious illnesses, pregnant and lactating women.
The physical and chemical composition of cheese varies depending on the characteristics of the raw materials, production technology, and recipe. All varieties contain to a greater or lesser extent:
- essential amino acids - lysine, isoleucine, methionine, tryptophan, valine, phenylalline, leucine;
- unsaturated fatty acids, namely linoleic acid, which is especially important for the body;
- vitamins PP, E, D, C, A, B2, B12;
- minerals - calcium, phosphorus, potassium, magnesium, sodium, copper and iron.
The composition of the cheese is as close as possible to the composition of milk, only with a significantly higher concentration of biologically active components.
What determines the cholesterol content in cheese?
The amount of cholesterol in cheese depends on its type, or more precisely, on the percentage of fat content. And this parameter, in turn, is directly dependent on the chemical composition of the ingredients.
- Milk. This is the direct raw material for making cheese. The amount of cholesterol contained in cheese depends on its initial fat content. Fermented milk products are made not only from cow's milk. The starting raw material for various types of cheese can be goat, sheep, or buffalo milk. The fat content of the final product (cheese) depends on what kind of milk was used in production.
- Leaven. This is a component with which raw milk is fermented. Traditionally, lactic acid bacteria are used in this capacity. This technology gives the cheese a characteristic, recognizable taste and dense consistency.
- Salt (to avoid disturbances in mineral metabolism, for frequent regular consumption it is strongly recommended to choose the least salty varieties of cheese).
- Rennet element. As a rule, this is a complex of substances similar to digestive enzymes. It is this chemical substance that “turns” milk into cheese.
The modern food industry, in addition to cheeses, also produces so-called cheese products. The difference is that the cheese product, in addition to animal fats, also contains vegetable fats. This combination significantly reduces the amount of cholesterol contained in the final product. Vegetable fats have their own properties that are quite beneficial for the body.
Such a product, from the point of view of its lower content of animal fats, is significantly more harmless for the human body, accustomed to the systematic consumption of cheese, but suffering from hypercholesterolemia.
Beneficial features
To produce high-quality cheese, milk (cow, goat, sheep), a starter of lactic acid bacteria or natural rennet is used - a substance that helps curdle milk and subsequently transform its consistency. Based on the method of precipitation of casein, cheese is classified as rennet or fermented milk.
The value of cheese is determined by its rich composition:
- calcium, together with phosphorus, strengthens bone tissue and regulates mineral metabolism in the body;
- potassium is responsible for heart health and normalizes metabolic processes;
- magnesium increases immune defense, minimizes the risk of developing diabetes, stroke, myocardial infarction;
- sodium regulates neuromuscular activity, promotes the movement of sugar;
- linoleic acid stimulates weight loss, reduces the content of harmful cholesterol fractions;
- vitamins B2 and B12 normalize the function of the nervous system, optimize blood formation, promote hemoglobin synthesis, improve the absorption of amino acids, thereby reducing the saturation of the blood with low-density lipoproteins;
- amino acids activate the breakdown and excretion of lipids, prevent fatty liver hepatosis, and slow down the development of atherosclerosis.
Thanks to proteins and fats, hard cheese is one of the ten highest calorie foods. Less nutritious are soft pickled varieties; they are a more preferable component of a low-calorie diet menu.
Cholesterol rating of cheeses
Based on this composition of the cheese, questions naturally arise: is cheese harmful for high cholesterol levels in the blood and what kind of cheese can people suffering from hypercholesterolemia eat?
There are no types of cheese that do not contain cholesterol at all.
Cheeses made from skim milk contain minimal amounts of cholesterol. Firm, mature varieties, on the contrary, are very rich in this substance.
- Adyghe cheese. Cholesterol is present in its composition, but in a rather small concentration. But this unusual product contains a large amount of polyunsaturated fatty acids, very beneficial for the body, amino acids and proteins. This unique composition makes this product very valuable. Moreover, a number of active substances contained in Adyghe cheese can improve metabolism, somewhat reducing the concentration of harmful fats in the blood.
- Mozzarella. This is another type of cheese that contains small amounts of cholesterol. It is even classified as a dietary product, because it contains a large number of useful substances: antioxidants, essential acids, vitamins.
- Ricotta. This type of cheese differs from others in that the raw material for its preparation is not milk, but whey remaining after the fermentation of dairy raw materials. Since whey has a significantly lower percentage of fat content compared to milk, it is allowed to be eaten with an increased concentration of cholesterol in the blood.
- Brynza. The fat content of this pickled cheese is also low. The properties of the product largely depend on the period during which it was kept in saline solution. It is known that cheese that has been in brine for 40 - 50 days has the most beneficial qualities. It also contains the least amount of cholesterol. Only processed varieties contain less cholesterol than these types of cheese. However, the range of useful nutrients they contain is not so rich.
- Full-fat cream cheese has the highest cholesterol content.
Definition of the term
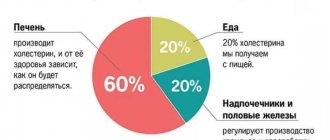
Cholesterol (another name is cholesterol) is a fatty (lipophilic) alcohol formed during natural metabolic processes. 80% of the substance is synthesized by the following internal organs: liver, small and large intestines, kidneys and adrenal glands, gonads. Only 20% is replenished with food.
Cholesterol combines with proteins to form high- and low-density lipoproteins for transport in the blood. High molecular weight (HDL) and low molecular weight (LDL) compounds are formed.
They perform different functions in the body:
- High molecular weight cholesterol is involved in the formation of cell membranes, dissolution with further absorption of the fat-soluble group of vitamins, digestion (bile acids), synthesis of steroid hormones, including cortisol, cortisone, aldosterone, estrogen, progesterone and testosterone, stimulation of serotonin receptors in the brain and other functions.
- Low molecular weight cholesterol is useful only by transporting fats from the liver through tissues, but it has the negative property of being deposited inside the walls of blood vessels, forming into cholesterol plaques that block blood flow.
Therefore, by high cholesterol we mean an increase above normal in the total level of cholesterol, most of which is formed by low molecular weight (4 times more). If measures are not taken in time, a dangerous indicator leads to atherosclerosis of blood vessels, which is subsequently fraught with ischemia, heart attack, stroke and other cardiovascular pathologies caused by circulatory disorders.
Yes or not?
Based on the data on the saturation of various types of cheese with cholesterol, it becomes obvious that cheese is by no means prohibited for people with high levels of this substance in the blood.
For example, consuming 100–150 grams of cheese 2–3 times a week is enough to supply the body with the required amount of nutrients and biologically active substances that this product is so rich in. And at the same time, eating cheese in such quantities cannot lead to a noticeable increase in blood cholesterol. Is it possible to eat with hypercholesterolemia? You can, but you will have to limit yourself to the specified amounts so as not to increase your already prohibitive cholesterol level.
In addition, it should be noted that specialists in the field of nutrition and healthy eating are increasingly placing emphasis on soft varieties of cheese in their recommendations.
Separately, we should dwell on the features of Adyghe cheese. Its difference lies in the fact that in its production, cow and sheep milk are used in a certain combination. In this case, a special biologically active complex is formed that is capable of removing cholesterol from the body and thereby reducing its concentration. This property is especially important for people with high cholesterol levels.
The main condition, subject to which the eaten product will not cause harm to the body, is a balanced diet.
Treatment and prevention of vascular diseases
Cheese with all its varieties is the most popular product. For many peoples it is part of the traditional diet. There are also many culinary recipes where cheese is an integral ingredient. It gives dishes a unique delicate taste and increases their nutritional value. However, is it as useful as is commonly believed? Doesn't it cause harm to the body? Such doubts are caused by some substances that cheese contains, and cholesterol is one of them.
There is an opinion that hypercholesterolemia and eating cheese are incompatible things. Is it really? Should we be so categorical and completely exclude a healthy product from the diet?
Contraindications
It is recommended to limit cheese for people with urolithiasis, pyelonephritis, gastritis, high stomach acidity, and colitis.
Excessive consumption of cheese is dangerous:
- Significant increase in cholesterol levels. Those suffering from hypercholesterolemia are advised to choose a product with a fat content of no more than 20%.
- Increased blood pressure. Due to its high sodium content, cheese has a hypertensive effect, which is extremely undesirable for people prone to regular or occasional increases in blood pressure.
- Sleep disorders, headaches. According to research, the substance tyramine - a component of animal proteins - can cause headaches and insomnia.
Blue cheese is not recommended for pregnant women and people suffering from functional disorders of the gastrointestinal tract. Molds can disrupt the functioning of the digestive system and also provoke a bacterial disease - listeriosis.
Additional advice for patients
You need to eat 4-5 times a day, but in small portions and you need to drink 1.5-2 liters of water per day
To maintain normal cholesterol levels, it is not enough to limit yourself to just eating cheese. It is important to exclude from your diet all foods containing large amounts of unhealthy fats.
A gentle diet is developed by the attending doctor. It should include not only avoiding junk food, but also preventing weight gain. If your body weight is normal, your cholesterol levels will fluctuate less.
Therefore, it is important to adhere to the following recommendations when following a diet:
- Eat small meals, that is, 4-5 times a day, but in small portions.
- Do not violate the diet prescribed by your doctor.
- Do not drink alcohol.
- Eliminate from the diet everything fatty, fried, as well as foods containing many carcinogens and other harmful substances.
- Maintain drinking regime. You need to drink 1.5-2 liters of water per day.
Diet alone will not help manage cholesterol. Experts also advise engaging in moderate physical activity to prevent weight gain. You can’t strain yourself too much; it’s enough to take walks and do exercises every day.
These recommendations will help lower cholesterol, but only temporarily. In any case, the patient must take special medications as prescribed by the attending physician.
You can eat cheese if you have high cholesterol. You just need to give preference to varieties with a low degree of fat content. However, it is not recommended to eat the product daily. It is acceptable to use once every three days.
Source: holesterin.guru
How to choose
Not all cheeses on store shelves are healthy. Some include the “baggage” of vegetable fats, preservatives, dyes, and pathogenic microorganisms. When choosing a quality product, three points should be considered:
- Compound. Natural milk, salt and milk-clotting component (bacterial or animal) are the only correct components of natural cheese. The presence of vegetable fats automatically defines it as a “cheese product”. Quality cheese does not contain antibiotics, preservatives, dyes – E160 a, E160b, E102, E110, E251.
- Appearance. Stale cheese can be identified by eye. Dried edges, black inclusions, mold, “plastic” crust, uneven color, heterogeneous structure indicate its staleness.
- Package. It is recommended to buy cheeses that were originally packaged by the manufacturer. The product, cut into pieces and wrapped in plastic, is not airtight, so it remains fresh for a short time. In addition, there is no information about the composition. The maximum that a buyer can find out is the name, weight, and price of the block. Lying on the counter for a long time provokes the proliferation of pathogenic microorganisms under the plastic film.
The cheese product is positioned as a budget replacement for natural cheese. Instead of milk fat, the recipe involves the use of vegetable oil, most often palm oil. Naturally, its nutritional value cannot be compared with the original. But at the same time, a high-quality cheese product contains significantly less cholesterol, so it is recommended for consumption by patients with cardiovascular diseases.