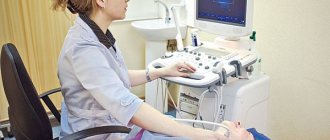
Dopplerography is a modern diagnostic method that makes it possible to visualize large vessels in real time. The method is based on the “Doppler effect” - the ability of an ultrasound beam to pass through motionless tissue. In most cases, Doppler is used to diagnose cardiovascular pathologies. Using this study, you can evaluate the speed and turbulence of blood flow, and also makes it possible to determine the condition of the walls of blood vessels. Based on the results of Doppler sonography, the doctor will be able to identify abnormalities, make a diagnosis and decide on treatment tactics.
What is a cardiac echo?
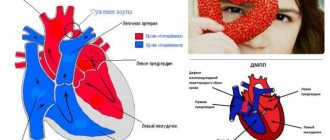
Echocardiography is the leading method for diagnosing pathologies of the cardiovascular system.
High information content, safety for humans and relatively low price of cardiac ultrasound (compared to other types of diagnostics) are the three main parameters due to which the method has become widespread. Cardiac echocardiography is a non-invasive ultrasound diagnostic method. During the examination, the doctor, in real time, evaluates the activity, size and structure of all structures of the heart:
- heart muscles,
- chambers (atria and ventricles),
- valve apparatus,
- walls,
- main vessels.
Using an ultrasound examination of the heart, a doctor can confirm or exclude many pathologies of the heart and large vessels in both children and adults:
- acquired congenital heart defects,
- post-infarction cardiosclerosis,
- atrial fibrillation,
- heart tumors,
- intracavitary thrombi,
- hypertension,
- ischemic disease,
- valve damage, etc.
Ultrasound of the heart with Dopplerography
We can try to answer this question.
In Ukraine, there is a regulatory framework in this regard only for schoolchildren and applicants in the form of a medical certificate of form 086-1/o “Certificate of a student of a general education institution on the results of a mandatory medical preventive examination.” Certificate 086-1/o indicates information about the dates of the last medical examinations, a medical report, determines the state of health and the functional group of physical education. Depending on the age of the child, the medical board includes different specialists. In addition, all schoolchildren undergo the Ruffier test to determine the functionality of the cardiovascular system.
Ruffier's test (or Ruffier-Dixon test) is an assessment of the performance of a child's heart under minimal physical exertion. Initially, the pulse of a child in a calm state is calculated for 15 seconds. Then the child does 30 squats - and the pulse is measured again after physical activity and rest after exercise. Then, using a special formula, the so-called index is calculated. This test is needed for competent selection of load in physical education lessons in educational institutions.
For an adult, there are no mandatory checks before additional physical activity. Unfortunately, because of this, many people only worsen their health while playing sports.
What the European Radiological Center recommends that everyone do before starting to play sports:
— EchoCG (also known as echocardiography/ultrasound of the heart with Dopplerography) — ultrasound examination of the heart at rest; a standardized ultrasound examination of the heart to study the morphology and function of the heart, which allows you to evaluate the structure, size and condition of the heart muscle, valves and large vessels.
At this stage, patients with manifestations of heart failure, valvular and septal heart defects, and cardiopathy are identified. Such people need dynamic monitoring by a cardiologist, and generally physical education classes in the main group are not suitable for them.
An echocardiography study with physical or pharmacological stress is called “stress echocardiography” - a method for determining areas of the myocardium with latent ischemia (malnutrition - used when studying patients with coronary heart disease. It is carried out according to a special protocol. The appropriate software for stress echocardiography must be installed on the ultrasound machine Ruffier's test is not a type of stress echocardiography.
— ECG is a standard method for studying the electrical activity of the heart. This method allows you to identify patients with heart rhythm disturbances - impulse conduction blockades, accelerated impulse conduction and accelerated rhythm disturbances.
Exercise ECG is bicycle ergometry. It is performed to detect ischemic changes in the myocardium hidden at rest, that is, for ischemic heart disease (coronary heart disease). Also used in high-performance sports to determine whether a load can be given that leads to a submaximal or maximum heart rate. Against the background of maximum loads, rhythm stability and the absence of ischemia can be assessed.
— HRV (heart rate variability) is a modified type of ECG that performs a spectral analysis of the heart rhythm. HRV is studied at rest: a 5-minute recording (the minimum time for assessing indicators), then active orthostasis (the subject actively stands up). The test is repeated for another 5 minutes. Thus, the effect of physical activity on the heart is assessed primarily at the level of autonomic (nervous) regulation. An assessment is made of the correctness of the response of regulatory systems and the degree of its severity.
For a primary assessment of the cardiovascular system, this complex is quite sufficient: it assesses the structure, all functions of the heart, as well as regulation of elementary load (assesses its adequacy and severity).
This analysis reflects the influence of regulatory factors on the heart rhythm - nervous (autonomic nervous system) and endocrine. Considering that the autonomic nervous system is the main system responsible for adapting the heart rate to physical activity, assessing its condition is the most adequate assessment of adaptation to physical activity.
What other additions are possible?
Complex with assessment of myocardial deformation (strain)
This complex is especially indicated for those who, according to ultrasound examination of the heart, have been diagnosed with thickening of the wall of the left ventricle. Since if the subject has adaptive (adaptive, physiological) hypertrophy, then the deformation properties of the myocardium are not impaired. If the hypertrophy is pathological, then the functions are impaired. That is, there are pathological changes in myocardial deformation. The study of myocardial deformation (strain) in subjects without hypertrophy is also useful for the early detection of impaired myocardial contractility.
Echocardiography with Doppler analysis
In our center, in addition to standard echoCG (one-dimensional and two-dimensional), with which the doctor can identify heart pathologies, echocardiography with Doppler analysis is performed. Our equipment allows us to perform an advanced assessment of the functioning of the heart and great vessels using the following techniques:
- pulsed wave dopplerography
. Serves to assess the pumping function of the heart. Allows you to record the clicks of opening and closing valves. Registers the speed of blood flow in the valves and great vessels;
- continuous wave Dopplerography.
Allows you to measure high blood flow velocities. Also serves to calculate pressure in large vessels and cavities of the heart in different phases of the cardiac cycle;
- color dopplerography
. Allows you to evaluate not only the speed, but also the direction of blood movement through the main vessels. Used to assess pathological blood flow through the heart valves.
Possibilities of modern echocardiography
Ultrasound scanner WS80
An ideal tool for prenatal research.
Unique image quality and a full range of diagnostic programs for an expert assessment of a woman’s health.
Echocardiography has been one of the main methods of cardiac imaging over the past 15-20 years. Like any diagnostic method, echocardiography has its advantages and disadvantages. The widespread introduction of the method into practice is due to the high level of modern equipment, the absence of harmful effects on the patient and the doctor, and the relative cheapness of the method compared to others. The presence of a large number of research options allows you to obtain accurate anatomical and hemodynamic information about the patient and avoid invasive interventions. The disadvantage of echocardiography is its pronounced dependence on the qualifications of the researcher. A specialist involved in ultrasound diagnostics of the heart must be a cardiologist, have a perfect knowledge of the topographic anatomy of the chest, hemodynamics of the heart, and have spatial thinking. In the absence of one of these qualities, the researcher’s percentage of diagnostic errors increases sharply.
In this review we will try to highlight all the options for modern echocardiographic research.
Echocardiography Options
1. Two-dimensional echocardiography
— image of the heart along the long or short axis in real time. Two-dimensional echocardiography (B-mode) allows real-time assessment of the size of the heart cavities, the thickness of the walls of the ventricles, the condition of the valve apparatus, subvalvular structures, global and local contractility of the ventricles, the presence of cavities thrombosis, etc.
2. M-mode
- a graphical representation of the movement of the heart walls and valve leaflets over time. M-mode allowed for the first time real-time assessment of heart size and ventricular systolic function. Currently used as an auxiliary mode when conducting echocardiographic studies, mainly for measurements. In the case when, in the parasternal position, the M-mode cursor is positioned strictly perpendicular to the image of the heart, measurements can be made with great accuracy. If the heart image and cursor are positioned at an angle, all cardiac chamber sizes will be significantly overestimated and may be misinterpreted. This error occurs among specialists with little work experience. Therefore, measurements should be taken in B-mode at the end of diastole if M-mode cannot be used. Currently, a number of companies have proposed using the anatomical M-mode, which allows you to change the cursor angle.
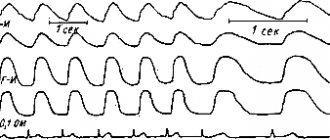
On the M-scan graph, distance is plotted vertically and time horizontally. Depending on the position of the cursor on the screen, you can get a graph of vibrations of a series of points located along the cursor, extended in time, i.e. monitor their fluctuations in systole and diastole.
3. Doppler echocardiography
- pulsed, continuous wave, color, color M-mode, energy, tissue color, tissue pulse, tissue C-mode, etc. - a method that allows non-invasive assessment of central hemodynamic parameters. The active use of the technique in medicine can be dated back to the early 80s.
Conducting a Doppler study requires high technical skill in conducting two-dimensional studies, knowledge of the topographic anatomy and hemodynamics of the heart.
The following Doppler options are used in echocardiography:
- Pulse Doppler (PW - pulsed wave).
- Pulsed high-frequency doppler (HFPW - high frequency pulsed wave).
- Continuous wave Doppler (CW - continuous wave).
- Color Doppler.
- Color M-mode.
- Power Doppler.
- Tissue Velosity Imaging.
- Pulsed Wave TissueVelosity Imaging.
Pulsed Wave (or PW) Doppler.
The graphical layout of pulsed wave Doppler reflects the nature of blood flow at a specific point, at the site where the control volume is installed. The control volume setting point is called the baseline. The flow velocity is plotted vertically on the graph, and time is plotted horizontally. All flows that move towards the sensor at a given point are located on the graph above the baseline; all flows that move from the sensor are below the zero line. In addition to the shape and nature of the blood flow, the graph can record clicks of the opening and closing of the valve leaflets, additional signals from the chords of the leaflets and the walls of the heart. The pulse Doppler has a speed limit (no more than 2.5 m/s), so it cannot be used to register high-velocity flows.
Pulsed high-frequency doppler (HFPW - high frequency pulsed wave).
Several control volumes are located one after another at different depths. This allows you to record blood flow, the speed of which exceeds 2.5 m/s.
Continuous Wave Doppler (CW - Continuous Wave Doppler).
Allows you to record high-speed streams. The disadvantage of the method is that all flows along the beam are recorded on the graph. The CW Doppler technique allows you to calculate the pressure in the cavities of the heart and great vessels in one or another phase of the cardiac cycle, calculate the degree of significance of stenosis, etc. The basic equation of CW is Bernoulli's equation, which allows one to calculate the pressure difference or pressure gradient. The equation can be used to measure the pressure difference between chambers under normal conditions and in the presence of abnormal, high-velocity blood flow.
Color Doppler.
Color Doppler is an analogue of pulsed Doppler, where the direction and speed of blood flow is mapped in different colors. Thus, blood flow to the sensor is usually mapped in red, and from the sensor - in blue. Turbulent blood flow is mapped in blue-green-yellow color.
Color M-mode.
Comparison of the M-modal mode and color Doppler when moving the cursor through one or another plane allows one to understand the phases of the cardiac cycle and pathological blood flow.
Power Doppler.
It is used to record low-speed blood flow, so it is not yet actively used in cardiology. When using power Doppler, the direction of blood flow is lost. Currently, power Doppler is used in combination with contrast agents (Levovist, etc.) to study myocardial perfusion.
Tissue Doppler (Tissue Velocity Imaging).
The principle of this method is based on mapping the direction of tissue movement with a specific color. Thus, red color indicates movement towards the sensor, blue color indicates movement away from the sensor. By studying the directions of movement of the walls of the left and right ventricles in systole and diastole using TVI, it is possible to detect hidden zones of impaired local contractility. Combining a two-dimensional study in TVI mode with M-modal increases diagnostic accuracy.
Pulsed Wave Tissue Velocity Imaging.
Allows you to graphically evaluate the nature of the movement of the ventricular wall at a specific point. There are systolic components, early and late diastolic components. This version of Doppler allows for mapping of the myocardium and increases the accuracy of diagnosis in patients with coronary heart disease.
Thus, Doppler techniques make it possible to obtain a large amount of information without the use of invasive research methods.
4. Transesophageal echocardiography
(mono-, bi-, and multiplane). Examination of the heart through the esophagus using special sensors. The information content of the method is very high. A contraindication is the presence of esophageal stricture.
5. Stress echocardiography
(using physical activity, transesophageal electrical stimulation or medication). Widely used in patients with coronary heart disease.
6. 3D and 4D heart modeling
— computer image analysis and construction of a three-dimensional image of the heart chambers, valve leaflets, blood flow, etc.
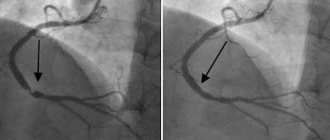
7. Intravascular ultrasound
— study of the coronary arteries using a special small-diameter intravascular sensor. Invasive ultrasound method. Used in parallel with coronary angiography.
8. Contrast echocardiography
- used for contrasting the right chambers of the heart when a defect is suspected, or the left chambers of the heart to study myocardial perfusion. The information content of the method of contrasting the left chambers of the heart is comparable to myocardial scintigraphy. A positive factor is the absence of radiation exposure to the patient. Negative factors are the invasive nature of the method and the high price of the drug (Levovist, Albunex, etc.).
Modern echocardiographic devices
Currently, the market offers ultrasonic devices from the simplest to the most complex with the possibility of three- and four-dimensional modeling.
A screening examination of the heart can be performed on any ultrasound device, provided there is an appropriate cardiac sensor and B- and M-modes. In this case, you can use inexpensive ultrasound scanners. The level of diagnosis and the percentage of error in this case largely depend on the qualifications of the specialist.
Modern echocardiographic examination should include, in addition to B- and M-modes, color Doppler, pulsed wave Doppler and continuous wave Doppler. In the presence of pathology, only continuous wave Doppler will allow you to measure high-speed pathological flows, carry out all the necessary calculations and measurements, and assess hemodynamics.
The amount of information received depends on the capabilities of the sensor. Intravascular sensors are used in parallel with angiographic examination and are used by cardiac surgeons. Transesophageal sensors can be monoplane, biplane and multiplane.
Modern technologies (tissue Doppler, contrasts) can greatly increase the information content of the study, especially in patients with myocardial pathology.
Programs for work with echo contrasts are being widely developed abroad, however, in our country this area of ultrasound is not sufficiently represented.
Conclusion
Modern echocardiography has a wide range of diagnostic techniques. Echocardiographic ultrasound devices range from low-cost to high-end. Equipment exhibitions, congresses and conferences, as well as magazines and books on ultrasound diagnostics allow us to correctly navigate the ultrasound market.
Bibliography
- Marvel Craig. Diagnostic Medical Sonography. Echocardiography. / JBLippincott Company, Philadelphia. 1991. b. 77-151.
- Catherine M. Otto, Alan S. Pearlman. Textbook of Clinical Echocardiography. / WB Saunders Comhany. Philadelphia. 1995. b. 30-45, 50-62.
- N. Schiller, M.A. Osipov. Clinical echocardiography. Moscow. 1993. pp. 19-44.
- Liv Hatle, Biorn Angelsen. Doppler Ultrasound in Cardiology. Second edition. / Lea and Febiger. .Philadelphia.1982. p. 78-93.
- Harvey Feigenbaum. Echocardiography. Fifth edition. / Lea and Febiger.Philadelphia.1994. R. 71-105, 181-215.
- Eugene Braunwald. Heart Disease. /WBSaunders Company. Philadelphia. 1988. b. 83-139.
- Mitkov V.V. Sandrikov V.A. Clinical guidelines for ultrasound diagnostics. Volume 5. / Ed. Vidar. 1998. Pp. 55-68.
- L.V. Osipov. Ultrasonic diagnostic devices. Moscow. 1999. pp. 164-173.
Ultrasound scanner WS80
An ideal tool for prenatal research.
Unique image quality and a full range of diagnostic programs for an expert assessment of a woman’s health.
Indications for echocardiography (echocardiography)
Diseases of the cardiovascular system in both children and adults can often develop without symptoms. In order to notice in time and prevent the development of a minor pathology into a serious disease, it is recommended to undergo echocardiography once a year. If the following symptoms occur, a study is required:
- acute pain in the heart and chest;
- feeling of lack of air and shortness of breath;
- dizziness;
- loss of consciousness;
- swelling of the legs;
- frequent bluishness of the skin: ears, hands and fingers, around the lips;
- fast fatiguability;
- heart rhythm disturbances and detection of noise during listening;
- frequent headaches;
- hypertonic disease;
- atherosclerosis.
An ultrasound of the heart of a child under one year of age is most often performed on the direction of a cardiologist or therapist. It is given when noise is detected during listening or if one of the immediate family suffers from severe cardiac diseases. In addition, it is recommended to perform an ultrasound of the child’s heart in the following cases:
- the baby weakly sucks the breast;
- there is blueness around the mouth and nose when crying and sucking;
- with stunted growth and weight gain;
- with increased sweating.
For older children, echocardiography (echoCG) is prescribed if the child:
- often suffers from pneumonia,
- loses consciousness
- complains of pain in the heart area,
- gets tired quickly.
The price of echocardiography for adults and children is the same.
Diseases that can be detected using Doppler ultrasound
Doppler sonography plays an important role in identifying diseases of the cardiovascular system. These diseases are today considered one of the most dangerous and widespread in the world; they can lead not only to human disability, but also to death. Cardiac Dopplerography is prescribed to narrow the range of diagnostic alternatives; it allows one to identify abnormalities and make a decision on treatment, significantly increasing the chance of a positive outcome.
Congenital heart defect in a child
Heart defects can manifest themselves in both acute and latent forms. The cause of their occurrence is heredity, influenced by the age of the spouses, as well as external influences in the form of viral or infectious diseases. In this case, ultrasound examination of the heart vessels is extremely necessary, since the pathology can lead to tragic consequences.
Myocardial infarction (or pre-infarction condition)
Narrowing of the lumen of a blood vessel is a pre-infarction condition. Complete closure of the vessel and lack of oxygen supply to the heart muscle is a myocardial infarction. The cause may be a plaque or blood clot in the arteries. Such conditions are usually preceded by angina pectoris in an advanced form. Ultrasound of the heart and echocardiography
allow you to examine the organ and identify any abnormalities, make a conclusion about the condition of the blood vessels and determine whether conservative or surgical treatment is needed.
Pressure disorders - hypotension and hypertension
First of all, it is necessary to examine the heart in case of pressure disorders. It is not enough to select drugs that normalize blood pressure and intensity of blood flow; it is important to identify the cause of this phenomenon, since it may lie in heart pathology.
Acquired vices
Ultrasound scanning of the heart is often prescribed for suspected valve defects, otherwise known as “acquired” defects. They lie in the fact that due to infections, inflammatory processes, autoimmune reactions, dilatation and overload of the chambers of the heart, certain changes occur. They can be morphological or functional or combined.
How is cardiac echocardiography performed?
In our clinic or directly at the patient’s home, tests are carried out only by certified diagnosticians specializing in cardiovascular diseases. Thanks to their extensive experience and special training, they are well aware of how the structures of the heart are displayed on an echocardiogram, normally and in the presence of pathologies.
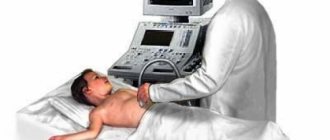
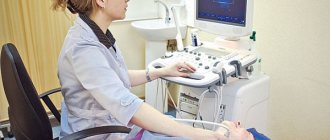
The procedure for echocardiography and ultrasound of the heart vessels (Dopplerography), performed at home or in the clinic, is simple and does not require special training. During the examination, the patient is placed on the couch on his back or left side. The doctor, using a special sensor, scans the heart in various positions to obtain images of all its parts and surrounding vessels.
After the procedure, a conclusion is issued. Depending on what the ultrasound of the heart shows, the doctor may prescribe additional studies and tests.
General characteristics of the examination
A procedure such as Doppler ultrasound can be performed both to identify violations when indicated, and for preventive purposes. The whole point is the absence of radiation exposure to the patient’s body, as well as the fact that it will be possible to visualize areas that are inaccessible to other research methods.
Ultrasound scanning of the heart vessels is done using a special sensor that generates ultrasound signals and receives the echo reflected by the tissues. Special software is responsible for converting such signals into images.
How is the stress echo CG procedure performed?
At the CBCP clinic, stress echocardiography is performed in two ways:
- using horizontal and vertical bicycle ergometers;
- using special stimulant drugs.
The study is carried out under the supervision of certified and experienced specialists:
- a cardiologist with special training in performing stress tests;
- diagnostician working in the field of stress echocardiography and cardiac ultrasound.
First, the patient, who is at rest, undergoes echocardiography and records the indicators. After which the body is exposed to strictly calculated physical activity or medicinal stimulants. Doctors monitor changes in the well-being and functional state of the patient’s heart, processing the results using a computer.
Stress echo CG makes it possible to obtain images of the heart at various stages of the examination. The indicators recorded under load are analyzed and compared with the indicators at rest.
Benefits of stress echocardiography
Stress echo CG is a safe study that can be repeated as many times as necessary. Highly sensitive equipment is highly informative and detects even asymptomatic abnormalities in the heart.
This method also makes it possible to:
- diagnose silent myocardial ischemia and angina pectoris;
- assess heart rate;
- determine the viability of the myocardium after a heart attack;
- identify blood flow disorders;
- record changes in blood pressure at rest and after exercise.
Indications
In what cases can a doctor prescribe a Doppler ultrasound of the heart?
- Pain in the heart area is the most common symptom when Doppler ultrasound is recommended. If the patient is bothered by discomfort and pain in the chest, Dopplerography of the heart vessels is a mandatory part of the examination.
- Heart murmurs discovered at an appointment with a therapist or cardiologist. This symptom may indicate a heart defect, so additional diagnostics are necessary.
- Patient's complaints about heart failure. These may be arrhythmias or extrasystoles, tachycardia or bradycardia.
- Complaints of frequent dizziness and shortness of breath. These symptoms may be associated with heart failure, therefore, to clarify the diagnosis, Doppler sonography is required in combination with other types of examination.
- Pathological changes on the ECG.
- Suspicion of a blood clot. Thanks to diagnostics, it is possible to identify its size and exact location.
- Suspicion of compaction in the pericardium.
Doppler ultrasound of the heart and blood vessels can also be prescribed for preventive purposes, for example, if there is a predisposition to heart disease. In addition, the study is necessary for patients who are planning to undergo heart surgery.
If your doctor advises you to undergo a Doppler ultrasound, you should not refuse this procedure. Pathologies in the early stages of development are much easier and faster to treat.
Interpretation of cardiac ultrasound results
The results of the study are interpreted using an echocardiograph. Diagnostics provides information on more than 100 indicators of heart condition.
After the procedure, you will receive a transcript of the study results. Do not attempt to independently analyze the data obtained, much less draw conclusions about the use of any medications. This is especially true for ultrasound data of a child. Only a cardiologist can accurately and correctly interpret the obtained indicators.
Doctors at the CBCP clinic will explain to you in detail the meaning of the parameters indicated in the report and make an objective diagnosis. You will receive further recommendations regarding treatment and a prognosis of your health situation.
How is research done?
The procedure does not involve surgical intervention, that is, it is non-invasive. There is also no radiation exposure, so the study can be carried out both for certain indications and for preventive purposes.
After the patient comes to see the doctor, he is asked to remove clothes that interfere with the examination and lie down on a special couch. After this, a special gel is applied to the sternum, which will help the sensor glide over the skin. Using a sensor, the doctor examines the organ and takes pictures, and also notes the condition and size of all structures. The data obtained will be compared with the norm of Doppler ultrasound of the heart, after which the doctor will draw up a conclusion and give it to the patient.
Benefits of echocardiography (echoCG) at the CBCP clinic
Cardiac ultrasound, both directly at the CBCP clinic and at the patient’s home, is performed using modern equipment by highly qualified specialists. Our doctors have extensive experience in conducting functional studies, as well as certificates confirming successful training in ultrasound diagnostics in the field of cardiology. The clinic uses additional research methods to make the most accurate diagnosis.
You can get detailed information on heart ultrasound for adults and children (including at home), as well as echocardiography with Doppler analysis in Moscow, the price of the procedure and the possibility of making an appointment by calling, or by leaving a request on the website.
On-site diagnostics at home
The basic package includes the following services:
| Name of service | Price, rub.) |
| Basic complex | |
| Preliminary consultation with a cardiologist | |
| ECG 12 leads with interpretation | |
| EchoCG (ultrasound of the heart) | |
| Final consultation with a cardiologist with selection of therapy and recommendations | |
| Within the Moscow Ring Road cost | 10 000 |
| Outside the Moscow Ring Road (cost of one kilometer) | 150 |
Re-departure of the team*:
- consultation with a cardiologist - 5,000 rubles
- consultation + ECG with interpretation - 6000 rubles
- consultation + echocardiography (ultrasound of the heart) - 8000 rubles
* outside the Moscow Ring Road the cost of one kilometer is 150 rubles.