To obtain accurate results on the condition and functioning of the heart in electrocardiography, the use of additional leads is often practiced. As a rule, this additional measure allows for timely diagnosis of the development of myocardial infarction and other pathologies. Symptoms of this problem are not always noticed during routine diagnostics using standard parameters, which is explained by the varying strength of the manifestation of changes. The most popular is the Sky ECG, less used are the orthogonal lead and Arrighi.
A person who specializes in this area knows exactly how the axes of the leads along the Sky are connected and the probable possibilities of diagnosing them. This knowledge helps not to repeat standard techniques.
Carrying out an ECG using Neb
To carry out Neb diagnostics, it is first necessary to correctly position the electrodes. There are three of them in total, painted in different colors. To improve the contact properties between the electrode and the patient’s skin, a special paste with a slightly thick consistency, made from baby soap and plain water, is used. To avoid staining the sheet that is placed under the body of the subject, you need to use oilcloth.
The connection occurs as follows:
- The first to attach is the electrode, which is active and yellow in color. Using a special flat electrode plate, it is installed under the left shoulder blade in its lower corner. Installation in the V7 position is allowed - it was noticed that in this position the result is more accurate. In addition, this method greatly facilitates the diagnosis of bedridden patients.
- The next one is a red electrode, which, unlike yellow, is passive. It is attached using a pear-shaped suction cup. The location of this electrode is the second intercostal space on the right side of the chest.
- The last electrode is painted green and is attached to the body, like the red one, using a suction cup. Unfortunately, it is often the green conductor that is not fixed where it is needed. Its correct location is at the apex of the heart. The correct place can be determined by palpation - apical impulses are felt in the right place. Often the location is determined incorrectly and the electrode is installed in the fifth intercostal space, on the left side of the clavicular line.
After connecting all the electrodes, you can determine the triangle with the heart inside. The ECG procedure occurs by switching a toggle switch to connect various axes in series:
- the first axis is formed from the red and yellow electrodes. This lead is parallel to the back of the heart. This standard position is written with the letter “D” and is considered the most accurate indicator for determining the presence of cardiac pathologies, and more precisely, for myocardial infarction associated with the left ventricle;
- the second position is indicated by the letter "A". The axis, which is formed when the toggle switch is switched for the second time, is located on the side of the front wall of the organ. The data that needs to be taken at this stage does not greatly affect the originally obtained values;
- the third switch remains similar to axes V2 and V3, the only difference is the location of the heart organ in the chest. The results of the third switch are written with the letter “I”, but they also do not greatly affect the data obtained during the first switch.
So, we can draw the following conclusion - the most accurate and important data in diagnostics is obtained when the toggle switch is first switched and the axis with the letter “D” is formed.
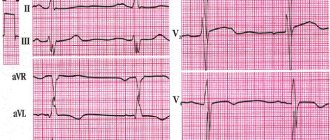
The ECG showed distinctive signs, which consisted of the ST line. It can be raised and have a hump-shaped shape, which directly indicates myocardial infarction, or it can be lowered and imply hypertrophy of the left ventricle of the heart. When analyzing the results, it is also important to pay attention to the shape of the tooth - it can be negative symmetrical and negative asymmetrical.
General rules for applying electrodes
When recording an electrocardiogram, electrodes are installed on several areas of the body. This ensures the conduction of electrical impulses through the heart, and the results are more accurate. The correct location of the terminals is the key to reliable recording of heart function.
General rules for installing electrodes:
- The skin at the site where the electrode is applied is degreased with alcohol;
- Pronounced hair when using reusable electrodes is treated with a soap solution (otherwise the hair is shaved off);
- The electrodes are coated with a special gel that improves electrical conductivity (it can be replaced with an isotonic solution, but this is not recommended, as the contact will worsen);
- The use of gauze pads instead of a special gel is also not an alternative to the gel, since they dry out quickly (such pads are absolutely prohibited for long-term studies, for example, Holter monitoring);
- It is important to follow safety rules when working with electrical devices, in particular grounding (not required when recording ECGs using portable battery-powered electrocardiographs).
All electrodes are divided into reusable and disposable. Each type has advantages and disadvantages and, as a rule, the option for recording is selected by medical personnel.
Features of disposable electrodes
You can purchase disposable electrodes in the Avicena-med online store, where only high-quality elements made in Italy are sold. They are suitable for daily monitoring or stress tests, which involve the patient’s physical activity.
Advantages of disposable electrodes:
- No risk of transmission of infectious diseases;
- Easy to install (doctors consider them more practical);
- High degree of adhesion (does not fall off after prolonged use);
- Good conductivity and high-quality contact;
- Suitable for patients with excessive sweating.
Unlike disposable electrodes, reusable designs are often used in government agencies, as they are more economical and durable.
Other additional methods of performing an ECG
There are several types of additional leads that increase the efficiency of the study: ECG according to the Sky: orthogonal and the Arrini method.
Diagnosis by ECG can be carried out in several ways
Orthogonal leads for ECG
Orthogonal leads are measured exclusively in three planes. Moreover, they are further divided into two types – corrected and uncorrected.
Orthogonal leads are measured along three types of axes. For each measurement, the most accurate and important are the indicators recorded when the toggle switch was first switched. The difference lies in the different locations of the electrodes during formation:
- in the first method, the red electrode is fixed on the right side of the axillary line, focusing on the apex of the heart, and the yellow electrode is attached in accordance with the standard position of V5 on the left side. Thus, the specialist receives X-axis indicators;
- in the second method, a positive yellow electrode is attached to the left leg, and a red one is attached slightly above the middle of the left collarbone. According to this scheme, the Y axis is formed;
- The third axis, labeled Z, is measured with the red electrode directly at the angle of the left shoulder blade, and the yellow electrode in the standard V3 position.
With this arrangement of the axes, three planes are formed, which are perpendicular to each other. If we display these planes schematically, they will intersect in the region of the heart.
It is worth noting that experts do not highlight any major advantages in this method of conducting an ECG over the standard system. But in this way, it is possible to obtain additional information about the patient’s heart. The orthogonal lead method is most often used in sports medicine and in computer-monitor studies, when the goal is to obtain as much information as possible about the organ with the least amount of time spent on diagnosis.
Where and how to apply electrodes?
There are 12 leads in the electrocardiogram: 3 main, 3 enhancing and 6 chest. To take data, 10 electrodes are installed: on all limbs and the chest. For ease of use, they often differ in appearance and color.
Features of installing electrodes on the limbs
Applying electrodes to the limbs implies the well-known color order of the traffic light. The terminal installation is as follows:
- A red electrode is applied to the right hand;
- A yellow electrode is attached to the left hand;
- A green electrode is placed on the left leg;
- The right leg is meant to be grounded and a black electrode is attached to it.
Electrodes are placed on the proximal limbs: wrists and ankles, which are pre-treated and gelled. If a person is missing one or another limb, then the terminal is placed on the stump. Sometimes the electrodes are additionally secured with rubber bands.
The nuances of the location of electrodes on the chest
Chest electrodes may look different. Most often they are rubber suction cups. Sometimes the electrodes look like ordinary rectangular plates, then they are additionally secured with an elastic band.
There are 6 chest leads in total. Depending on the equipment of the ECG room, all electrodes are applied at once or the nurse has only one branch, which she installs one by one and records each lead separately.
The procedure for installing chest electrodes:
- The first is the fourth intercostal space to the right of the sternum;
- The second is the fourth intercostal space to the left of the sternum;
- Third - fifth rib along the left parasternal line;
- Fourth - fifth intercostal space along the left midclavicular line (or exactly in the place where the apical impulse is projected, that is, 1.5 centimeters inward from the midclavicular line normally);
- Fifth - fifth intercostal space along the anterior axillary line;
- Sixth - fifth intercostal space in the midaxillary line.
Each chest lead is responsible for a specific part of the heart, so their correct application is of great importance.
How does the procedure work?
An electrocardiogram of the heart is performed in an outpatient or hospital setting. However, this technique is also used as an emergency method for diagnosing pathologies, which is why ambulance crews have an electrocardiograph. The procedure is sometimes carried out directly in the car or at the patient’s home.
Important! When conducting an ECG, regardless of where it is performed, the distance from the patient to the nearest power supply must be at least 2 meters. This will avoid unnecessary electrical interference and record accurate information.
ECG on the Sky is carried out as follows:
- First, the attending physician examines the patient, checks all devices for functionality,
- a special electrically conductive gel is applied to the body at the sites where the electrodes are supposed to be installed,
- treats the skin with an antiseptic,
- correctly applies electrodes,
- performs ECG recording.
Read also: What nuances of ECG voltage do you need to know? Causes of appearance during diagnosis
When performing electrocardiography, the patient should be in a calm, relaxed state, preferably lying down.
Application
- Determination of frequency (see also pulse) and regularity of heart contractions (for example, extrasystoles (extraordinary contractions), or loss of individual contractions - arrhythmias).
- Indicates acute or chronic myocardial damage (myocardial infarction, myocardial ischemia).
- Can be used to identify metabolic disorders of potassium, calcium, magnesium and other electrolytes.
- Detection of intracardiac conduction disorders (various blockades).
- Screening method for coronary heart disease, including stress tests.
- Gives an idea of the physical condition of the heart (left ventricular hypertrophy).
- May provide information about non-cardiac diseases such as pulmonary embolism.
- Allows you to remotely diagnose acute cardiac pathology (myocardial ischemia) using a cardiophone.
- Can be used in studies of cognitive processes, alone or in combination with other methods
Decoding the results
The interpretation is performed by a functional diagnostics doctor. The subject of his consideration is a tape with a cardiogram on which the teeth are depicted. The specialist evaluates the intervals, height and makes a diagnosis about the condition of the heart muscle.
As indicated, lead D is the most informative of the three considered. The presence of ischemic changes is indicated by three main indicators on the cardiogram:
- increased voltage in the QRS complex;
- non-compliance with the norm of the ratio of the amplitudes of the Q and R waves;
- expansion of the Q wave (also fixed in the second switching).
It is impossible to independently determine the condition of the heart using a cardiogram. Wait for a consultation with a specialist from the NEARMEDIC clinic or with your attending physician if you are undergoing examination and treatment in another clinic.
The information value of the method becomes higher when used in addition to recording electrocardiography in 12 leads and other techniques (according to Arrighi, in orthogonal leads). In addition to the ECG, data on the condition of the heart are provided by electrocardiography, color circulation and ultrasound with Dopplerography. In difficult cases, several techniques are used.