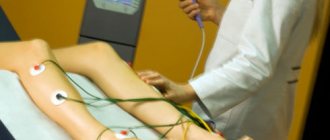
A stroke is an acute disorder of cerebral circulation, which is always associated with damage to certain areas of the brain. The extent and nature of the disorders depend on the location of the lesion, but in most patients, motor and speech functions are primarily affected. Extensive strokes leave a person bedridden, depriving him of the ability to stand up, walk, eat and care for himself independently. The return of at least part of the lost abilities is possible subject to proper rehabilitation, which must begin immediately after the end of the acute period of the disease. The key to success is an integrated approach to solving existing problems and regular work on oneself.
The main method of rehabilitation after a stroke is kinesitherapy, or “healing through movement.” There are a lot of options for exercises for recovery after acute cerebral circulation disorders, and one of the methods of alternative medicine is kinesitherapy by Dr. Bubnovsky.
Doctor of Medical Sciences Sergei Bubnovsky has developed a unique system of movement therapy
Rehabilitation after stroke
Rehabilitation after stroke is a comprehensive program for restoring neurological motor deficits after an acute disruption of the blood supply to the brain.
It’s not for nothing that a stroke is called a brain catastrophe - as a result of a lack of blood flow, brain cells gradually die, leading to the loss of motor, speech and cognitive functions. Fortunately, the human brain has enormous compensatory capabilities. The task of rehabilitation is to take advantage of them and restore the functioning of damaged, but still living neurons, so that they take on the functions of dead nerve cells.
Based on the mechanism of occurrence, there are two types of stroke: ischemic and hemorrhagic.
- An ischemic stroke is called a cerebral infarction. With this pathology, blood supply is disrupted as a result of narrowing or blockage of blood vessels in the brain.
- Hemorrhagic stroke occurs when a blood vessel ruptures. Therefore, such a stroke is also called a cerebral hemorrhage.
Although it is believed that the course of ischemic stroke is milder than hemorrhagic, any disruption of the blood supply leads to complications and requires rehabilitation.
Rehabilitation of a patient after a stroke should begin as early as possible. Ideally, immediately after recovery from an acute condition and discharge from the hospital. This is due to the fact that, over time after a stroke, the rate of functional recovery decreases and the chances of returning to normal life decrease.
The sooner rehabilitation begins, the faster neurological defects go away and functions are restored to a greater extent.
Regardless of how long ago the stroke was suffered, rehabilitation is indicated for anyone who wants to avoid the risk of another stroke.
Recurrent vascular lesions are always more severe and carry the risk of even greater disability. Patients who have suffered a stroke should pay special attention to blood pressure, blood sugar and cholesterol levels, control bad habits and monitor their sleep and active rest patterns.
Neglect of prevention and a healthy lifestyle leads to repeated ischemic attacks with a high probability of death.
Causes of heart attack
In 95-97% of cases, the cause of blockage of the coronary arteries is thromboembolism due to atherosclerosis of the arteries. A blockage of a vessel occurs with a blood clot, which has broken away from the place of its formation (heart, vessel) and entered the bloodstream. Very rarely, myocardial infarction develops as a result of complications of other diseases. In order to prevent the disease, you need to know the risk factors for heart attack:
- Hyperlipoproteinemia (increased lipid levels in human blood)
- Physical inactivity (low physical activity)
- Obesity
- Diabetes
- Smoking
- Hypertension (high blood pressure)
- Hereditary predisposition
- Age
- Male
Rehabilitation in the Bubnovsky center
Bubnovsky’s comprehensive kinesitherapy program for recovery after a stroke gradually and very gently returns a person to normal life. This is a long process that requires the patience and desire of the patient himself. The best results are achieved by patients who are emotionally involved in the rehabilitation process and are ready to share responsibility for its results with the doctor.
Rehabilitation work with patients begins with an initial consultation. Through a manual examination, the kinesitherapist assesses the criteria for the patient’s motor deficit and his rehabilitation potential. Based on functional testing and the collected medical history, an individual motor program is drawn up, goals and objectives of rehabilitation are set.
Rehabilitation in the centers includes mandatory training on the Bubnovsky multifunctional simulator (MTB) and basic rehabilitation simulators. During training, special couches, belts, cuffs, and straps are used. All exercises are simple and safe, but have powerful rehabilitation potential.
Stroke patients are always at risk of having another attack. Therefore, all loads at the Bubnovsky Center are individual, strictly dosed and controlled by a kinesiotherapist.
Classes in the gym are held under the mandatory supervision of an instructor. He coordinates the technique of performing exercises, teaches diaphragmatic breathing and independent exercises.
Patients undergo mandatory cardiac monitoring and control ultrasounds of peripheral vessels.
Timely stroke rehabilitation is not only an objective opportunity to restore lost body functions and avoid disability, but also a real chance to return to a full-fledged family and social life.
Sign up for a consultation
Prices in your city
Russia
- Russia
- Kazakhstan
- Azerbaijan
- Belarus
- Kyrgyzstan
- Latvia
- Uzbekistan
- Ukraine
Moscow
- Adler
- Almetyevsk
- Anapa
- Angarsk
- Arkhangelsk
- Astrakhan
- Balashikha
- Barnaul
- Belgorod
- Biysk
- Blagoveshchensk
- Bratsk
- Bryansk
- Vladivostok
- Vladimir
- Vologda
- Voronezh
- Grozny
- Ivanovo
- Irkutsk
- Yoshkar-Ola
- Kazan
- Kaliningrad
- Kaluga
- Kemerovo
- Korolev
- Kostroma
- Kotlas
- Krasnodar
- Kyzyl
- Leninogorsk
- Magnitogorsk
- Makhachkala
- Moscow
- Naberezhnye Chelny
- Nazran
- Nalchik
- Nizhnekamsk
- Nizhny Novgorod
- Novodvinsk
- Novokuznetsk
- Novosibirsk
- Omsk
- Pavlovo
- Penza
- Permian
- Petrozavodsk
- Pskov
- Pushkino
- Rostov-on-Don
- Ryazan
- Samara
- Saint Petersburg
- Saransk
- Saratov
- Sarov
- Sevastopol
- Smolensk
- Sochi
- Stary Oskol
- Sterlitamak
- Tambov
- Tomsk
- Tula
- Tyumen
- Ulan-Ude
- Ulyanovsk
- Ufa
- Khabarovsk
- Khimki
- Chelyabinsk
- Yaroslavl
Select a branch
- m. Aviamotornaya - Moscow, st. Aviamotornaya, 10, building 2
- m. Academicheskaya - Moscow, st. Dm. Ulyanova, 31
- metro station Altufyevo - Moscow, Altufevskoe highway, 70, building 2
- m. Bagrationovskaya - Moscow, st. Novozavodskaya, 27A
- m. Belorusskaya - Moscow, 1st st. Yamskogo Polya, 24
- m. Boulevard Dm. Donskoy - Moscow, st. Feodosiyskaya, 2
- metro station Butyrskaya - Moscow, 17th proezd Maryina Roshchi, 4, building 1
- m. Kashirskaya - Moscow, Kashirskoe highway, 43, building 4
- Khodynka metro station, CSKA metro station, Polezhaevskaya metro station - Moscow, Berezovaya Roshchi passage, 12
Is exercise therapy necessary for a hernia?
Exercise therapy for a hernia is mandatory. The goal of such therapeutic exercises is to improve the patient’s physical condition, remove pain, and prevent its occurrence. Well-designed lessons:
- stimulate vital functions;
- increase the endurance of muscle structures and the reactivity of the body (the ability to respond to various factors);
- involve mechanisms that are involved in the pathological process in the general reaction, which contributes to their elimination.
Therapeutic exercise does not harm the body, since the exercises are designed to reduce the load on the spine. They not only relieve pain, but also “teach” the body to avoid injury in the future.
Regular exercise therapy helps:
- Relieve pain and speed up the healing process.
- Form correct posture.
- Improve strength, endurance, coordination.
- Evenly distribute the load across the parts of the spinal column.
- Restore mobility.
- Prepare the body for strength and aerobic exercise.
Therapeutic exercises strengthen the muscles that support the spine and prevent the appearance of new hernias. Exercises involve not only the back, but also the abdominal muscles. The body begins to move better, stiffness disappears, and the risk of injury decreases.
FAQ
Will exercise therapy help you recover faster after a hernia removal?
Yes, it will help. The main thing is to strictly follow all the doctor’s advice, do not rush, and do not increase the load ahead of time.
Is it possible to do exercise therapy for Schmorl's hernia?
Yes. Exercise therapy can be done for any type of hernia, when the acute pain subsides. The main thing is to choose the right set of exercises. If you have a Schmorl's hernia, you definitely need to pump up and strengthen the muscles, especially the back and abdomen. It is important to remember: weight bearing is contraindicated.
Is it possible to do exercise therapy for a sequestered hernia?
It is possible, but we must proceed from the fact that exercise therapy cannot be done during the acute phase. When the pain subsides, light exercise is allowed after consulting a doctor. Water gymnastics gives a good effect.
Themes
Intervertebral hernia, Spine, Pain, Treatment without surgery Date of publication: 11/12/2020 Date of update: 03/16/2021
Reader rating
Rating: 5 / 5 (3)
Other therapeutic exercises
In addition to physical therapy, the following are used to treat spinal hernia:
- Bubnovsky method;
- exercises according to Dikul;
- water gymnastics;
- yoga and pilates.
Each of these methods has its own characteristics. Before you start performing them, find out their differences from conventional physical therapy, the benefits and harms of a hernia, when you can do it or not.
According to the Bubnovsky method
Dr. Sergei Bubnovsky wrote about back hernia in the book “Spinal hernia is not a death sentence.” He developed most of the exercises taking into account the simulators that are available in his clinic.
Opinions about the method are mixed. There are many cases that after treatment in his clinics hernia:
- not only did it not decrease, but increased, it was even necessary to resort to surgery;
- the pain disappeared in one place, appeared in another, requiring hospital treatment and even surgical intervention.
The main reasons for failure are rigid, heavy exercises, which are strictly prohibited in case of a spinal hernia (strength loads, twisting).
If you still decide to try gymnastics using this method, avoid training that is prohibited if you have a back hernia. It is better to do the complex for prevention, when the acute phase has passed, there is no pain.
According to Dikul
Exercises suggested by Valentin Dikul, director of a rehabilitation center for patients with back injuries, have a good effect on the spine. You can learn about his method in his book “Treating the back from hernias and protrusions.” He offers different types of training, including standard therapeutic exercises that can be performed for spinal hernia (half-cobra, cat).
The complex that Dikul offers consists of several stages:
- Exercises aimed at eliminating pain. They are performed with a small amplitude, without additional load. Basic movements are a standard exercise therapy complex. Course – 3 times a week for 2-4 months.
- Exercises aimed at strengthening muscles are a rehabilitation period when the pain has gone away. At this stage, you can include strength training. Course – 4 times a week for 2-3 years.
- Complete workouts designed taking into account the presence of a hernia, without negative effects on the affected area.
Exercises must be performed in strict sequence, do not change places, and do not increase the number of repetitions. The load (light dumbbells) can be taken no earlier than the complex is mastered and the pain disappears. Between exercises you need to rest for 2-3 minutes.
Exercises in water
Swimming gives good results in the treatment of spinal hernias. Water relieves stress from the back and calms the nervous system. It helps to better stretch the space between the discs and reduce the pressure of the hernia on the nerve fibers. The main thing is to choose the right instructor and exercises.
The following activities have a good effect:
- The face is lowered into the water, the arms are extended, holding a swimming board (you can use a crossbar installed around the perimeter of the pool), the back is straight. The legs swim in the crawl style.
- Lie on your side, your right hand rests on the board, your left along your torso. The legs work in the crawl style.
- Swim on your back. Hands hold the board on your stomach, legs swim in crawl style.
If the pool is shallow (water up to your chest), you can take steps in place with your knees raised high. At this time, the arms move as if running. Gentle turns of the body to the right and left have a good effect.
The only contraindication for water exercises is the acute phase of pain. Jumping into the water is strictly prohibited. You can't swim with your head held high. The breaststroke and butterfly styles are undesirable.
Yoga and Pilates for hernia
Yoga and Pilates are based on slow loads without overexertion. They improve the condition of muscles, tendons, and stretching. But with a herniated disc, many exercises are prohibited (bridges, twisting, strong stretches). Moreover, they cannot be done during an exacerbation period.
When giving preference to these methods, pay attention to exercises that are designed specifically for spinal hernia. The basic complex is not much different from exercise therapy - cobra, cat, bird-dog.
During the period of pain, avoid any strength or other prohibited exercises. If pain occurs, stop exercising. Additional equipment that is often used in Pilates (dumbbells, other weights) can be taken only at the stage of remission, when the pain has gone.
Set of exercises
Each case has its own characteristics, so a training complex should be developed by a doctor. This is an important point: wrong actions can enlarge the hernia and increase pain.
A set of exercises for hernia of the lumbar and lumbosacral region
The lumbar region not only bears the weight of the body, but is also responsible for cushioning (softening) the shocks to which the back is exposed. Therefore, any displacement of the disc at the bottom of the spine leads to serious consequences, and hernias of the lumbosacral region cause severe pain. A person cannot turn the body to the right or left, bend over, and sometimes sit, stand, or lie down. Regular exercise therapy will prevent this.
Read about lumbar hernia here.
Correct position for exercise therapy for lumbar hernia
Exercises for lumbar hernia should be performed lying down. In this position, the load on the lower vertebrae does not exceed 25 kg. At the same time, when a person stands, this number increases by 4 times, while sitting – by 6 times. When the body moves, the numbers increase even more.
Exercise therapy for a herniated lumbar spine should be done:
- on the stomach;
- on the back;
- on the side;
- On knees.
The best exercises for the lumbar region with a hernia
The simplest and most effective exercise looks like this:
- Lay out a mat and sit near a wall.
- Lie on your back so that your legs are stretched up the wall. Hands should be along the body.
- Lie like this for a few minutes. If possible, there is no pain, half an hour is possible.
- For comfort, place a bolster or pillow under your lower back.
The simplest and most effective exercise for spinal hernia
The best exercise therapy exercises for the prevention and treatment of hernia in the lumbar region are also considered half-cobra, cobra, cat, and bird-dog.
half-cobra
One of the most effective exercise therapy exercises for hernia of the lumbosacral spine is the half-cobra. It helps return the protrusion inside the disc and speed up healing. Do the exercise slowly and carefully. If pain occurs, it is better to refuse to perform it:
- Lie on your stomach with your elbows bent so that your palms are on both sides of your face.
- Slowly arch your back upward. Elbows on the floor, level with the shoulders.
- Stay in this position for 10 seconds.
- Slowly return to the starting position.
- Repeat 10 times.
- Gradually increase the time to 30 seconds.
Half cobra exercise
Cobra
This exercise therapy exercise for lumbosacral hernias is a heavier version of the half-cobra. It also helps to return the herniation inside the disc and speed up healing. Plus - it stretches ligaments better and makes the spine more flexible.
Do this exercise no earlier than you have mastered the half-cobra pose. Instructions:
- Lie on your stomach, arms bent at the elbows, palms near your face.
- From a lying position, begin to slowly straighten your back, without lifting your palms from the floor, until your arms are completely straight.
- Hold the position for 10 seconds. (gradually increase to 20-30 seconds)
- Return to the starting position.
- The maximum number of actions is 10 times. If you feel pain and you are not ready for the exercise yet, don’t do it.
Exercise cobra
Cat
Cat is one of the most popular exercises for lumbar hernias. It reduces pressure on the painful area, improves the mobility of the spinal column, relieves pain, and relieves tension.
Do the exercise like this:
- Bend your legs, stand on all fours, arms straight, resting on the floor at shoulder level.
- Take a deep breath and bend your spine upward, lower your head, look into your navel.
- Exhale and bend your lower back towards the floor so that your head looks up at the ceiling. The stomach should lower to the floor as much as possible, but do not bend your arms.
- Repeat 5-10 times.
Exercise cat
Bird dog
The Bird Dog exercise strengthens and stabilizes the lower back and deep muscles of the spine. It helps improve posture and avoid the appearance of a hernia.
The action plan is as follows:
- Get on your knees. Your arms should be straight.
- Raise your left arm and extend it forward until it is parallel to your torso. At the same time, lift your right leg, take it back, it should be at the same level as your left hand.
- Maintain this position for 2-3 seconds.
- Return to the starting position.
- Repeat with your right arm and left leg.
- Do this 10 times.
Bird-dog exercise
Prohibited exercises
If you have a lumbar hernia, you cannot:
- do a leg press, when a weight is attached to a platform, and a person in a lying position must push it up;
- bending over with straight legs - this increases the load on the intervertebral disc and lower back pain;
- do exercises to twist the spine, including lateral, oblique, double - they increase the protrusion of the intervertebral hernia and cause complications.
- jump, do aerobics, run.
What types of intervertebral hernias are most difficult to treat?
4 stages of treatment for intervertebral hernia
A set of exercises for thoracic hernia
Thoracic hernias are more difficult to treat than others. The main reason is that the spine in this area is excessively bent and it is not easy to straighten it in order to reduce the pressure of the hernia on the nerve endings. The task of exercise therapy for thoracic hernia is to solve this problem.
Read about the symptoms, types and treatment of thoracic hernias here.
Correct positions for exercise therapy for thoracic hernia
Therapeutic exercises for a thoracic hernia can be done lying down, sitting on a chair, or standing. Perform exercises slowly, with calm breathing.
Best exercises
- Stand straight, arms along your body. Rotate your shoulders first forward, then back (3-5 times). Hands walk along the body.
- Asynchronous shoulder rotation - right up, left down. The head looks forward.
- Sit on the floor, grab your heels with your hands, legs bent at the knees. Start doing soft rolls on your back (3-5 times). As you inhale, roll so that your cervical region (preferably the back of your head) touches the floor; as you exhale, your heels should touch it.
- Lie on your back on a cushion, place it under your thoracic spine. Slowly roll on the roller so that it first rises to the cervical region and then descends to the lumbar region.
- Starting position, as in exercise No. 4. Raise your hands to your face, elbows on the floor. Place your chin on your palms, extend your fingers, and stay there as much as possible.
Roll on your back and exercise on a roller for a thoracic hernia
Prohibited exercises
If you have a thoracic hernia, you cannot do exercises with weights or do pull-ups on the horizontal bar. Active movements are prohibited - jumping, fitness, aerobics. Fast running is prohibited; preference is given to jogging.
A set of exercises for cervical hernia
Pain from an upper hernia affects the upper back. It has a sharp, piercing character. It is difficult for a person to raise his arm, turn or tilt his neck. The task of exercises for hernias of the cervical spine is to stretch the distance between the vertebrae so that the protrusion puts less pressure on the nerves.
Read all about the symptoms and treatment of cervical hernia in this article.
Correct positions for exercise therapy for cervical hernia
If you have a cervical hernia, you can do the following:
- standing;
- lying down;
- sitting on a chair;
- On knees.
Best exercises
The activities described below can be done standing or sitting in a chair:
- Relax your shoulders, keep your back straight. Slowly lower your head onto your left shoulder. Do not rush, especially if the pain is felt on this side. Fix the position, count to 7, straighten your neck. Repeat the exercise on the other side.
- Return to the starting position. Move your head slowly up and down.
- Next, start turning your head - to the right and left. Having fixed the turn, count to 7, return to the starting position.
Head tilt with cervical hernia
The “half-cobra” exercise (see above) gives good results. It allows you to effectively stretch the spine, incl. cervical region
Prohibited exercises
For a cervical hernia, the following are prohibited:
- pull-up at a tournament;
- exercises with weights and twisting;
- push-ups