Stroke is a complex disease that disrupts the normal functioning of the brain. Develops against the background of diabetes mellitus, coronary heart disease, atherosclerosis, hypertension, aneurysms. A stroke disrupts brain function and entails changes in the functional characteristics of a number of organs, impaired mobility, and sensitivity.
Stroke ranks first among the causes of disability in middle-aged and elderly people. Moreover, 30% of cases occur in people of working age – up to 65 years.
In case of a stroke, proper first aid plays a significant role. In the process of rehabilitation - competent treatment and care for patients after a stroke. Even after the most severe form of an attack, the victim can regain partial mobility.
Caring for patients after a stroke: what is worth knowing?
While a person who has suffered a stroke is in hospital, he is looked after by qualified medical personnel. But sooner or later the patient is discharged, and then his relatives have to look after him. To help your loved one recover and to maintain the strength to perform the necessary procedures, it is worth learning the basics of correct and high-quality general nursing care.
From a medical point of view, there are two types of paralysis: right-sided and left-sided. The behavior of patients with different types of paralysis differs significantly. This is worth considering when developing an exit strategy. With right-sided paralysis, damage to the left side of the body, the patient’s motor function on the left side of the body is impaired. As a result, he:
- does not feel the left lower and upper limbs;
- does not understand where they are located;
- does not perceive the surrounding space (while walking he bumps into doors, cannot calculate the distance to the nearest object);
- loses place of reading.
Tips that will make life easier for such a patient:
- the bed must be placed so that the patient can see with his right eye the center of the room and whoever enters the room;
- Place household items on the side of your right hand;
- encourage your ward to talk more, as speech helps to quickly restore spatial perception.
With left-sided paralysis, damage to the right side of the body, the patient’s emotional background is disturbed. He is in a lethargic depressed state and does not experience any emotional experiences. Patients with left-sided stroke:
- have problems with speech, it is difficult for them to pronounce words and form sentences;
- have difficulties with perception, do not understand what is being said to them;
- they forget words and names of objects.
Tips on how to make the life of such a patient more comfortable:
- at first, replace words with gestures, facial expressions, and gentle touches;
- speak slowly, clearly, avoid complex sentences;
- try using written language instead of spoken language;
- perform smooth, unhurried movements;
- ask the doctor to develop a speech therapy complex, help the patient perform the developed speech therapy exercises.
Prevention of recurrent stroke in the elderly
There is a high risk of complications if no preventative measures are taken. The likelihood of a second attack increases tenfold, and statistics say that in 70% it ends in the death of the patient.
To avoid relapse you need:
- take medications that strengthen the walls of blood vessels;
- reduce blood viscosity by taking anticoagulants;
- reduce high cholesterol;
- do not drink alcohol, do not smoke, maintain normal weight;
- the daily routine should include light physical activity;
- if necessary, increase the functionality of blood vessels through surgery.
To effectively combat other complications of stroke, a set of measures has been developed, the quality of which determines the patient’s recovery and his further well-being.
1. Medicines to keep blood pressure levels under control. They improve blood supply function and saturate the blood with vital oxygen. Since a stroke kills cells and they cannot be restored, the main task is to prevent complications and prevent a recurrence.
If the patient is deeply depressed, antidepressants are prescribed. Anticonvulsants are taken to stop seizures, and muscle relaxants are taken to relieve muscle tone.
Anticoagulants and antiplatelet agents are the main medications that help avoid relapse of the disease.
During the recovery period, chronic diseases may worsen. To prevent this from happening, vitamins are taken as preventative measures to maintain immunity. If there is a lack of oxygen, doctors prescribe nootropics that help restore attention and memory.
2. Non-drug treatment. These include physical therapy, physiotherapeutic sessions, and therapeutic massage. Stressful situations, excessive workload, drinking alcohol and smoking are unacceptable. Medicines must be taken strictly on time.
3. Active communication with a bedridden elderly person, during which it is necessary to be tolerant of his possible fears, grievances, and irritability. The patient is weakened not only physically, but also morally, so it is especially important for him to know that he is loved.
We recommend
“Low blood pressure in older people: causes, symptoms and treatment” Read more
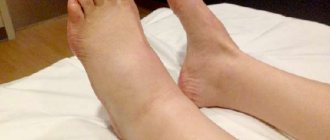
Preventing swelling of the arms/legs
Poor circulation causes the formation of edema in the upper and/or lower extremities. Factors indicating the appearance of edema are cold, red extremities. Tips on how to prevent the problem:
- Sore limbs should be in a comfortable position. It is important to ensure that they do not hang down.
- Frequently changing the positions of the limbs helps avoid blood stagnation.
- In a sitting position, you can place a soft pillow/cushion under your arm and a strong support (small stool, hard cushion) under your leg. You can place a pad under your calves to improve support.
- In a sitting position, you must ensure that your back fits snugly against the back of the chair or other support.
What you should pay attention to?
Let's look at the rules that everyone needs to know:
- Maintaining optimal air temperature.
- Checking the integrity of the skin, preventing bedsores and dermatitis.
- Strict adherence to recommendations for feeding the patient.
- Measuring body temperature, if fever appears, it must be brought down.
- Psychological support for the elderly, you should not let him fall into depression.
In some cases it is worth calling a doctor:
- When severe pain appears in paralyzed areas of the body.
- A sharp increase in body temperature.
- Deterioration of the patient's well-being.
- The appearance of swelling and bedsores.
Naturally, not every person has the opportunity to provide an elderly relative with proper rehabilitation. If you want an elderly person to recover faster and restore health, you should go to a paid nursing home. This decision will save the life of your loved one, provide him with professional care and will not require restructuring your lifestyle.
Prevention of thrombosis
Almost every stroke patient leads a sedentary lifestyle. This causes the development of physical inactivity—a weakening of muscle tone. As a result, blood clots begin to form in the lower extremities. This process is dangerous due to the occurrence of thrombosis. You can prevent a dangerous condition:
- performing preventive exercises;
- using compression stockings, elastic bandage;
- taking medications to thin the blood (prescribed by your doctor).
Introduction
When you find out that someone you know has had a stroke, it can be a big shock to you. This information provides a brief explanation of what a stroke is, how it affects the person affected, and how a caregiver can help. Its important purpose is to show how you can help people with daily activities such as eating and drinking, washing and dressing.
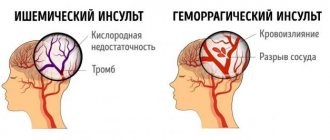
What is a stroke?
A stroke occurs when a blood vessel in the brain ruptures and blood leaks into the brain, or when a blood vessel becomes blocked or narrowed, reducing the flow of blood to the brain area. Both types of stroke cause damage to brain cells, some of which die.
How does a stroke affect a patient?
Because the brain controls the body, the impact of a stroke is determined by which part of the brain is damaged. A stroke can cause problems with normal body functions, such as eating and swallowing food, or movement and perception, including coordination. Visual perception, hearing, speech and the ability to regulate urination and bowel movements may also be affected. As a caregiver, you should monitor these changes, noting both positive and negative changes.
Stroke patients may feel tired and have difficulty thinking or controlling their emotions. They may be susceptible to depression.
The effects of some types of stroke can last minutes or hours, while recovery from more severe types of stroke can take months or years as other areas of the brain learn to take over the functions of the affected areas. However, sometimes the action remains unchanged.
What is rehabilitation?
Rehabilitation is the process of coping or learning to correct the dysfunction caused by a stroke. With the help of special exercises, stroke patients regain lost abilities or gradually learn new ways to cope with daily activities.
Sometimes professional help may be helpful to help restore speech and language abilities (speech therapist), improve mobility and muscle control (physical therapist), or perform daily tasks (occupational therapist).
How can a caregiver help with rehabilitation?
Sometimes improvement may seem slow.
Maintaining a daily routine can help maintain morale for the stroke patient and their caregiver. The routine should include regular short intervals for the stroke patient to exercise and teach skills.
Patience is required from both the stroke patient and their caregiver. Sometimes it may seem that improvement is happening very slowly. Constant support and praise from the caregiver, even for small accomplishments, helps build trust and maintain morale.
It is very important to provide help when it is needed. The provision of assistance must be balanced between encouraging the patient to gain independence and maintaining confidence in success.
Prevention of pneumonia
Prolonged bed rest causes stagnation of blood in the lungs. Against the background of this problem, pneumonia occurs. The danger of the phenomenon is its asymptomatic occurrence. Over time, the bedridden patient experiences weakness, cough, shortness of breath or heart failure, and fever. Pneumonia can occur at an early stage of a stroke (2nd - 3rd day of the disease) or a late stage (2nd - 6th week of the disease). To prevent the occurrence of pneumonia you must:
- perform a drainage massage - lightly tap the back at the level of the lungs (do not touch the spine);
- ventilate, moisten the room - dry air dries out the nasal mucosa, which becomes a breeding ground for infection;
- do passive gymnastics - several times a day the patient should be raised in bed, raise and lower the upper limbs, thus improving breathing;
- perform breathing exercises;
- give expectorants (as prescribed by a doctor).
Cost of treatment and how to get there
The cost of living in the Resource boarding house for those who are bedridden after a stroke is affordable, so you will have no reason to worry. The final price depends on:
- living conditions (type of room, need for additional medical equipment);
- patient independence;
- length of stay.
Often, boarding houses for rehabilitation after a stroke require a lot of paperwork when registering guests, which often takes away already precious time. Sanatorium "Resource" can accept patients the next day after submitting an application. To do this, you need to fill out the form on the website or call the number provided.
Preventing constipation
People after a stroke often have problems with bowel movements. Drinking plenty of fluids, abdominal massage, medicinal and natural laxatives (beets, dried apricots, prunes, bran, bananas, and other foods) help combat constipation. Abdominal massage is performed with light circular movements. The intestinal area can be massaged with gentle pressing touches.
You can help improve the bowel movement process by developing a bowel movement routine: daily enemas/suppositories should be done until the natural process is restored. Developing a reflex to have a bowel movement at the same time helps avoid constipation.
You can improve natural intestinal motility with proper nutrition. The patient's diet should include vegetables and fruits, cereals, and dairy products. You should not eat spicy or fatty foods, baked goods, alcohol, or sugar. It is better to steam or bake food.
What factors influence the healing process?
Belief in the recovery of patients in a boarding house after a stroke - this can be called one of the most important factors. And we are absolutely sure that there are no hopeless patients! Stroke is considered a serious disease that can lead to disability. From the first day of stay in our institution, we begin activities aimed at returning to independence and independence. Residents who have lost the ability to move receive daily professional care, and the rooms where they stay are kept clean. Please note that our rooms have a homely atmosphere; you can bring things that are dear to the patient and arrange them according to the room.
It has been proven that only 15% of victims achieve full recovery after a stroke. Those who remain have to learn to live in a new way and adapt to changes in the body. This is why we develop individual rehabilitation programs. Rehabilitation periods may vary. They depend on the scale of cerebral damage, general health, the age of the patient, and the speed and quality of medical care that has already been provided.
When drawing up a rehabilitation plan, we adhere to some rules:
- Choosing a course. A rehabilitation program should only be drawn up by a competent specialist. Our professional specialists, who have many years of experience, will study your medical history in detail and select the optimal solution for rehabilitation measures.
- Fast start. It is necessary to begin a rehabilitation course immediately after the end of the acute period of a stroke. It is strictly forbidden to hesitate, because some of the consequences may become irreversible. It is recommended to bring the patient to us as early as possible, in this case success is most likely.
- Time. Do not expect quick, instant results from rehabilitation (no matter where it takes place). The recovery process is gradual and takes a long period.
- Regularity. We responsibly and systematically follow the doctor’s instructions, which gives a high chance of successfully restoring lost body functions.
- Faith in success. We do not allow the patient to become despondent and depressed. We let him know that after a stroke it is possible to live an almost full life. Only confidence in success, positive emotions and comprehensive support! All these factors together help you recover much faster.
Preventing the formation of bedsores
Bedsores are formed under the influence of a number of factors:
- body overheating;
- unsuitable underwear and bed linen - injure the skin;
- illiterate care can provoke the appearance of long-term non-healing wounds;
- untimely treatment of abrasions, cuts, and other damage to the epidermis.
A bedsore is a source of infection entering the blood, which causes complications in the course of the disease. Bedsores appear in places where the skin is in constant contact with a hard surface. This is easy to avoid - you need to periodically change the position of your body. Do all manipulations of turning over and changing body position slowly and carefully. The client must be left in the selected position for 2 – 3 hours. Make sure that no folds form under the body and that the laundry does not bunch up.
Air baths are a good prevention of skin necrosis. Light massage of areas prone to bedsores (shoulder blades, hips, sacral area, heels, other areas) helps avoid damage to the epidermis. Before massage, it is best to lubricate the skin with camphor oil. The massage is done until the surface of the epidermis becomes slightly red, which indicates restoration of blood circulation.
Patient Assessment
Treatment of pressure ulcers begins with a complete assessment of the patient's general condition and the characteristics of the wounds. The development of pressure ulcers indicates the need to reconsider preventive measures.
A standardized approach should include initial assessment, appropriate treatment planning, and monitoring of wound healing.
Figure 2 Typical locations for pressure ulcers
The condition of the wound, dressing and surrounding skin, any possible complications and pain control should be assessed and recorded daily. The description should be supplemented by a rating on one of the scales developed for pressure ulcers.
Table 1 Stages of development of pressure ulcers (The National Pressure Ulcer Advisory Panel (NPUAP)
| Stage | Description |
| I | The skin is intact, the area of hyperemia does not disappear >1 minute after the pressure is removed. |
| II | Blisters or other skin lesions with partial damage to the dermis; Possible wound infection. |
| III | Full-thickness tissue damage. Subcutaneous fatty tissue can be seen in the wound; destruction extends to muscles; Possible wound infection. Detachment of the epidermis and the formation of fistulas are possible. |
| IV | Full-depth skin involvement, involvement of bones, tendons or joints; Possible wound infection. Often accompanied by detachment of the epidermis and the formation of fistulas. |
| The stage cannot be determined | Damage to the skin to its full depth, in which the base of the wound is made of necrotic masses and/or the surface is covered with a scab. |
| Deep tissue damage is expected | A bright red or maroon area surrounded by healthy skin or a blister filled with blood that has formed due to compression and/or displacement of the underlying tissue. |
Figure 3 Stages of development of pressure ulcers (The National Pressure Ulcer Advisory Panel (NPUAP)
Prevention of contractures
A side effect of a stroke is loss of mobility. Against the background of this functional disorder, contractures occur—limited mobility of the upper and lower extremities. Limitation of mobility leads to the fact that the patient cannot move, work with his arms and legs. This joint disease is easier to prevent than to treat later. Preventive measures:
- Correct body position - in bed, the patient should lie in a position close to normal physiological. To reduce muscle tone, you need to use rollers, pillows, and other means. Orthoses help keep your limbs in the correct position. To prevent your hand from clenching into a fist, it is convenient to use a massage ball, dumbbell, etc.
- Therapeutic gymnastics - exercises should affect all joints. Start gymnastics by warming up the muscles. For maximum effect, you can use a special gel. Therapeutic gymnastics lasts 20–30 minutes, includes 5–10 repetitions. A set of exercises must be practiced from the first days of the disease. This will avoid joint contracture and guarantee a better result.
Caring for a patient who has suffered a stroke requires great patience and perseverance from the caregiver.
Remember, high-quality home care, compliance with doctor’s orders, and emotional support are the conditions for the patient’s rapid recovery. In contact with
Help with rehabilitation
Caring for a person after a stroke at home is a set of rules that must be followed:
- Constant surveillance;
- Performing gymnastics and massage;
- Compliance with nutrition and diet;
- Drug treatment prescribed by a doctor;
- Consultation with a specialist about the relative’s condition.
To provide proper care to a person after a stroke, it is important to follow the rule of physical therapy and massage, which is performed every 3-4 hours. It is advisable that the nurse performing the massage has appropriate training.
Additional Information
Impact on relationships
A stroke patient may be dependent on a caregiver, at least initially and perhaps permanently. Caregivers may perform activities previously performed by those who are ill, such as keeping track of finances, driving, or shopping and preparing meals.
It is important that family and friends help cope with the burden of worries. The caregiver must select and determine their assistance in carrying out exercises/activities with the patient or being with the patient while the caregiver is absent.
Practical aids
Home appliances make life easier for the patient to continue leading a normal life. These include special equipment such as ladders to get up and down, installing a shower instead of using a bathtub, or attaching handles to the bathtub to make it easier to get in and out of the bathtub.
Mobility assistance such as a wheelchair may be needed.
Specially equipped devices for one-handed use can make daily tasks possible - peeling vegetables, dentures or nails, opening cans or a stick with a hook to help with dressing. A floating bath thermometer will prevent accidental scalding.
Sometimes a new way of performing a familiar task may be needed to overcome a physical disability. For example, cooking vegetables in a pan of water may require careful rethinking, step by step, as it can be done while sitting or with one hand.
How to help a sick person wash
As a caregiver, you can make washing easier by preparing the bathroom in advance. Make sure there is enough hot water and that towels, shampoo, soap and dental supplies are easily accessible.
Make sure that the place where the washing procedure will take place is warm and there is no draft. Place a non-slip mat in your bath or shower; Make sure the floor around your bathtub or shower is not slippery.
Make sure the path to the bathroom is clear of any obstacles.
Railings or handrails fixed to the walls can help the patient get in and out of the bath.
Always add hot water to cold water, never the other way around. Check the temperature with your elbow.
First, wash the patient's face and hands. The genital area should be washed last.
Make sure that the shampoo and soap are rinsed off well and that the washed area is well dried.
The patient can sit in a chair while he or she washes in the bath or shower; The chair should have rubber tips on the legs or be placed on a towel to prevent slipping.
A portable shower is most convenient for washing your hair and partial bathing. A shower with a long hose is easier to use.
Use as little shampoo as possible for minimal rinsing.
Please note that washing a patient in a lying position is more convenient and safer than moving him in the bathtub. If you decide this is the best option, make sure you wash and dry each body part in turn; keep only the part of the body being washed uncovered.
Assisting patients in brushing their teeth should be careful every morning, evening and after meals. Never force a patient to open their mouth. Use a toothbrush and very little toothpaste to avoid choking.
When helping a patient shave, it should be noted that an electric razor is safer than a regular razor and is recommended to be used.