Stroke is a dangerous disease with an acute circulatory disorder in the brain, which develops as a result of blockage of blood vessels or their damage. Most often it affects older people.
Stroke is the second most common cause of death after cardiac ischemia. Among diseases leading to disability, it ranks first.
If a stroke occurs, emergency medical care is required and should be provided within the first 3-8 hours. Even if help was timely and the patient survived, the consequences can be severe. Partial or complete loss of motor function, leading to disability, cannot be ruled out. According to statistics, about 80% of patients become disabled after a stroke, and a quarter of them require constant care throughout their lives. Only a fifth of all stroke survivors can return to relatively normal work activities after rehabilitation measures. Depending on the severity of the condition, the patient may be assigned disability group 1, 2 or 3.
Types of stroke
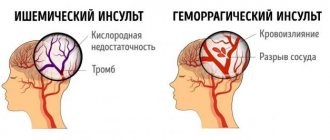
There are two types: hemorrhagic stroke and ischemic stroke.
Ischemic
This type of disease is the most common - about 80% of all cases. Most often occurs in older people. It is also called cerebral infarction. Ischemic stroke occurs due to impaired blood circulation in the brain due to narrowing of the lumen of blood vessels or blockage by blood clots. As a result, part of the brain is no longer supplied with blood and tissue death (necrosis) of this area occurs.
In a hemorrhagic stroke, a blood vessel ruptures and bleeds into the brain.
Hemorrhagic
It occurs from a rupture of a brain vessel. There are two types of hemorrhagic stroke: cerebral hemorrhage and subarachnoid hemorrhage.
The first is the most common and usually develops in people around 50 years of age. The main cause is hypertension, less often - atherosclerosis.
The second type is a hemorrhage into the space between the membranes of the spinal cord and brain, which contains the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). Such a stroke can occur at the age of 30. Its main causes are arterial hypertension, smoking, alcoholism, and taking a large dose of alcohol at one time.
New rules in 2021
Government Decree No. 92 of 02/01/2021 extended the temporary procedure for recognizing a person as disabled until the end of 2021.
At the same time, changes were made to the rules for conducting a medical and social examination (MSE) in absentia and the rules for recognizing a person as disabled in 2021 without being called to a commission. ConsultantPlus experts discussed how to apply for disability. Use these instructions for free.
to read.
Who is given disability
Not all stroke survivors can apply for disability. The group can be obtained strictly for medical reasons. It is prescribed in accordance with the Federal Law and its amendments based on the results of all necessary examinations. It is usually given to those patients in whom part of the brain has not fully recovered, movement, speech, and other functions are impaired.
- The first group is indicated for patients who have lost the ability to care for themselves and need constant help and care, as well as for those who can partially care for themselves, while they need to provide the necessary social and everyday functions.
- The second group includes patients whose dysfunction is persistent and severe, but they have not lost the ability to care for themselves.
- The third group is assigned to people with moderate impairments and moderate limitations in functions, which may subsequently disappear. In this case, the ability to work can be preserved, but some types of work are prohibited.
Criteria for establishing a disability group
Disability group I is assigned to severe visible impairments in the functions of movement and self-care. The second disability group is assigned to patients who have obvious impairments in the functions of movement, communication, orientation, behavior control and self-care of the second degree. Patients with mild impairments of mobility, ability to work and first degree can apply for assignment to the third disability group.
During the re-examination, experts take into account whether the patient will be able to return to work if his health improves. If, within five years, disabled people of the first or second group do not experience improvement, disability is established without an expiration date.
If the patient has been refused recognition of disability, he can file an application to appeal the decision of the MSEC. The patient always retains the right to an independent examination. To do this, he can go to court, however, the decision received after the court can no longer be challenged.
Citizens are assigned a disability group without specifying a period for re-examination, and citizens under 18 years of age are assigned the category “disabled child” until the citizen reaches the age of 18:
- no later than two years after the initial recognition as disabled of a citizen who has diseases and defects, irreversible morphological changes, dysfunctions of organs and systems of the body;
- no later than four years after the initial recognition of a citizen as disabled, if it is revealed that it is impossible to eliminate or reduce during the implementation of rehabilitation measures the degree of disability caused by persistent irreversible morphological changes, defects and dysfunctions of organs and systems of the body.
Call and they will make an appointment with a neurologist. Specialists at the Yusupov Hospital use the most effective medications, individual treatment and rehabilitation regimens to minimize the consequences of ischemic stroke. Most patients return to work and do not need to be assigned a disability group.
How to get
Every patient who has suffered a stroke and has medical indications for this has the right to receive disability. The assignment of the group is carried out by a medical expert commission. During a special examination, the patient’s condition, his ability to work are assessed and restrictions on physical activity are prescribed.
Registration will take quite a long time. First of all, the patient needs to receive a referral from the attending physician for a medical and social examination (MSE), then take tests and undergo all the necessary examinations.
Thus, you need to prepare the following documents:
- statement;
- a referral from a doctor for examination with the signature of the chief physician and the seal of the medical institution;
- results of examinations and tests that are not in the medical history;
- an outpatient card from the clinic where he is being treated;
- ID card (passport);
- if a person is employed - a copy of the work record book, salary certificate;
- sick leave (if any) and a certificate of occupational diseases and injuries.
All examinations can be completed in a hospital or in a clinic (if the person is walking). A referral for an examination is given at the clinic after the medical history and test results have been reviewed.
After a stroke, the patient may lose the ability to move independently.
After submitting the application, the patient will be given a date to undergo the commission, which usually includes three specialists. Based on all the documents provided, a decision will be made to assign disability or refuse. During the examination, all the conditions in which the patient is located are analyzed: labor, household, social.
The group is determined by the following categories:
- the patient’s dependence on others;
- limited self-care abilities;
- ability to move;
- ability to navigate in space;
- ability to control one’s behavior and communicate with others.
During the examination, a protocol must be kept. In both the case of assignment of disability and in case of refusal, an act is drawn up, which is an official document.
After receiving the group, a person needs to apply to the pension fund in order to be assigned a pension, and to the social fund to receive benefits.
If the patient is refused and does not agree with the decision of the commission, he has the right to submit a written application within three days to the ITU bureau, where he was examined, for a re-examination. If he is not satisfied with the answer again, he can appeal it at another level - to the Federal Bureau of ITU.
To obtain a disability, you need to undergo an examination and receive a referral to ITU
If the disability is not lifelong, then it is necessary to undergo an annual examination for groups 2 and 3 and once every two years for group 1. It is appointed to monitor positive dynamics and possible revision of the group. The annual examination can be canceled when a woman reaches 50 years of age and a man reaches 60 years of age.
If disability is assigned for life, but the person does not agree with the group, he can apply for re-examination.
Patients from the following categories are more likely to receive a disability group:
- previously had a stroke and were not treated;
- hypertensive patients;
- patients with disorders of the heart and blood vessels;
- people with kidney failure;
- patients with diabetes;
- people with chronic diseases that limit normal life activities;
- patients with bad habits.
What disability group is assigned?
Depending on the dysfunction of the body resulting from an ischemic stroke and impairment of certain functions, patients are assigned disability group I, II or III. If the patient is under 18 years of age, he is recognized as a “disabled child.”
Disabled people of the first group must undergo re-examination every two years, and disabled people of the second and third groups – every year. This is necessary so that the commission can track deterioration or improvement of health. Depending on the results, the disability is either extended or the relevance of the previously assigned group is revised.
The patient is recognized as disabled after suffering an ischemic stroke, based on the following reasons:
- deterioration of health with a pronounced deterioration in neurological functions, which is caused by the consequences of an ischemic stroke;
- partial or complete loss of self-care, independent orientation and movement, loss of control of one’s behavior or speech impairment;
- progressive course of heart disease;
- repeated disturbances of cerebral blood flow;
- previous ischemic strokes.
A medical and social examination can be carried out at the patient’s place of residence, registration or attachment to a medical institution. If a health care institution issues a conclusion that the patient is unable to appear for an examination due to health conditions, an examination at home or in a hospital is allowed. If there is a special note in the documents about permission to conduct a medical and social examination at home, the disability group can be carried out in absentia using the documents provided.
Diseases for group II
For group II, the indicator is a deviation from the norm of 70-80%. A person is able to perform simple actions (including resorting to special means or the help of other persons). He works despite physical or mental disabilities, but under special conditions. Among the diseases:
- fecal fistula;
- chronic pulmonary insufficiency or absence of one lung;
- irreversible visual impairment;
- cirrhosis of the liver;
- mental illness;
- skull defects;
- leg paralysis
What does disability give?
Disability is the status of an individual, which is acquired in connection with deviations in his state of health, accompanied by a persistent disorder of body functions due to illness or injury. The law established a list of diseases for which the status of a disabled person is granted, and the rules for obtaining it. The status of a disabled person makes it possible to receive support measures established by the state - cash payments, free medicines, tax, labor or other benefits.
| Support measure | Characteristics | Base |
| Pension provision | Insurance part of the pension (if you have even 1 day of service without reference to age) | Art. 9 Federal Law No. 400-FZ dated December 28, 2013 |
| Social pension (in the absence of grounds for assigning insurance) | Art. 11 Federal Law No. 166-FZ dated December 15, 2001 | |
| EDV | Indexed annually. Installed when refusing a set of social services. The payment amount is:
| Art. 28.1 Federal Law No. 181-FZ dated November 24, 1995 |
| Set of social services | Prescription medications, sanatorium-resort vouchers by referral, travel by suburban or intercity transport to the place of treatment and back | Art. 6.1 Federal Law No. 178-FZ dated 17.97.1999 |
| In the world of work | Shortened working week - 35 hours (for grades I and II) | Art. 92 Labor Code of the Russian Federation |
| Length of working day, shifts according to medical indications | Art. 94 Labor Code of the Russian Federation | |
| Admission to night and overtime work only with the consent of the disabled person | Art. 96, 99 Labor Code of the Russian Federation | |
| Work on weekends and holidays in the absence of medical prohibitions | Art. 113 Labor Code of the Russian Federation | |
| Vacation at your own expense up to 60 calendar days per year at a time convenient for the disabled person | Art. 128 Labor Code of the Russian Federation | |
| In the field of education | Admission to universities according to a quota (disabled people of grades I and II, from childhood, with war trauma) | Art. 71 Federal Law No. 273-FZ dated December 29, 2012 |
| In the field of employment | Employer quotas for jobs | Federal Law No. 181-FZ |
| Tax | Deduction in the amount of 500 rubles. for each month of the calendar year in terms of income that is subject to personal income tax | Art. 224 Tax Code of the Russian Federation |
| Reduction of the tax base for land tax by the cadastral value of 600 m² of land area owned by a disabled person since childhood | Art. 391 Tax Code of the Russian Federation | |
| Exemption of disabled people from childhood from property tax (in part 1 of each type of taxation object) | Art. 407 Tax Code of the Russian Federation |
Diseases for group III
It can be difficult to distinguish healthy people from group III disabled people based on external signs. Citizens with this group have the right to work, since the rate of loss of function is 40-60%.
Diseases for assignment to disability group III include:
- incipient cancer;
- absence of one eye;
- ptosis of one eye (permanent, persisting after treatment);
- bilateral deafness;
- jaw defects in the absence of the ability to chew;
- facial defects that can only be corrected through surgery;
- defects of the skull bones;
- paralysis of the hand or one of the limbs, causing muscle wasting;
- the presence of a foreign object in the brain after injury;
- installation of a foreign body in the heart area (pacemaker, artificial valve);
- amputation of the hand, one or more fingers;
- one kidney or lung.