Life expectancy after myocardial infarction
Sometimes complications from myocardial infarction occur that can affect the prognosis.
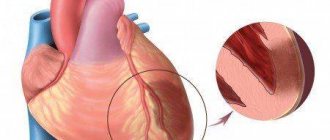
This is cardiogenic shock, acute heart failure, severe arrhythmia. More often they develop with extensive MI 3-6. Most of the long-term consequences of MI are associated with the formation of a connective tissue scar at the site of cardiomyocyte death. If the area of myocardial infarction (necrosis of the heart muscle) can be limited using thrombolytic therapy initiated in the first 4-6 hours or cardiac surgery (coronary artery bypass grafting, percutaneous coronary intervention), then the likelihood of adverse consequences can be reduced 3-6.
Otherwise, the connective tissue does not allow this part of the myocardium to fully contract, various conduction disorders develop, and cardiac output suffers. As a result, heart failure develops; organs suffer from a lack of oxygen, which negatively affects the functioning of the entire body.
During the rehabilitation process, the functions of the affected area will be taken over by neighboring areas. This requires a certain time, compliance with the stages of rehabilitation, continuity of the prescribed treatment and a gradual increase in physical activity under the strict supervision of a health care professional.
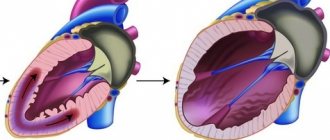
- A cardiac aneurysm is a thinning and bulging of the heart wall in the form of a sac, which leads to a decrease in cardiac output and the progression of heart failure.
- Thromboembolic complications can develop due to non-compliance with physical activity or deviation from the treatment plan, which always includes drugs that affect blood clotting.
- Chronic heart failure develops due to impaired contractile function of the left ventricle. Manifested by edema of the lower extremities, shortness of breath during exercise, etc.
The risk of such complications persists throughout the first year after MI 1. After a year, the likelihood of complications is less if the patient adheres to the prescribed treatment and is regularly monitored by a cardiologist 1.
Many patients who have had a heart attack, as well as their relatives, ask the doctor the question: how many years can one realistically live after such an attack? But it’s difficult to give an exact answer; there are many reasons for this. The first and most important aspect is age. Old people are less likely to survive up to 10 years after a heart attack, because it is often accompanied by other diseases. For young people, the chances are more encouraging. There are other important points that should also be taken into account.
The second aspect, which is directly related to the length of years, is the types of complications after a heart attack. They are divided into early and late. If the lesion is small, then there will be fewer complications.
- Pulmonary edema.
- Heart rhythm failure.
- Acute heart failure.
- Thrombosis.
Most often, the disease affects the left ventricle of the heart, which is why failure occurs in this department. Its characteristic symptom is breathing problems. Forms of heart rhythm disturbances are also dangerous. Doctors say that long-term complications are not as dangerous to health as acute ones, but they appear much more often.
Cardiosclerosis is a characteristic disease for all heart patients, and directly affects life expectancy after an attack. This condition is associated with how quickly the cardiac scar heals; in the diffuse form, deviations in the activity of the heart muscle begin.
So, the maximum opportunity to live after a heart attack for a long number of years remains for patients whose health is not complicated by other diseases and unpleasant consequences. If you follow the recommendations during recovery, it is quite possible to significantly reduce the risk.
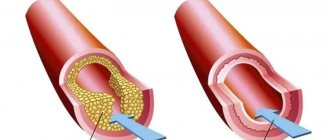
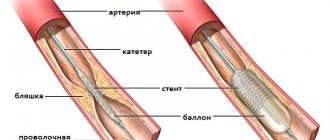
A procedure such as stenting, when the walls of the arteries are cleared of atherosclerotic plaques, also prolongs the life of heart attack patients. The blood flow is restored, the heart continues to work without overstrain.
- Early and late complications of myocardial infarction. Consequences of myocardial infarction
The first recommendations of doctors are to protect the patient from severe stress. Fear, joy, fright - any shock can become fatal for the body, even with positive prognosis. If such nervous shocks have happened often in the past, and promise to happen in the future, it is problematic to talk about the patient’s long life expectancy. But in their assessments, doctors also take into account the forms of the disease.
After a micro-infarction
Most often it occurs in men, starting from the age of 30, women last longer. In addition, they rarely pay attention to the symptoms of the disease, attributing it to general malaise or fatigue. Meanwhile, the consequences of a microinfarction are no less dangerous, since the next stage may already be a heart attack.
- pain behind the sternum, radiating to the left arm;
- shortness of breath, feeling of lack of air;
- nausea;
- heart rhythm disturbances.
With proper treatment, it is possible to recover and live for more than one year. The patient does not feel any sharp restrictions after a microinfarction; only strong physical activity and stress are prohibited.
After a heart attack
After a heart attack, recovery is much more problematic, because part of the heart tissue dies. During an extensive attack, most of the organ suffers, which affects the general condition of the patient. According to statistics, the process of destruction in most heart attack patients is observed in the right ventricle. If necrosis covers up to 10 cm in width, blood flow in the coronary artery is severely impaired.
The statistics of life after a heart attack are very sad. Only if the assistance was provided competently and at a high level, we can talk about good chances. If a person lives for 10 years after an attack, then his life expectancy is equal to that of a healthy person.
The second attack is much more dangerous and most often occurs in those suffering from hypertension. This disease is detected in all heart attack patients and is often accompanied by asthma and heart rhythm disturbances. This time the symptoms will be less noticeable, since the affected organ reacts much weaker. In 80% of cases, a repeated heart attack is provoked by atherosclerosis.
- pain radiating to the arm;
- severe suffocation;
- pressure decreases;
- fainting.
It is difficult for doctors to predict whether there will be a relapse or not, since it depends on the general health of the patient and how well he follows his diet and daily routine. A distinction is made between repeated and recurrent infarction. In the first case, a heart attack may occur a couple of months after the first one. In case of relapse, this may happen earlier. Moreover, the survival rate after a second or recurrent heart attack is low.
To avoid such manifestations and live for more than one year, you must try to reduce the amount of bad cholesterol in the blood, in medical terms - low-density lipoproteins. Dietary nutrition, drug treatment, and traditional methods will help with this.
Risk factors
There are a number of factors that affect how long a person can live after an attack.
- Nature of the disease. Some people have one large scar on their heart after a heart attack, while others have several small ones.
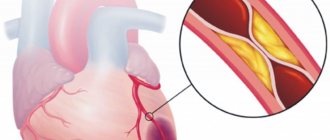
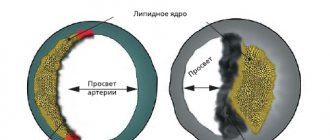
- The appearance of atherosclerotic plaques that block the arteries.
- In men, cardiovascular diseases are provoked by a lack of large amounts of estrogen in the blood, which is why heart attacks occur more often in them than in women. But this situation is typical only up to 70 years of age, then the incidence rate is the same.
- Diabetes or excess weight, which greatly overloads the heart muscle.
- Heavy loads during the recovery process.
It is difficult to give an exact figure for how many years people live after a heart attack, since personal characteristics of the body, the severity of the disease, and heredity are also taken into account.
Helps the body return to normal, live for several years with a competent menu and giving up alcohol and cigarettes. You also need to regularly do special exercises; swimming and walking can help restore recovery. But all physical activity is only on the recommendation of a specialist.
- Chances of surviving after a major myocardial (heart) infarction, consequences, how to improve the prognosis
It is difficult to predict the chances after a heart attack; it all depends on how sensitive a person is to his health. It is very important to undergo diagnostics on time and consult with specialists. If the disease is recognized at an early stage, such a patient has a much greater chance of recovering quickly and without consequences.
Possible complications
In the first hours and days after the development of the disease, complications may appear. They significantly worsen the course of the disease and reduce the chances of successful treatment.
Most patients complain of interruptions in the heart (arrhythmia can be different). They can persist for several days. Particularly dangerous during this period is ventricular fibrillation, which then turns into fibrillation. A person's risk of death increases significantly.
Left ventricular failure has the following symptoms: congestive wheeze, pulmonary edema and some manifestations of asthma. Cardiogenic shock, which rapidly develops with a large infarction, poses a huge danger. Often doctors simply do not have a chance to save a dying patient. The main signs of such shock are: a sharp drop in blood pressure, rapid heartbeat, cyanosis, and impaired consciousness.
Often, patients experience rupture of muscle fibers, which can subsequently provoke cardiac tamponade. In less than 4 percent of cases, a person experiences a severe disruption of blood flow in the lungs. This complication is also characterized by increased mortality.
Another complication is acute cardiac aneurysm, which gradually turns into a chronic stage. As a result, heart failure occurs.
Fibrin deposition that occurs on the endocardial walls is a direct threat to various internal organs, including the kidneys, brain and lungs. Because of this complication, signs of a heart attack are especially severe in men and women.
The later period of the disease is accompanied by complications such as pericarditis and eosinophilia. There are also other serious illnesses.
After treatment…
After inpatient treatment, an important period of rehabilitation begins, which lasts up to 12 months. The doctor prescribes the necessary drug therapy, which includes combination therapy with various classes of drugs. Some medications require constant taking, i.e. for the rest of my life. If you follow all the doctor’s instructions: quit smoking, follow a diet and constantly take medication, people after myocardial infarction live a full and comfortable life for many years.
Diagnosis of the disease
The peculiarity of diagnostic procedures is that they can be prescribed not only during the examination period, but also during the treatment of the disease. The doctor should systematically study data on the activity of serum enzymes, as well as electrocardiogram indicators. This allows you to avoid various complications in the future, which in turn increases the patient’s chances of successful treatment.
A person can come to a specialist with various complaints. They directly depend on the degree of development of the disease, its form and duration. A heart attack is detected when severe pain in the chest area persists for 30 minutes (the attack lasts up to one hour). In this case, the patient feels acute heart failure. Other heart attack symptoms may also appear in women and men.
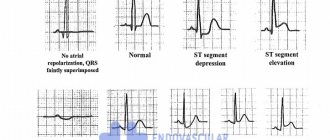
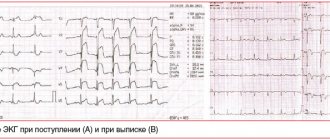
An electrocardiogram, among other things, allows you to record various changes in the activity of the heart. For example, the doctor has the opportunity to detect a negative T wave, a pathological QRS complex and other negative phenomena. After this, the doctor needs to conduct a number of other diagnostic examinations, or prescribe an urgent operation.
In the first few hours after the onset of severe pain, there is a sharp increase in myoglobin in the blood. This is a special protein whose main task is to supply oxygen inside the cells.
8 hours after the onset of a heart attack, a noticeable increase in creatine phosphokinase activity may be observed. Gradually the indicators are normalizing. The stabilization process takes about two days, sometimes less. The level of creatine phosphokinase in the blood should be measured several times a day. This should also be classified as diagnostic procedures that are of particular importance to the patient.
In the later stages of the disease, doctors also use different diagnostic methods, despite the fact that the risk of death increases. In particular, a specialist needs to determine the enzyme lactate dehydrogenase. The indicator returns to normal only after one week. It often takes two weeks for lactate dehydrogenase enzyme levels to normalize and stabilize.
Unstable angina can provoke an increase in troponin protein isoforms. Doctors detect these changes through tests. Symptoms of a heart attack in a man or woman may also subside.
The blood test that the patient gives allows the doctor to see an increase in the level of ESR, leukocytes and other elements. The clinical picture looks more complete, which contributes to successful treatment in the future.
Many cardiologists prescribe echocardiography, the main task of which is to identify various disorders of ventricular contractility, as well as thinning of its wall.
In more prestigious clinics, a modern diagnostic procedure is performed - coronary angiography. It allows the specialist to identify thrombotic occlusion of the artery. In addition, this diagnostic method allows the doctor to determine whether it is advisable to perform surgery on the patient’s heart or not. In other words, the likelihood of bypass surgery or angioplasty is assessed. Such radical treatment methods are often the only path to salvation when serious heart diseases are detected.
Clinical manifestations
The clinical picture of acute myocardial infarction is distinguished by its diversity, which makes it difficult to make a correct diagnosis in the shortest possible time and can confuse the doctor, and the patient himself may think about a completely different disease that he may have had earlier in life.
Typically, myocardial infarction causes the following symptoms:
- Prolonged (more than 30 minutes), highly intense, squeezing pain behind the sternum, which can radiate to the left arm, neck, back or shoulder blade area;
- The pain does not go away after taking nitroglycerin;
- Pale skin, cold sweat;
- Fainting, up to loss of consciousness;
Myocardial infarction does not always manifest itself with a typical clinical picture. A person may only feel discomfort in the chest or interruptions in the functioning of the heart. In some cases there is no pain at all. This is the so-called “painless form of myocardial infarction,” which a person can find out about completely by accident, for example, while undergoing a regular medical examination. In addition, there are atypical cases of myocardial infarction, when the disease manifests itself as difficulty breathing with shortness of breath or abdominal pain. Such cases are especially difficult to diagnose.
Reasons for the development of the disease
Heart attack is an acute form of IHD (coronary artery disease). In the vast majority of cases (more than 95 percent), the cause of the disease is atherosclerotic damage to the arteries. This, in turn, provokes a narrowing of the lumen. Quite often, doctors record cases where atherosclerosis is combined with acute thrombosis of a part of the heart that has already been affected. All this leads to a complete (or partial) cessation of blood supply to the heart.
A heart attack can also develop due to the following diseases and factors:
- Diabetes.
- High pressure.
- Obesity and poor nutrition.
- Constant stress, depression and other nervous and mental illnesses.
- Constant use of cigarettes and alcoholic beverages. They also provoke symptoms of myocardial infarction.
Features of making a prognosis for a heart attack
The peculiarity is that only after the acute period of the disease has passed, the doctor can give a positive prognosis. If the patient has some complications, then experts usually give a negative prognosis.
A heart attack itself is a very serious and in many cases fatal disease. There is a high probability of various complications occurring. In most cases, death occurs within the first 24 hours after the attack occurs. When more than half of the entire area of the myocardium is damaged, the heart can no longer function normally, resulting in the rapid development of cardiogenic shock and death. Even if the myocardium is damaged by 40 percent or less, the heart may not be able to cope with sudden loads, and severe complications appear, one of which is heart failure.