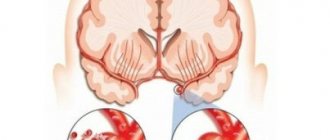
What is a stroke
The essence of a stroke is the cessation of blood supply and functioning of a part of the brain as a result of damage to a vessel.
The larger the affected area, the more severe the stroke. Necrosis of a portion of the brain substance is called an infarction [3]. There is a high risk of death in the first few hours, and then in the period up to 28 days after a vascular accident. The annual mortality rate from stroke in the Russian Federation is 374 cases per 100,000 [10]. In 2018, 35% of patients died in the acute period of stroke; by the end of the first year, this figure increases by 15%, and in general, in the first 5 years, the mortality rate of strokes is 44% [11]. The mortality rate from stroke was 92.9 per 100,000 population, and the hospital mortality rate was 19.1% [5].
Long-term disability is most likely for patients who have suffered a stroke. The prevalence of primary disability due to stroke in 2018 was 3.2 per 10 thousand population [2]. Of these, 31% need constant care, 20% have severe mobility limitations, and only 8% return to work [3]. The prevalence of recurrent strokes in 2014 was 0.79%, of which ischemic
strokes account for 87.5% [9].
Speech rehabilitation after a stroke in an elderly person
After an attack, an elderly patient may lose his previous ability to speak. This is a big blow to the mental health of any of us, and even more so for an elderly person. If such problems do affect you, they must be eliminated as soon as possible.
Rehabilitation after a stroke at this phase requires special actions. Speech pathologies (aphasia) are divided into several types:
- Motor type speech disorder.
An elderly person hears and understands well the speech of others, but due to severe damage to the speech centers, he cannot independently express his thoughts in words.
- Speech disorder of sensory type.
A serious pathology arising from damage to Wernicke's center. An elderly person hears and repeats words, but does not understand their meaning.
Rehabilitation of speech functions must be quick and competent; due to the inability to express their thoughts, an elderly person’s psyche suffers and their moral state deteriorates. It is important that relatives or medical workers should be the first to take the initiative in communication.
For the best effect from the rehabilitation of speech skills, caregivers or loved ones must follow the main rules:
- An elderly patient cannot be left alone and isolated from people; communication must be constant.
- If the patient cannot finish a phrase or word due to damage to the speech center, you cannot help and finish speaking for him. At the same time, you must focus all your attention on what he is saying.
- In especially severe cases, it is recommended to learn to express thoughts with gestures or other communication methods.
- It is necessary to perform exercises for the muscles of the tongue together with the patient.
- For rehabilitation of an elderly person after a stroke, it is very important to find constant contact with the patient and maintain a dialogue on any topic that interests him.
It is ideal if you seek professional help from a speech therapist-aphasiologist. All rehabilitation should take place under his leadership.
Causes of stroke
Depending on the cause of cerebrovascular accident, ischemic and hemorrhagic strokes are distinguished.
Ischemic stroke occurs as a result of blockage of cerebral vessels by a blood clot, when gradually less and less blood flows to an area of the brain. Hemorrhagic stroke develops as a result of rupture of a vessel and hemorrhage in the brain tissue, as a result of which the blood supply to its area abruptly stops. Hemorrhage can be into the subarachnoid space (SAS) or directly into the cerebral substance (ICH). The ratio of ischemic and hemorrhagic strokes is 4-5:1 [4].
Pathologically, a stroke can be cardioembolic, lacunar, atherothrombotic, or another, including unknown, etiology (TOAST classification) [10].
Predisposing factors:
- men from 45 to 59 years old;
- age 70 years and older (for both sexes) [4];
- arterial hypertension;
- atrial fibrillation;
- atherosclerosis of cerebral vessels;
- coagulopathy, thrombophilia, anemia;
- arteriovenous malformations;
- osteochondrosis with damage to the vertebral artery;
- brain tumors;
- dyslipoproteinemia;
- obesity;
- diabetes;
- intermittent claudication;
- mechanical prostheses of heart valves and blood vessels;
- IHD, myocardial infarction less than 6 months before the stroke;
- other cardiac diseases;
- smoking, alcoholism;
- family history of stroke;
- sedentary lifestyle;
- stress [1, 3].
A set of measures to restore the hand after a stroke
Restoration of hand motor skills after a stroke occurs under the supervision of physiotherapists. The list of measures includes procedures in different areas:
- physical rehabilitation therapy;
- drug treatment;
- psychological counseling.
Physical rehabilitation therapy
Physical rehabilitation is a critical part of restoring arm movement after a stroke. It involves doctors of various specializations, but primarily physiotherapists, neurologists and rehabilitation specialists. Treatment is aimed at developing and strengthening everyday motor abilities.
The process uses:
- physical therapy and gymnastics
: physical exercises on the arm - from the simplest gradually to more complex, developing fine motor skills; - action and observation therapy
- during these procedures, the patient watches another person performing some actions with his hand (in person or on video), and then repeats after him. The method triggers the work of similar areas of the brain, and this helps restore motor skills of the hand; - mirror therapy method
- within the framework of this rehabilitation technique, a mirror is placed between the patient’s hands in such a way that the image of the movement of the healthy limb creates the illusion of the same normal movement of the affected arm; - tekar therapy
- radio wave exposure to the body to produce endogenous heat. This helps reduce pain and speed up the tissue healing process; - massage techniques
; - acupuncture, modeling
from dough, plasticine or clay; - hydrotherapy methods
: hydromassage baths, contrast and circular showers.
The rehabilitation department has an occupational therapy department and a neuromotor department for the upper limbs. Robotic technologies are used here, including virtual reality. Neuromotor rehabilitation using such high-tech systems is a modern method of restoring hand motor abilities.
The greatest effect is achieved when the doctor competently combines all these methods. In this case, the specialist must first assess the extent to which the patient’s condition allows him to undergo these measures.
Drug treatment
In most cases, rehabilitation of the hand after a stroke requires drug treatment. However, it must be strictly under the supervision of the attending physician.
There are no universal dosages and regimens; each patient needs his own therapy. To make a decision about which drugs and in what doses the patient needs, the specialist studies all available information about him. In particular, medical history, anamnesis, data on clinical manifestations, results of previous examinations and tests.
The doctor may also change your medication regimen during treatment if he has reason to believe that the current dosage is ineffective or insufficient. The basis is new biometric data, information from the patient’s daily records (“diary of a stroke patient”). First of all, we are talking about the dynamics of blood pressure, heart rate, as well as side effects from medications.
Types of drug therapy that are used to restore limb activity after a stroke:
- intramuscular and intravenous injections
, which are aimed at increasing vascular activity and strengthening neurons. These include Botox injections, which significantly reduce muscle spasticity; - lymphotropic drugs
, which are injected directly into the lymphatic system so that the active substance gets into the arm faster; - analgesics
(to reduce pain in the arm),
muscle relaxants
(to relax the muscles of the limb),
anticoagulants
(to prevent the formation of blood clots),
antidepressants
(to treat depression that has developed due to illness) and other drugs, including antibiotics, vitamins and potent drugs - of necessity.
Psychological counseling
The patient’s internal state greatly influences the process and result of restoring the activity of the arms and legs.
Rehabilitation in a specialized center forces a person to change his usual way of life: he distances himself from society, loses independence and independence even in everyday worries. This cannot but affect the psychological state and leads, at a minimum, to discomfort, and at most to the development of depression.
The patient needs understanding, respect and care, but may also experience anger and powerlessness due to loss of control over his own body. To deal with this, a psychotherapist is needed. He will develop the correct technique for working with the emotional state and select a communication method for the family. The doctor will also prescribe pharmaceutical treatment to the patient if it is necessary and fits into the overall drug treatment plan.
Signs of an incipient stroke
The onset of a hemorrhagic stroke is characterized by the following symptoms:
- severe headache;
- increased blood pressure;
- vomit;
- dizziness;
- loss of consciousness;
- weakness in the limbs;
- visual impairment;
- seizures [1].
The onset of ischemic stroke is gradual; within an hour, some of the following symptoms appear:
- facial asymmetry, numbness;
- difficulty speaking – incoherent, impaired understanding;
- double vision, visual disturbances;
- headache;
- numbness, limited mobility in the limbs, often on one side;
- dizziness, imbalance, staggering, staggering gait;
- confusion with disorientation, subsequently there may be loss of consciousness [3].
If one or more of these signs appear, you should:
- Sit the patient down, providing access to fresh air.
- Call emergency medical help immediately.
- If the patient is conscious and able to chew and swallow, give him one aspirin tablet.
The patient must be hospitalized in a neurological or neurosurgical department, where stroke treatment will be carried out. The sooner the patient is in the hospital, the more effective the therapy.
Disorders after right-sided stroke
Apoplexy on the right side of the brain can cause disturbances in:
- establishing connections;
- motor activity;
- vision and touch;
- thinking;
- perception;
- behavior.
With a right-sided stroke, pathological phenomena usually do not affect the person’s ability to speak. He also most often understands the information he hears and sees. However, the patient may have problems initiating and maintaining conversations. It is difficult for him to consistently express his thoughts, since he cannot correctly formulate the order of speech structures. Often the victim’s speech is perceived as nonsense. A person has problems writing words and sentences, making spelling and lexical errors, and not correctly connecting individual elements of a phrase.
With right-sided brain damage, a person may have problems with motor activity. Paralysis or paresis may occur. The patient feels muscle weakness on the left side of the body. A characteristic phenomenon is the inability to maintain balance. A common consequence of right-sided stroke is loss of the ability to plan the sequence of complex motor acts. A symptom of the disease is poor coordination of movements. Muscle tone may be too high (spasticity) or too low (flaccidity). The patient indicates constant physical fatigue and reduced endurance. Movements are performed at too fast a pace; individual motor acts are characterized by impulsiveness and inappropriateness.
A person may have problems in the sensory system. There is either increased sensitivity to touch or decreased or loss of sensation on the left side of the body. Deterioration or loss of left-sided vision occurs. The patient can see things on the right side better. Ignoring objects located on the left and the phenomenon of tunnel vision are detected. The victim indicates double vision or blurring of visible objects. Nystagmus is often recorded - uncontrolled eye movements. A characteristic symptom is impaired perception of distance and depth: the patient has difficulty judging how far or deep something is.
A typical sign of a right-sided stroke is being easily distractible. Although there is no problem concentrating on a given stimulus, the person has difficulty maintaining attention and is unable to complete tasks that require prolonged concentration on a topic. Difficulties arise with remembering and storing received information, and there are problems with learning new material. A standard symptom of damage to the right hemisphere of the brain is impulsiveness of judgment: the patient often makes hasty conclusions without subjecting the information to the required analysis.
The consequences of a stroke are disorientation in time: five minutes seem like an hour to the patient. There is confusion regarding the current day, month, year, time of day. He cannot recognize the time on the watch. It is difficult for the patient to follow the established daily routine.
Disorientation in space may appear: a person cannot indicate the place where he is, does not know in which direction he needs to go. He easily gets lost even while on well-explored streets. Can't show where his home is. There are problems estimating the distance, size and position of an object.
A common sign of stroke on the right side of the brain is meaningless speech persistence: the patient repeats the same thing over and over again. It is not easy for him to isolate and process important components from the flow of information. Sequence of actions suffers: the individual is unable to complete tasks in the correct order. A person cannot plan events, draw correct conclusions and make logical decisions. He gets lost when conducting monetary transactions, is unable to solve simple mathematical problems, or dial a phone number without errors.
The sphere of perception undergoes changes - awareness of one’s own body, the environment and other people. The patient has problems with self-care. He has difficulty dressing, brushing his teeth, bathing, and combing his hair. Sometimes the patient indicates that the left arm or leg seems to belong to someone else. He is unable to understand the tone of voice or facial expression of the interlocutor. There are problems with separating a part from a whole object, for example, a door handle from a door.
Behavioral disorders are recorded. A person cries or laughs at inappropriate times (emotional lability). It shows a lack of interest in previously enjoyable activities (apathy). Doesn't want to complete the task (lack of motivation). He fails to start the process of solving the problem (initiation).
After a right-sided stroke, typical manifestations are changes in the characterological portrait. The patient is irritable and nervous. Has problems controlling impulses and emotions, displaying a short temper. He is distinguished by a pronounced depressive mood. Anxiety and anxiety intensify at night. He is self-oriented (egocentric). Shows a lack of sensitivity to the experiences of others.
Often the victim tries to do something without outside help. An additional threat is posed by lack of awareness of the consequences of stroke. The patient does not recognize the defects that have arisen and overestimates his own abilities. In such a situation, the person should not be left unattended to prevent actions that could cause harm.
Symptoms of a stroke
Stroke leads to various brain injuries, depending on the location of the lesion and the pathological type of cerebrovascular accident:
- disturbances of movement in the limbs: from restrictions (paresis) to complete paralysis. When the lesion is localized on the right, the left limbs suffer; with a left-sided lesion, right hemiparesis is formed; in some cases, movements in all limbs may stop (tetraparesis or double hemiparesis);
- sensory disturbances on one or both sides;
- speech disorders (dysarthria - poor articulation; aphasia - inability to pronounce and understand words, write and read);
- ataxia (impaired coordination of movements, “overshooting”, unsteadiness, imbalance, tremor);
- visual impairment: from blindness to double vision and gaze paresis;
- hearing impairment and dizziness;
- violation of mental functions (consciousness, thinking, attention, memory, will, behavior);
- paresis of the soft palate and pharynx, swallowing disorders;
- disorders of urination and defecation;
- depression of respiration and vascular tone;
- increased intracranial pressure;
- patients complain of headaches, vomiting, hiccups, yawning, shoulder pain;
- consciousness is gradually depressed to the point of coma [1, 3].
Causes of death may include cerebral edema, pneumonia, heart failure, and recurrent stroke. In severe cases, “locked-in syndrome” may develop: the patient is conscious, but cannot move, swallow or speak [3].
What does recovery depend on?
Factors that reduce the chance of recovery:
- Diseases of the joints of a dystrophic nature;
- Inability to feel your own body;
- Disorders of consciousness and thinking;
- The degree of muscle hypotonia;
- The severity of damage to certain brain structures.
The patient’s complete recovery depends not only on timely assistance and correctly prescribed therapy, but also on how good care is provided. If a person is immobilized due to paralysis, then bedsore prevention is mandatory to avoid deterioration of the general condition and infection. Massage begins from the first days of treatment. The diet must be properly formulated so that the patient receives all the necessary nutrients. If independent food intake is not possible, the patient is fed through a special tube. Moral support and attention from medical staff and relatives are very important. The victim’s apathy or depression should not be perceived as a conscious refusal to help.
Consequences of a stroke
There are transient ischemic attack (less than a day), minor stroke (from 1 day to 3 weeks) and stroke with persistent residual effects. The consequences of a stroke are expressed mainly in motor and sensory disorders, the formation of muscle contractures (pronounced constant restriction of movements in the joints), speech and swallowing disorders. General symptoms may also remain, including confusion, disturbances in thinking, will, and emotional regulation. Complications can develop: from epilepsy to bedsores, encephalopathy and anxiety-depressive syndrome [1, 3].
Dangerous consequences
Complications that appear after an ischemic stroke on the left side depend on the location of the lesion on the cerebral hemisphere (hemisphere). Let us consider the consequences characteristic of left-sided ischemic stroke that may persist after treatment and rehabilitation.
Physical activity
If the motor centers are affected, then a person develops:
- sagging of half the face (half-lowered eyelid, swollen cheek, distorted mouth);
- decreased muscle strength (in severe cases, paralysis occurs);
- impaired sensitivity (the skin of the affected limbs reacts poorly to external irritations).
Difficulty in movement and sensory disturbances in left-sided cerebral ischemia occur on the right side of the body.
Internal organs
Ischemic stroke in the left hemisphere is not limited only to disruption of the innervation of muscles and skin; organs located on the right (kidney, lung, and partially the digestive tract) are affected.
The degree of change in the functioning of organs depends on how severe the innervation disorder is:
- Easy. The deviation is minor, the functions are preserved.
- Average. There is a decrease in organ functions. The patient's right side of the chest lags behind when breathing, and there may be problems with digestion and bowel movements.
- Heavy. Paralysis and complete cessation of functions occurs.
Stopping the functioning of the lung, liver or kidney is considered one of the dangerous consequences of an ischemic stroke on the left side. It is noteworthy that the severity of external and internal deviations are not related to each other. People may be paralyzed on the right side of the body, but the functionality of the internal organs is not impaired.
Speech
The centers responsible for speech are on the left. Depending on the area of damage to the hemisphere, the victim will have:
- Difficulty in grammatically constructing sentences. People begin to speak in short, simple phrases reminiscent of telegraph style. Intonation disappears. This occurs when the anterior lobes of the hemisphere are affected.
- Problems with sounds. The patient confuses sounds, placing them incorrectly in words. This is typical for stroke of the posterior lobe.
- Problems with the perception of spoken language. A person hears words addressed to him, but cannot associate them with known concepts. Similar problems arise when trying to read text. Such patients speak mainly in prepositions or conjunctions, with long, but uninformative phrases. The disorder appears with ischemia of the temporal lobe.
- Complete aphasia. Extensive ischemic stroke of the left hemisphere is often accompanied by a complete loss of the ability to speak and perceive speech.
There is also false aphasia, when the impairment of the ability to speak is associated with paralysis of the muscles of the tongue or larynx. Such people understand what is being said to them and can adequately formulate their thoughts, but when they try to speak, the result is slurred, blurred speech or isolated sounds.
Ability to think
The left side of the brain marks the ability for logical thinking. The consequence of a left-sided stroke can be:
- loss of ability to remember numbers (dates, phone numbers);
- inability to perform simple arithmetic operations in the mind (add, multiply);
- difficulty in perceiving abstract concepts;
- difficulty when trying to draw conclusions from the information received;
- difficulty making independent decisions.
Such people do not always understand their condition and often commit stupid or ridiculous actions. They are uncritical of their actions.
- Stroke on the left side: consequences and features of recovery. How long do people live with this diagnosis?
Psycho-emotional sphere
Another consequence of a stroke in the left hemisphere is a change in the psyche. The patient may experience depression associated with limited mobility and dependence on the care of loved ones. The person becomes:
- Maudlin. He often feels sorry for himself and cries, saying that he has become a burden to his relatives.
- Restless. Anxiety and fear appear associated with the fear of being left without outside help.
- Aggressive. The patient finds fault with others, conflicts over trifles. May complain to strangers about poor feeding or care, attracting attention to himself.
- Irritable. Such people are dissatisfied with everything, find fault with little things, and often accuse loved ones of waiting for their death.
Often, those who have suffered a cerebral infarction experience sudden mood swings when, during a calm conversation, a person becomes angry, starting to throw objects or punch the bed.
Diagnosis of strokes
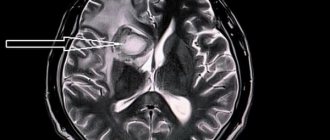
First of all, it is necessary to conduct a detailed neurological examination. Instrumental diagnostic studies and laboratory tests are also prescribed. In case of a stroke, in the first hours, an MRI or CT scan of the brain is performed, if necessary, CT or MR angiography, color Doppler mapping of blood flow, ECG or Holter monitoring, echocardiography as indicated, monitoring of blood pressure, saturation, assessment of the risk of developing bedsores, assessment of swallowing function [ 1, 3, 6].
Tests for stroke
- Complete clinical blood test, including erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR).
- Biochemical blood test with determination of C-reactive protein and homocysteine, glucose level, platelet count, activated partial thromboplastin time, INR.
- Interleukin 10.
- Extended coagulogram.
- Determination of acid-base status.
- General urine analysis.
To prepare for neurosurgical intervention, a blood test is additionally performed for hepatitis, syphilis, HIV, blood group and Rh factor determination.
Diagnosis and treatment
Diagnosing a stroke on the left side begins with a few simple steps:
- Ask the patient to smile or stick out their tongue.
- Raise both hands up.
- Say any phrase, say your name or date.
During a stroke, a person's face will be distorted and movements will be limited or completely impossible. Speech is usually slurred and consciousness is confused.
- Periods of stroke: main stages, critical moments, recovery, prognosis
Further diagnostic measures are carried out by a neurologist in the hospital. He usually prescribes a number of procedures:
- general blood test and biochemistry;
- studying the composition of urine;
- study of coagulation;
- Magnetic resonance imaging;
- CT scan;
- Ultrasound of the heart;
- electrocardiogram.
Blood pressure, pulse, respiratory rate and temperature are also constantly measured.
Based on the results of the examination, a plan for further action is drawn up.
Therapy begins even before the doctor arrives. What should be done?
- Place the patient so that his head is at an angle of at least 30° above the surface of the bed. To do this, you need to place pillows under his head and shoulders.
- Open the windows to ensure air flow.
- Unfasten your clothes and remove your belt.
- Measure the pressure.
If the patient begins to vomit, you need to turn his head so that the vomit does not enter the respiratory tract.
Already in the hospital, the doctor will decide how to proceed. Treatment of ischemic stroke of the left hemisphere of the brain has several goals:
- normalize blood pressure;
- improve the functioning of the heart and respiratory system;
- reduce body temperature to normal;
- prevent or remove cerebral edema;
- restore normal blood circulation;
- improve metabolic processes;
- protect the patient from the development of complications;
- eliminate the manifestations of the disease.
Sometimes there is a need for specific therapy, the purpose of which is to destroy blood clots.
Treatment begins with taking medications:
- Question: Childbirth after a stroke. Is it possible to give birth after a stroke?
Fibrinolytics. If taken within the first 3 hours after a stroke, the risk of complete paralysis is minimized.
Anticoagulants. There are direct and indirect actions. Appointed in 2 weeks.
Antiplatelet agents. These are drugs that prevent the formation of new blood clots.
Vasoactive agents. Strengthen the walls of blood vessels and improve blood circulation. They have an antispasmodic effect.
Antihypertensive drugs. These include ACE inhibitors and calcium antagonists. Reduce blood pressure.
Neuroprotectors. They improve blood circulation in the brain and normalize its functioning.
Massages, physiotherapeutic procedures, and therapeutic exercises are also indicated.
If necessary, the doctor may decide to perform surgery. It is needed if a focus of ischemia is found during the examination. The surgeon expands the damaged vessel or replaces part of it with an implant.
It will take a long time to treat a stroke. After the patient leaves the hospital, a long recovery period will begin. It often takes years.
Stroke treatment
Treatment of stroke is regulated by relevant clinical guidelines and the Procedure for providing medical care to patients with acute cerebrovascular accident. In the first hours, thrombolytic therapy is carried out and subsequently - prevention of thrombus formation. For hemorrhagic stroke, neurosurgery may be performed. They normalize blood pressure, water-electrolyte balance, glucose levels in peripheral blood and urine, support the basic vital functions of the body and prevent complications. Drug therapy is also aimed at improving the affected functions of the nervous system [1, 3, 6].
Consequences
What are the consequences after suffering a stroke on the left side of the body?
The human brain, in particular the cerebellum, is very complex. One of its features is that it is connected to other parts of the body through a special network of neurons. The so-called “nerve threads” that are directed from the right hemisphere can be partially or completely destroyed by hemorrhage, as a result of which the transmission of impulses to the left side of the body worsens or completely stops.
Musculoskeletal disorders
If a stroke develops, in which the left side suffers, one can expect consequences manifested by disturbances in the functioning of the musculoskeletal system:
- Paralysis of the right side - a large proportion of the complex consequences are due to hemorrhagic stroke;
- Hemiparesis, which causes the effect of weakening and drooping of the lateral muscles;
- Dysfunction of various parts of the body, which may persist even after treatment and rehabilitation;
- Articulation impairment;
- Muscular dystrophy is a dangerous consequence of deterioration in controllability of the tongue and, as a result, slurred speech. Many patients begin to communicate only with slurred sounds or small fragments of words.
It should be noted that even if you are completely cured of the disease, after some time a person may complain of numbness of the facial muscles, their convulsive twitching, as well as partial dysfunction.
Behavior and speech disorders
If the stroke affected the left hemisphere of the brain, then in the prognosis doctors often indicate possible problems with logical thinking, as well as oral and written speech:
- Partial or complete loss of language skills;
- Deterioration of speech control;
- Oral and written dyslexia, in which a person begins to confuse not only the words themselves, but also the letters in them;
- Loss of the ability to analyze new information and perceive it correctly;
- While writing or reading, significant difficulties arise. Some people who have had this disease may not even remember how to hold a pen or write letters;
One of the largest and most problematic consequences of pathology can be loss of work due to disability. After all, a patient who could previously quickly and easily perform computational operations and think logically often loses his abilities after an attack. However, even after this you can live quite well: people with disabilities are assigned tasks that they can do.
Emotional disorders
If the left side of the brain was damaged during a stroke, the patient has problems with orientation in space. In addition, he is limited in contact with others due to the manifestation of written and speech dysfunction, and a violation of the analysis of the information received. This condition is somewhat similar to a certain form of autism, as a result of which the person becomes withdrawn.
Experts identify several more characteristic changes in the emotional background:
- The patient loses the ability to correctly correlate the proportions of various objects, as well as the scale of his actions. As a result, people complain about difficulties in doing even simple tasks such as tying their shoes, dialing a phone number, cutting groceries, and more. The reason for this is that it is not possible to correctly assess the shape, parameters and location of an object. In some cases, it is not possible to determine the size of your body;
- A microstroke sometimes leads to the loss of individual body parts, as well as organs;
- Ischemic stroke often causes unconscious performance of various actions, which may result in harm to others;
- Passive behavior;
- A person may not understand why it is necessary to restore the functions of a weakened musculoskeletal system.
If the patient managed to survive the attack, then these are the consequences that become the most terrible. After all, a person does not worry about his own condition, he behaves carefree and, to some extent, complacently. In addition, the clinical picture of the disease (symptoms and defects) is practically unnoticed by them. However, at the same time, he begins to move much more slowly, which is not caused by laziness or a short-term depressive state. In such conditions, the patient needs emergency care.
Stroke rehabilitation
Stroke is a disease in which rehabilitation and care are of the utmost importance.
Recovery from a stroke begins in intensive care, from the moment vital functions are stabilized. A multidisciplinary rehabilitation team works with the patient, which includes a rehabilitation doctor, physical therapist or exercise therapy instructor, speech therapist, massage nurse, physiotherapist and physical therapy nurse, psychologist, occupational therapist, guard and rehabilitation nurse. Diagnosis is carried out using special scales that reflect the degree of dysfunction and limitations in the patient’s activity, the influence of environmental factors on the rehabilitation potential. The rehabilitation process continues throughout the entire period of hospitalization. At the second stage, patients with serious disabilities who are unable to move independently are sent to rehabilitation departments or specialized hospitals. Those who can walk independently or with support are rehabilitated in outpatient centers based in clinics and sanatoriums.
The rehabilitation process should not be interrupted, so classes must be continued at home. Of course, there are no high-tech robotic complexes or physiotherapeutic equipment at home, but exercise therapy, massage, and work with a psychologist, speech therapist and occupational therapist are possible. For this purpose, telemedicine technologies are used and visits to rehabilitation specialists are organized.
The individual rehabilitation program includes not only a referral for rehabilitation treatment, but also technical means of rehabilitation. However, usually relatives also have to devote significant physical and financial resources to achieve the best effect [7].
Rehabilitation after a stroke at home
After overcoming the acute period in the hospital, a rehabilitation period begins for a pensioner with a stroke. Relatives need to decide where it is better for an elderly person to undergo a recovery course: at home or in a rehabilitation center.
You may also be interested in the article: How to obtain patronage for an elderly person
If the family has decided to independently care for the patient after a stroke, they need to follow the recommendations of the attending physician and maintain constant contact with specialized specialists: a psychologist, a neurologist, a speech therapist.
At home, a separate place is assigned to a bedridden patient after a stroke. The bed is equipped with an anti-decubitus mattress. A small table is placed nearby, on which essential items are placed: a bottle of water, care products, a table lamp.
Specialists can come to the home 1-2 times a week, work with the patient and teach home methods of conducting developmental activities. The rest of the time, family members carry out the recommended exercises with the pensioner for 10-20 minutes several times a day. During weekly visits, specialists monitor the dynamics of changes, make additions and adjustments.
Motor abilities are restored using a complex of therapeutic exercises. Before performing the exercises, it is advisable for the patient to take a shower or bath to warm up the body. If there are contraindications to taking a bath or other difficulties, the affected areas are warmed with a heating pad. The muscles will be more flexible and there will be no pain.
Examples of gymnastic exercises:
- pulling up while lying on your back, holding the headboard of the bed;
- eye movements left and right, up and down with closed and open eyelids;
- alternately raising the right and left arms and legs;
- bending the knee and grabbing the shin with the hand;
- joint movements of healthy and motionless limbs to the right and left with a rubber ring put on them.
When carrying out therapeutic exercises, the pensioner’s condition is closely monitored. He shouldn't get tired. If such signs are observed, it means that the amount of stress does not correspond to the physical strength of the patient. We need to make an adjustment: reduce the pace and number of exercises.
Speech is restored by memorizing poetry and tongue twisters. At the initial stage, simple children's poems are chosen, which are easier for a pensioner to recite after a stroke. Gradually more complex material is selected.
Looking at family photographs can activate the process of remembering, since it is easier for the patient to recall the past in his memory. An elderly person remembers acquaintances and friends in the images, then the events associated with them. He tries to pronounce the names of the places he has visited, the objects he sees in the images.
Scientists believe that singing has a beneficial effect on people who have suffered a stroke. If they hear singing, sing together with loved ones, speech activity will be restored faster.
For rehabilitation to be successful, an elderly person should not be in a social “vacuum”: you constantly need to communicate with him, talk, ask questions, even if at first he cannot answer them. In this way, the patient’s desire to speak is stimulated, he remembers words and their meaning.
Chess, checkers, and dominoes are used to develop thinking abilities. In a family, even a small child can take part in restoring the health of a grandfather or grandmother by putting together puzzles, mosaics, or playing a board game.
A separate issue is the organization of nutrition for an elderly person after a stroke.
Excluded from use:
- alcoholic drinks;
- fatty and spicy foods;
- coffee, strong tea;
- sweets.
It is advisable to add to the diet:
- drink liquid of at least 1.5 liters. per day;
- increase consumption of fruits and vegetables;
- eat whole grains;
- replace sweets with dried fruits.
Food should consist of useful substances and be easily digestible so that the body is not overloaded.
It is useful to cook boiled vegetables, dishes from lean fish and meat, and porridge with low-fat milk. If there are paresis and problems with swallowing, the patient is fed through a tube with ready-made nutritional mixtures. As soon as the opportunity arises, you need to take the patient for a walk. Staying in the fresh air is good for brain activity, the body receives oxygen and vitamin D, and appetite appears.
You may also be interested in the article: How to choose a private facility for the elderly
The moral atmosphere in the house is of great importance. Patients who receive family support recover faster. If they experience hostility from others or rudeness, the healing process is slowed down. There is no need to criticize and laugh at clumsiness and awkwardness. Only with encouragement will an elderly person develop a strong desire to overcome the disease.
Prevention of strokes
Hereditary predisposition to stroke, the presence of cardiac diseases, pathology of blood vessels and blood composition, age over 40 years, obesity and diabetes require a number of preventive measures:
- Maintaining normal blood pressure, taking antihypertensive drugs as prescribed by a doctor, monitoring blood pressure.
- Maintaining a normal level of physical activity, exercise, walking 30-40 minutes a day (for example, walking the dog).
- Conducting preventive examinations, including a standard set of laboratory parameters. During a preventive examination, the following tests are additionally required: gene diagnosis of CADASIL syndrome using the PCR method, plasma factors of the blood coagulation system, antibodies to prothrombin of the IgG and IgM classes to determine the risk of thrombosis, determination of polymorphisms associated with the risk of arterial hypertension, diabetes mellitus, lipid disorders exchange, in order to identify a predisposition to diseases that increase the risk of stroke, von Willebrand factor (a glycoprotein that ensures the formation of blood clots), complex laboratory tests for preclinical diagnosis of cardiovascular diseases are offered (“ELI-ANKOR-Test-12”, “Cardiorisk”).
- Avoiding chronic and acute stress, maintaining mental hygiene.
- Normalization of weight (BMI <25 kg/m2).
- Healthy eating (for example, Mediterranean diet, limiting salt to 5 5 g/day).
- Quitting smoking and taking psychoactive substances.
- Treatment of diseases that are a risk factor for stroke [8, 11].
Bibliography
- Hemorrhagic stroke in adults: clinical recommendations of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation, 2021. Developers: Association of Neurosurgeons of Russia. - Electronic text. - URB: (access date 08/18/2020).
- Efremova M.D. Stroke as an urgent socio-psychological problem / M.D. Efremova – electronic text//Skif. Questions of student science.- 2021 - No. 2(24) URB: (date of access 08/17/2021) Access mode: Cyberleninka electronic library system. — Text: electronic.
- Ischemic stroke and transient ischemic attack in adults: clinical recommendations of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation, 2021 developers: All-Russian Society of Neurologists, National Association against Stroke, Association of Neurosurgeons of Russia, Association of Neuroanesthesiologists and Neuroreanimatologists, Union of Rehabilitologists of Russia. - Electronic text. - URB: ( access date 08/18/2020).
- Machinsky P.A. Comparative characteristics of incidence rates of ischemic and hemorrhagic stroke in Russia / P.A. Machinsky, N.A. Plotnikova, V.E. Ulyankin [and others] – Direct text.// News of higher educational institutions. Volga region. Medical Sciences.- 2021.- “2(50)-P.112 – 132 DOI 10.21685/2072-3032-2019-2-11.
- Monitoring the implementation of the federal project “Combating Cardiovascular Diseases” - Presentation Department of Organization of Medical Care and Sanatorium Affairs of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation URB: (date of access 08/17/2021).
- Order of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation dated November 15, 2012 N 928n “On approval of the Procedure for providing medical care to patients with acute cerebrovascular accidents.” — URB: (access date 08/17/2021) Access mode: Electronic library system “Garant”. — Text: electronic.
- Order of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation dated July 31, 2021 No. 788n “On approval of the Procedure for organizing medical rehabilitation of adults.” – URB: (date of access 08.17.2021).- Access mode: Electronic library system “Garant”. — Text: electronic.
- Prevention of cerebrovascular accidents: textbook. manual / Compiled by: L.B. Novikova, A.P. Akopyan. – Ufa: Publishing house of the State Budgetary Educational Institution of Higher Professional Education BSMU of the Ministry of Health of Russia, 2015.-58 p.
- Stakhovskaya L.V. Analysis of epidemiological indicators of recurrent strokes in the regions of the Russian Federation (based on the results of the territorial-population register 2009-2014) / L.V. Stakhovskaya, O.A. Klochikhina, M.D., Bogatyreva, etc.]. CONSILIUM MEDICUM, 2021, vol. 5, no. 9, p. 8-11.
- Shamalov N. A. Analysis of the dynamics of the main types of stroke and pathogenetic variants of ischemic stroke / N. A Shamalov, L. V Stakhovskaya, O. A Klochikhina [and others]. Direct text. // Journal of Neurology and Psychiatry named after. S.S. Korsakov. Special issues. 2019;119(3-2):5-10. doi.org/10.17116/jnevro20191190325.
- 1RRE Electronic edition. Updated daily Stroke Day is celebrated on October 29, 2021 URB: (accessed 08/17/2021).
Author:
Pugonina Tatyana Alekseevna, Therapist
Ischemic stroke: symptoms, consequences, treatment - MEDSI
Table of contents
- Forms of ischemic stroke
- Causes of ischemic stroke
- Main symptoms
- Diagnosis of stroke
- Ischemic cerebral stroke - treatment
- Nutrition after stroke
- Rehabilitation measures after a stroke
- Prevention and prognosis of ischemic cerebral stroke
- Advantages of carrying out the procedure at MEDSI
Ischemic stroke
is a condition that occurs against the background of damage to brain tissue due to impaired blood circulation in its vessels and is accompanied by various neurological signs. As a result of its appearance, the functioning of parts of the brain is disrupted (depending on the focus of the disease).
Of the three existing types of strokes, ischemic stroke is the most common, occurring in 80% of cases. The other 20% are subarachnoid hemorrhage and hemorrhagic stroke.
Stroke has especially dangerous consequences: impaired cognitive and neurological functions, paralysis, problems with oral and written speech, etc.
Forms of ischemic stroke
There are several classifications of stroke: by reason of occurrence, by the degree of damage to brain tissue and by severity.
- Reasons for appearance:
- Lacunar – the syndrome affects a tissue area up to 15 mm in size and is accompanied by a small number of neurological symptoms
- Thromboembolic - occurs due to blockage of a blood vessel by a thrombus
- Hemodynamic - in this case, vascular spasm is prolonged, and brain cells stop receiving the necessary nutrients
- Transient attack - the lesion is small, and neurological signs quickly disappear
- Small – brain functions are restored within 21 days
- Progressive - its neurological signs do not appear immediately and accumulate over time; after treatment, some of these symptoms may persist
- Extensive - signs of its appearance are recorded for a long time, including after treatment
- Mild – symptoms are mild and disappear within a few days
- Medium – signs appear, but are not accompanied by a disorder of consciousness
- Severe – in this case consciousness is depressed and brain tissue is severely damaged
Causes of ischemic stroke
The causes of stroke include diseases and dysfunctions of the body such as:
- Hypertension
- Cardiac ischemia
- Arrhythmia
- Bleeding disorder
- Various diseases of the vascular system
- Pathologies of blood vessels of the neck and head
- Migraine
- Kidney diseases
- Diabetes
- Atherosclerosis
- Obesity
- Thrombophlebitis
The following people are also at risk:
- Heavy and frequent smokers
- Experiencing constant psycho-emotional overload
- Those who have suffered blood loss
- Suffering from chronic headaches
- Excessive alcohol drinkers
- Regular overeaters
Given the above factors, men and women over 50 years of age are especially at risk of ischemic stroke.
Main symptoms
Signs of ischemic stroke consist of general signs characteristic of all types of stroke and symptoms that reflect the nature and location of damage to brain tissue.
- General symptoms:
- Fever
- Vomiting and nausea
- Loss of consciousness
- Headache
- Problems with orientation in space
- Inability to move limbs or move incorrectly
- Dizziness
- Speech difficulties - problems with reading, speaking, understanding what is said, writing, counting
- Visual dysfunction – sudden deterioration, double vision
- Swallowing dysfunction
- Inability to perform simple everyday activities (comb your hair, etc.)
- The occurrence of amnesia and other serious memory impairments
- If the left hemisphere is affected, paralysis may also occur
- With damage to the temporal lobe - depression, impairment of cognitive and logical functions
Diagnosis of stroke
A qualified neurologist can determine the presence of a stroke quite quickly. But in order to prescribe the most effective treatment, he needs to identify both the localization of the lesion and the causes of its appearance, concomitant diseases. For this, the following diagnostic procedures and equipment are used:
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and magnetic resonance angiography
- Doppler ultrasound of cerebral vessels
- Computed tomography (CT)
- Cerebral angiography using contrast agent
- Blood biochemistry for sugar and cholesterol
- ECHO-KG
- Electroencephalogram
- ECG
- Coagulogram (blood clotting test)
Ischemic cerebral stroke - treatment
Since this phenomenon disrupts brain function, ischemic stroke requires treatment that will be complex and long-term. Otherwise, swelling, thromboembolism and other negative consequences may occur.
- A patient in acute condition is sent to the ward or intensive care unit
- First of all, medical personnel restore the functioning of the respiratory and circulatory systems
- If necessary, surgery may be performed to remove the blood clot.
- Medicines can also be used to liquefy the clot.
- In general, in the process of treating a patient, the following types of drugs are used: anticoagulants, blood thinners, vasoactive drugs, antiplatelet agents, angioprotectors, neurotrophics, antioxidants
Remember, all medications must be prescribed by a doctor. Self-medication is dangerous!
Nutrition after stroke
If the patient is diagnosed with ischemic stroke, treatment should not be limited to hospital stay. An important part of the fight against the consequences of a stroke is proper nutrition and rehabilitation measures.
It is necessary to include in the diet such products as:
- Porridge
- Lean fish, meat and seafood (boiled)
- Vegetables (cabbage, spinach, beets, etc.)
- Berries (blueberries, cranberries, etc.)
- Fruits
- Dairy
- Vegetable oil
The following should be strictly avoided:
- Fried
- Smoked
- Fat
- Dishes with a lot of spices
- Flour products
It is also necessary to reduce the amount of salt in food.
It is important to remember that after a stroke you need to get rid of bad habits (smoking, drinking alcohol).
Rehabilitation measures after a stroke
Since a stroke can lead to many negative consequences (impaired speech skills, memory, cognitive functions, paralysis), it is better to undergo rehabilitation procedures in a specialized institution (sanatorium). To restore a number of functions, you need to contact professionals:
- Speech therapist – for restoration of speech and graphic skills
- Physical therapy specialist – to improve coordination and motor function
- Specialist in physiotherapeutic procedures (electrical stimulation, reflexology, etc.) - to accelerate the regeneration of nerve tissue and improve blood supply
- Neurologists and psychologists – to eliminate cognitive and emotional disorders, restore memory
Prevention and prognosis of ischemic cerebral stroke
If concomitant diseases or other risk factors persist, ischemic stroke may recur. Therefore it is necessary:
- Regularly undergo preventive examinations of the circulatory system and heart
- Treat hypertension and other concomitant diseases in a timely manner
- Contact a doctor immediately if you feel unwell
- Adhere to a healthy lifestyle and proper nutrition
According to statistics, the occurrence of a stroke ends in death in the first weeks in 25% of cases, in 50% of cases the patient lives after a stroke for about 5 years, the remaining 25% can live at least 10 years.
Advantages of carrying out the procedure at MEDSI
- A full range of services for the management of patients with stroke: from stabilizing the patient to prescribing rehabilitation procedures and therapy
- MEDSI specialists are candidates of medical sciences, have high qualification categories and have extensive experience working with stroke patients
- Experienced surgeons of a specialized department perform precise operations on blood vessels through mini-accesses using the latest expert-level equipment
- All studies and procedures are in one place
- MEDSI doctors provide follow-up care for patients who have suffered a stroke, including at home
- At the first signs of a stroke in you or your relatives, call 8 (495) 7-800-500