The term stroke is understood as an acute disorder of cerebral circulation with a persistent decrease or complete loss of certain body functions. A stroke can be a focal stroke (micro-stroke) or extensive, in which paresis can occur, most often of one half of the body. A condition in which a person experiences weakness or complete lack of movement in the left or right half of the body is called hemiparesis. Paralysis of the left side or paralysis of the right side during a stroke often occurs as a result of rupture of a cerebral artery, if qualified help is not sought in a timely manner.
Recovery from paralysis after stroke
Paralysis after a stroke indicates that ischemia or even necrosis of a large area of the cerebral cortex has occurred. If paralysis develops, the victim needs immediate, highly qualified medical care, which can be obtained at the Clinical Institute of the Brain, which employs highly qualified neurological and vascular specialists. Treatment largely depends on topical diagnosis and determination of the form of stroke. Treatment can be carried out conservatively or operatively (surgically).
Often, a paralyzed person after a stroke needs surgery, which consists of making a burr hole in the skull to avoid serious complications associated with compression and dislocation of the brain.
Symptoms
The main symptoms by which you can determine the beginning of the process of brain damage:
- Decreased sensitivity of the limbs. Often there is a strong tingling sensation, accompanied by poor health, numbness in the arm or leg.
- Unnatural position of the corners of the mouth, the face seems skewed, the lower eyelid most often droops on one side.
- Loss of control over oneself, orientation in space.
- Decreased vision, unfocused gaze.
- Pain in the head, often increasing, dizziness.
- Severe vomiting, convulsions.
- Noticeable impairment of speech function.
It is important to notice stroke symptoms within three to six hours of their onset. If you seek help in a timely manner, you can avoid the development of irreversible changes in the brain.
A person can independently diagnose a stroke on the left side of the brain based on the following signs:
- How long do people live after a stroke, how do the consequences and age affect life expectancy?
- nausea and vomiting;
- numbness of the limbs;
- blurred vision;
- disorientation .
The presence of even two signs is a reason to consult a doctor.
If you notice a person's lack of coordination or speech, you should ask him to smile. In this case, it immediately becomes clear that a stroke has occurred - the corners of the lips will rise unevenly. Another way to diagnose a pathological condition before doctors arrive is to ask the person to stick out his tongue. The tip of the tongue will be directed to the side. Also, the patient will not be able to raise his arms up.
Why can our articles be trusted?
We make health information clear, accessible and relevant.
- All articles are checked by practicing doctors.
- We take scientific literature and the latest research as a basis.
- We publish detailed articles that answer all questions.
If at least one problem is detected, you need to call an ambulance.
All symptoms that can be detected with ischemic stroke of the left hemisphere are divided into three groups:
- General signs. Symptoms occur when the meninges become inflamed and when blood pressure increases. With the development of left-sided hemisphere damage, there are practically no indicators by which one can immediately understand that pathology has arisen. If the stroke is extensive and the necrosis comes into contact with the meninges, then the signs become more noticeable, especially impaired consciousness, vomiting and nausea, and headache.
- Vegetative symptoms, expressed in heartbeat disturbances, pressure fluctuations. Skin color changes. At the same time, a person often begins to feel the fear of death and tries to fight it.
- Signs of the neurological picture of the disease, which appear depending on the size of the inflammatory focus and its location. Paralysis of the limbs, impaired sensitivity, loss of memory, vision, and hearing occurs.
All these signs can be detected immediately after the development of a stroke. Other symptoms often appear during the recovery stage.
First aid
This involves hospitalizing the victim as quickly as possible. To do this, when identifying signs of a stroke, you must first report the incident to the emergency medical service and call a specialized team. It is necessary to provide the patient with rest, a supine position and an influx of fresh air. At home, it is unlikely that anything can be done to prevent the progression of a stroke. Only early initiation of drug therapy or surgery can prevent serious health consequences from a stroke.
Difficulties in treatment and recovery after stroke with left-sided paralysis
Patients who have suffered a stroke, which resulted in left-sided paralysis, are passive in relation to rehabilitation measures, since their perception of their own body is distorted. They do not feel motor disturbances, do not strive for recovery, and the period of immobility is more protracted. With such indifference of the patient, rehabilitation is difficult, the recovery period after a stroke is too long, and the effectiveness of the measures is reduced because of this.
For cognitive impairment, nootropil, cerebrolysin, gliatilin, as well as some antidepressants without sedation, such as fluoxetine, imipramine, are prescribed.
Rehabilitation measures after a stroke consist of massages, therapeutic exercises, and physiotherapeutic procedures. Invaluable help can be provided by loved ones who will constantly encourage the patient to undergo treatment. A right-sided stroke requires the mandatory intervention of a psychotherapist.
Diagnosis of ischemic stroke
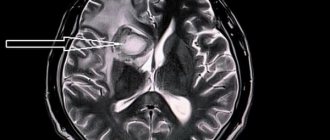
If an ischemic stroke is suspected at the Yusupov Hospital, the patient undergoes laboratory tests and is examined using instrumental methods using modern equipment from leading companies in Europe, the USA and Japan. The results of the examination allow us to make an accurate diagnosis and prescribe adequate therapy. In order to determine the type of stroke and determine whether the left or right side of the brain is affected, computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging is performed. Immediately after neuroimaging of a stroke, the following studies are performed:
- electrocardiography;
- ultrasonography;
- blood tests.
The patient is then examined by an ophthalmologist and an endocrinologist. Later, additional diagnostic procedures are performed:
- X-ray of the skull;
- chest x-ray;
- electroencephalogram;
- echocardiography.
After an accurate diagnosis is made, treatment for ischemic stroke is prescribed.
Home care for patients after a stroke
No matter how severe the stroke may be, with proper treatment and the patient’s active participation in rehabilitation procedures, most of the body’s functions are restored.
The patient needs a full range of procedures for rehabilitation, including therapeutic exercises and massage.
Turn a bedridden patient every two hours to prevent the formation of bedsores. Properly position the patient's paralyzed arm and leg:
In the supine position:
1. To prevent the development of stiffness in the shoulder joint and the appearance of pain in it:
- Place a stool next to the bed, on the paralyzed side, and place a large pillow on it so that the corner of the pillow is under the patient’s shoulder joint.
- Extend your client's arm at the elbow. Place it palm up, straighten your fingers, apply a splint and bandage it to your arm. The longueta should reach the middle of the forearm.
- Move the patient's arm to the side 90° (maintaining a palm-up position) and place it on a pillow so that the shoulder joint and the entire arm are at the same level horizontally.
- Place a roller between your arm and chest so as to fix your arm in the correct position; if necessary, place a 0.5 kg bag of sand on the roller.
2. Bend the patient’s paralyzed leg at the knee 15-20°. Place a cushion under your knee.
3. Place your foot in the middle position between flexion and extension and secure it with a stand.
In the “healthy side” position:
- Bend the patient’s paralyzed arm at the shoulder and elbow joints and place a pillow under it;
- bend the paralyzed leg at the hip, knee and ankle joints and place a pillow under it.
In the “lying on the paralyzed side” position:
- tilt the patient's head down slightly;
- Stretch the patient’s paralyzed arm forward at a right angle to the body and turn it palm up;
- place the patient’s healthy arm to one side or move it back (but not forward!);
- slightly bend the patient’s paralyzed leg at the knee joint, but straighten it at the hip;
- Bend your healthy leg at the hip and knee joints and place a pillow under it.
To maintain mobility of the joints in the paralyzed arm and leg, perform “passive exercises” with the patient: first take the patient’s hand and carefully make certain movements, and then make movements with the patient’s paralyzed leg.
Perform a set of therapeutic exercises with your ward every 4 hours.
Make sure that the movements are smooth and do not cause pain.
Make sure that the patient does breathing exercises. Breathing affects muscle tone.
Keep in mind that the behavior of patients with right-sided paralysis differs from the behavior of patients with left-sided paralysis.
| RIGHT-SIDED violation paralysis of the LEFT side of the body |
| Underestimating the scale of movement disorders, the patient is indifferent to his situation |
Characteristic
|
What to pay attention to:
|
| LEFT SIDE disorder paralysis of the RIGHT side of the body |
| Lethargy, passivity. loss of difficult emotional experiences |
Characteristic
|
What to pay attention to:
|
Restoring motor activity after a stroke.
Exiting bed rest should be done gradually and only in consultation with a doctor.
First, they teach the patient to sit down, then do exercises for the legs, then stand up, and only then walk.
If the person in your care cannot sit up independently:
1. Help him sit up first.
2. Then he needs to learn to sit in bed.
3. Provide the bed with special devices so that the patient can sit up without your help.
4. Teach the patient to lower his legs from the bed and transfer to a nearby chair or wheelchair.
5. Gradually teach the patient:
1) stand;
2) transfer the weight of the body from one side of the body to the other;
3) take steps on the spot;
4) to learn to walk, purchase a walker.
6. When teaching walking, stay close to the patient on the affected side..
Helping patients eat after a stroke.
The physician should assess the patient's ability to swallow and chew and prescribe an appropriate diet.
It is easier for a patient with impaired chewing and swallowing functions to swallow soft food than liquid food.
If you are drooling from the paralyzed side of your mouth, make sure your face is dry and clean. Lubricate the skin near your mouth with a protective cream.
Always serve food to your client from the side, on the uninjured side, and place it on the side of the mouth that is not affected.
After eating, make sure that there is no food left in the patient's mouth.
Monitoring the patient.
Watch your skin and take all measures to prevent bedsores.
Such patients often have urinary and fecal incontinence; take proper care of the patient.
To restore a normal sleep cycle:
- lower the air temperature in the patient’s room at night;
- reduce the calorie content of food and its temperature (after a hot, hearty meal a person falls asleep);
- Organize your ward’s daytime so that he has something to do all the time.
Call a doctor if
- There was an increase in temperature and severe pain in the side. Bedridden patients have a high risk of pneumonia;
- swelling has appeared on the paralyzed side - this may be a sign of vein thrombosis.
Provide your client with emotional support. Reassure him that his family loves and appreciates him regardless of his condition.
Therapist (head) of the day care department Lyudmila Vyacheslavovna Narab
What is the prognosis for hemiplegia?
After a stroke, it is important to begin rehabilitation as early as possible. In some cases, this can significantly reduce paralysis and even completely overcome it. Most patients need to be taught to live with some restrictions. Continuous therapy and constant practice allow them to adapt to a new situation and develop further. There are also various assistive devices, devices and technologies that allow patients to be more independent in everyday life.
Rehabilitation equipment
To receive a commercial offer for equipment, please write to Our managers will answer all your questions.
Specifics of right-sided strokes
When the pathological focus is localized in the right hemisphere, the opposite (left) side of the body is affected. Muscle tone changes in a spastic manner, all types of sensitivity suffer, and muscle contractures appear. When a stroke develops, the patient in most cases loses consciousness for a relatively short time. With a significant size of the lesion, a “cerebral coma” cannot be ruled out.
Characteristic cerebral manifestations are also:
- severe dizziness;
- intense headache;
- unsteadiness of gait or falls caused by impaired coordination of movement.
The hemorrhagic form is characterized by central pain syndrome, persistent sleep disturbances and decreased visual acuity in the left eye (in severe cases, blindness is possible). In addition, the patient has difficulty swallowing. The most important problem is paralysis and the resulting muscle contractures and arthropathy (joint pathologies). Prolonged immobility during paralysis causes bedsores. Recovery after a stroke on the right side in such cases should begin as early as possible. The ischemic form is characterized by a rather slow development. The rehabilitation process is often slowed down, since many patients develop disturbances in the emotional-volitional area, and they do not notice that the left side is paralyzed.
Possible complications of the ischemic form (cerebral infarction) include:
- hydrocephalus due to cerebral edema;
- recurrent stroke;
- transformation of the ischemic form into the hemorrhagic one;
- dysfunction of the pelvic organs.
Symptoms of left-sided ischemic stroke
In accordance with the localization of the brain catastrophe in a particular part of the brain, a stroke can be right-hemisphere or left-hemisphere. The disease develops according to the principle of “reverse symmetry”: with a right hemisphere stroke, paralysis of the left side of the body develops, with a left hemisphere stroke, on the contrary, paralysis of the right side.
The hemispheres of the brain are responsible for different functions. The left is for language and thinking abilities, the right is for creative and emotional. In view of this, with a left hemisphere stroke, the patient experiences a speech disorder, which is manifested by slurred speech, difficulties with the coherent expression of one’s thoughts, and with understanding what is heard. With a right hemisphere stroke, these symptoms are usually absent, and therefore this form of stroke is much more difficult to recognize.
Most often, the main cause of vascular circulation disorders in the brain is blood clots. They arise due to hypertension and lead to blockage of the lumen of the vessel. In addition, pathology can be caused by diseases such as high blood viscosity, rapid clotting, disorders of the heart and blood vessels, metabolism, diabetes mellitus, and slow blood circulation. Very often, ischemic stroke affects those who have had a heart attack, surgery to install a heart valve, or suffer from frequent headaches and migraines.
Make an appointment
The majority of cases (up to 60%) occur in right hemisphere stroke. To diagnose it, it is necessary to take into account that this type of stroke affects the appearance of the left side of the face and the condition of the body. A left-sided stroke is manifested by disruption of the facial muscles on the left side: drooping of the corner of the mouth and the outer corner of the eye. Partial or complete paralysis of the left side of the body occurs. The function of internal organs located on the left side of the body may be impaired.
In addition, left-sided stroke is manifested by other symptoms:
- paralysis of the left eye;
- hearing impairment;
- impaired perception of the left side of the body: the limbs become disobedient, it is difficult to assess the distance from the limbs to objects or the size of the limb;
- the appearance of inexplicable aggression, inappropriate behavior, depression;
- inability to perceive colors.
- change in speech;
- disturbance of mental activity;
- memory loss;
- misunderstanding the meaning of words.
When a part of the brain located in the central part is damaged, as a rule, complete immobility of the limbs occurs. When the lesion is localized in the parietal region, the patient has difficulty perceiving heat, cold, and pain.
After confirming the diagnosis, it is important to provide first aid to the patient competently and promptly. The specialists at the Yusupov Hospital have extensive experience in treating strokes; thanks to their practical skills, it is possible to minimize the severe consequences of this disease.