Atherosclerosis is a pathological process in blood vessels that is chronic. Danger of atherosclerosis: over time, this disease causes serious circulatory problems. There is a disruption in both fat and protein metabolism in the human body.
Atherosclerosis must be treated without fail, otherwise it can lead to such serious diseases as heart attack, stroke, aortic aneurysm, coronary heart disease, cerebral ischemia, inflammatory processes in the gastrointestinal tract, renal failure and others.
The disease process is as follows:
- There is a violation of fat/protein metabolism. There is an increased amount of lipids in the blood.
- “Excess” amounts of lipids remain on the walls of the arteries.
- After this, overgrowth with fibrous tissue occurs.
- The vessel narrows and ceases to supply the organs and tissues with blood in the required volume.
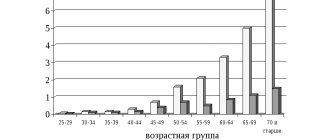
This disease is mostly related to age: most often it affects men - 40-60 years old, women - 50+ years old. However, there is an alarming trend in the number of sick people and the age under 40 years of age. This is largely caused by improper and unbalanced nutrition and the worsening environmental situation.
Atherosclerosis “strikes” the arteries, including the aorta, carotid arteries, arteries of the brain, and heart. For this reason, this disease is one of the most common causes of myocardial infarction and coronary heart disease, stroke, and circulatory problems.
Vessels susceptible to atherosclerosis
With atherosclerosis, large main arteries are affected - the aorta and its branches.
Among the sections of the aorta, the abdominal aorta is most susceptible to atherosclerosis. Clinically significant atherosclerosis of the aortic arch and thoracic aorta is much less common. From the peripheral arteries and directly the branches of the aorta, the following should be distinguished:
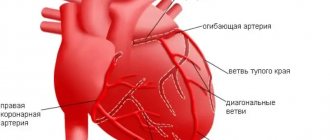
- coronary (coronary) vessels,
- nourishing the heart,
- brachiocephalic arteries (BCA),
- subclavian arteries,
- common and internal carotid arteries (ICA),
- vertebral arteries,
- arteries of the limbs,
- renal arteries,
- celiac trunk,
- mesenteric arteries.
When several arterial basins are affected, they speak of generalized (widespread) atherosclerosis. Most often, atherosclerosis affects the coronary, brachiocephalic basins, as well as the vessels supplying blood to the lower extremities.
Classification of the disease
The formation of atherosclerotic plaques can occur in individual vessels or affect most of them. Depending on the organ in which blood flow is reduced and the affected artery, the following forms of the disease are distinguished:
- Heart shape. Ischemic atherosclerosis with damage to coronary vessels and valves.
- Kidney form. The renal arteries are affected.
- Brain (cerebral) form. The disease spreads to intracranial vessels.
- Intestinal form. The mesenteric arteries are affected.
- Atherosclerosis of the aorta. Its abdominal region is most often affected.
- Atherosclerosis of the arteries of the lower extremities, mainly femoral.
- Atherosclerosis of brachiocephalic vessels. These include the right carotid, vertebral and subclavian arteries.
Why is atherosclerosis dangerous?
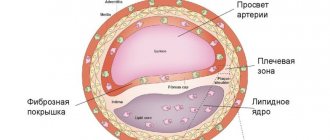
Atherosclerotic or, as they are also called, cholesterol plaques, gradually narrow the lumen of the arteries and make them less elastic. This creates an obstacle to normal blood flow and leads to insufficient blood supply to the feeding organ.
The narrowing of the lumen of a vessel by an atherosclerotic plaque is called stenosis, and complete blockage of the lumen is called occlusion. Symptoms of the disease begin to appear at a certain degree of arterial stenosis, in which case we can talk about stenosing vascular atherosclerosis. For example, if the arteries of the heart narrow, the blood flow to the heart muscle (myocardium) decreases. This can cause chest pain and shortness of breath, which can ultimately lead to a heart attack. Particles of atherosclerotic plaque can break off from the walls of the arteries and be transported with the blood to narrower vessels, completely blocking their lumen.
In addition, the danger of atherosclerosis lies in the fact that particles of atherosclerotic plaque can break off from the walls of the arteries and be transported with the blood to narrower vessels, blocking their lumen. Blood clots can form in the area of atherosclerotic plaques, partially or completely blocking the lumen of the artery. In such cases, there is an acute disruption of the blood supply to the feeding organ, which can lead to dangerous, often life-threatening complications. The described mechanisms are often the cause of stroke, myocardial infarction, thrombosis and obliterating atherosclerosis of the vessels of the lower extremities.
What it is
Atherosclerosis is one of the most common chronic arterial diseases. Because of it, an atherosclerotic plaque of cholesterol (cholesterol) forms in the wall of the vessel. These plaques narrow the lumen of the vessel, which affects blood flow, and in extremely advanced cases, plaques can completely block the blood flow. If this happens in a large artery, then the situation is fraught with serious complications, including death: cardiovascular diseases have been one of the main causes of mortality for many years. In addition, the presence of a plaque in a vessel changes the flow of blood: turbulence appears, which contributes to the formation of blood clots (platelet sticking together). The appearance of blood clots poses a risk of their breaking off and clogging the vessel in a narrow place.
Clinical picture or symptoms of atherosclerosis
Symptoms of atherosclerosis depend on the organ that feeds the vessels affected by atherosclerotic plaques. Thus, when the coronary arteries are damaged, the heart muscle (myocardium) suffers, and coronary heart disease (CHD) develops. Signs of angina appear - chest pain and shortness of breath during exercise or at rest.
Among the vessels supplying the brain, the internal carotid and vertebral arteries are most often affected by atherosclerosis. In this case, patients may experience dizziness, impaired memory and vision, episodes of loss of sensitivity or movements in the face and limbs, and speech disorders. With the long-term existence of an atherosclerotic plaque in the lumen of the carotid artery, ulcerations may occur on its surface, as well as blood clots, which can be carried with the bloodstream into the vessels of the brain, causing clinical manifestations such as paresis/paralysis, sudden loss of sensation in the limbs or in the face, as well as temporary blindness.
When the vessels of the legs are damaged, symptoms of intermittent claudication appear - pain in the calf (less often in the gluteal and thigh) muscles that occurs when walking. With the progression of obliterating atherosclerosis of the vessels of the lower extremities, trophic ulcers and gangrene of the extremity ultimately occur. With atherosclerosis of the iliac arteries, potency disorders (erectile dysfunction) may also occur.
Atherosclerosis of the cerebral arteries
When cholesterol plaques form and the arteries of the brain narrow, the brain cells experience a lack of blood and nutrients. The following symptoms may indicate this condition:
- periodic dizziness,
- noise in ears,
- headache,
- increased fatigue,
- disturbances in coordination of movements.
The narrowing of the main carotid artery supplying the brain is identified as a separate diagnosis - carotid artery stenosis. Damage to the vessels supplying the brain carries the threat of a serious disease - ischemic stroke of the brain.
Causes of atherosclerosis
The causes of atherosclerosis remain not fully understood. It is believed that the initial stages of atherosclerosis occur already at a young age, but it usually reaches its clinical significance in people of the older age group (over 50 years). There are risk factors for atherosclerosis, the impact of which can significantly slow down its progression, reduce the severity of its manifestations and prevent the occurrence of complications.
Risk factors for atherosclerosis
- High blood pressure,
- High levels of cholesterol in the blood - low-density lipoprotein (LDL),
- Diet high in animal fats
- Smoking,
- Obesity,
- burdened heredity,
- Diabetes.
Cholesterol and atherosclerosis
It is important to regularly monitor blood tests for the so-called “bad” cholesterol, which is deposited in the artery wall and causes the appearance and growth of atherosclerotic plaques. If the level of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol is elevated, you should consult a physician, cardiologist or vascular surgeon. In the absence of contraindications, it is recommended to take statins - medications that reduce the level of “bad” cholesterol in the blood.
Treatment
Treatment of atherosclerosis begins with correction of diet and lifestyle changes.
All patients are recommended to lose weight, moderate physical activity, and quit smoking and alcohol. Often the cause of atherosclerosis is a nutritional factor, so diet plays a very important role. To reduce the concentration of cholesterol in the blood, it is important to avoid meat broths, fatty, salty, smoked foods, semi-finished products, spicy, spicy, fried foods, and limit the consumption of table salt.
Prohibited products include:
- sugar;
- confectionery, sweets;
- mayonnaise, tomato and other store-bought sauces;
- bakery products made from wheat flour;
- offal;
- sweet carbonated drinks;
- industrially produced juices and nectars;
- cocoa;
- canned meat and fish;
- dried fruits high in sugars;
- strong coffee and tea.
It is recommended to eat split meals five times a day, including a sufficient amount of fiber, protein (lean meats and fish, low-fat cottage cheese), fresh vegetables (except potatoes), fruits, and dairy products.
Drug therapy is aimed at:
- decreased cholesterol synthesis (statins, fibrates);
- decreased absorption of fats from food (cholesterol absorption inhibitors, bile acid sequestrants);
- prevention of thromboembolic complications (antiplatelet agents);
- relief of symptoms of atherosclerosis (painkillers, antispasmodics).
To determine indications for surgical treatment, the degree of disruption of blood flow in the vessel is determined.
An overlap of its lumen of less than 50% is considered hemodynamically insignificant; with stenosis of 50-70%, only drug therapy is usually carried out. Correction of arterial obstruction surgically must be performed in the third stage of atherosclerosis and narrowing of the lumen by more than 70%. There are two main types of surgical intervention:
- Balloon angioplasty. A balloon is inflated inside the affected vessel, while the atherosclerotic plaque is flattened and evenly distributed along the artery wall. At the end of the manipulation, the device is removed.
- Arterial stenting. During the operation, a thin lattice cylinder is inserted and opened in the area of narrowing. It also presses against the plaque, but remains in the lumen of the vessel, gradually growing into its endothelium.
Prevention of vascular atherosclerosis
The best treatment for atherosclerosis is its prevention. It is necessary in order to prevent the occurrence of the first signs and symptoms of the disease, which will help overcome atherosclerosis already in the initial stages. Prevention consists primarily of diet: do not abuse fatty foods, as well as mandatory smoking cessation. If you have hypertension (hypertension), it is necessary to maintain normal blood pressure values by monitoring it, as well as taking medications, after consulting with a therapist or cardiologist. In the presence of diabetes mellitus, it is recommended to maintain normal blood glucose levels by taking glucose-lowering drugs prescribed by an endocrinologist, daily monitoring of blood glucose levels, and regular monitoring by an endocrinologist.
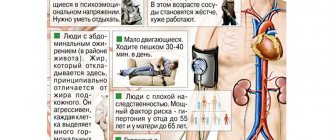
Risk factors
The main risk factors for the development of atherosclerosis:
- diabetes;
- obesity;
- low physical activity;
- poor nutrition;
- smoking;
- alcohol consumption;
- stress.
Diabetes
Diabetes mellitus, in which there is a persistent increase in blood glucose levels, day after day, year after year, provokes disorders that are hardly noticeable to the patient - a gradual deterioration in the functioning of many organs and systems, including blood vessels. When small vessels are affected, it is customary to speak of microangiopathy, and when large vessels are affected – macroangiopathy.
In the first case, kidney function is disrupted, vision decreases, and wounds on the body do not heal well. Frequent headaches and dizziness are also a consequence of microangiopathy. In the second case, the arteries of the brain and heart are affected. If diabetes mellitus is not treated for a long time or is treated incorrectly, then over time plaques form on the walls of blood vessels, which provoke the development of atherosclerosis, and with it coronary heart disease, stroke, and heart attack.
obesity
Obesity is a problem that today affects people in all countries, regardless of race, gender, age and social status. Scientists are seriously concerned about this issue, since excess weight requires additional expenditures from the state budget, reduces the productivity of citizens, causing great economic damage.
Increasingly, children are being diagnosed with obesity, and this is already a large-scale health problem. Excess fat in the body is deposited not only on internal organs, but also changes the lipid profile of the blood plasma.
As a result of this metabolic disorder, an imbalance occurs between the lipid (fat) components of the plasma, which leads to damage to the walls of blood vessels by atherosclerotic plaques. A person develops a whole bunch of cardiovascular diseases, starting with hypertension and arrhythmia, ending with coronary heart disease and cardiosclerosis.
Obesity significantly shortens life expectancy, which is why it is so important to keep your weight at a normal level. Even a small decrease in body weight significantly improves a person’s health and eliminates many unpleasant symptoms.
Little physical activity
Physical inactivity is the scourge of modern man. If in prehistoric times people were forced to earn their own food by their own labor, chasing mammoths, today to satisfy their hunger it is enough to dial the number of a pizza delivery service. Manual labor of representatives of many professions has become automated over time, and rising incomes and quality of life have made it possible to purchase their own car and abandon traveling on foot or by public transport.
Experts say that even with proper nutrition, lack of physical activity can negatively affect the functioning of the cardiovascular system. The heart, like any organ, needs to be trained. After all, this is also a muscle, and it becomes stronger when a person leads a healthy lifestyle and plays sports. Many people make the excuse that it's hard for them to work out in the gym, carrying heavy weights, but there are many other ways to increase your activity. Nordic walking, water aerobics, dancing, even an ordinary thirty-minute walk, provided regularity, can bring great benefits to the health of the heart and blood vessels. It's never too late to start training, but you need to choose the load wisely.
If a person is overweight, especially obese, then most sports are contraindicated for him. The main focus should be on Nordic walking and swimming. They practically do not load the joints, which in such people suffer first. Over time, when the weight begins to gradually go away, you can add cardio exercises - riding an exercise bike, an ellipsoid. The most important thing is to choose a sport you like so that it brings pleasure. Only under this condition a person will not have to force himself to study. He will do it with pleasure.
Poor nutrition
The fast pace of life, the abundance of genetically modified products on store shelves, enriched with fats and other not very healthy additives, the increasing number of cafes and fast food stalls - all this leads to the fact that a person builds his diet incorrectly and does not even think about it. For a resident of a metropolis, it is quite natural to have lunch and dinner outside the home. And if you don’t want to go anywhere, you can order food from a restaurant.
Some people simply don’t have enough time to cook their own food, and this leaves its mark on the daily menu. However, with a strong desire, everything is possible. Today there are many organizations that offer the opportunity to order meals at home that meet all the principles of rational nutrition, although it is better to cook the food yourself. Nutritionists advise using lean meat, fish, especially sea fish, and seafood for this purpose. They contain a large amount of polyunsaturated fatty acids, which do not increase, but lower blood cholesterol levels.
Vegetable oils are especially rich in omega fatty acids. They are recommended to replace animal fats - their abundance in the diet, along with sweets and baked goods, provokes excess weight gain. Unlike candies, buns and cookies, which contain quickly digestible simple carbohydrates, cereals contain complex varieties of carbohydrates that provide long-lasting energy, prolonging the feeling of fullness. Cereals should be prepared as a side dish for meat and fish, and used to prepare porridge for breakfast.
There should also be plenty of fruits and vegetables on the menu of those who want to eat healthy and have a healthy heart and blood vessels.
Smoking
Scientists from different countries are studying the effect of this bad habit on the functioning of the cardiovascular system and come to a disappointing conclusion. It has been proven that smoking increases the risk of developing heart and vascular diseases. Here's how tobacco, smoke, tar and other negative components affect the walls of blood vessels:
- reduce the vasodilatory effect;
- increase proliferation (reproduction) of smooth muscle fibers of the vascular walls;
- Tobacco smoke damages the cells that make up the inner wall of blood vessels - endothelial cells.
All these changes fall under the definition of endothelial dysfunction, which creates favorable conditions for the development of cardiovascular pathologies. Not everyone knows that atherosclerosis today is considered a lifestyle disease, where smoking is the main factor in its development. Smokers are 1.5-6 times more likely to experience this disease compared to those who do not depend on this addiction. The severity of the disease depends on how many cigarettes a person smokes per day. If the number exceeds a dozen, then doctors diagnose more extensive vascular damage. Such patients are 8 times more likely to develop atherosclerotic aortic aneurysm.
They are worried about more frequent attacks of angina pectoris, and anginal pain worries them every day, several times. Therefore, anyone who experiences such unpleasant symptoms needs to minimize the number of cigarettes they smoke per day, or it is better to completely abandon this bad habit. Fortunately, today there are many ways to do this painlessly for yourself and your psyche.
Alcohol consumption
Alcohol both directly and indirectly affects the functioning of the cardiovascular system. Once in the blood, it forces the main “motor” of the body to work with increased load for 5-7 hours, increasing the rhythm, increasing blood pressure and disrupting blood circulation. Its action is two-phase: first there is a strong dilation of blood vessels, and then a narrowing. Due to excessive work, the delivery of oxygen and nutrients to organs and tissues is disrupted. In the future, a person will experience cardiomyopathy, heart attack, arrhythmia, hypertension, bull's heart, and epicardial obesity. And also atherosclerosis if a person abuses alcohol.
Alcohol in moderation is even beneficial. Its ability to dilate blood vessels and thin the blood has a beneficial effect on blood circulation. Moderate drinkers are less likely to experience a sudden heart attack, unlike heavy abstainers and heavy drinkers. However, few people stop after a couple of drinks. For most people, the brakes jam and the amount they drink quickly exceeds the healthy limit. But alcohol is a drug and a poison that gradually destroys all organs and cells of the body, worsening its functioning. In the long term - complete degradation of personality due to the destruction of brain cells. Therefore, such prevention of atherosclerosis should be treated with great caution.
Stress
Stress today is a real “plague” of modern man. Experts tend to distinguish two main types: eustress and distress. The first acts as a kind of hardening, mobilizing the body and positively influencing the functioning of all organs and systems. Distress, especially when chronic, undermines human health, reduces immunity and leads to the development of serious diseases. It’s not for nothing that people are increasingly talking about the psychosomatics of many ailments.
When stressed, the hormone adrenaline is released into the blood. The heart begins to beat faster, pressure rises sharply, blood flows more actively through the vessels. If this happens rarely, and even more so when positive emotions are overwhelming, then it is very useful for the body. It's another matter if this state of affairs becomes permanent. The body is simply not capable of being in tension all the time. Such stress sooner or later affects your health. This especially applies to people with an initial form of atherosclerosis. Their risk of developing thrombosis and the risk of dying from artery blockage increases significantly.
Which doctor treats vascular atherosclerosis?
If atherosclerosis is suspected, an examination by a specialist is necessary:
- Angioneurologist - for atherosclerosis of cerebral vessels;
- Cardiologist - for atherosclerosis of the heart vessels;
- Vascular surgeon - for signs of diseases of the arteries of the arms or legs, neck, chest and abdominal cavity.
It is necessary to see a specialist (vascular surgeon) if you have one or more risk factors for atherosclerosis, and also have complaints characteristic of arterial diseases. It is especially important to seek qualified help during the initial manifestations of the disease, when it is possible to prevent the development of severe complications of atherosclerosis.
Before prescribing instrumental diagnostic methods, the doctor must evaluate the patient’s complaints. Collect information about past illnesses and past treatments. An objective examination provides detailed information about the severity and extent of the disease.
In some cases, the diagnosis of atherosclerosis can be excluded at the stage of the initial examination. If vascular atherosclerosis of one location or another is detected, the doctor may prescribe an additional examination.
Laboratory and instrumental studies that can be used to diagnose atherosclerosis:
- ultrasound duplex scanning of blood vessels,
- X-ray contrast angiography,
- CT scan,
- Magnetic resonance imaging,
- ECG,
- treadmill test,
- lipidogram, etc.
How to treat vascular atherosclerosis: drug treatment of atherosclerosis
Vascular atherosclerosis can be combated conservatively and surgically. Conservative treatment of atherosclerosis is used for mild and non-stenotic forms of atherosclerosis. It includes the fight against risk factors for atherosclerosis, as well as taking medications such as statins (Simvastatin, Atorvastatin, Rosuvastatin, etc.) and antiplatelet agents (acetylsalicylic acid, clopidogrel, etc.), which prevent further growth of atherosclerotic plaques and the formation of blood clots on them. surfaces. Medications are prescribed for permanent or long-term use.
Surgical intervention
Treatment of atherosclerosis involves surgical methods when the disease is in its final stages and the patient’s life is in danger. The method of solving the problem is determined by the cardiologist if conservative therapy does not bring results. Modern medicine offers the following types of surgical interventions:
- Coronary bypass surgery. Prostheses are inserted into the vessels to restore blood circulation to the proper volume.
- Angioplasty. Mechanical expansion of the coronary vessels by inserting special catheters with a balloon. When the balloon is inflated, the cholesterol plaque is “flattened” and, accordingly, the capacity of the vessel is restored.
- Stenting. A rigid frame is inserted into the cavity of the vessel, which expands and fixes the lumen of the artery.
Preventive examination and early diagnosis will help to avoid dangerous surgical intervention. The initial stages of the disease respond well to treatment and prevention of dangerous complications.
Can vascular atherosclerosis be reversed?
At the moment, there are no drugs that can get rid of atherosclerosis and cleanse blood vessels from atherosclerotic plaques.
Atherosclerosis is an irreversible disease and cannot be completely cured. For advanced forms of atherosclerosis, surgical treatment is often used. Modern surgical methods make it possible to perform the operation effectively, in a low-traumatic manner and without serious consequences for the body, to restore the lumen of a vessel affected by atherosclerosis and to resume sufficient blood flow to the organ.