In any case, the death of a person becomes a severe shock for relatives. If the death was the result of a long-term illness, loved ones are partly prepared for a tragic ending. However, the death of a completely healthy baby or an adult who has not shown any health complaints can occur completely unexpectedly, for no apparent reason.
What is sudden death
According to international medical recommendations, a person’s death within 6 hours after the appearance of the first symptoms of a pathological condition is considered sudden. Instant death, or translated into English sudden death, occurs without a known cause. In addition, there are no morphological signs on the basis of which an appropriate diagnosis of the patient’s sudden death can be made at autopsy.
However, during a post-mortem examination of a person, a pathologist, having compared all available data, can make a logical conclusion about the instantaneous or violent death of the person. In most cases, instant death is supported by changes in organs in which continuation of life for the shortest period of time is impossible.
Healthy foods for the heart
Proper nutrition is the key to health and longevity; support your body with heart-healthy foods.
- Red grape juice.
- Low-fat milk.
- Fresh vegetables and fruits (legumes, bananas, carrots, pumpkin, beets, etc.).
- Sea fish.
- Lean meat (chicken, turkey, rabbit).
- Nuts.
- Vegetable oils.
A healthy lifestyle is the answer to the question, how to avoid sudden death?
There are many diets designed to strengthen and maintain good heart condition. Regular exercise will strengthen the body and make you feel more confident and healthier.
Active lifestyle and physical culture
Regular dosed physical activity with an emphasis on “cardio training”:
- Running in the fresh air.
- Bicycle rides.
- Swimming.
- Cross-country skiing and skating.
- Yoga class.
- Morning exercises.
Causes of sudden death
Statistics show that the main cause of most deaths is heart disease: ischemic pathology, the onset of ventricular fibrillation. At the same time, when answering what causes instant death, experts often name chronic illnesses that occur in a latent form for a long time, after which they suddenly worsen and lead to the unexpected death of a person. One of these deadly diseases is cancer.
In most cases, oncology develops asymptomatically and makes itself felt when the patient is often considered hopeless. Thus, malignant liver disease is the main cause of unexpected deaths in China. Another insidious disease that can lead to sudden death is AIDS, which claims millions of lives in Africa every year. In addition, it is worth mentioning separately about Mexico. This is the only country in which cirrhosis of the liver is the main cause of high mortality in the population.
In young age
Today, young men and women are exposed to the negative influence of modern lifestyle every day. From TV screens and the covers of fashion magazines, the cult of a slender (often dystrophic) body, accessibility and promiscuity is imposed on young people. Therefore, it is quite understandable that the mortality rate of people just beginning their life journey will increase over time. The main causes of instant death among boys and girls under 25 years of age are considered to be:
- alcohol;
- smoking;
- promiscuity;
- drug addiction;
- poor nutrition;
- psychological sensitivity;
- hereditary diseases;
- severe congenital pathologies.
In a dream
Unexpected death in this condition occurs due to the loss of special cells responsible for the contractility of the lungs. Thus, scientists from the USA were able to prove that people die in their sleep in most cases due to central sleep apnea. In this case, a person may even wake up, but still leave this mortal world due to oxygen starvation caused by a stroke or cardiac arrest. As a rule, elderly people are susceptible to this syndrome. There are no specific treatments for central sleep apnea.
Sudden infant death
This syndrome was first described in the early 60s of the last century, although cases of instant death of infants were recorded earlier, but they were not subjected to such a thorough analysis. Young children have very high adaptive abilities and incredible resistance to a variety of negative factors, which is why the death of an infant is considered an exceptional situation. However, there are a number of external and internal reasons that can lead to sudden child death:
- prolongation of the QT interval;
- apnea (the phenomenon of periodic breathing);
- deficiency of serotonin receptors;
- overheat.
Pathogenesis
Children commonly have abnormalities in serotonin , which is thought to impair the ability to regulate arousal and breathing normally, particularly in potentially life-threatening situations such as sleep and turning the baby onto his or her stomach. In addition, changes in the polymorphism of anti-inflammatory cytokines and reduced mandibular size are determinants of death. Another chain of mechanisms that causes sudden cessation of breathing is associated with the process of accumulation of high concentrations of carbon dioxide and insufficient blood oxygenation.
In general, there are several theories of the development of thanatogenesis mechanisms - respiratory, cardiac and metabolic.
Risk factors
Due to the fact that the main cardiogenic cause of instant death is ischemic disease, it is quite logical to assume that the syndromes accompanying this heart pathology can be fully attributed to conditions that can increase the likelihood of sudden death. With all this, it has been scientifically proven that this connection is mediated through the underlying disease. Clinical risk factors for the development of clinical death among patients with ischemic syndrome are:
- acute myocardial infarction;
- post-infarction macrofocal sclerosis;
- unstable angina;
- heart rhythm disturbance due to ischemic changes (rigid, sinus);
- ventricular asystole;
- myocardial damage;
- episodes of loss of consciousness;
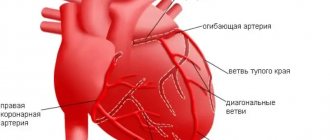
- damage to the coronary (heart) arteries;
- diabetes;
- electrolyte imbalance (eg, hyperkalemia);
- arterial hypertension;
- smoking.
Why do men die more often?
If we summarize all of the above, we can conclude that men are more likely than women to suffer from one or another heart disease with a fatal outcome.
This is due to several factors:
- Most genetically determined pathologies are transmitted according to an autosomal dominant mode of inheritance. This implies the transmission of symptoms and diseases from father to son.
- In a woman’s body, the sex hormones estrogens are present in greater quantities, which have a beneficial effect on the development of atherosclerosis and arterial hypertension.
- Men are more involved in heavy physical work and are thus more susceptible to overload.
- The prevalence of alcoholism and drug addiction among men is greater than among women.
- The cost of living of men in all countries of the world is lower than that of women.
How does sudden death occur?
This syndrome develops in a matter of minutes (less often hours) without any warning in the midst of complete well-being. In most cases, instant death affects young men aged 35 to 43 years. Moreover, often during the pathological examination of the deceased, vascular causes of sudden death are discovered. Thus, studying the increasing cases of instant death, experts came to the conclusion that the main provoking factor in the occurrence of this syndrome is a violation of coronary blood flow.
Last day of life
No matter how hard it may be for you to watch the suffering of a loved one, do not leave him in his last minutes. It is not at all necessary to sit next to him all the time, but if you approach him once every 5-15 minutes, talk, show concern, take his hand, wipe the sweat from his forehead, lightly stroke him - this will be enough. When you leave, explain your reason. For example, you went to turn off the kettle, put vegetables in a pan, or go to the store. The fact that you do not leave a person until the last moment will help him not to be afraid of death and will facilitate his natural departure to another world.
For heart failure
In 85% of cases, immediate death is recorded in individuals with structural abnormalities of the organ that pumps blood into the vessels. In this case, sudden cardiac death looks like a lightning-fast clinical variant of coronary disease. Medical practice shows that in a quarter of people who die instantly, bradycardia and episodes of asystole are observed before the onset of primary symptoms. Death from cardiac arrest occurs due to the launch of the following pathogenetic mechanisms:
- Reducing left ventricular fractional ejection by 25-30%. This syndrome greatly increases the risk of sudden coronary death.
- Ectopic focus of automatism in the ventricle (more than 10 ventricular extrasystoles per hour or unstable ventricular tachycardia), arising as a consequence of ventricular arrhythmias. The latter mostly develop against the background of acute transient myocardial ischemia. An ectopic focus of automatism is usually classified as a risk factor for sudden arrhythmic death.
- The process of spasm of the blood vessels of the heart, which leads to ischemia and contributes to the deterioration of the restoration of blood flow to damaged areas.
It is worth noting that tachyarrhythmia is a particularly significant electrophysiological mechanism resulting in sudden coronary death in a person with heart failure. At the same time, timely treatment of this condition using a defibrillator with a modified pulse configuration significantly reduces the number of deaths among patients who have suffered sudden cardiac arrest.
From a heart attack
Blood enters the heart through the coronary arteries. If their lumen closes, the formation of primary foci of necrosis and ischemia in the heart occurs. Acute manifestation of cardiac pathology begins with damage to the vascular wall with further thrombosis and spasm of the arteries. As a result, the load on the heart increases, the myocardium begins to experience oxygen starvation, which affects its electrical activity.
As a result of a sudden coronary spasm, ventricular fibrillation occurs, a few seconds after which a complete cessation of blood circulation to the brain occurs. At the next stage, the patient experiences respiratory arrest, atony, and absence of corneal and pupillary reflexes. After 4 minutes from the onset of ventricular fibrillation and complete cessation of blood circulation in the body, irreversible changes occur in the brain cells. In general, death from a heart attack can occur in 3-5 minutes.
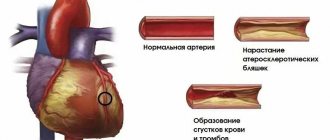
From a blood clot
In the venous bed, these pathological formations arise due to the uncoordinated work of the coagulation and anticoagulation systems. Thus, the onset of the appearance of a clot is caused by damage to the vascular wall and its inflammation against the background of thrombophlebitis. Perceiving the appropriate chemical signal, the coagulation system comes into action. As a result, fibrin threads form near the pathological area, in which blood cells become entangled, creating all the conditions for the blood clot to break off.
In arteries, the formation of clots occurs due to narrowing of the vascular lumen. Thus, cholesterol plaques block the path of free blood flow, resulting in the formation of a lump of platelets and fibrin threads. It is important to note that in medicine a distinction is made between floating and mural thrombi. Compared to the first type, the latter has a slight chance of breaking off and causing a blockage (embolism) of the vessel. In most cases, the causes of sudden cardiac arrest from a blood clot are due to the movement of a floating thrombus.
One of the serious consequences of the separation of such a clot is blockage of the pulmonary artery, which is expressed in a strong cough and bluish skin. Often there is respiratory failure followed by cessation of cardiac activity. An equally serious consequence of the detachment of a blood clot is a violation of cerebral circulation due to embolism of the main vessels of the head.
- How to pickle mushrooms: recipes with photos
- How to get rid of beer belly at home
- How to expel fluid from the body for weight loss
Cardiomyopathies
One of the most common sudden cardiac arrests is cardiomyopathies. This term refers to a group of diseases of the heart muscle of various origins that are associated with mechanical or electrical dysfunction.
The main manifestation is thickening of the muscle fibers or expansion of the chambers of the heart. There are:
- Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy is a genetically determined disease that affects the heart muscle. The process progresses steadily and with a high degree of probability leads to sudden death. This type of cardiomyopathy, as a rule, is familial in nature, that is, close relatives in the family are sick, however, isolated cases of the disease occur. In 15-20% there is a combination of coronary atherosclerosis and hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
- Dilated cardiomyopathy is a disorder characterized by abnormal expansion of the heart cavity and impaired contractility of the left ventricle or both ventricles, leading to changes in heart rate and death. Typically, dilated cardiomyopathy manifests itself at the age of 30-40 and more often affects men. Women are affected three times less than men.
Based on the causes of occurrence, they are distinguished:
- cardiomyopathy of unknown origin;
- secondary or acquired dilated cardiomyopathies caused by viral infections, including AIDS, alcohol intoxication, and micronutrient deficiencies
- Restrictive cardiomyopathy is a rare form characterized by thickening and proliferation of the inner lining of the heart.
Diagnosis of sudden death
A timely physical examination is the key to the success of further cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) measures. Diagnosis of instant death is based on symptoms characteristic of the patient's natural death. Thus, absence of consciousness is determined if no external stimuli cause reactions on the part of the person being resuscitated.
Diagnosis of breathing disorders is noted when within 10-20 s. observation fails to detect coordinated movements of the sternum and the noise of the air exhaled by the patient. In this case, agonal breaths do not provide adequate ventilation of the lungs and cannot be interpreted as spontaneous breathing. During ECG monitoring, pathological changes characteristic of clinical death are detected:
- ventricular fibrillation or flutter;
- cardiac asystole;
- electromechanical dissociation.
Clinical manifestations
In 25% of cases, sudden death occurs instantly without any warning signs. Some patients, a week before clinical death, complain of various prodromal manifestations: increased pain in the sternum, general weakness, shortness of breath. It is important to note that today there are already methods for preventing heart attacks based on early diagnosis of the warning symptoms of this condition. Immediately before the onset of sudden death, half of the patients experience an anginal attack. Clinical signs of a patient’s imminent death include:
- loss of consciousness;
- absence of pulse in the carotid arteries;
- dilated pupils;
- lack of breathing or the appearance of agonal breaths;
- change in skin color from normal to gray with a bluish tint.
Question and answer
The sudden death of a baby is extremely hard for his mother to bear.
How and with what can you help her? Close people, husband and relatives should support her and not let her be left alone with her grief. Pediatricians who directly observed the child can, for their part, give some explanations for what happened.
Is it necessary to perform artificial respiration along with a cardiac massage for a person who has suddenly lost consciousness?
Experts believe that if there is no appropriate training and experience, it is better not to do artificial respiration in such cases.
What are the sudden infant mortality rates in Belarus?
In our country, this phenomenon is infrequent; Belarusian SIDS statistics on average correspond to European ones.
Medical care for sudden death
Typically, most cases of unexpected cardiac arrest occur outside the hospital. For this reason, it is extremely important to master the technique of providing emergency care in case of sudden clinical death. This is especially true for subjects of society who, due to their job responsibilities, come into contact with a large number of people. Remember, competent resuscitation actions immediately in the first minutes after the onset of symptoms of cardiac arrest will help gain time until medical workers arrive.
Urgent Care
The main problem that arises in unconscious persons is obstruction of the airways by the root of the tongue and the epiglottis due to muscle atony. It must be said that this condition develops in any position of the body, and when the head is tilted forward, it develops in 100% of cases. Therefore, the first thing that needs to be done is to ensure proper airway patency. For this purpose, you need to use P. Safar’s triple technique, consisting of the following sequential actions:
- Throwing back the head;
- Moving the lower jaw forward;
- Opening the mouth.
Once airway patency is ensured, you should proceed to artificial pulmonary ventilation (ALV). When providing first aid, this activity is carried out using the mouth-to-mouth method. So, one hand is placed on the victim’s forehead, while the other pinches his nose. Then the resuscitator fixes his own lips around the mouth of the person being revived and blows air, while controlling the excursion of the patient's chest. When it is visible, you need to release the victim’s mouth, giving him a chance to exhale passively.
At the next stage, artificial maintenance of blood circulation is carried out, to ensure which an algorithm for performing indirect cardiac massage or chest compression is used. For this purpose, you need to correctly lay the person being resuscitated on a flat surface. Next, you should determine the compression points: by palpating the xiphoid process and moving away from it 2 transverse fingers upward.
The hand must be placed on the border of the middle and lower part of the sternum so that the fingers are parallel to the ribs. Pushes are performed with the limbs straightened at the elbows. Chest compression is performed at a frequency of 100 compressions per minute with a break for artificial ventilation. The depth of the shocks is about 4-5 cm. Measures to restore cardiac activity should be stopped if:
- A pulse appeared in the main arteries.
- The actions taken do not have the desired effect within 30 minutes. The exception is the following conditions that require prolongation of resuscitation:
- hypothermia;
- drowning;
- drug overdose;
- electrical injury.
Resuscitation measures
Today, the concept of CPR is based on strict rules that ensure complete safety of the activities carried out for human life. In addition, an algorithm for the resuscitator’s actions in case of sudden cardiac arrest or sudden loss of respiratory function in the injured person is presented and scientifically substantiated. In the development of these conditions, time plays a major role: only a few minutes separate a person from death. The algorithm for performing cardiopulmonary resuscitation involves performing the following actions:
- Determining the condition of the victim, on the basis of which the range of measures necessary for revival is selected;
- Early initiation of CPR, which involves performing two manipulations: chest compressions and artificial ventilation.
- If the second stage is ineffective, they proceed to defibrillation. The procedure involves applying an electrical impulse to the heart muscle. In this case, direct current discharges should be applied only if the electrodes are correctly positioned and have good contact with the victim’s skin.
- At this stage, as a rule, the victim is provided with specialized medical care, including the following early treatment measures:
- artificial ventilation with tracheal intubation;
- drug support, involving the use of:
- catecholamines (adrenaline, atropine);
- antidiuretic hormones (Vasopressin);
- antiarrhythmic drugs (Cordarone, Lidocaine);
- fibrinolytic agents (Streptokinase).
- intravenous drip administration of electrolyte or buffer solutions (for example, sodium bicarbonate is administered for acidosis)