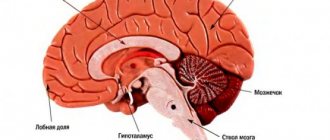
Lacunar stroke is a type of ischemic stroke that results in the formation of a cavity or softening in the tissues of the gray matter of the brain. The term “lacuna” (from the French meaning softening, cavity) was introduced into medical circulation in the 19th century by the physician Decambre. Later, at the end of the 20th century, this term began to be used to name this subtype of ischemic stroke.
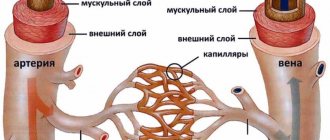
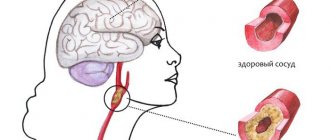
This type of stroke is quite common and occurs in 30% of cases. Lacunar ischemic stroke is characterized by small lesions (less than 1 cm) and occurs due to impaired blood flow in the area of small arteries. Most often, such lesions occur in the area of the brain stem, cerebellum, and basal ganglia. One of the main causes of vascular damage is long-term arterial hypertension.
Due to the small size of the lesion, it is very difficult to identify the clinical picture of this disease. This poses a great danger to human life and health. Such small and practically asymptomatic heart attacks can lead to acquired dementia (dementia). A person not only loses the ability to acquire new skills, but also loses previously acquired ones. One of the types of multi-infarct dementia is Binswangen disease. As a result of this complication, a person’s gait is also impaired.
General information
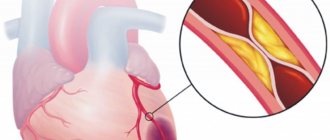
One of the types of cerebral infarction (ischemic stroke) is lacunar infarction, which is a small (up to 15 mm in diameter) brain damage that occurs when local blood circulation and gas exchange are disrupted. The reasons for this situation are varied and not fully understood, but most often it is blockage of supply vessels as a result of changes in their walls (atherosclerosis, inflammation), emboli (blood clots, fat droplets, bacterial colonies, etc.). Most of them are found in the periventricular region, basal ganglia, and thalamus - the central, deep structures of the brain. Lacunar infarctions account for 20-30% of all strokes.
Clinical manifestations
Lacunar stroke, unlike other forms, is not accompanied by acute impairment of consciousness, speech, vision, or motor functions, since cortical structures are not involved in the pathological process.
All symptoms arise and increase gradually, depending on the location of the cavity, pressure on a specific subcortical center or its destruction. Complexes of symptoms are combined into syndromes; about 20 of them have been identified. Neurologists speak of a “lacunar state” of the brain.
When passively trying to flex and straighten the limbs, the doctor determines increased resistance
Main syndromes:
- motor - partial or complete loss of movement develops in half the body or one limb and face, all other functions are preserved (half of all stroke cases);
- ataxic hemiparesis - weakness in the arm or leg, more in the hand and feet, with preserved strength;
- combination of hemiparesis and loss of sensitivity (35% of cases);
- dysarthria and “awkward hand” - a combination of speech changes and weakness in the hand, difficulties in the functioning of the joints, possible disturbances in the contractions of the muscles of the face and legs on the same side;
- hyperkinesis (multiple excessive movements) - accompanied by large tremor of the hands, obsessive movements of the torso, twitching of the shoulders and head, at the same time there is a violation of tone in certain muscle groups;
- isolated sensory syndrome (5% of cases) - typically a violation of sensitivity in half the body to complete loss, the temperature of objects, the sharp and blunt end of a needle are not felt, sometimes combined with a change in pain.
Other symptoms include:
- cramps and increased muscle tension on both sides;
- memory loss;
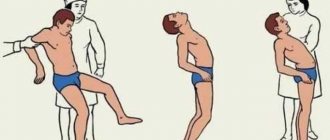
- staggering when walking, impaired balance;
- loss of control of the pelvic organs, involuntary urination and bowel movements.
Neurologists pay attention to the deterioration of the patient’s condition in the morning. Patients report a headache in the evening, which is associated with fatigue and overwork, and take painkillers. Lacunar stroke occurs in a sleepy state. The patient wakes up and discovers changes.
Lacunar formations may be located in “silent” zones and not manifest clinical symptoms.
Risk factors
Lacunar infarction can occur at any age, but the likelihood of its occurrence increases with age and reaches its maximum after 85 years. More often, cerebral circulatory disorders occur in men. The most significant risk factors for the occurrence of lacunar cerebral infarctions are:
- hypertonic disease,
- diabetes,
- chronic renal failure,
- post-infarction cardiosclerosis,
- abnormalities in the circulatory system and heart defects,
- rheumatism,
- cardiac arrhythmias,
- disorders of the blood coagulation system, blood diseases.
Causes
A significant role in the formation of pathological changes in the penetrating arteries of the brain is assigned to:
- hypertension with uncontrolled changes in blood pressure, frequent crises, lack of or inadequate treatment;
- the consequences of metabolic changes (impaired carbohydrate metabolism and ionic balance) in diabetes mellitus;
- conditions and diseases accompanied by increased blood clotting and a tendency to thrombus formation (extensive injuries and burns, shock, large loss of fluid with prolonged vomiting, diarrhea, dehydration, polycythemia and others);
- diseases of the arteries of an inflammatory nature (arteritis and vasculitis) with infectious or allergic causes that impede the general blood flow through the cerebral vessels;
- hereditary changes in the structure of the vascular wall.
Rarely, the cause of a lacunar stroke may not be ischemia with tissue necrosis, but a small area of hemorrhage in the adjacent area. Instead of atherosclerosis with the presence of cholesterol plaques from the inside, the penetrating vessels become denser, lose hyaline and become sclerotic.
Diagnostic method
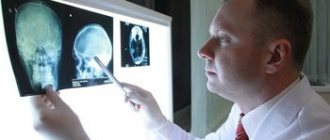
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is the most preferred method in determining the location, and most importantly, in assessing the stage of development of the ischemic process. In the acute phase, the most information is carried by diffusion-weighted images (abbreviated as DWI) - images obtained using a specialized pulse sequence provided in expert-class MRI scanners, which we use in the study of all patients without exception.
Using DWI, you can see a minimal change in the diffusion (speed of movement) of fluid in brain tissue at the molecular level, which is the first sign of ischemic brain damage. In addition, when examining the brain of a patient with suspected lacunar infarction (as in all other cases), we use the entire set of pulse sequences that comply with the international standard to identify possible associated changes.
Symptoms and signs of lacunar stroke
- Convulsions of the victim's limbs;
- Migraine, severe prolonged headache;
- Movement and gait disturbances, the patient is no longer able to perform movements correctly;
- Pronounced primitive reflexes (trembling of the jaw, pulling out the lips into a tube when touching them, etc.);
- The articulatory apparatus is impaired, but the ability to recognize speech and write is preserved;
- Sensitivity may be partially impaired depending on the lesion.
To make a correct diagnosis, an examination is performed by a neurologist and an anamnesis is collected. Next, laboratory tests are carried out on the victim’s blood. Computed tomography allows you to determine the location in the brain where exactly the lesion occurred. Modern research methods also recommend diffusion-weighted and routine MRI, as these results will provide more reliable information. Echocardiography is mandatory. It allows you to exclude the presence of embolism in the vessels.
Classification
Clinical classification is based on clinical symptoms and is discussed in the section on symptoms of lacunar infarction.
In the development of the disease there are:
- the most acute period is the first 3 days;
- acute – 28 days;
- early recovery – the next 6 months after suffering a circulatory disorder;
- late recovery – for 2 years.
Due to mild symptoms and the absence of pronounced motor, speech and sensory disorders, it is very difficult to describe the features of each interval. Therefore, this division is of secondary importance.
Treatment Options
The main goal of ridding patients of the disease is to stabilize and maintain normal blood pressure levels, as well as prevent the formation of cardioembolism and conduct and changes in lipid metabolism. In some situations, regular appointments with a cardiologist are prescribed to monitor the correctness of therapy. It is he who prescribes additional antihypertensive measures and the use of antithrombotic drugs. To correct lipid metabolism, doctors prescribe statins. Also, therapeutic treatment is carried out using neurotropic components. Positive effects were noticed by experts after performing special exercises aimed at developing attentiveness, improving memory and level of thinking. If the patient suffers from depression, mild antidepressants are prescribed.
Consequences of the disease
Brain damage, the consequences of which can be very different, due to lacunae or ischemia, most often provokes a relapse of the disease. But most often, lacunae lead to disturbances in the patient’s mental state; the following are observed:
- loss of memory, most often partial, for the names of relatives and friends, etc.;
- nervousness, tearfulness and hysteria prevent a person from adapting to society;
- complete or partial disorientation in location and time, sometimes patients fall into childhood or youth.
Such people require constant monitoring and self-care, because... in this state they can easily die or injure themselves. Death from the disease itself is extremely rare, and most often occurs with repeated lacunar stroke.
This is caused by the lack of therapy and preventive measures. Despite the fact that the prognosis after this disease is most often positive, not a single doctor will say how long his patient will live.
And this is connected not only with how the patient will control his illness, but also with how the lacunae affected the cortical structure.
Preventive measures for lacunar stroke do not differ from those recommended for any other type of ischemia:
- Remove excess stress, both physical and mental, focus on feasible types of sports activities, giving preference to walking.
- Work on self-hypnosis, yoga classes. It has been proven that regular yoga classes lead to normalization of the entire body.
- Bringing weight to standard values, adjusted for age.
- Building a diet on a diet against sclerosis with a complete rejection of foods that provoke it.
- Strict control of blood pressure indicators.
- Timely detection of hypertension and its proper treatment.
- Completing a full course of rehabilitation if you have previously had a stroke or heart attack.
- When the prothrombin index increases, use special drugs aimed at reducing it. It is imperative to control this process so as not to provoke health problems, which can be caused by excessive thinning of the blood.
- If you experience any symptoms that indicate problems with the brain, immediately consult a doctor for help.
- Rest. It must be regular and complete. You cannot burden yourself with either physical activities or mental stress. It is the latter that becomes the cause of all diseases, including lacunar stroke.
Therefore, it is so important to quickly respond to the signals that your body sends you. Due to the fact that the risk group is elderly people, their relatives should be as attentive as possible to them, monitor changes in their behavior and health
golovaum.ru
With lacunar cerebral infarction, the consequences are different. They depend on the following factors:
- areas of brain damage;
- size of the infarct area;
- timeliness of diagnosis and adequacy of care.
The most common consequences of lacunar stroke are:
- memory impairment;
- development of dementia;
- disruption of the process of defecation and urination;
- hypersalivation;
- stiffness of movements;
- unsteadiness of gait;
- impaired coordination of movements;
- speech disorder.
Often the mental state of the affected person changes. He becomes whiny and hysterical. All these changes, unlike a major stroke, do not pose a threat to life. However, the quality of life deteriorates significantly. It sometimes takes years to restore motor functions and speech.
Complications after a lacunar cerebral infarction can be very diverse. They will depend on the following range of factors:
- Areas of brain damage;
- Size of the damaged area;
- Timeliness of diagnostic measures and adequacy of treatment.
- The consequences of lacunar infarction can lead to such negative complications as:
- Coordination disorder;
- Intellectual impairment such as dementia;
- Decreased memory;
- Decreased ability to analyze.
- Problems with urination and defecation;
- Speech defects;
- Changes in a person's mental state. The patient is characterized by tearfulness, hysteria, and depression.
What vascular agents and neuroprotectors are most active in cerebral ischemia?
To support and develop collateral blood flow, drugs such as Cavinton, Nicergoline, Cinnarizine, Eufillin are used. In modern neurology, these drugs are not recommended due to the identified “steal syndrome” (increased blood flow through dilated collaterals further increases the ischemic area, since blood flows into a new direction).
The need to activate metabolism and energy production in damaged brain cells requires drugs with neuroprotective and antioxidant effects. For this purpose: Glycine, Semax, Cerebrolysin, Nootropil, Mexidol, Cortexin are used.
The modern level of medicine takes into account the evidence base of clinical effectiveness. And, unfortunately, it does not exist for these drugs. However, many neurologists consider the use to be practically effective and justified.
Rehabilitation period
During the rehabilitation period, a whole range of measures is carried out, both medical and pedagogical, legal, social and psychological. All of them are aimed at restoring lost functions as a result of a lacunar stroke.
Principles of the rehabilitation program:
- If rehabilitation measures are started as early as possible, for example, from the first days of the onset of symptoms of the disease, recovery occurs much faster and more fruitfully. This is an excellent chance to avoid possible secondary complications, such as contractures, congestive pneumonia, thrombophlebitis and others.
- Rehabilitation should be carried out only under the supervision of specialists. If events are organized incorrectly, the chance of full recovery will be significantly less.
- Recovery requires the participation of a physical therapy methodologist, a neurologist, a physiotherapist, a psychotherapist, an occupational therapist and a speech therapist.
- The rehabilitation process involves the presence and support of the patient’s loved ones. It is best to entrust the patient with the most basic household chores on weekends or in the afternoon.
Preventive measures
Lacunar cerebral infarction can be prevented by quitting smoking and reducing the amount of salt, fat, and sugar in the diet. It is recommended to regularly consume fruits and vegetables, and include at least 30 minutes of physical activity (walking, exercise, gardening) in your daily schedule. It is advisable to limit alcohol consumption and maintain optimal body weight. For people over 50 years of age, it is advisable to regularly measure their blood pressure. Hypertension is a major risk factor for stroke.
Patients who have had a stroke or lacunar infarction are at high risk of recurrence, which is often more severe. Therefore, secondary prevention is necessary. It includes lifestyle changes, elimination of risk factors, pharmacological, and in some cases surgical or endovascular treatment of existing diseases that can cause a stroke.