Risk factors for stroke and heart attack
Planning a preventative treatment regimen is based on addressing risk factors that are largely similar for heart attack and stroke.
Metabolic risk factors include:
- dyslipidemia (impaired lipid metabolism - organic compounds, including fats and fat-like substances);
- arterial hypertension;
- obesity;
- metabolic syndrome;
- diabetes mellitus and other endocrinopathies;
- coagulopathies (diseases that develop as a result of disorders of the blood coagulation and anticoagulation systems).
Common markers of heart attack and stroke are:
- previous cardiovascular diseases;
- peripheral vascular pathology;
- calcium index;
- stress test results;
- hypertrophy (thickening of the wall) of the left ventricle.
Atherosclerotic stenosis of the carotid arteries and brain tumors increase the risk of stroke. The provoking factors of a heart attack are:
- atrial fibrillation;
- dysplasia (developmental disorder) of connective tissue;
- arteritis;
- diabetes.
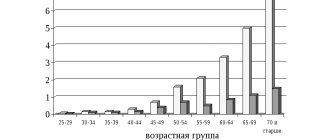
Although the incidence of stroke is higher in men, it is more severe in women, and about half of deaths from stroke occur in women.
Make an appointment
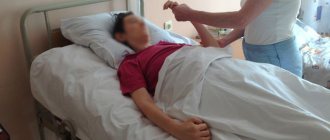
What to bring to the hospital
Relatives do not always know what can be brought to the hospital after a stroke and often forget necessary things and bring prohibited food.
You can bring to the hospital:
- Toilet supplies (soap, toothbrush, comb).
- Change of clothes.
- Diapers. Even if a person with a stroke goes to the bathroom on their own, at night, due to the inability to quickly get out of bed, an annoying nuisance can occur. This usually occurs in older people.
- Convenient dishes. It is difficult for a patient after a stroke to drink from a glass, and a drinking cup can improve the comfort of self-service.
- Homemade food. People with hemorrhagic stroke or after acute ischemia need to follow a diet. But, despite the fact that the hospital provides adequate food, homemade food seems tastier. From food you are allowed to bring boiled cutlets, vegetable and fruit purees, stewed meat and fish without spices.
If the patient is bedridden, it is recommended to bring large wet wipes. This will make it easier to carry out hygienic treatment when changing diapers.
Signs of a stroke
To diagnose cerebral blood supply disorders, it is necessary to use stroke recognition techniques:
- When trying to smile, you need to pay attention to the corners of the mouth - in case of a stroke, it can be directed downwards, the smile looks crooked and asymmetrical;
- When trying to speak, it may be difficult to pronounce even the simplest words and sentences;
- When trying to raise both arms, asymmetry is observed;
- The protruding tongue falls to the side.
If at least one of the symptoms is positive, you must immediately call an ambulance. Under no circumstances should you give him water, feed him, lift him, or take him by handy transport to the nearest hospital, as this can cause harm.
Symptoms of a stroke
- disturbance of consciousness, up to its loss;
- asymmetry of the face and drooping corner of the mouth;
- speech disorder;
- impaired sensitivity of the face and limbs.
Our expert in this field:
Shakhnovich Viktor Alexandrovich
Neurologist, MD
Doctor of Medical Sciences
Experience: More than 33 years
Call the doctor
Call the doctor
A patient suspected of having a stroke is asked to raise his hands, smile and state his full name. If this exercise cannot be performed or there is obvious asymmetry, urgent medical attention is needed. The first 3 hours are the best period to start treatment, since at this time it is still possible to dissolve the blood clot and reduce the degree of disability.
Help in the acute period
Which doctors are needed in the treatment of stroke depends on the period of the disease, but in any case, they must be experienced, highly qualified specialists who know how to properly provide assistance in this situation.
When diagnosing an ischemic stroke in a patient, the doctor’s goal is to restore blood supply with subsequent rehabilitation. This may require blood thinning medications or mechanical removal of the clot using a catheter. To remove atherosclerotic plaques, endarterectomy is performed, and to increase the diameter of blood vessels, plastic surgery with stenting is performed.
How long to stay in hospital if you have a stroke
Poor blood circulation in the brain, in other words, stroke, treatment involves three stages:
- prehospital;
- stay in the intensive care unit;
- treatment in a general ward.
The length of stay of a patient in a hospital, according to treatment standards, is 21 days, provided the patient has no violations of vital functions, and 30 days in case of serious violations. When the length of a patient’s stay in a hospital is insufficient, a medical examination is carried out followed by the development of an individual course of rehabilitation.
All patients diagnosed with stroke are subject to hospitalization. The length of stay in intensive care depends on a number of factors, including:
- depression of vital functions;
- degree of damage to brain tissue. With a major stroke, patients stay in intensive care longer;
- the need for constant monitoring if there is a high risk of recurrent stroke;
- severity of the clinical picture;
- level of depression of consciousness and others.
Basic and differentiated therapy
Treatment of a patient in the intensive care unit involves basic and differentiated therapy.
Basic treatment is aimed at:
- fight against cerebral edema;
- restoration of normal functioning of the respiratory system;
- patient nutrition;
- maintaining hemodynamics at an acceptable level.
Differentiated therapy involves:
- normalization of arterial and intracranial pressure, elimination of cerebral edema after hemorrhagic stroke. In the first two days, a decision is made regarding the need for surgery. Neurosurgeons at the Yusupov Hospital daily perform surgical interventions to eliminate the consequences of stroke and save the lives of hundreds of patients. All manipulations are carried out using modern medical equipment using effective proven techniques;
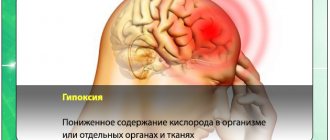
- accelerating metabolic processes, improving blood circulation and increasing the resistance of brain tissue to hypoxia when diagnosed with ischemic stroke. The length of stay in intensive care directly depends on the timely and adequate course of treatment.
In most cases, young people recover much faster than older patients.
It is possible to transfer a victim from the intensive care unit to a general ward after meeting a number of criteria:
- the patient can breathe independently, without the support of devices;
- the patient is able to call a nurse or doctor for help;
- there is a stable level of heart rate and blood pressure;
- the possibility of bleeding is excluded.
Only after the patient's condition has stabilized can the doctor transfer the patient to the ward. In a hospital setting, various rehabilitation procedures are prescribed to quickly restore lost functions.
In the neurology department of the Yusupov Hospital, patients are not only developed an individual course of rehabilitation therapy, but also given psychological support.
If necessary, psychologists work with loved ones and relatives of the patient to teach them the basics of caring for a person who has suffered a stroke.
How long do they stay in the intensive care unit?
Relatives are interested not only in the prognosis of the patient’s recovery, but also in how long they spend in intensive care after a stroke.
How long you will have to stay in the intensive care unit is determined by the condition of the victim. For an uncomplicated ischemic attack, when vital organs are not affected, the patient is in the department for 21 days.
They stay in intensive care longer in the following cases:
- patient after surgery for hemorrhagic hemorrhage;
- the patient is in serious condition and is on a ventilator;
- the patient did not recover from the coma;
- if it does not improve after therapy and the condition is unstable.
Often relatives hear diagnoses and do not always understand what is said correctly. Let's consider frequently asked questions from loved ones of a stroke patient:
- The condition is extremely serious, he is in intensive care: what does this mean? This term means that a person is confused or comatose and their vital signs are unstable.
- Stable severe condition during stroke: what could such an assessment mean? There is no serious cause for concern here. The term “stablely severe” means that the person is breathing independently and vital signs are within normal limits. There is a good prognosis for recovery.
Doctors cannot answer how long they are in intensive care for complicated stroke attacks. How long the resuscitation period will last depends on the victim’s body’s ability to restore functions.
Recovery period
The rehabilitation period is aimed at restoring lost functions and improving the quality of life of patients who have suffered a stroke. The doctor develops a rehabilitation program individually for each patient, taking into account the scale of the vascular accident, age, comorbid pathology, etc.
In case of strokes, doctors assign a special role to the prevention of recurrent strokes, which includes proper nutrition, giving up bad habits, eliminating excess weight, and regular monitoring by a doctor.
Is full recovery possible after a stroke?
The patient’s relatives play a significant role in the rehabilitation of a patient after a stroke. It depends on their attention, care, patience and correct actions whether the patient’s lost functions can return.
The recovery process after a stroke is a difficult period, both for the patient himself and for his loved ones. The rehabilitation time depends, first of all, on the degree of damage to brain tissue. Patients may have impaired coordination of movements, mobility of limbs, speech, memory, hearing, and vision.
The patient’s persistence and positive attitude can speed up the recovery time of lost functions.
An experienced team of doctors will speed up the rehabilitation process thanks to a well-designed individual treatment program.
Levels of recovery after stroke
After hemorrhagic and ischemic strokes, there are three levels of recovery:
- the first is the highest. We are talking about the complete restoration of lost functions to their original state. This option is possible in the absence of complete death of nerve cells in a region of the brain;
- the second level is compensation. The early stage of recovery, usually in the first six months after a stroke. Lost functions are compensated by the involvement of new structures and functional restructuring.
- The third level involves readaptation, that is, adaptation to the emerging defect. The patient’s relatives and friends play a significant role in this process. They are the ones who help the patient learn to live with the emerging defect.
Specialists at the Yusupov Hospital, if necessary, work with the patient’s relatives, teaching them the specifics of care, as well as providing them with psychological support.
Inpatient therapy
Treatment methods for stroke in a hospital differ from those used in ARC. The standard of treatment for stroke in a hospital consists of the following measures:
- drug therapy aimed at restoring brain functions;
- rehabilitation.
Rehabilitation activities include physiotherapy, massage, exercise therapy. Patients with speech disorders receive additional treatment from a speech therapist.
How stroke complications are treated depends on the nature of the abnormalities that arise. The nature of the attack has almost no influence on the prescribed therapy. Treatment of ischemic stroke and hemorrhagic lesions follows a similar scheme.
How many days the therapy will continue depends on the prescribed course of treatment. Typically, the treatment period for ischemic stroke is slightly shorter than after cerebral hemorrhage.
Prognosis for recovery after stroke
Favorable factors for recovery after a stroke include:
- timely early start of rehabilitation therapy;
- spontaneous early recovery of lost functions.
Among the unfavorable factors of recovery after a stroke are:
- advanced age of the patient;
- large area of brain tissue damage;
- poor blood circulation around the affected brain tissue;
- damage to cells in functionally important areas of the brain.
Basics of Stroke Recovery
In the process of rehabilitation, the positive attitude of the patient himself and his desire to return to independent life are important. Psychological support and assistance from the patient’s relatives plays a huge role. You can make an appointment with a neurologist by phone.
Memory recovery after stroke
Treatment of patients after a stroke takes place in the neurological department. Memory restoration depends on many factors: the size of the area of brain damage, the location of the damage, and the timeliness of medical care. The faster blood circulation in the brain is restored, the greater the chance of memory recovery after a stroke.
Memory restoration after a stroke is possible with the participation of several specialists - a neurophysiologist, psychologist, neuropsychologist, neuropsychiatrist. Help for a patient after a stroke is provided at the rehabilitation clinic of the Yusupov Hospital. In the hospital, the patient is treated according to an individual recovery program; many specialists take part in the development of such a program. When developing the program, the patient’s health condition, the severity of brain damage, and memory impairment are taken into account.
In some cases, it takes several years to restore memory and speech; during recovery, the doctor prescribes medication, a special diet, various trainings - color therapy, rhythm therapy, music therapy and others. Memory restoration at home is not always successful due to the lack of a training program and knowledge in the field of rehabilitation of patients after a stroke.
You can make an appointment with a neurologist at the Yusupov Hospital by phone. Consultation with a specialist, full patient care, rehabilitation using innovative equipment, massages and exercises will help the patient regain full memory.
Restoring a hand after a stroke
A positive attitude and support from family have an impact on rapid recovery from illness. Partial paralysis of the arm is a common occurrence after a stroke and is characterized by stiffness of movement and limited motor ability of the arm. Functional paresis (partial paralysis) refers to neurological syndromes, caused by disruption of the nervous system, damage to the nervous system pathway due to damage to the cerebral cortex after a stroke. Paralysis of the arm is the complete absence of voluntary movements of the limb.
Recovery from a stroke may involve the hand or the entire limb. With partial paralysis, the ability to move the arm or hand freely is impaired; the person cannot fully care for himself or perform basic actions. To restore motor ability, the patient must perform daily exercises for finger motor skills and limb motor skills.
The rehabilitation process of restoring motor activity of the limbs requires patience from the patient and a lot of work - this will allow you to return to a full life after a stroke. You can make an appointment with a neurologist by phone. The rehabilitation doctor will develop individual exercises for the patient, the patient will be under constant medical supervision and receive qualified assistance from specialists.
Causes of stroke
To understand the causes of stroke, you should know that there are two types of stroke: ischemic and hemorrhagic. They differ both in origin and in treatment methods.
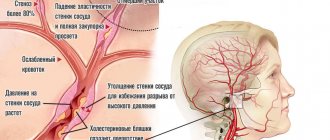
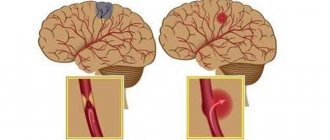
Ischemic stroke occurs due to the formation of a blood clot or clot that blocks the arteries of the brain and disrupts the blood supply.
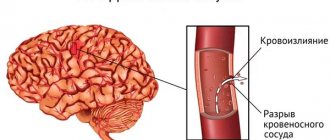
A hemorrhagic stroke occurs due to a rupture of a blood vessel in the brain, which causes blood to accumulate in adjacent tissues. The blood formed in large quantities puts high pressure on the brain tissue, as a result of which their work is disrupted.
In medicine, there are many reasons for the development of such a terrible disease as stroke. Among them are:
- high blood pressure – constant changes in blood pressure impair the elasticity of blood vessels and lead to their ruptures,
- frequent arrhythmias - interruptions in heart rhythm can lead to the formation of blood clots that impair blood circulation in the brain,
- exceeding the permissible level of cholesterol in the blood - increased cholesterol contributes to the formation of plaques that block blood vessels and lead to the development of a stroke,
- increased blood sugar causes fragility and fragility of the walls of blood vessels, as a result of which the likelihood of their rupture increases,
- formation of aneurysms on the vessels of the brain,
- poor blood clotting leads to the formation of clots in blood vessels,
- overweight,
- alcohol consumption,
- smoking.
The most common causes of stroke are thrombosis, internal bleeding in the brain.
Thus, the main cause of stroke is damage to nerve cells, which are located in the brain and are responsible for all functions of the human body.
Factors influencing the speed and quality of rehabilitation
There are many factors that influence the speed of recovery after a stroke, so predicting the duration of rehabilitation and likely results is quite difficult.
How long rehabilitation after a stroke will last depends on the individual parameters for each person, as well as on other factors:
- volume of damage: an extensive stroke significantly worsens the severity of the patient’s condition, and also causes many neurological complications that adversely affect the timing of recovery and its quality;
- patient’s age: the older the victim, the longer the recovery;
- localization of damage: circulatory disorders of deep structures are difficult to treat;
- type of stroke: hemorrhagic strokes are less common, but occur in a more aggressive form, and also have a high mortality rate, although the prognosis for rehabilitation is more favorable than for ischemic stroke;
- caused by disorders: the presence of multiple cerebral symptoms, comatose states, severe paralysis and sensory disturbances give an unfavorable prognosis for recovery;
- timeliness of therapy: the most positive results of therapy can be achieved by starting treatment measures in the first 4 hours after the onset of the first symptoms; seeking help at a later time worsens the prognosis;
- compliance with medical recommendations: after the patient is discharged from the medical institution, the patient is given recommendations that can improve the quality of life, prevent the formation of relapse and negative complications.
The severity of the lesion has the greatest impact on the likelihood of restoration of lost functions and the timing of rehabilitation. With extensive strokes, violations of the most important functions are observed, even if the prescribed rehabilitation program is followed, the prognosis is rather disappointing. The greatest difficulties arise with the complete return of speech and motor functions. Close relatives who will devote a lot of time to special activities with the patient can positively influence the situation.
ONMC: four letters, one diagnosis, a lot of questions
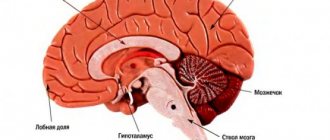
A stroke is an acute cerebrovascular accident (CVA), resulting from blockage of a vessel or rupture of a vessel, manifested by neurological symptoms (paresis, paralysis, speech impairment).
What is happening in the body at this moment:
-The vessel is blocked by a blood clot or plaque
-Vessel rupture occurs
- Death of nerve cells in the brain occurs
-The body loses the functions for which these cells were responsible (paralysis, loss of speech, vision)
About 500 thousand people a year in Russia and more than 6.5 million worldwide suffer from stroke.
Today we spoke with the head of the specialized department of the regional vascular center of the Alexander-Mariinsk Regional Clinical Hospital, where stroke patients are treated every day. Elena Vitalievna Asfandiyarova is a neurologist of the highest qualification category, whose work experience is more than 30 years, including more than 10 years in emergency neurology, since 2013 in the department for patients with stroke.
-Elena Vitalievna, let's start right away with the most important thing. Are there warning signs of a stroke that can appear long before it, and how can a person recognize them?
Precursors of ischemic stroke can be transient ischemic attacks, or transient cerebrovascular accident. This is when a person, due to high blood pressure, experiences numbness or weakness in the limbs of the same name, sometimes with speech impairment. This condition can be observed for several minutes, less often – one hour, after which the symptoms disappear. After such symptoms, the probability of having a stroke in the next month is more than 60%. Therefore, in this situation, the issue of further examination of the patient and the prescription of drugs that prevent the occurrence of stroke is urgent.
Very often, patients do not treat high blood pressure: they take medications only during a crisis, do it irregularly, or do not take them at all. In such a situation, the brain vessels may not be able to withstand another surge in pressure, and a hemorrhagic stroke or cerebral hemorrhage will occur.
-Tell us a little about these types of stroke. What is the difference?
An ischemic stroke occurs when, due to blockage of a vessel by a blood clot or atherosclerotic plaque, blood flow to one or another part of the brain stops and necrosis of brain tissue occurs. About 80% of all strokes are ischemic strokes. At this time, within a few minutes, a stroke core is formed - an area that cannot be saved. Often this zone is not so large. And around the core of the stroke, a penumbra zone is formed - brain cells that have reduced blood flow, but are still viable. This zone, as a rule, is several times larger than the nuclear zone of the stroke; the cells in it live up to 4.5-6 hours. It is for the preservation of this zone that the struggle takes place in the first hours after the onset of a stroke. That is why it is necessary to deliver the patient to a specialized department as soon as possible for possible pathogenetic treatment.
Hemorrhagic stroke is a rupture of a vessel due to pathology of its wall, for example, an aneurysm (thinning and protrusion). This often occurs with a sharp increase in blood pressure. As a result, hemorrhage occurs in the brain, a hematoma is formed, which, due to the closed volume of the skull, puts pressure on the substance of the brain and disrupts the functioning of any of its areas. This pathology accounts for 20% of the total number of strokes. Often, hemorrhagic stroke can be treated with surgery.
-What are the main symptoms of a stroke?
Symptoms of a stroke are general cerebral: headache, nausea, vomiting, impaired consciousness. There is also a disturbance of movement and sensitivity in the limbs of the same name, a distortion of the face and a speech disorder.
In addition, signs of a stroke may include blurred vision, dizziness, and unsteadiness when walking, which occur acutely against a background of high blood pressure.
— What should be the actions of a person who observes such symptoms in himself or someone else?
Even at the slightest suspicion of a stroke, the first thing a person should do is call an ambulance, since only in a specialized department is it possible to make an accurate diagnosis and begin the necessary treatment in a timely manner. All patients with suspected stroke undergo computed tomography. Even if the symptoms of a stroke were relieved within a few minutes or hours, this condition also requires immediate hospitalization and a decision on further tactics with the patient - treatment in a hospital, prevention of stroke, or possibly surgical treatment in the department of vascular surgery (for pathology of the main arteries of the brain).
-How can a person who happens to be nearby help you before the specialists arrive?
If you suspect a person is having a stroke, then first of all you need to provide him with rest. If there are signs of nausea or vomiting, then turn your head to the side so that vomit does not enter the respiratory tract, unfasten everything that is tight: buttons, locks, belt and provide access to fresh air (open windows, doors).
IMPORTANT TO REMEMBER: IF YOU SUSPECTED A STROKE, IT IS STRICTLY PROHIBITED TO TAKE MEDICINES BEFORE THE ARRIVAL OF THE AMBULANCE Crew!!!
“Many people don’t see a doctor because they’re not sure what’s really going on with them. How dangerous are such delays for human life?
It often happens that a person has signs of a stroke, but does not seek help at the hospital. Moreover, this does not depend on the level of awareness in this issue or education - this can even happen to medical workers. Having noticed numbness in the limbs, for example, many people hope for the Russian “maybe” and wait for everything to go away on its own. As a rule, over time, the symptoms increase, the patient’s general condition worsens, and only then does the person seek help from specialists. These lost hours, unfortunately, in many cases lead to disappointing prognoses, and can cost someone their life. If you end up in the hospital on time, then the chances of undergoing treatment that will completely relieve the person from the neurological deficit increase.
Today, in the Astrakhan region there are a sufficient number of specialized hospitals to provide care to patients with stroke at any time of the day.
-I have often seen such headlines as “Stroke is getting younger.” What do you think is the reason for the occurrence of this dangerous disease in young people?
There has always been such a concept that stroke is a disease of middle-aged patients. Unfortunately, it is not. Every year more and more young people are affected by this disease. This is most often associated with an incorrect lifestyle, high workload, and stressful situations. But when children suffer from strokes, the situation is a little different. If in adults the cause lies in the pathology of the heart and blood vessels, then in children it is in increased blood clotting. In our department there were also young people with congenital heart defects. With this pathology, cardiac output to large vessels of the brain is disrupted. There were young people with congenital vascular pathology, which they did not even suspect. The stroke occurred due to sudden movements while playing sports. At this moment, the vessel is dissected (ruptured). A hematoma forms between the walls, it stratifies, forming blood clots, which also “fly” to the head. This variant of ischemic stroke quite often occurs in young people during sports activities. Unfortunately, it is impossible to predict its appearance.
That is, there are no diagnostic tests that could determine increased blood clotting in a young patient or find a damaged vessel?
Probably not possible to predict. If there are any prerequisites for increased blood clotting, then the doctor will prescribe special tests. If young patients have high blood pressure or have any abnormalities in the functioning of the heart, these young people should be observed by doctors and periodically undergo preventive examinations. It is possible to examine the blood for increased coagulability (if there is a need for it), and it is also possible to examine the vessels of the head and neck after a doctor’s prescription.
-Can you remember the youngest patient diagnosed with stroke in your practice?
The youngest patient in my memory was 21 years old at the time of admission to the hospital. He just had congenital features with blood clotting. He was admitted in a timely manner, in the first hours after the onset of an ischemic stroke, with severe paresis of the limbs. The patient had speech disorders for a long time. But, fortunately, the rehabilitation was successful and he fully recovered. Today I have already graduated from college. We continue to communicate with him, and he periodically seeks advice.
-How long can a patient spend in hospital after a stroke, and what treatment does he receive?
If the patient goes to the hospital on time and is diagnosed with a transient cerebrovascular accident, then within 7 days he is given a full range of examinations and preventive measures are prescribed to prevent a stroke.
Patients with moderate ischemic stroke spend about two weeks in the hospital. There are strokes with minimal deficiency, these patients are treated for up to 10 days, secondary prevention of recurrent strokes is prescribed and the patient is sent for outpatient treatment. In the case of a severe stroke, the length of hospital stay increases significantly – up to one month. Next, the issue of rehabilitation is resolved.
What methods have been introduced today for the treatment of stroke? How is he treated in the hospital?
A patient with suspected stroke is admitted to the hospital, bypassing the emergency department to the examination room of the regional vascular center. First of all, he undergoes a computed tomography scan of the brain and is examined by specialists. Once the diagnosis is confirmed, all patients are sent to the intensive care ward, where they remain for at least 24 hours. There, treatment begins from the first minutes and their condition is monitored around the clock. When the condition stabilizes, the patient is transferred to the early rehabilitation ward. If a patient is admitted to the hospital during the so-called “golden hour” - this is up to 4.5 hours from the onset of an ischemic stroke and, in the absence of contraindications, he is given thrombolytic therapy. Thrombolysis is the administration of a special, expensive intravenous drug. This procedure is included in the standards of care for patients with ischemic stroke and is carried out within the framework of compulsory medical insurance. When using this treatment method, we see the result already “on the needle.” A real miracle occurs: the patient’s face straightens out, his limbs begin to work, and his speech returns. This is the most effective method of treating ischemic stroke today, which is used throughout the world. We have been using thrombolysis in our practice since the opening of the department - more than 6 years. But this method is not suitable for everyone, as it has more than 20 contraindications. And, unfortunately, we cannot use it as often as we would like. This is due to the fact that most patients seek medical help too late.
-If you find yourself in the hands of doctors in time, is it possible for a person to return to his normal life in the future?
Stroke is a serious disease. More than 30% of patients die after a stroke within the first month, 65 survive, of which 10-12% return to normal life, the rest remain disabled. Disability is an equally terrible outcome of this pathology. It is not enough to save the patient; it is necessary to ensure that he returns to social life. After all, there is life after a stroke! Therefore, I repeat, the sooner the patient is admitted to a specialized department, the sooner rehabilitation measures begin - and they begin already in the intensive care ward - the better the result from the treatment received.
-Which specialists treat stroke in the hospital?
Not only a neurologist and a resuscitator care for the patient. A multidisciplinary team is involved in the work. It also includes a cardiologist, a medical psychologist, a doctor and exercise therapy instructor, a physiotherapist, a speech therapist, and nursing and junior medical personnel. All these people work with patients who have suffered a stroke.
I heard that there are cases when, after a severe stroke, the patient’s relatives want to immediately take him home, not seeing the point in rehabilitation. That's the right decision?
In this situation, of course, we cannot hold back. But we try to explain that it is better to remain under the supervision of doctors and visit your loved one in the hospital. In our hospital, classes are held with the relatives of patients, a psychologist communicates with them, and here they explain how to care for the patient. Let me cite one proven fact: if one person in the family suffered a stroke and became bedridden, then about 8 relatives are “excluded” from society (if they are caring relatives, of course). Everyone should be involved with this patient. Therefore, we convince you that it is necessary to stay in the hospital for the first time in order to prepare to independently care for your loved one. In addition, there are cases when we do not see results in the first week, but they appear a little later. The patient requires ongoing rehabilitation after a stroke.
What role do loved ones play in the patient’s recovery process?
Colossal! It has been proven that a patient who has suffered a stroke must be in society. No expensive medicine can replace communication with relatives. Bringing you to the window, talking, showing photos and trying to get a response - this is the minimum that loved ones should do every day. Stroke is a disease that requires the joint efforts of specialists and relatives. In the first days, we often encounter anger from relatives: they blame the doctors for what happened. They can be understood, because this is a huge stress for the family. But, as a rule, this condition passes, the relatives come to understand everything that is happening, and then we begin to work with them as a team. There are two identical strokes with different outcomes. Do you know what the difference is? – No, not in treatment or rehabilitation. It’s just that one patient’s relatives visit him every day and sincerely worry about him, but in another case this is not the case.
-How many stroke patients are treated in your department every month?
I can say that today the department is overcrowded. Apparently, the abnormal weather also affects temperature changes. On average, we discharge more than 100 patients with a positive outcome every month. Unfortunately, we also have negative results when we cannot help save our patient. The mortality rate in our department is low compared to other similar departments in our region and much lower than the national figures. We are proud of this. I believe that this is the merit of our close-knit team, whose work is focused on results. Our attitude towards patients is always warm, we try to support them not only with medications and special classes, but also morally, we know all patients by name, we often know their life stories, we will always find time to talk with the patient on abstract topics. The department has our personal library, where patients are happy to borrow books, read them in the department, and sometimes take them with them. In the intensive care unit, we often play music: sometimes classical, sometimes according to the wishes of our patients; if the patient cannot say about his preferences, then we ask the family what their relative prefers to listen to. We remain friends with many patients even after discharge.
-Elena Vitalievna, how can we still reduce the risk of stroke? Are there effective prevention measures?
Considering that in most cases, stroke is caused by arterial hypertension, the main preventive measure is blood pressure control. It is necessary to regularly use antihypertensive drugs. Precisely regularly, since they tend to accumulate in the body and maintain normal blood pressure. It is also necessary to control cholesterol levels, treat diabetes and chronic diseases, lead a healthy lifestyle, and devote enough time to physical activity and physical education. You need to walk a lot, not run, but walk. There is an expression: “Running from a heart attack leads to a stroke.” This implies that the body requires reasonable physical activity. Everything is good in moderation!
As for diet, it is important to limit the consumption of animal fats and give preference to fish, vegetables and fruits. And, of course, a positive attitude, less anxiety and stress. Live for today, please your loved ones and enjoy life yourself. Find happiness in the little things, be outdoors more often, do what you love, and don’t forget to look after your health!!!
Stroke Prevention
Prevention of heart attack and stroke in women and men are links in one chain of measures that prevent disability and death in people suffering from cardiovascular diseases.
Cardiologists and neurologists at the Yusupov Hospital use modern diagnostic methods to examine patients, allowing them to identify risk factors for vascular diseases and take measures aimed at preventing diseases. Medicines for the prevention of stroke and heart attack allow you to control the course of the disease, reduce the incidence of acute cardiovascular crises, and the likelihood of complications.
Chance of full recovery after stroke
The rehabilitation period is individual; for some, a few months are enough; for others, it will take years to achieve a positive result. The earlier restoration procedures are started, the more favorable the prognosis. At the same time, the patient’s attitude and focus on results is important; The greater a person’s desire to return to a full life, the more effective the classes and exercises.
At the Yusupov Hospital, a well-coordinated team of professionals (neurologists, rehabilitation specialists, therapists, cardiologists, speech therapists, psychologists) takes part in the rehabilitation of patients after a stroke. Doctors create an individual program for each patient, aimed at the best possible result, observing the following principles:
- early start of restorative procedures;
- systematicity and duration of events;
- complexity of procedures;
- multidisciplinarity of classes;
- compliance of procedures with the patient’s condition;
- active interaction between doctors and the patient and his family.
You can make an appointment with the doctors at the Yusupov Hospital and find out how much rehabilitation after a stroke costs by calling.