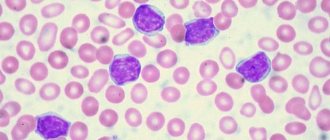
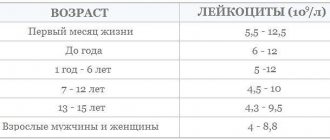
Leukemia, which is often called blood cancer or leukemia, is a serious cancer. It affects the hematopoietic organs and causes changes due to which the number of leukocytes in the patient’s blood sharply increases. As the disease progresses, the blood gradually ceases to perform its functions in the body, which causes death if left untreated. The disease affects not only adults, but also children, and is found with equal frequency in men and women.
Types of disease
The modern classification of leukemia includes several principles of division into types. First of all, it is worth mentioning the division of cases of the disease according to the nature of the course into:
- acute, characterized by rapid development and the formation of a large number of immature blood cells - blasts;
- chronic, which are characterized by a long course and pathological production of mature leukocytes with altered properties.
Another principle for classifying leukemia is based on the level of differentiation of the affected cells, which can be:
- undifferentiated;
- quotational;
- blast.
In addition, oncologists distinguish many types of leukemia according to the types of cells whose pathological changes underlie the disease. According to this principle, lymphoblastic, monoblastic, myeloblastic, lymphocytic, myeloma and other types of disease are distinguished.
Treating oncology under compulsory medical insurance – what is needed for this?
You can receive FREE medical care at the Oncology Center under the State Guarantee Program of Compulsory Medical Insurance (Compulsory Medical Insurance) and High-Tech Medical Care.
The service is valid for all Russian citizens.
To find out more details, as well as for what nosologies and services this program works, please call +7, or you can read in more detail here.
Treatment and diagnosis of oncology are expensive medical services. The examinations alone cost a lot of money, and this is only the beginning of an already difficult path. Therefore, many patients are forced to postpone cancer treatment, since financial losses can literally ruin them. In this regard, the Sofia Clinic offers a number of services under the health insurance policy. Free cancer treatment under compulsory medical insurance is available to all Russian citizens. First of all, patients with very serious diagnoses, for whom treatment is a matter of life and death, can count on it. Such cancer patients are provided with quotas, which are financed from the federal and local budgets. As part of treatment under compulsory medical insurance, the following procedures are performed:
- PET/CT;
- radiation therapy;
- chemotherapy;
- IHC;
- surgery.
The decision to provide free oncology treatment under compulsory medical insurance is made by three commissions - the clinic, the health department and the medical institution itself. You can shorten this path if you immediately contact us and ask what procedures our clinic issues quotas for. The doctor (therapist or oncologist) will prepare a statement with the diagnosis and information about what diagnostics you have already undergone. You will need to submit to the regional health authority:
- medical direction;
- application for treatment of cancer under the compulsory medical insurance policy;
- Russian passport and insurance policy;
- SNILS;
- consent to the processing of personal data;
- pension certificate (for pensioners).
Symptoms
The course of different types of disease is not accompanied by specific symptoms of leukemia. On the contrary, its manifestations are the same for all types of pathology and are poorly diagnosed in the initial stages. These include:
- increased susceptibility to colds and seasonal ailments;
- night sweats;
- joint and bone pain;
- swelling of the lymph nodes;
- instability of body temperature, constant sharp changes;
- pallor, grayish skin tone;
- general malaise, weakness;
- long-term healing of even minor injuries;
- causeless loss of body weight.
In the later stages of the disease, more distinct signs of leukemia appear:
- characteristic yellowness of the skin and eye whites;
- deterioration of vision, up to complete dysfunction;
- severe headaches;
- difficulty breathing, pneumonia;
- frequent nausea, vomiting;
- problems with cardiac activity;
- numbness of the facial muscles, partial or complete.
In later stages, due to increased fragility of blood vessels, subcutaneous and internal hemorrhages often develop. Ulcerative-necrotic tissue lesions and severe tonsillitis may appear.
When to see a doctor
You should seek help from an oncohematologist if your health condition worsens if the following symptoms and signs are present:
- a sharp deterioration in health;
- unreasonable increase in body temperature;
- the appearance of rashes and bruises on the body;
- poor wound healing;
- pain in bones and joints;
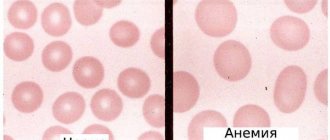
- symptoms of anemia;
- hemoglobin levels and immunity are reduced.
Signs of deteriorating health in any case are a reason to contact the oncology center so that the doctor can prescribe additional tests and adjust the treatment.
Causes and risk factors
A specific relationship between certain exposures and the occurrence of blood cancer has not yet been discovered, but risk factors that increase the likelihood of developing the disease are well known to oncologists.
- Heredity. If there are cases of the disease in the family, the risk increases 3-5 times. In addition, genetic diseases are a significant risk factor.
- Radiation. Significantly more often than usual, symptoms of leukemia occur in people exposed to radiation.
- Chemical substances. Dozens of chemical compounds that people come into contact with during their professional activities have pathogenic effects that provoke mutation of blood cells. In particular, these include gasoline vapors.
- Smoking. In people who smoke, the risk of acute myeloblastic leukemia increases several times.
The presence of one or even several of the listed factors does not mean that a person will necessarily get sick, but the likelihood of blood cancer is significantly increased.
Stages
Acute and chronic blood cancer differ somewhat in the nature of the disease. Oncologists distinguish the following stages of acute leukemia:
- full clinical development, in which the patient experiences bleeding, inflammatory processes in various organs, the number of red blood cells decreases, and hemoglobin decreases;
- remission, when clinical manifestations decrease and the number of immature cells in the bone marrow does not exceed 5%;
- relapse, when the patient’s well-being worsens with an increase in the number of immature leukocytes in the bone marrow and blood;
- terminal, in which the tumor progresses, and almost all blood cells become pathological, which is why ulcerative-necrotic processes develop in many organs.
The stages of remission and relapse can be repeated cyclically several times, with relapses becoming more and more severe, and remissions becoming short and less pronounced.
Chronic leukemia is divided into the following stages:
- initial, lasting up to a year, during which the number of neutrophilic leukocytes in the blood increases and the alkaline phosphatase level drops several times;
- developed, lasting up to five years, with a clinical picture characteristic of the disease, when the bone marrow gradually ceases to produce normal blood cells, the spleen increases in size, and the altered cells gradually penetrate into the peripheral bloodstream;
- terminal, the duration of which does not exceed six months, characterized by the spread of cancer cells to all vital organs through the bloodstream.
Diagnostics
The main procedures in diagnosing leukemia are laboratory blood tests: general, biochemical, genetic.
Equally important are bone marrow and cerebrospinal fluid puncture studies:
- cytogenetic, identifying atypical chromosomes characteristic of altered cells;
- cytochemical, which makes it possible to detect the acute form of the disease at an early stage;
- immunophenotypic, as a result of which it becomes clear what types of cells have undergone malignant changes;
- myelogram, which allows you to determine the stage of the disease and the dynamics of the process.
At the same time, the patient is prescribed instrumental studies of internal organs - ultrasound, CT, MRI to determine leukemic infiltration.
Treatment
After leukemia is detected, treatment is selected in accordance with the form and stage of the disease, the level of damage to vital organs, age, and general condition of the body. The treatment method is chosen by a specialist - an oncologist, an oncohematologist, and his goal is to restore the normal hematopoietic process, achieve long-term remission, and ideally, a complete cure.
The choice of method largely depends on the form of the pathology. In acute cases of the disease, chemotherapy has a good effect; in cases of chronic disease, the most effective method is often a bone marrow transplant or stem cell treatment. Adverse symptoms are relieved by detoxification and hemostatic therapy, the introduction of healthy platelets and leukocytes, and courses of antibiotics.
Prices
| Name of service | price, rub. | Unit measurements |
| Consultation with an oncologist and radiotherapist | 1 500 | PC. |
| Consultation with a pediatric oncologist | 0 | PC. |
| Repeated consultation with specialists | 500 | PC. |
| Primary topometry on a specialized computed tomograph | 15 000 | procedure |
| Repeated topometry on a specialized computed tomograph | 7 000 | procedure |
| Primary dosimetric planning of radiation therapy (tomotherapy) | 20 000 | PC. |
| Repeated dosimetric planning of radiation therapy (tomotherapy) | 7 000 | PC. |
| Radiation therapy (tomotherapy), including IMGRT (*) | 315 000 | well |
| Radiation therapy (tomotherapy) stereotactic radiofrequency surgery (*) | 315 000 | well |
| Accompanying drug therapy: intravenous administration in the treatment room (excluding the cost of medications) | 1 000 | procedure |
| Accompanying drug therapy: intramuscular administration in the treatment room (excluding the cost of medications) | 200 | procedure |
| Topometric marking | 750 | procedure |
| Conducting a study of the radiation therapy plan using absolute dosimetry on a specialized phantom “Cheese Phantom Accuray” | 15 000 | procedure |
| Carrying out the quality assurance (QA) procedure for the radiation therapy plan on the specialized phantom “PTW Octavius” | 30 000 | procedure |
The type of radiation therapy and the number of sessions of the course are determined by the medical commission individually for each patient based on the location, nosology of the tumor and taking into account the medical history.
Free online consultation
Sign up
Forecasts
The success of leukemia treatment depends on many factors, but in most cases the prognosis is favorable. Acute forms are more complex, since the rapid course of the disease leaves less time for the doctor to act. In the chronic form, favorable outcomes, according to statistics, account for up to 85% of cases.
In any case, there remains a chance for a long-term remission and complete relief from the disease. In adults, the probability of a positive outcome is at least 40%, in children - up to 90%.
Make an appointment
Our oncology clinic is located in the very center of Moscow, close to several metro stations - Novoslobodskaya, Tverskaya, Chekhovskaya, Belorusskaya and Mayakovskaya. For visitors arriving by car, there is ample parking available on the medical grounds. Our employee will help you find your way around the clinic, take you to the right department and tell you where this or that office is located.
You can make an appointment with a specialist:
- by calling a phone number;
- online by filling out a special form on the website;
- ordering a call back.