A general clinical blood test can deservedly be considered one of the most effective diagnostic procedures. It is impossible to underestimate the importance of laboratory blood testing along with external examination and questioning of the patient. It is by the structure, volume, quantity, and scale of distribution of formed cells in the blood flow that the condition of the internal organs and the functioning of the body systems can be determined with a high degree of probability.
In order to understand what pdw is in a blood test and why it is needed, you must first get an idea of the concept itself.
Platelets and the concept of pdw in the bloodstream
The abbreviation RDW can be deciphered as “platelet disintegration width by volume.” On the laboratory form it represents the platelet distribution index. These cells are the most microscopic in size compared to other elements of the blood channel, their size varies from 2–5 micrometers. Platelets are often called platelets because they have a flat, oval shape with projections. These shaped particles are transparent and do not have a nucleus.
Purpose of platelets:
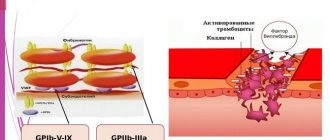
- Release of factors for blood clotting with the aim of forming blood clots in the area of violation of the integrity of the internal or external soft tissues of the body.
- Production of growth factors for the restoration of blood vascular walls and their nutrition, by providing biologically active components.
- Supply of immune complexes to the sites of the inflammatory process to eliminate it.
- Filtration of blood from antigens destroyed by combining them with antibodies.
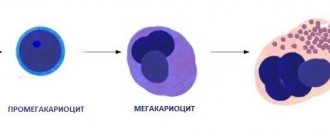
The synthesis of flat, nuclear-free bodies occurs in the main hematopoietic organ - the bone marrow. The predominant number of platelets, about 80%, is present in the bloodstream, while a small part of about 20% is constantly located in the spleen. Here and partly in the liver, the disposal of obsolete colorless, flat cells is carried out. The existence of platelets lasts only 8–12 days.
The formation and elimination of platelets and other formed microparticles of blood is carried out continuously. At the same time, the circulatory system contains cells that are at different stages of development.
There are five stages of platelet existence:
- Youth phase.
- Maturity stage.
- The period of old age.
- Stage of irritation.
- Degenerative moment.
The volume of the cell depends on the stage of formation - new cells are larger in size. As they mature and get closer to aging, they decrease in size. The pdw readings just demonstrate the heterogeneity and width of platelet distribution throughout the volume of the blood substance. In other words, this indicator determines the heterogeneity of platelets.
Data in laboratory forms are displayed in percentage terms and have an indirect meaning.
Consequently, if the coefficients of the remaining formed cells have a stable value, then non-critical changes associated with platelets do not indicate pathological processes in the body. Pdw blood test is performed at the same time as determining MPV, which means mean platelet volume.
EGFR mutations
Changes in the EGFR gene have been identified in a wide variety of types and forms of oncology.
The frequency of EGFR expression is extremely high and reaches:
- Non-small cell lung cancer – up to 80%;
- Colon oncology – up to 77%;
- Ovarian oncology – up to 70%;
- Prostate cancer – up to 40%;
- Stomach oncology – up to 35%;
- Breast cancer – up to 30%.
Due to increased EGFR activity, cancer cells multiply faster, they are aggressive, grow into neighboring tissues and organs, and metastasize. In addition, the process of formation of blood vessels that feed the tumor begins.
Numerous studies and medical practice show that mutated EGFR significantly worsens the prognosis for the patient.
This understanding led scientists to the idea of creating drugs that can block this protein.
But the problem is that molecular genetic properties and histological type of cancer are not always related to each other. Even if we consider two identical types of cancer, it may turn out that in one the EGFR activity is higher than normal, and in the other, on the contrary, it is low.
Therefore, the question of the effectiveness of medications from the group of EGFR blockers is called into question. To resolve this issue, special tests are needed.
Normal pdw value
The predominant number of platelets in the blood should be in a mature form. It is at this stage that flat blood cells are able to cope with their main purpose - to influence blood clotting. The permissible fluctuation in the number of mature platelets, both upward and downward, is 10%. Severe excess of the norm threatens the formation of blood clots, which gradually clog the vessels. A significantly reduced level of platelets is fraught with blood loss.
In a healthy body, the normal width of platelet distribution in children under 18 years of age is from 10 to 15%. In adults, the normal pdw index ranges from 15 to 17%. In a situation where the norm has significant deviations from standard values, this may be a sign of a disruption in the functioning of certain organs and systems in the human body. This may also signal the possible development of pathology.
Functions of EGFR
One of the key words in the name EGFR is “receptor”. This is what they call nerve endings that allow you to feel something, for example, taste, warmth, etc.
If we talk about molecular biology, the receptor is localized on the cell surface, with one part of it outside and the other inside the cell, and contributes to the cell’s sensitivity to molecular signals.
When a signaling molecule comes into contact with a cell and its interaction with the receptor begins, the protein begins to activate and triggers multiple biochemical reactions in the cell. As a result, cell reproduction begins.
For the normal functioning of the human body system, such signals must occur at a strictly defined time, otherwise the consequences can be very serious.
It is the increased activity of the receptor that causes uncontrolled cell proliferation, which leads to cancer.
Increase pdw
When the pdw value of a blood test when deciphered is higher than normal, this is a sign of strong platelet heterogeneity in volume. This state of the circulatory system entails serious consequences. As a result of gradual clogging of blood vessels and capillaries, blood circulation becomes difficult. Which leads to numerous consequences, ranging from a slowdown in metabolism to a list of heart attacks.
Increased platelet volume occurs in the following pathologies:
- Bleeding as a result of surgery or injury results in a high level of platelet concentration in the bloodstream.
- Pdw is increased in blood tests with anemia, which provokes oxygen starvation, due to which flat blood cells may be subject to deformation.
- Oncological pathologies in which systematic damage to blood cells and platelets occurs, including. As a result, their volumes change and lead to disruption of the distribution of platelets in the blood mass.
- Inflammatory processes, during the development of which the number of platelets is increased, and hence the width of their distribution by volume. If, in addition, there is an increased level of leukocytes, then all the signs of inflammation are present.
If pdw is elevated, then this is not necessarily evidence of any serious abnormalities in the body. The reason may be non-compliance with simple measures recommended before taking an analysis to determine the extent of platelet distribution in the blood flow. Blood must be donated in the morning and always on an empty stomach; at least 10–12 hours must pass after the current meal. You should refrain from strong physical and emotional stress on the eve of the examination. It is not advisable to take any medications, even multivitamins.
What is EGFR
The human body is a complex system, for the normal functioning of which individual cells must obey general laws. Cells violating their “role” leads to imbalance and disease.
Scientists isolate proteins and molecules responsible for regulating the life of cells and their normal functioning.
Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR for short) is one such molecule. Its discovery by S. Cohen and R. Levi-Montalcini was awarded the Nobel Prize in 1986.
Decrease pdw
If a clinical study shows that the relative width of the platelet volume distribution is below normal, then this is a sign of a low number of flat blood cells. A low percentage of platelet index is not always a harbinger of various pathologies. It must be taken into account that pdw may be reduced in women during menstruation. It can be lowered due to an unhealthy lifestyle, poor nutrition and due to the physiological characteristics of the body.
The pdw index is lowered with certain deviations:
- Pathologists of the hematopoietic organs.
- Oncological diseases.
- Liver disorders.
- Ingress of viruses and infections.
- As a result of taking cytostatics.
- Myelodysplastic and DIC syndrome.
- Anemia associated with a lack of vitamin B12 and folic acid.
A drastic decrease in the number of platelets and their incorrect distribution in the volume of the blood mass is no less life-threatening for a person than an excess. Because it leads to loss of integrity of the circulatory organs and other body systems. But even when the pdw index is not significantly reduced, this circumstance should not be neglected. It is necessary to normalize this blood indicator and maintain it at the proper level.
Hemoglobin in the general blood test (HGB, Hb)
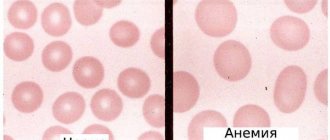
The gas exchange function is carried out due to the presence of red blood cells containing hemoglobin. It is a complex protein consisting of ionized iron (heme) and four globular proteins (globin). It is in this combination that Hb is able to bind to oxygen in the lungs and transport it to the tissues. In the opposite direction, hydrogen protons are added, which is important in maintaining the pH (acidity) of the blood and a small amount of carbon dioxide (about 5%). Transport of most CO2 (approximately 95%) occurs by dissolution and chemical transformation in plasma.
This study is of great value for diagnosing various pathological conditions. The norm for men is 130-160 g/l, for women – 120-140 g/l. More often there is a decrease in the indicator, which may be a manifestation of:
- Deficiency of the main components - iron, vitamin B12, folic acid. The deficiency occurs due to their limited intake from food, the pathology of the absorption of nutrients in the intestines, the greater needs of the body during pregnancy, during periods of active growth and with constant physical activity;
- Acute or chronic blood loss;
- undergone surgery;
- Recovery period after severe infections;
- Taking antibacterial drugs, chemotherapy;
- Pathologies of red bone marrow and liver;
- Erythropathies with a change in shape, decreased elasticity and, as a result, increased breakdown of these cells (hemolysis) with the destruction of the hemoglobin protein they contain.
Low HGB is manifested by pale skin (jaundice in hemolytic anemia), weakness, disruption of the heart and other internal organs, especially the central nervous system, which is most sensitive to hypoxia.
The increase in concentration is a consequence of:
- Dehydration;
- Hypoxia (with cardiovascular, pulmonary diseases, living in high mountains, smoking);
- Work in conditions with reduced oxygen content (mines, foundries, rooms with poor ventilation, high levels of carbon monoxide);
- Tumors of the kidneys and red bone marrow with damage to the sprouts of erythrocyte hematopoiesis;
- Increased secretion of androgens and corticosteroids.
There are no specific symptoms of hyperhemoglobinemia, but there may be hyperemia of the skin, increased blood pressure, heaviness in the left hypochondrium in the area of the spleen and a tendency to thrombus formation.
For timely diagnosis, a general analysis must be performed at the first symptoms, as well as for preventive purposes at least once a year.
Methods for characterizing EGFR mutations
The first stage of the study is a biopsy. It is important that the study material contains enough cancer cells and is large in size.
To detect the changed EGFR gene, polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is often used. This method allows you to create multiple copies of DNA using enzymes.
Upon completion of the analysis, there can be 2 conclusions:
- A mutation in the EGFR gene has been detected, with its characteristics required;
- No mutation detected.
Taking this into account, the doctor determines which treatment tactics to choose.