First aid is a set of measures aimed at restoring or preserving the life and health of the victim. It should be provided by someone who is next to the victim (mutual aid) or by the victim himself (self-help) until a medical worker arrives. The life of the victim and, as a rule, the success of subsequent treatment depends on how skillfully and quickly first aid is provided. Therefore, everyone should know how to provide first aid and be able to provide it to the victim and themselves.
The sequence of actions when providing first aid to a victim:
- eliminating the impact of dangerous and harmful factors on the victim’s body (freeing him from the action of electric current, removing him from a contaminated atmosphere, extinguishing burning clothing, removing him from water, etc.);
- assessment of the victim’s condition;
- determining the nature of the injury that poses the greatest threat to the life of the victim, and the sequence of actions to save him;
- carrying out the necessary measures to save the victim in order of urgency (restoring the airway, performing artificial respiration, external cardiac massage, stopping bleeding, immobilizing the fracture site, applying a bandage, etc.);
- maintaining the victim’s basic vital functions until medical personnel arrive;
- calling an ambulance or a doctor or taking measures to transport the victim to the nearest medical facility.
Release from the action of electric current.
In case of electric shock, it is necessary to free the victim from the action of the current as quickly as possible, since the severity of the electrical injury depends on the duration of its effect on the body. You can turn off the electrical installation using a switch, knife switch or other disconnecting device, as well as by removing fuses, plug connections, creating an artificial short circuit on the overhead line (overhead line) by “throwing”, etc.
If it is not possible to quickly turn off the electrical installation, then measures must be taken to separate the victim from the live parts that he touches. In all cases, the person providing assistance should not touch the victim without taking proper precautions, as this is life-threatening. He must also ensure that he himself does not come into contact with a live part or live step while in the zone of spreading of the ground fault current.
At voltages up to 1000 V, to separate the victim from live parts or wires, use a rope, stick, board or some other dry object that does not conduct electric current. You can pull the victim away from live parts by clothing, while avoiding touching surrounding metal objects and parts of the victim’s body not covered by clothing. To isolate the hands, the person providing assistance, especially if he needs to touch the body of the victim who is not covered by clothing, must wear insulating gloves or wrap his hand in a scarf, put a cloth cap on it, pull the sleeve of a jacket or coat over his hand, throw a rubber carpet or rubberized material over the victim ( raincoat) or just dry cloth. You can also isolate yourself by standing on a rubber carpet, a dry board or some kind of non-electrically conductive bedding, a bundle of dry clothes, etc. When separating a victim from live parts, you should act with one hand.
If an electric current passes into the ground through the victim and he convulsively squeezes the current-carrying element in his hand, you can cut the wire with an ax with a dry wooden handle or make a break using a tool with insulating handles. It is necessary to cut the wires in phases, i.e. cut the wire of each phase separately.
At voltages above 1000 V, to separate the victim from live parts, it is necessary to use protective equipment: wear dielectric gloves and boots and use a rod or insulating pliers designed for the appropriate voltage. On 6-20 kV overhead lines, when it is impossible to quickly turn them off from the supply side, it is necessary to create an artificial short circuit to disconnect the overhead line. To do this, a flexible non-insulated conductor must be thrown onto the overhead line wires, which must have a sufficient cross-section to avoid burnout when a short circuit current passes through it. Before throwing a conductor, one end of it must be grounded (attached to the body of a metal support, a grounding descent or a separate ground electrode, etc.), and it is advisable to attach a load to the other end for ease of throwing. When throwing a conductor, you must use dielectric gloves and boots.
The person providing assistance must be aware of the danger of step voltage if the live part is lying on the ground. You need to move in this area with extreme caution, using protective equipment for insulation from the ground (dielectric galoshes, boots, carpets, insulating stands) or objects that do not conduct electricity well (dry boards, logs). Without protective equipment, you should move in the zone of spreading current from a ground fault by moving your feet on the ground and without lifting them from one another. After separating the victim from live parts, he should be taken out of this area at a distance of at least 8 m from the live part.
First aid in case of an accident: save a life
It may turn out that at this moment you will look beautiful, young, in a good jacket or dress. Or maybe not very beautiful, for example, without a lower jaw, with a crushed skull, with a crooked scalp sewn together. And they will bury you in a closed coffin, quickly and without unnecessary pathos.
Although I'm sure no, you don't have such perverted fantasies as I do. And I have, because I have seen enough of people who are brought in after a car accident. Already standing at a bus stop, I can imagine the unfastened driver at the moment when the car falls on its side into a cliff, and he shakes himself out the window, and the whole one and a half ton colossus crushes him, releasing his intestines. I've seen that too.
And all because some people still haven’t realized that a car is not an adult toy, but a means of increased danger.
So how can you protect yourself from road accidents? Firstly, traffic rules are the bible that will protect your health and the health of your loved ones. The main thing to do is fasten your seat belts. And even more so, if you are good parents, then buckle your child in the car! Of course, you need to obey the speed limit... And one day my friend, a policeman, said: “Volodya, remember - everyone on the road is a fool! Any person has periods when he gets stuck, when he is inattentive, when he confuses the gas and brake pedals. Therefore, never be distracted from what is happening on the road and always be ready to react to the inappropriate actions of another fool.”
What to do if you see a car accident - are you obligated to help? Obliged! There is criminal liability for failure to provide assistance and leaving someone in danger. And even if the criminal code is not a decree for you, just be human, stop, find out if you need help. How can you help?
Procedure for providing assistance in case of an accident
1. The first thing to do is to ensure the safety of victims and rescuers.
Be sure to install a warning triangle and warning lights. The sign is placed at a distance of at least 15 meters in populated areas and 30 meters outside.
Often, victims in shock fly under the wheels of passing cars, hoping that they will stop. And there are cases when the rescuers themselves are hit by a car at night.
2. Second, call the rescuers:
0911 or 112, ambulance team - 03 (from mobile: 003 or 030).
During negotiations, it is necessary to briefly describe the situation, the number, gender, approximate age of the victims, visible damage and the location of the accident. Leave your coordinates so that later they know who to give the medal for their help and can call back to clarify the location of the accident.
3. Third - direct help.
It begins with the evacuation of the injured person from the car. Here you must remember the eternal rule: DO NO HARM!
Open the door, and if it doesn’t work, carefully knock out the glass and press the sash. Help the victim get out. If it's pinched, don't pull it out! If it didn’t work out, then wait for the rescuers, they have more capabilities. In this case, ensure the fire and electrical safety of the car: turn off the ignition, remove the terminals from the battery. Wrap up the victim, give an analgin tablet from the first aid kit.
If you are alone, grab the victim from the back, running your hands under his armpits, grab his forearms, pull the victim out so that his head lies on your chest (do everything calmly, without fuss, do not overdo it). Place it on a hard surface, without stones or unnecessary objects, and place a small cushion under your head.
Assess the degree of consciousness. If he is conscious, ask about his well-being, what worries him, is it hard to breathe, does he feel his limbs. Let him move his arms and legs.
Breathing and pulse
If the victim is unconscious, determine whether he is breathing?
Breathing is determined by the rhythmic movements of the abdomen; listen with your ear to the movements of air near the mouth. Feel the pulse in your neck (use your index and middle fingers, starting from the corner of the lower jaw, move downwards until you reach the hole where the pulsation is most obvious. There is no need to press hard, do not block the blood flow).
If there is a pulse, but breathing suffers.
Tilt your head back (not possible if you suspect a spinal fracture!), open your mouth, push your lower jaw forward. This will improve the airway in the vast majority of cases. If there are blood clots, mucus, or foreign bodies in your mouth, wrap your finger in a clean cloth and try to remove everything. In addition, you will find an air duct in the first aid kit. Thanks to it, airway patency can be improved. When you insert the air duct into your mouth, make sure that you do not tilt your tongue with the device.
If there is no breathing, but there is a pulse
, inhale into the victim, after pinching his nose and putting a bandage on his mouth. Make sure that during inhalation the chest rises, and the passive exhalation is felt by the noise and movement of air.
There is no breathing, no pulse - you can’t hesitate and wait for help from doctors!
This condition is called “clinical death”. You immediately need to carry out a set of resuscitation measures, which I will write about separately.
Injuries
If breathing and heartbeat are not currently affected, it’s time to pay attention to the skin.
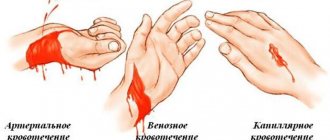
Are there signs of external bleeding? It comes in three types: capillary, venous and arterial.
1. Capillary bleeding
characterized by diffuse saturation of tissues with dark blood, it is not intense, not threatening. Stops with a simple pressure bandage (do not forget to treat the wound with a solution of iodine or brilliant green).
2. Venous bleeding
characterized by a constant, fairly intense flow of dark blood. After treating the wound, apply a pressure bandage. Bleeding can be easily stopped by lightly squeezing the tissue below the wound.
3. Arterial bleeding
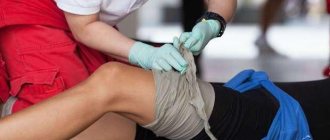
intense, pulsating with scarlet blood. Here delay is like death! As soon as you see such a wound, press the vessel firmly with your fingers. If the damaged vessel is superficial, then you will be able to stop the bleeding by strongly squeezing the tissue just above the wound. By the way, take gloves from the same first-aid kit; the infection has not yet been canceled. Take out the tourniquet. In case of arterial bleeding, a tourniquet is applied above the wound, tightly wrapped around the limb. Be sure to record the time of installation of the harness!
It often happens that, in a rush, rescuers forget that it is necessary to relax the tourniquet every half hour in winter and no more than an hour in summer, to allow the blood flow to temporarily restore and nourish the tissues - such patients are brought in ready for limb amputation.
While relaxing the tourniquet, apply finger pressure to the wound.
There is no tourniquet - use twists made of fabric (bandage, scarf, soft fabric), secured with a stick. You cannot make twists from ropes or laces.
Head wounds
should be treated with an antiseptic and bandaged. Place the removed scalp back as best you can and secure with a circular bandage.
Penetrating wound to the chest.
In this case, when the patient inhales, air is noisily sucked into the pleural cavity. Air will begin to fill the pleural cavity, compressing the lungs, heart, aorta and other organs, dramatically disrupting their function. To prevent this, you need to immediately cover the wound either with a sealing cloth from the first aid kit, or with a bag, plastic, or adhesive tape. It is better to fix the bandage while exhaling.
Wound in the stomach.
It is easier for such patients when they bring their knees towards the body (transport them that way). If the wound is open, treat it with an antiseptic from the first aid kit and apply a bandage. We leave all penetrating foreign bodies (knives, glass, fragments) in place, fix them with a bandage so as not to cause more harm, and send them to a hospital facility. The surgeons will figure out what's what.
Patients with injuries are not allowed to drink or eat, no matter how much they ask! Only a doctor can give permission to eat. This is associated with the risk of anesthesia, the risk of aspiration with vomit, and in case of intestinal wounds - leakage of contents into the abdominal cavity.
Limb fractures.
Pain, unnatural position of the injured limb, bone fragments in the wound indicate a bone injury. It is impossible to transport the patient without fixing such a limb, since fragments can damage the tissue surrounding the wound.
They use special medical splints, but you can also make do with improvised materials (skis, ski poles, boards), and place cotton wool or rags under them at the point of contact with the bone. It is necessary to fix at least two joints so that the limb is completely immobilized. The splint is applied over clothing after treating the wound. A bluish, cold limb may indicate excessive compression of the tissues with a bandage.
If a neck fracture is suspected - and now in case of any car accidents - a collar is placed on the neck. There is no special one - you can make one out of towels. In general, spinal cord injury patients are transported on a rigid surface, such as a door, on their back or on their stomach.
Today I have outlined to you the basic knowledge and skills very concisely and briefly, but they will also give you the opportunity not to get confused and not harm the victim, and if done correctly, even help.
Vladimir Shpinev
Photo thinkstockphotos.com
Related products: [product](first aid kit)
First aid
Methods of providing first aid depend on the condition of the victim. The signs by which you can quickly determine the health status of the victim are as follows:
- consciousness: clear, absent, impaired (the victim is inhibited or excited);
- color of the skin and visible mucous membranes (lips, eyes): pink, bluish, pale;
- breathing: normal, absent, impaired (irregular, shallow, wheezing);
- pulse in the carotid arteries: well defined (rhythm correct or incorrect), poorly defined, absent;
- pupils: dilated, constricted;
With certain skills and self-control, the person providing assistance must assess the condition of the victim in a minute and decide in what volume and order assistance should be provided to him. If the victim is unconscious, it is necessary to monitor his breathing and, in case of breathing problems due to the recession of the tongue, move the lower jaw forward. To do this, with four fingers of both hands, grab the lower jaw from behind by the corners and, resting your thumbs on its edge below the corners of the mouth, pull it back and push it forward so that the lower teeth stand in front of the upper teeth. It should be maintained in this position until the tongue stops sinking. If the victim breathes very rarely and spasmodically, but his pulse is palpable, artificial respiration should be started immediately.
If the victim has no consciousness, pulse, breathing, the skin is bluish, and the pupils are dilated, you should immediately begin to restore the vital functions of the body by performing artificial respiration and external cardiac massage.
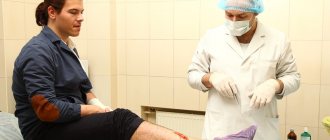
Artificial respiration.
Artificial respiration is carried out in cases where the victim is not breathing or breathing very poorly (rarely, convulsively, as if with a sob), and also if his breathing is constantly deteriorating, regardless of what caused it: electric shock, poisoning, drowning, etc. The most effective method of artificial respiration is the “mouth to mouth” or “mouth to nose” method, since this ensures that a sufficient volume of air enters the victim’s lungs.
To carry out artificial respiration, the victim should be laid on his back, unbuttoned clothing that restricts breathing and ensure the patency of the upper respiratory tract, which in the supine position and in an unconscious state is closed by a sunken tongue. In addition, there may be foreign contents in the oral cavity (vomit, slipped dentures, sand, silt, grass, if the person was drowning), which must be removed with the index finger wrapped in a scarf (cloth) or bandage, turning the victim’s head to the side. After this, the person providing assistance is located on the side of the victim’s head, puts one hand under his neck, and with the palm of the other hand presses on the forehead, throwing his head back as much as possible. In this case, the root of the tongue rises and frees the entrance to the larynx, and the victim’s mouth opens. The person providing assistance leans towards the victim’s face, takes a deep breath with his open mouth, then completely tightly covers the victim’s open mouth with his lips and exhales vigorously, inhaling air into his mouth with some effort; at the same time, he covers the victim’s nose with his cheek or the fingers of his hand on the forehead. In this case, be sure to observe the victim’s chest, which should rise. In order for the exhalation to be deeper, you can gently press your hand on the chest to help the air leave the victim’s lungs.
External cardiac massage.
If there is not only breathing, but also a pulse in the carotid artery, artificial respiration alone is not enough to provide assistance, since oxygen from the lungs cannot be transferred by the blood to other organs and tissues. In this case, it is necessary to restore blood circulation artificially, for which external heart massage should be performed. The indication for resuscitation measures is cardiac arrest, which is characterized by a combination of the following signs: pallor or cyanosis of the skin, loss of consciousness, absence of a pulse in the carotid arteries, cessation of breathing or convulsive, irregular breaths. In case of cardiac arrest, without wasting a second, the victim must be laid on a flat, hard base: a bench, the floor, or, in extreme cases, a board placed under his back.
If one person is providing assistance, he is located on the side of the victim, and, bending down, gives quick energetic blows (using the “mouth to mouth” or “mouth to nose” method), then unbends, remaining on the same side of the victim, Place the palm of one hand on the lower half of the sternum, stepping back two fingers higher from its lower edge, and lift the fingers. He places the palm of his second hand on top of the first across or lengthwise and presses, helping by tilting his body. When applying pressure, your hands should be straightened at the elbow joints. The pressure should be applied in quick bursts so as to displace the sternum by 4-5 cm, the duration of pressure is no more than 0.5 s, the interval between individual pressures is no more than 0.5 s. During pauses, the hands are not removed from the sternum if assistance is provided by two people, the fingers remain raised, and the arms are fully straightened at the elbow joints.
If the revival is carried out by one person, then for every two deep injections he makes 15 pressures on the sternum, then again makes two injections and again repeats 15 pressures, etc. In a minute it is necessary to make at least 60 pressures and 12 blows, i.e. perform 72 manipulations, so the pace of resuscitation measures must be high. When two people participate in resuscitation, the “breathing-massage” ratio is 1:5, i.e. after one deep insufflation, five compressions are applied to the chest.
Universal first aid scheme at the scene of an accident
For residents, a universal scheme for providing first aid at the scene of an incident
If there is no consciousness and no pulse in the carotid artery, begin resuscitation. 1. Make sure there is no pulse in the carotid artery, the pupils are dilated and there is no reaction to light.
There is no time to waste identifying signs of breathing! Remember, cardiac arrest is preceded by: short-term spasms of the body and facial muscles; frequent hiccups, involuntary bowel movements; loss of pulse, arrhythmia; cessation of breathing, pale skin!
2. Free the chest from clothing, unfasten the waist belt, and place the victim on a hard surface. 3. If there is no pulse, begin chest compressions. Pressing frequency 50-80 times per minute. The depth of compression of the chest is 3-4 cm. The thumb is directed towards the head (legs) of the victim.
You must not place your palm on your chest so that your thumb is pointed at the rescuer!
4. Inhale artificial respiration. Pinch your nose, grab your chin, throw back the victim’s head and exhale as much as possible into his mouth (preferably through gauze, a napkin, a handkerchief, etc.). Check if the chest rises.
You cannot “inhale” artificial respiration without first pinching the victim’s nose! If air does not pass, turn the victim onto his stomach and press his fist on the stomach
.
5. Perform a resuscitation complex: 1 rescuer - 2 “breaths” - 15 pressures; 2 rescuers - 2 “breaths” - 5 pressures.
6. When a pulse appears, turn the victim onto his stomach.
Remember! To quickly return blood to the heart, elevate the victim’s legs. To preserve brain life, apply cold to the head. To remove air from the stomach, turn the victim on his stomach and press with his fist below the navel. Monitor the constriction of the pupils and the pulse in the carotid artery. If there is no consciousness (more than 4 minutes) and there is a pulse in the carotid artery (coma).
7. Turn the victim onto his stomach. Only in the “lying on his stomach” position should the victim wait for the arrival of doctors.
You cannot leave a person in a coma lying on his back!
8. Remove mucus and stomach contents. Periodically remove mucus and stomach contents from the mouth using a napkin. 9. Apply cold to the head (cold water in a bottle, bag, ice).
Remember!
If you are in a coma, leave the victim until medical personnel arrive and transport him only in the “lying on his stomach” position,
not on his back!
Signs of biological death:
drying of the cornea of the eye (appearance of a “herring” shine), deformation of the pupil when squeezing the eyeball with fingers, cadaveric spots and rigor mortis.