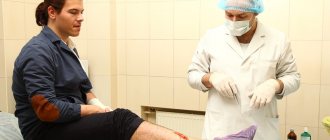
General principles of first aid for arterial damage
Providing first aid for arterial bleeding is based on several principles:
- Stop the bleeding and call an ambulance.
- Disinfection of the wound. To prevent the entry of pathogenic microorganisms, work with clean hands whenever possible. It is necessary to treat the edges of the wound with alcohol, vodka, cologne, lotion or other available means; apply sterile material to the damaged surface before bandaging; bandage the wound.
- Fixation of the injured limb with a scarf or splint.
- Anesthesia. If a person has a serious injury, then to prevent pain shock it is recommended to use painkillers (analgin tablets, tramadol capsules, ice).
- Safe transportation to a medical facility or awaiting the arrival of emergency doctors.
Treatment
In the acute period, the following manipulations are performed to stop bleeding:
- Drug hemostasis: the patient is injected intramuscularly with hemostatic drugs (Vikasol, Etamzilat, Aminocaproic acid).
- Endoscopic hemostasis (vessel clipping, photocoagulation, sclerotherapy).
- Arterial embolization.
- Surgical intervention (vascular ligation).
At the same time, the volume of circulating blood is replenished: saline solutions are administered (Disol, Trisol, Ringer's solution), microcirculation in the vessels is improved (Reopoliglyukin).
In case of severe blood loss, blood is transfused and iron-containing drugs are administered. In the future, iron supplements are prescribed for 3-6 months.
After stopping the bleeding, treatment tactics will depend on the disease that caused the disease.
First aid
For stomach bleeding, there is little that can be done at home. If you suspect a pathology, you must:
- urgently call an ambulance;
- the patient should be placed with the leg end raised; if he loses consciousness, the head must be turned to the side to prevent aspiration of vomit;
- Ice should be placed on the patient’s stomach;
- You cannot give food or drink, or take medications on your own.
First aid for arterial bleeding point by point
When providing assistance to a victim with gushing bleeding, you need to act in the first minutes according to a clear plan:
- Position the victim so that the wound is above the level of the heart.
- Clamp the artery above the site of the vessel rupture. This should stop or reduce blood loss.
- Apply a rubber band a few centimeters above the tear. If you don’t have it at hand, you can make a homemade one from a belt, cord, rope or twisted natural fabric.
- It is imperative to write down the time when a tight bandage was applied so that doctors know the duration of the compression of the vessels. This is very important, since with prolonged application of a pressure bandage, tissue necrosis can occur, which means gangrene. This can cause a person to lose a limb or life.
- A sterile gauze bandage should be applied to the open wound to prevent infection.
- Be sure to transport the patient to the nearest hospital for professional help, or call an ambulance.
Now you know the rules for providing first aid for arterial bleeding point by point and will be able to act correctly if necessary. Next, we’ll look at how to properly install a pressure bandage.
Peculiarities
Separately, it is worth noting the arterial bleeding that occurs with wounds to the neck and the area around it. We are talking about damage to the integrity of the carotid artery and its main vascular branches.
Blood loss from the carotid artery leads, in most cases, to very serious consequences, in the form of disturbances in the functioning of the brain caused by the appearance of internal bleeding in this organ and the formation of edema.
In this case, patients' health rapidly deteriorates, and cerebral edema and coma often occur. It may be impossible to return a person to a normal state even after providing timely assistance and stopping arterial bleeding.
This phenomenon is called vascular ischemia, and concerns not only bleeding of the carotid artery. Ischemic disorders of the extremities are observed when they are severely damaged, when the walls of large arteries are torn or cut, and first aid was provided untimely, or with violations.
Stopping blood from an artery is not enough. If the artery is ruptured within two to six hours, depending on the location of the damage, toxic products from the damaged part of the limb begin to be absorbed into the blood and spread through the bloodstream throughout the body. Reperfusion syndrome may occur. Stopping bleeding from an artery is only the first, emergency aid, after which it is necessary to immediately restore the integrity of the arteries’ walls.
Stopping bleeding in places hard to reach for applying a tourniquet
Bleeding from the femoral artery is very dangerous. If the integrity of this blood vessel is damaged, the victim can die in 30-40 seconds, so first aid for arterial bleeding of a limb should be provided quickly. It is worth noting that applying a tourniquet to this area is not so easy. There is a very large muscle and fat mass on the thigh. It is difficult to squeeze the artery through it. To stop bleeding, it is recommended to press with your fist on the area where the blood vessel passes, and while applying a tourniquet, you should place something hard (a stone, a mobile phone) or a roll of bandage under it.
- How to apply a tourniquet for arterial and venous bleeding
When a violation of the integrity of the skin of the neck and arterial bleeding is detected, first aid is provided as follows:
- a piece of tissue is applied to the wound, and then the carotid artery and the affected area are clamped;
- after this, the injured person is laid down, his hand opposite to the wound is placed behind his head;
- Apply a roller made of a bandage or towel to the wound and apply a tourniquet, pulling it over the victim’s hand (the tourniquet should press the roller).
Signs of bleeding
Each type of pathology has a number of its own symptoms that characterize it. However, there are common signs of blood loss. Among them:
- weakness, increased drowsiness;
- feeling of thirst;
- dizziness;
- pallor of the skin, mucous membranes;
- presence of cold sweat;
- increased heart rate, feeling of lack of air;
- decreased blood pressure;
- weak but rapid pulse;
- dyspnea;
- disturbance of consciousness, and sometimes loss.
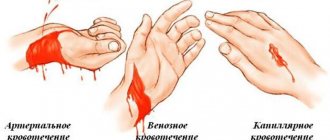
To correctly interpret the nature of the bleeding, you should take a close look at it. After all, it is precisely by such manifestations that the type of damaged vessel is determined.
- Capillary bleeding is characterized by large drops oozing from the wound over the entire surface. Losses are usually small. The blood is red.
- Venous bleeding expires much faster. Especially if a large vessel is injured. Blood flows down in streaks. Moreover, its color is dark red, and sometimes even burgundy. Intermittent bleeding may occur. However, pulsation is not characteristic of such a pathology.
- Arterial bleeding. Outflow from the wound occurs in pulsating impulses. Sometimes it resembles a fountain. The rhythm and frequency completely repeat the pulse and heartbeats. The blood is bright scarlet. At the same time, losses are quite fast and significant. These are the main signs of arterial bleeding. They allow you to visually determine the nature of the damage.
Duration of tourniquet application
The rules for providing first aid for arterial bleeding say that it is necessary to write down the time of installation of the tourniquet, and slip a note under its coils. The time is clearly indicated: both hours and minutes. The duration of the vessel being in a compressed state depends on the ambient temperature. In the warm season it is 2 hours, and at low air temperatures it is even less, up to 1–1.5 hours. If during this time the victim cannot be taken to the hospital, then the tissues must be allowed to resume blood circulation.
It is better to do this procedure together. One person should feel the damaged artery with a finger and press it above the tear. His assistant unfastens and removes the tourniquet or pressure bandage with smooth movements. It is necessary to give at least 5 minutes to restore blood circulation in the tissues, and then apply a tourniquet again, but a few centimeters above the previous place. It is advisable to compress the vessel as close as possible to the site of injury.
Ways to stop bleeding
The method of stopping severe bleeding can be temporary or permanent. The first includes pre-medical manipulations. The final stop is made after hospitalization.
If the wound is small, then sometimes primary care is enough, the main methods are:
- Finger pinch.
- Application of a tourniquet.
- Tamponade.
- Use of improvised means.
Finger compression is most effective for minor bleeding. You cannot do without it in those places where it is not possible to apply a bandage:
- In the temporal part.
- On the face or neck.
- In the armpit area.
- In the area of the popliteal area, groin.
In case of extensive bleeding, a tourniquet must be applied. If you don’t have a special one, then you can take a belt or scarf.
It is important that the strip is wide, as thin ropes can cause necrosis. The tourniquet is placed on top of the fabric or clothing above the damage by 3-5 cm.
You can check the correctness of the action by checking the pulsation of the artery below the bandage; the pulsation should be weak or completely absent. The first turn is made tight, the subsequent ones a little weaker.
- Providing first aid for venous bleeding: point by point
In order not to severely compress the artery, it is necessary to remove the tourniquet for 10 minutes or loosen it after a certain period of time. In summer, the bandage can last 1-2 hours, in winter - 30-50 minutes.
It is recommended to record the time of application of the tourniquet on a piece of paper. The method is suitable for wounds of the hip and shoulder.
Tamponade is performed if emergency treatment with a tourniquet does not help. To do this, use a bandage or gauze, from which a tampon is formed to stop the bleeding. Fix it with a bandage . If it is not possible to use sterile materials, then it is necessary to disinfect a homemade tampon before clamping the artery.
Improvised means are used only as a last resort. To do this, take any clean clothing and tear it into strips suitable in width for the tourniquet. Alcohol, vodka, and tincture are used as a disinfectant.